Topic perimeter in a sentence: Explore the versatility of "perimeter in a sentence" with vivid examples and practical applications. From defining perimeter to illustrating its significance in various contexts, this article offers a comprehensive understanding of how this mathematical concept is used in everyday language and specialized fields like geometry, security, and construction.
Table of Content
- Perimeter in a Sentence
- Table of Contents
- What is a Perimeter?
- Importance of Understanding Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter in Real Life
- Measuring Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas
- Perimeter vs. Area
- Perimeter in Geometry
- Perimeter in Security
- Perimeter in Construction
- Perimeter in Mathematics
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu rõ về diện tích và chu vi trong toán học. Hãy tìm hiểu cách tính và ứng dụng của chúng trong cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Perimeter in a Sentence
Here are some sentences showcasing the use of "perimeter":
- The police set up a perimeter around the crime scene.
- The perimeter of the square is equal to four times the length of one of its sides.
- They walked around the perimeter of the garden, admiring the flowers.
- Make sure to secure the perimeter of the building to prevent unauthorized access.
- The fence marks the perimeter of our property.
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
Based on the search results for "perimeter in a sentence," the comprehensive table of contents for the article can be structured as follows:
- Introduction to Perimeter in Everyday Language
- Perimeter in Real-Life Scenarios
- Understanding Perimeter Measurement
- Perimeter Examples and Applications
- Perimeter Formulas and Calculations
- Perimeter in Geometry and Mathematics
- Practical Uses of Perimeter in Security
- Perimeter Considerations in Construction
- Exploring Advanced Concepts of Perimeter
- Conclusion: The Significance of Perimeter in Various Fields
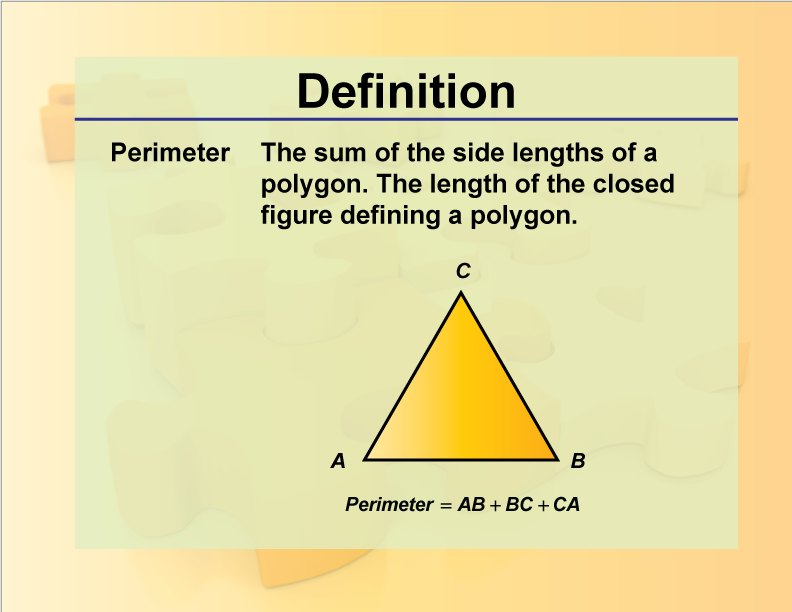
What is a Perimeter?
The section "What is a Perimeter?" provides a detailed explanation of the concept:
- Definition of Perimeter: Understand the fundamental meaning of perimeter as it relates to geometry and measurement.
- Components of Perimeter: Explore the elements that constitute the perimeter of a shape or object.
- Visualizing Perimeter: Learn how to visualize perimeter in various geometric figures such as squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles.
- Importance of Perimeter: Discover why understanding perimeter is essential in fields like mathematics, construction, and security.
- Examples of Perimeter: Illustrate the concept with practical examples and real-life scenarios.
Importance of Understanding Perimeter
The significance of comprehending perimeter is highlighted through various aspects:
- Foundation of Geometry: Perimeter serves as a foundational concept in geometry, laying the groundwork for more complex mathematical principles.
- Practical Applications: Understanding perimeter is crucial in practical fields such as architecture, engineering, and design, where accurate measurements are vital.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Proficiency in perimeter calculation enhances problem-solving abilities, allowing individuals to tackle geometric problems with confidence.
- Real-World Relevance: From fencing a garden to securing a property, the practical applications of perimeter are ubiquitous in daily life.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing perimeter requirements encourages critical thinking and spatial reasoning, fostering cognitive development.
Examples of Perimeter in Real Life
Real-life scenarios demonstrate the practical relevance of perimeter:
- Fencing a Garden: Calculating the perimeter helps determine the amount of fencing required to enclose a garden, ensuring accurate material estimation.
- Securing a Property: Establishing the perimeter of a property assists in implementing security measures such as installing fences, gates, or surveillance systems.
- Measuring Land Area: Understanding perimeter aids in measuring the boundaries of land parcels, essential for property surveys and land development projects.
- Designing Roadways: Engineers use perimeter calculations to plan road layouts, considering factors like road length, curves, and intersections.
- Constructing Buildings: Architects and builders utilize perimeter measurements to determine the layout and size of structures, optimizing space utilization.

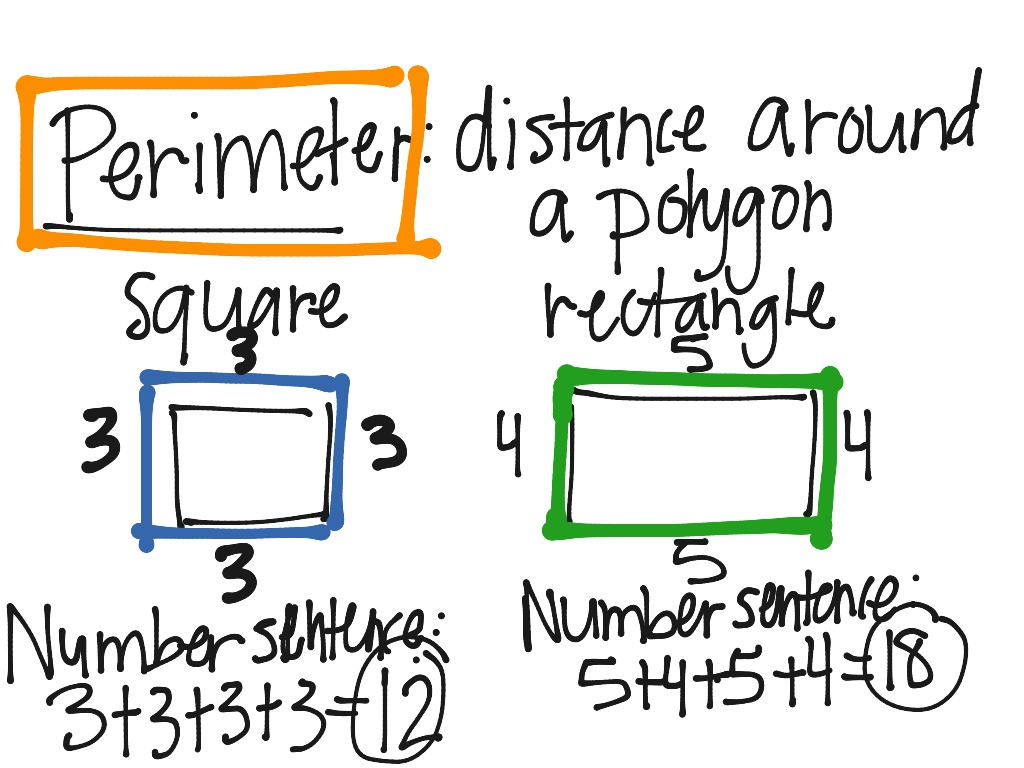
Measuring Perimeter
Measuring perimeter involves determining the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is a fundamental concept in geometry and is essential for various real-world applications such as construction, landscaping, and fencing.
There are several steps involved in measuring perimeter:
- Identify the Shape: Begin by identifying the type of shape whose perimeter you want to measure. Common shapes include squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and irregular polygons.
- Understand the Boundary: Understand the boundary of the shape, which consists of all the sides or edges that enclose the shape. Each side contributes to the total perimeter.
- Measure Each Side: Use a ruler, tape measure, or other measuring tools to measure the length of each side of the shape. Ensure accuracy by aligning the measuring tool properly and reading the measurement carefully.
- Sum of All Sides: Once you have measured all the sides, add up their lengths to find the total perimeter of the shape. For regular shapes like squares and rectangles, you can use specific formulas to calculate the perimeter more efficiently.
Additionally, it's important to consider units of measurement when determining perimeter. Ensure that all measurements are in the same units, whether it's inches, centimeters, meters, or another unit, to obtain a meaningful result.
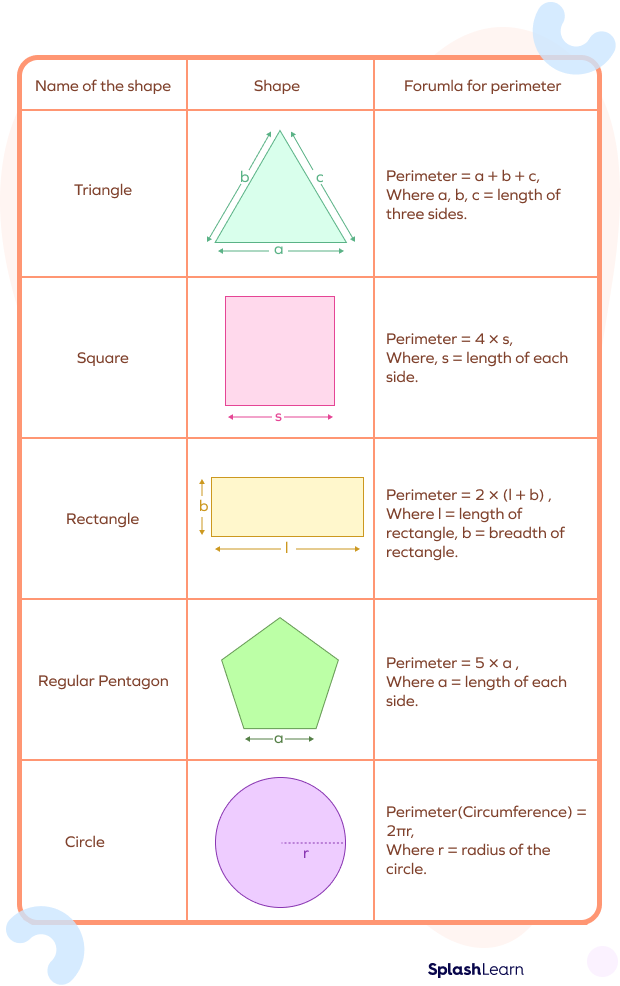
Perimeter Formulas
Perimeter formulas are mathematical equations used to calculate the total length of the boundary of various geometric shapes. These formulas are essential tools for determining perimeter efficiently.
Here are some common perimeter formulas for basic geometric shapes:
| Shape | Formula |
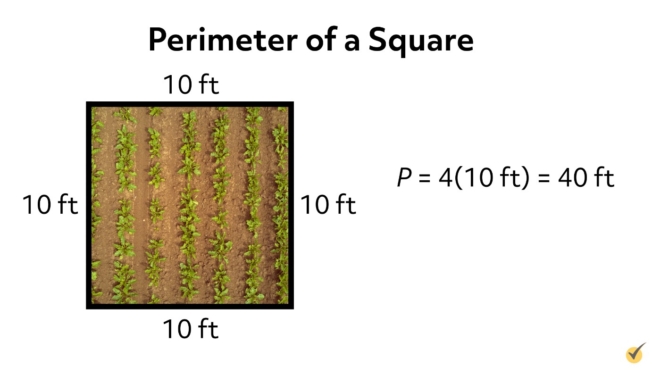
| Square | Perimeter = 4 * Side Length |
| Rectangle | Perimeter = 2 * (Length + Width) |
| Triangle | Perimeter = Side1 + Side2 + Side3 |
| Circle | Perimeter = 2 * π * Radius |
It's important to note that the units of measurement used for the lengths of sides or radius should be consistent when using these formulas to ensure accurate results.
Perimeter vs. Area
Perimeter and area are two fundamental concepts in geometry, each serving different purposes in measuring and describing shapes.
Perimeter:
- The perimeter of a shape refers to the total length of its boundary. It measures how long the outline of the shape is.
- Perimeter is expressed in linear units such as inches, centimeters, or meters.
- Perimeter is useful in real-world scenarios involving fencing, construction, and determining the amount of material needed to enclose a space.
Area:
- The area of a shape refers to the amount of space enclosed by the shape.
- Area is expressed in square units such as square inches, square centimeters, or square meters.
- Area helps in understanding the extent of coverage or surface within a shape and is crucial in various fields like agriculture, architecture, and urban planning.
In summary, while perimeter focuses on the length of the boundary of a shape, area quantifies the space enclosed by the shape, providing complementary information about its characteristics.
Perimeter in Geometry
In geometry, perimeter plays a crucial role in defining the boundary of various shapes and figures. It is an essential concept that helps in characterizing and analyzing geometric objects.
Key Points:
- Definition: The perimeter of a geometric shape is the total length of its boundary or the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Types of Shapes: Perimeter is applicable to various shapes in geometry, including polygons (such as triangles, rectangles, and pentagons), circles, and irregular shapes.
- Calculation: The method to calculate perimeter depends on the type of shape. For regular polygons, the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides. For irregular shapes, all the side lengths need to be added together.
- Units: Perimeter is expressed in linear units, such as inches, centimeters, meters, or any other appropriate unit of measurement.
- Applications: Understanding perimeter is essential in various geometric problems, including finding the length of fencing needed to enclose a garden, determining the perimeter of a plot of land, or calculating the circumference of a circle.
Overall, perimeter serves as a fundamental concept in geometry, providing valuable information about the size and shape of geometric figures.

Perimeter in Security
Perimeter plays a critical role in security measures, particularly in safeguarding physical spaces and facilities. Establishing a secure perimeter is essential for protecting assets, property, and people from unauthorized access or intrusion.
Key Aspects:
- Boundary Protection: A well-defined perimeter acts as the first line of defense against intruders by establishing clear boundaries that delineate protected areas from external threats.
- Physical Barriers: Security perimeters often incorporate physical barriers such as fences, walls, gates, or bollards to deter unauthorized entry and control access points.
- Surveillance Systems: Perimeter security is enhanced through the deployment of surveillance systems, including CCTV cameras, motion sensors, and alarm systems, to monitor and detect any suspicious activity along the perimeter.
- Access Control: Controlling access points along the perimeter through measures like access cards, biometric scanners, or security personnel helps in regulating entry and ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to restricted areas.
- Response Protocols: Establishing response protocols and security procedures is essential for addressing perimeter breaches effectively, including timely detection, notification, and intervention to mitigate security risks.
Overall, perimeter security measures are essential components of comprehensive security strategies, providing proactive protection and defense against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Perimeter in Construction
In construction, understanding perimeter is essential for various aspects of building design and implementation. The perimeter of a structure refers to the continuous line forming the boundary or outline of a building or a specific area within a construction site.
Here are some key points regarding the significance of perimeter in construction:
- Foundation Planning: Determining the perimeter helps in planning the foundation layout accurately. It allows builders to allocate resources efficiently and ensure structural stability.
- Material Estimation: Calculating the perimeter aids in estimating the quantity of materials required for construction, such as concrete for footings or fencing for enclosing the perimeter.
- Site Security: Defining the perimeter is crucial for establishing security measures, including the installation of perimeter fencing or monitoring systems to safeguard the construction site from unauthorized access and potential theft.
- Regulatory Compliance: Building codes often mandate specific requirements regarding the perimeter, such as setback distances from property lines or height restrictions for perimeter walls or fences. Adhering to these regulations is essential for obtaining necessary permits and approvals.
- Utilities Installation: Planning the perimeter allows for the installation of utility lines, such as water, electricity, and gas, ensuring they are properly routed around the building or site boundary.
Overall, considering the perimeter in construction projects is fundamental for efficient planning, compliance with regulations, and ensuring the safety and security of the site and its occupants.
Perimeter in Mathematics
In mathematics, the perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Understanding perimeter is fundamental in various mathematical concepts and applications:
- Basic Geometry: Perimeter is one of the basic properties used to describe geometric shapes. It is often taught alongside concepts like area and volume, providing a comprehensive understanding of shape properties.
- Measurement: Perimeter involves measuring distances along the outline of a shape. This measurement is essential for practical applications, such as determining the amount of fencing needed to enclose a garden or the length of wire required to outline a shape in a technical drawing.
- Formula Application: Different shapes have specific formulas for calculating perimeter. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides, while the perimeter of a circle is determined using the circumference formula.
- Problem Solving: Perimeter is often used in problem-solving scenarios, where students are required to find the perimeter of irregular shapes or to calculate missing dimensions given the perimeter and other known parameters.
- Real-world Applications: Understanding perimeter extends beyond the classroom, with applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. Professionals use perimeter calculations to plan construction projects, design roadways, and create blueprints for various structures.
Overall, a solid grasp of perimeter in mathematics is crucial for developing spatial reasoning skills, solving practical problems, and applying mathematical concepts in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concept of perimeter is essential across various disciplines, including mathematics, construction, and real-life applications. Whether it's measuring the boundary of a geometric shape, planning the foundation layout of a building, or estimating material quantities for construction projects, the notion of perimeter plays a crucial role.
By grasping the significance of perimeter, individuals can enhance their problem-solving skills, develop spatial reasoning abilities, and effectively apply mathematical concepts in practical scenarios. Furthermore, considering perimeter in different contexts enables professionals to plan and execute projects efficiently, ensuring compliance with regulations and maintaining the safety and security of both structures and surrounding environments.
Overall, recognizing the importance of perimeter empowers individuals to navigate mathematical challenges, contribute to construction projects, and innovate in various fields where spatial measurements and boundaries are integral.

Xem video này để hiểu rõ về diện tích và chu vi trong toán học. Hãy tìm hiểu cách tính và ứng dụng của chúng trong cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Diện tích và Chu vi
READ MORE:
Xem video này để học cách phát âm và xem ví dụ về việc sử dụng từ 'chu vi' trong câu và cụm từ. Đây là tài liệu hữu ích cho việc hiểu và sử dụng 'chu vi' trong giao tiếp hàng ngày.
Chu vi - Cách phát âm + Ví dụ trong câu và cụm từ