Topic khan academy area and perimeter: Discover the essential concepts of area and perimeter with Khan Academy. Our comprehensive lessons and practice exercises make learning geometry engaging and easy. From basic shapes to complex figures, we cover everything you need to master these important mathematical skills. Start your journey to better understanding geometry today!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Area
- Understanding Perimeter
- Area and Perimeter of Rectangles
- Area and Perimeter of Triangles
- Area and Perimeter of Circles
- Area and Perimeter of Composite Shapes
- Word Problems: Area and Perimeter
- Advanced Concepts in Area and Perimeter
- Practice Exercises and Quizzes
- YOUTUBE: Chu vi và diện tích: những kiến thức cơ bản | Chu vi, diện tích và thể tích | Hình học | Khan Academy
Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, often introduced in early math education. They are crucial for understanding various shapes and their properties.
Area
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside it. It is measured in square units. The formulas for calculating the area vary depending on the shape:
- Rectangle: (where is the width and is the height)
- Triangle: (where is the base and is the height)
- Circle: (where is the radius)
Perimeter
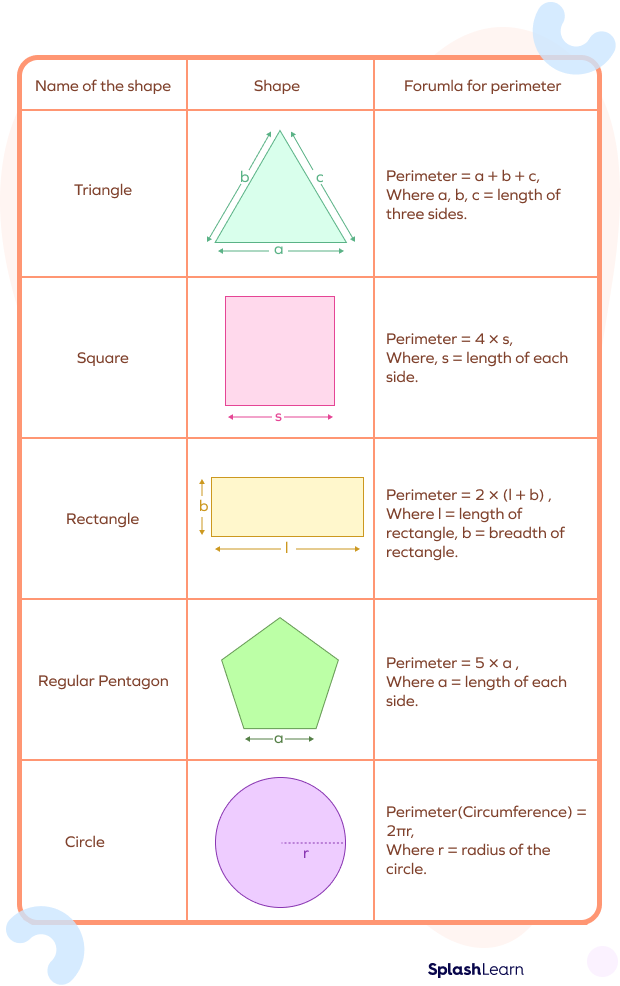
The perimeter of a shape is the total length around it. It is measured in linear units. The formulas for calculating the perimeter depend on the shape:
- Rectangle: (where is the width and is the height)
- Triangle: Sum of all three sides
- Circle (Circumference): (where is the radius)
Example Problems
Here are some example problems to help practice calculating area and perimeter:
- Find the area of a rectangle with a width of 5 cm and a height of 7 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm.
- Determine the circumference of a circle with a radius of 6 cm.
Practice on Khan Academy
Khan Academy offers extensive practice exercises and instructional videos on area and perimeter. These resources can help solidify understanding and improve problem-solving skills:
These resources include interactive exercises and quizzes to test your knowledge and track your progress.
Conclusion
Understanding area and perimeter is essential for various real-life applications, from construction to art. By mastering these concepts, students can build a strong foundation in geometry and enhance their mathematical skills.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry. Area refers to the amount of space inside a shape, while perimeter is the total distance around the shape's edges. These concepts are essential for solving real-world problems and are foundational in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
The area of simple shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles can be calculated using specific formulas. For instance, the area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length by its width: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \). The perimeter of a rectangle, on the other hand, is found by adding up the lengths of all its sides: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) \).
For triangles, the area is given by the formula: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \). The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its sides. Circles have a unique set of formulas where the area is calculated as \( \pi r^2 \) and the perimeter, also known as the circumference, is \( 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
Understanding these basic formulas and how to apply them allows students to solve various geometric problems efficiently. Practical applications of these concepts include determining the amount of material needed for construction projects or finding the boundary length for fencing a garden.
Understanding Area
Area is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the amount of space a two-dimensional shape covers. It's measured in square units, such as square meters or square inches. The area of a shape can be determined using various methods depending on the type of shape.
- Rectangle: To find the area of a rectangle, multiply its length by its width. The formula is \( A = l \times w \).
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, the area is the side length squared. The formula is \( A = s^2 \).
- Triangle: The area of a triangle is found by multiplying the base by the height and then dividing by 2. The formula is \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \).
- Parallelogram: Similar to a rectangle, the area of a parallelogram is the base multiplied by the height. The formula is \( A = b \times h \).
- Trapezoid: The area of a trapezoid is calculated by adding the lengths of the two parallel sides, dividing by 2, and then multiplying by the height. The formula is \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (a + b) \times h \).
- Circle: The area of a circle is found using the formula \( A = \pi r^2 \), where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
Understanding how to calculate the area is essential for solving various real-life problems, such as determining the amount of paint needed to cover a wall or the size of a plot of land. Practice and familiarity with these formulas will help in mastering the concept of area.
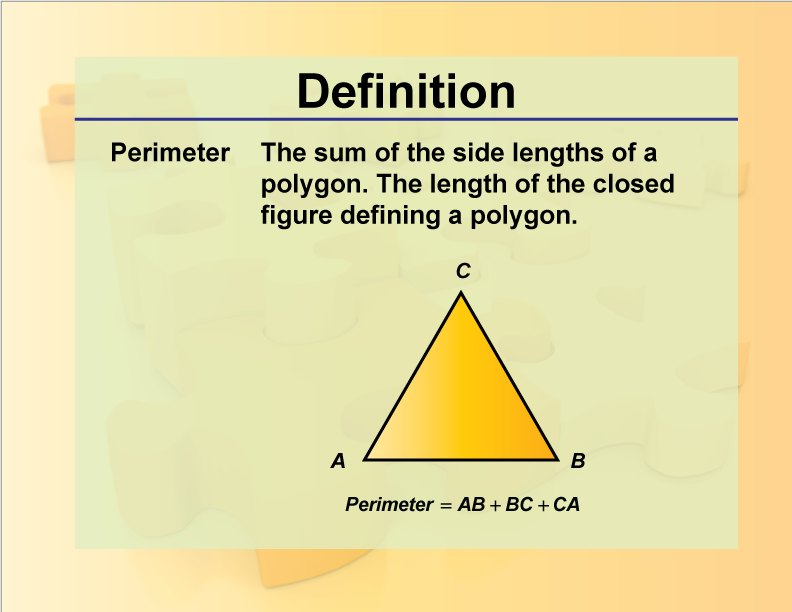
Understanding Perimeter
Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a shape. It is the sum of all the sides of the shape.
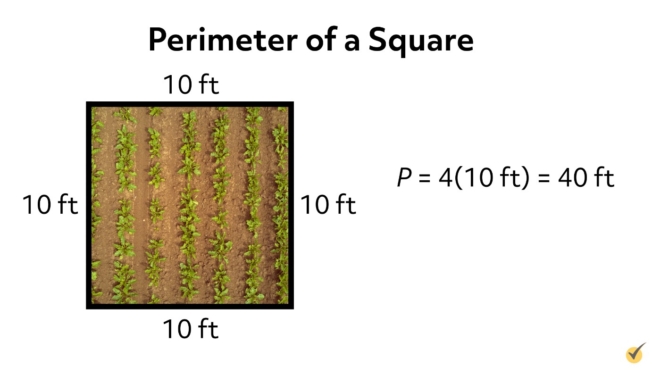
To find the perimeter of a shape, you simply add up the lengths of all its sides. For simple shapes like rectangles and squares, this means adding up the lengths of all the sides. For more complex shapes, you may need to break the shape down into simpler components and calculate the perimeter of each component separately before adding them together.
For example, the perimeter of a rectangle can be found by adding twice the length and twice the width of the rectangle: P = 2l + 2w, where l is the length and w is the width.
In the case of a triangle, you add the lengths of all three sides: P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides.
Similarly, for a circle, the perimeter is called the circumference and is found using the formula: C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
Understanding perimeter is crucial in various real-life applications such as fencing a garden, calculating the amount of material needed to frame a picture, or determining the length of wire needed to surround a circular pond.
Area and Perimeter of Rectangles
Rectangles are fundamental shapes in geometry, and understanding their area and perimeter is essential in various mathematical applications.
Area of a Rectangle:
The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length by its width. Mathematically, it can be expressed as A = l \times w, where l is the length and w is the width of the rectangle.
To visualize this, imagine a rectangular garden with length 5 meters and width 3 meters. To find the area, you multiply 5 meters by 3 meters, resulting in an area of 15 square meters.
Perimeter of a Rectangle:
The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of all its sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length, you can simplify the formula to P = 2l + 2w, where l is the length and w is the width.
For instance, consider a rectangular room with length 8 meters and width 4 meters. To find the perimeter, you add twice the length to twice the width: P = 2(8) + 2(4) = 16 + 8 = 24 meters.
Understanding the area and perimeter of rectangles is crucial in real-life scenarios such as calculating the floor space of a room for carpeting or determining the amount of fencing needed to enclose a rectangular garden.
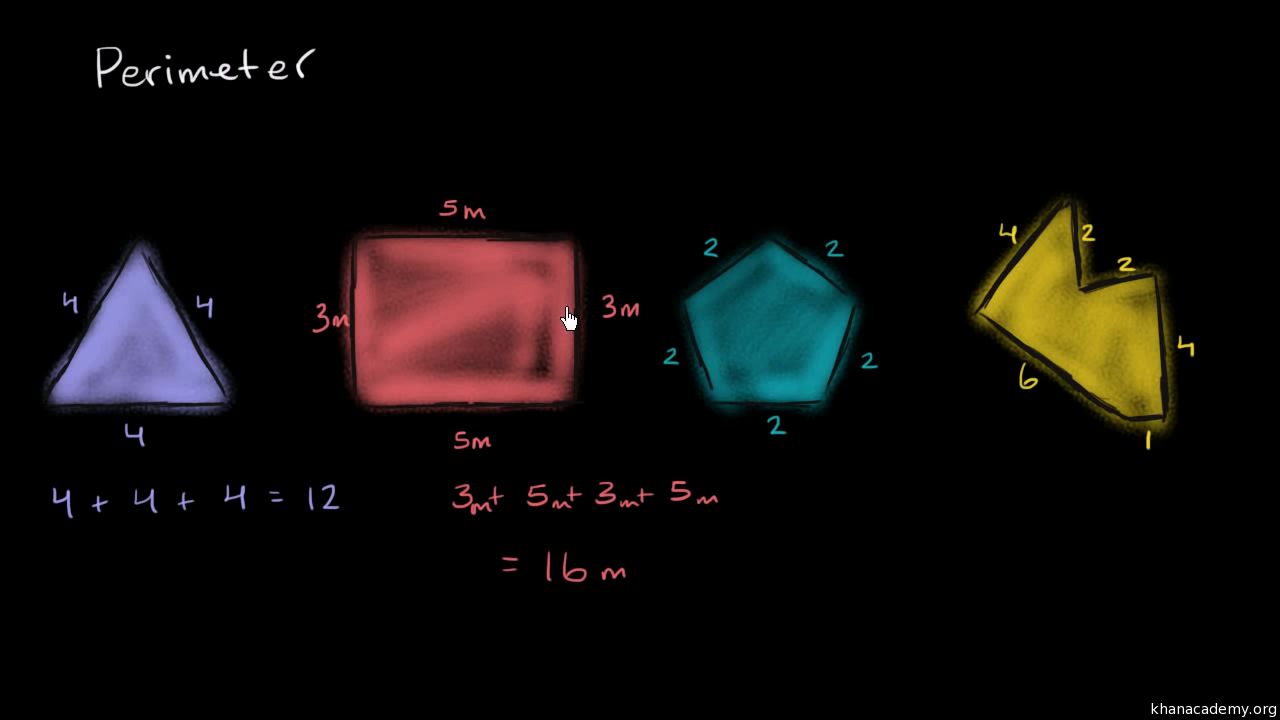
Area and Perimeter of Triangles
Triangles are fundamental geometric shapes with unique properties. Understanding how to calculate their area and perimeter is essential in mathematics.
Area of a Triangle:
The area of a triangle can be calculated using various methods, depending on the given information about the triangle.
- Using Base and Height: The most common method involves multiplying the base of the triangle by its height and dividing the result by 2. Mathematically, it can be expressed as A = \frac{1}{2}bh, where b is the length of the base and h is the height perpendicular to the base.
- Heron's Formula: If you know the lengths of all three sides of the triangle, you can use Heron's formula to calculate the area. It is given by A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}, where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides.
Perimeter of a Triangle:
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Mathematically, it can be expressed as P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides.
Understanding the area and perimeter of triangles is crucial in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and physics.
Area and Perimeter of Circles
Circles are one of the most important shapes in geometry, and understanding how to calculate their area and perimeter is essential in mathematics and various real-life applications.
Area of a Circle:
The area of a circle can be found using the formula A = πr^2, where r is the radius of the circle. This formula represents the area of the entire circle, including all the space inside its boundary.
To calculate the area, simply square the radius and multiply it by the mathematical constant π (pi), which is approximately equal to 3.14159.
Perimeter of a Circle:
The perimeter of a circle is more commonly known as the circumference. It is the distance around the edge or boundary of the circle.
The formula to calculate the circumference of a circle is C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle. This formula represents the length of the entire boundary of the circle.
In practical terms, finding the circumference of a circle is useful for tasks such as measuring the distance around a circular track or determining the length of a string needed to wrap around the rim of a circular object.
Area and Perimeter of Composite Shapes
Composite shapes are formed by combining two or more basic shapes. Calculating their area and perimeter involves understanding the individual components and applying appropriate formulas.
Area of Composite Shapes:
To find the area of a composite shape, break it down into simpler shapes such as rectangles, triangles, circles, etc. Calculate the area of each component separately and then sum them up.
Perimeter of Composite Shapes:
Calculating the perimeter of composite shapes requires adding up the lengths of all the sides. Again, break down the composite shape into simpler components, find the perimeter of each component, and then sum them up.
For example, consider a composite shape consisting of a rectangle and a triangle. Find the area of the rectangle using its length and width, and the area of the triangle using its base and height. Then, sum up the areas of both shapes to get the total area of the composite shape. Similarly, find the perimeter of the rectangle by adding twice its length and twice its width, and add the lengths of the three sides of the triangle to get the perimeter of the composite shape.
Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of composite shapes is important in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Word Problems: Area and Perimeter
Word problems involving area and perimeter help reinforce the application of mathematical concepts in real-life situations. Let's solve a few examples:
- Example 1: Sally wants to fence her rectangular garden. The garden is 12 meters long and 8 meters wide. How much fencing does she need?
- Example 2: John wants to carpet his triangular room. The base of the room is 6 meters, and the height is 8 meters. How much carpet does he need?
- Example 3: Lisa wants to fence her circular garden. The garden has a radius of 10 meters. How much fencing does she need?
Solution: To find the perimeter (fencing needed) of the garden, use the formula P = 2l + 2w. Substituting the given values, we get P = 2(12) + 2(8) = 24 + 16 = 40 meters.
Solution: To find the area (carpet needed) of the room, use the formula A = \frac{1}{2}bh. Substituting the given values, we get A = \frac{1}{2}(6)(8) = 24 square meters.
Solution: To find the perimeter (fencing needed) of the garden (circumference), use the formula C = 2πr. Substituting the given value, we get C = 2π(10) = 20π meters (approximately 62.83 meters).
Word problems provide practical contexts for understanding and applying area and perimeter concepts in everyday scenarios.

Advanced Concepts in Area and Perimeter
Advanced concepts in area and perimeter delve into more complex shapes and mathematical techniques.
Irregular Shapes:
Calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes involves breaking them down into simpler components and applying appropriate formulas. This may include using techniques such as decomposing the shape into rectangles, triangles, or other regular shapes, or employing advanced mathematical methods such as calculus.
Curved Shapes:
For curved shapes such as ellipses or irregular curves, determining the area and perimeter may require specialized formulas or numerical approximation methods. These calculations often involve calculus or advanced geometric principles.
Three-Dimensional Shapes:
In three-dimensional geometry, concepts of surface area and volume are closely related to those of area and perimeter in two dimensions. Calculating the surface area and volume of three-dimensional shapes such as cylinders, spheres, cones, and prisms involves understanding their properties and applying relevant formulas.
Advanced Problem-Solving Techniques:
Advanced problem-solving in area and perimeter may involve applying mathematical principles to real-world scenarios, optimizing shapes for efficiency, or solving geometric puzzles and challenges.
Mastering advanced concepts in area and perimeter opens doors to a deeper understanding of geometry and its applications in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and computer graphics.
Practice Exercises and Quizzes
Practice exercises and quizzes are invaluable tools for reinforcing learning and assessing understanding in the topic of area and perimeter.
Interactive Exercises:
Platforms like Khan Academy offer interactive exercises that allow learners to practice calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes. These exercises often provide immediate feedback, guiding students through the process and helping them identify areas for improvement.
Problem Sets:
Problem sets containing a variety of questions on area and perimeter help students apply their knowledge to different scenarios. These sets may include questions on finding the area and perimeter of rectangles, triangles, circles, composite shapes, and more.
Quizzes:
Quizzes serve as assessments to gauge understanding and retention of area and perimeter concepts. They may include multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, or even longer problem-solving exercises to challenge students' comprehension.
Customizable Practice:
Many educational platforms allow instructors to customize practice exercises and quizzes to align with specific learning objectives or cater to the individual needs of students. This flexibility enables targeted practice and assessment.
Engaging in regular practice exercises and quizzes not only solidifies understanding of area and perimeter but also builds problem-solving skills and mathematical fluency.
Chu vi và diện tích: những kiến thức cơ bản | Chu vi, diện tích và thể tích | Hình học | Khan Academy
Chu vi và diện tích: những kiến thức cơ bản | Chu vi, diện tích và thể tích | Hình học | Khan Academy
READ MORE:
Diện tích và chu vi
Diện tích và chu vi