Topic perimeter formula pentagon: Understanding the perimeter formula for a pentagon is essential for accurate geometric calculations. This article breaks down the formulas for both regular and irregular pentagons, providing clear examples and practical applications. Whether you're a student or a professional, mastering these concepts will enhance your mathematical skills and precision.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Formula for a Pentagon
- Introduction to Pentagon Geometry
- Understanding the Pentagon Shape
- Definition and Properties of a Pentagon
- Types of Pentagons
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- General Perimeter Formula
- Perimeter Formula for Regular Pentagon
- Perimeter Calculation for Regular Pentagon
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation for Regular Pentagon
- Perimeter Formula for Irregular Pentagon
- Perimeter Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
- Applications of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Practical Uses in Various Fields
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Calculations
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu về chu vi của ngũ giác, bao gồm cả ngũ giác đều và không đều, cùng với công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Perimeter Formula for a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total distance around the five sides of the polygon. To calculate the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all five sides.
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all five sides of equal length. If each side is denoted as \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. If the lengths of the five sides are denoted as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), \( d \), and \( e \), then the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
Examples
- For a regular pentagon with each side measuring 7 units, the perimeter is:
units. - For an irregular pentagon with sides measuring 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 units, the perimeter is:
units.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Pentagon Geometry
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon that can be either regular or irregular. Understanding the properties and formulas associated with pentagons is crucial for various mathematical and practical applications.
Properties of a Pentagon
- A pentagon has five sides and five angles.
- The sum of the internal angles of a pentagon is always 540 degrees.
- In a regular pentagon, all sides and angles are equal.
Types of Pentagons
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and interior angles are equal. Each interior angle is 108 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not necessarily equal.
Perimeter of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total distance around the polygon, which can be calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides.
Perimeter Formula for Regular Pentagon
For a regular pentagon with side length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
Perimeter Formula for Irregular Pentagon
For an irregular pentagon with sides of lengths \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), \( d \), and \( e \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
Understanding the Pentagon Shape
The pentagon is a five-sided polygon that can be found in both nature and human-made structures. Recognizing and understanding the shape of a pentagon is fundamental for geometry students and professionals alike.
Basic Characteristics of a Pentagon
- A pentagon has five sides and five vertices.
- The sum of the internal angles in any pentagon is always 540 degrees.
- In a regular pentagon, each interior angle is 108 degrees.
Regular vs. Irregular Pentagons
Pentagons can be classified into two main types: regular and irregular.
- Regular Pentagon: All five sides and angles are equal. This type of pentagon is symmetrical and has rotational symmetry of order 5.
- Irregular Pentagon: The sides and angles are not necessarily equal, leading to a more varied shape. Irregular pentagons do not have rotational symmetry.
Visual Representation
A pentagon can be easily identified by its distinct shape. Below is a visual representation of a regular and an irregular pentagon:
| Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
 |
 |
Geometric Properties
Understanding the geometric properties of pentagons is crucial for various applications:
- Area: The area of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the formula:
- Perimeter: As discussed, the perimeter of a pentagon is the sum of the lengths of its sides.
Definition and Properties of a Pentagon
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides and five angles. It is a fundamental shape in geometry and can be seen in various natural and human-made structures.
Definition
A pentagon is defined as a five-sided polygon. The term "pentagon" is derived from the Greek words "penta," meaning five, and "gon," meaning angle.
Properties of a Pentagon
- Sides and Vertices: A pentagon has five sides and five vertices.
- Internal Angles: The sum of the internal angles of any pentagon is always 540 degrees.
- Regular Pentagon: In a regular pentagon, all sides and angles are equal. Each internal angle is 108 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: An irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measures.
Mathematical Properties
Understanding the mathematical properties of pentagons helps in various geometric calculations:
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length of its five sides. For a regular pentagon with side length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
For an irregular pentagon with sides of lengths \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), \( d \), and \( e \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Area: The area of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the formula:
Examples in Real Life
Pentagons appear in various aspects of life, from architectural designs to natural formations. Recognizing the properties of pentagons can help in understanding and creating such structures.
Types of Pentagons
Pentagons, five-sided polygons, can be categorized into different types based on their sides and angles. The two main types of pentagons are Regular Pentagons and Irregular Pentagons.
- Regular Pentagon
A Regular Pentagon has all five sides of equal length and all interior angles equal to 108 degrees. This symmetry gives it unique geometric properties.
Properties of a Regular Pentagon:
- Equal side lengths
- Equal interior angles of 108 degrees
- It is both equilateral and equiangular
- Diagonals are equal in length and intersect at a common point inside the pentagon
Mathematical Representation:
The perimeter of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 5 \times s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. - Irregular Pentagon
An Irregular Pentagon has sides and angles that are not all equal. This type of pentagon can have a variety of shapes, depending on the lengths of its sides and the measures of its angles.
Properties of an Irregular Pentagon:
- Sides can be of different lengths
- Angles can be of different measures
- It does not have the symmetry of a regular pentagon
Mathematical Representation:
The perimeter of an irregular pentagon is the sum of the lengths of its five sides. It can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5
\]
where \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, \) and \( s_5 \) are the lengths of the five sides.

Basic Concepts of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. It is an important concept in geometry that applies to both regular and irregular shapes. The perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, feet, or inches.
To understand the perimeter better, consider the following key points:
- The perimeter of a shape is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- For regular polygons (shapes with all sides and angles equal), the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides.
- For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by adding the length of each side individually.
Formulas for Common Shapes
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Triangle | A triangle with sides 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm has a perimeter of |
|
| Square | A square with each side of 5 cm has a perimeter of |
|
| Rectangle | A rectangle with length 6 cm and width 4 cm has a perimeter of |
|
| Circle (Circumference) | A circle with radius 7 cm has a circumference of |
Example: Calculating Perimeter
Let's calculate the perimeter of a pentagon with sides of different lengths:
- Side 1: 5 cm
- Side 2: 7 cm
- Side 3: 6 cm
- Side 4: 8 cm
- Side 5: 4 cm
The perimeter P is the sum of all sides:
Real-World Applications
Understanding the perimeter is crucial in many real-world situations, such as:
- Fencing a garden: Knowing the perimeter helps determine the length of the fence needed.
- Framing a picture: Calculating the perimeter ensures the right amount of framing material is purchased.
- Installing baseboards: Measuring the perimeter of a room helps in buying the correct length of baseboards.
General Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundary. For different types of pentagons, there are specific formulas to calculate their perimeters. Understanding these formulas is essential for solving various geometrical problems.
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length. The formula for calculating the perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is straightforward:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. The formula for calculating the perimeter (P) of an irregular pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the five sides.
Example Calculations
- For a regular pentagon with a side length of 7 cm:
\[ P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \, \text{cm} \] - For an irregular pentagon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \, \text{cm} \]
Understanding these formulas allows you to calculate the perimeter for any pentagon, whether it is regular or irregular, enhancing your geometry skills and problem-solving abilities.
Perimeter Formula for Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon is a five-sided polygon where all sides are of equal length and all interior angles are equal. The perimeter of a regular pentagon can be easily calculated using a straightforward formula due to the uniformity of its sides.
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon with side length \( s \) is:
\[
P = 5 \times s
\]
This formula leverages the fact that a regular pentagon has five equal sides. Thus, multiplying the length of one side by 5 gives the total perimeter.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply this length by 5 to obtain the perimeter.
Example Calculation
Let's consider a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 units. The perimeter \( P \) can be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 5 \times 10 = 50 \text{ units}
\]
Therefore, the perimeter of this regular pentagon is 50 units.
Additional Notes
- The perimeter of a regular pentagon is always five times the length of one side.
- This simplicity makes the calculation for regular pentagons much easier compared to irregular pentagons, where each side length must be measured and summed individually.
Perimeter Calculation for Regular Pentagon
The perimeter of a regular pentagon can be calculated using a simple formula. A regular pentagon is a polygon with five equal sides and equal internal angles. The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is:
\( P = 5a \)
Where:
- P = Perimeter of the regular pentagon
- a = Length of one side of the pentagon
To calculate the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of one side of the regular pentagon. Let's denote this length as a.
- Multiply the length of the side a by 5, since all sides of a regular pentagon are equal.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
For example, if each side of the regular pentagon is 7 cm, the perimeter calculation will be:
\( P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \, \text{cm} \)
Thus, the perimeter of the regular pentagon is 35 cm.
Here is a step-by-step table to illustrate the calculation:
| Step | Description | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Measure the length of one side | a = 7 cm |
| 2 | Multiply by 5 | P = 5 × 7 |
| 3 | Result | P = 35 cm |
This straightforward approach ensures that you can quickly and accurately calculate the perimeter of any regular pentagon, provided you know the length of one of its sides.

Examples of Perimeter Calculation for Regular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is straightforward, as all its sides are equal in length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon is given by:
\( P = 5 \times a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the pentagon.
Let's go through some examples to understand the calculation process:
Example 1:
Consider a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 cm.
- Identify the length of one side \( a = 6 \) cm.
- Apply the perimeter formula:
\( P = 5 \times 6 \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 30 \) cm
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular pentagon with side length 6 cm is 30 cm.
Example 2:
Consider a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 cm.
- Identify the length of one side \( a = 10 \) cm.
- Apply the perimeter formula:
\( P = 5 \times 10 \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 50 \) cm
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular pentagon with side length 10 cm is 50 cm.
Example 3:
Consider a regular pentagon with each side measuring 15 cm.
- Identify the length of one side \( a = 15 \) cm.
- Apply the perimeter formula:
\( P = 5 \times 15 \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 75 \) cm
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular pentagon with side length 15 cm is 75 cm.
These examples illustrate the simplicity of calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon by multiplying the length of one side by 5.
Perimeter Formula for Irregular Pentagon
The perimeter of an irregular pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Since the sides of an irregular pentagon can have different lengths, there isn't a single formula like there is for a regular pentagon. Instead, you calculate the perimeter by adding up the lengths of each side.
Here is the step-by-step method to calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon:
- Measure the length of each side of the pentagon. Let's denote these lengths as \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, \) and \( s_5 \).
- Add all the measured lengths together to find the perimeter \( P \).
The formula for the perimeter of an irregular pentagon can be expressed as:
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \)
Let's look at an example:
Example
Find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 8 cm, 9 cm, 14 cm, 7 cm, and 11 cm.
Step-by-step calculation:
- Step 1: List the side lengths: 8 cm, 9 cm, 14 cm, 7 cm, and 11 cm.
- Step 2: Add the side lengths together:
\( P = 8 + 9 + 14 + 7 + 11 \)
\( P = 49 \text{ cm} \)
Thus, the perimeter of the irregular pentagon is 49 cm.
Perimeter Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, you need to sum the lengths of all its sides. Unlike a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, an irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths.
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter:
- Measure the length of each side of the pentagon. Let's denote these lengths as \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), and \(e\).
- Sum the lengths of all the sides using the formula: \[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \]
Let's go through a practical example:
Assume you have an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths:
- \(a = 5 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(b = 7 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(c = 6 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(d = 8 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(e = 4 \, \text{cm}\)
Using the perimeter formula, we calculate the perimeter as follows:
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular pentagon is \(30 \, \text{cm}\).
This simple approach can be applied to any irregular pentagon, no matter the side lengths. Ensure each side is measured accurately to obtain a precise perimeter.
Examples of Perimeter Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon involves adding the lengths of all its sides. Let's go through a few examples to understand this better.
Example 1
Consider an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths:
- Side a: 5 units
- Side b: 7 units
- Side c: 6 units
- Side d: 8 units
- Side e: 4 units
The perimeter (P) is calculated by summing these lengths:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e = 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 4 = 30 \text{ units}
\]
Example 2
For another irregular pentagon with the side lengths:
- Side a: 3.2 units
- Side b: 4.5 units
- Side c: 5.1 units
- Side d: 2.8 units
- Side e: 3.9 units
The perimeter (P) is calculated as follows:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e = 3.2 + 4.5 + 5.1 + 2.8 + 3.9 = 19.5 \text{ units}
\]
Example 3
Now, consider an irregular pentagon with these side lengths:
- Side a: 1.5 meters
- Side b: 2.3 meters
- Side c: 3.7 meters
- Side d: 4.6 meters
- Side e: 2.9 meters
The perimeter (P) can be determined by adding all side lengths:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e = 1.5 + 2.3 + 3.7 + 4.6 + 2.9 = 15.0 \text{ meters}
\]
These examples demonstrate how the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is simply the sum of the lengths of all its sides, making the calculation straightforward once all side lengths are known.
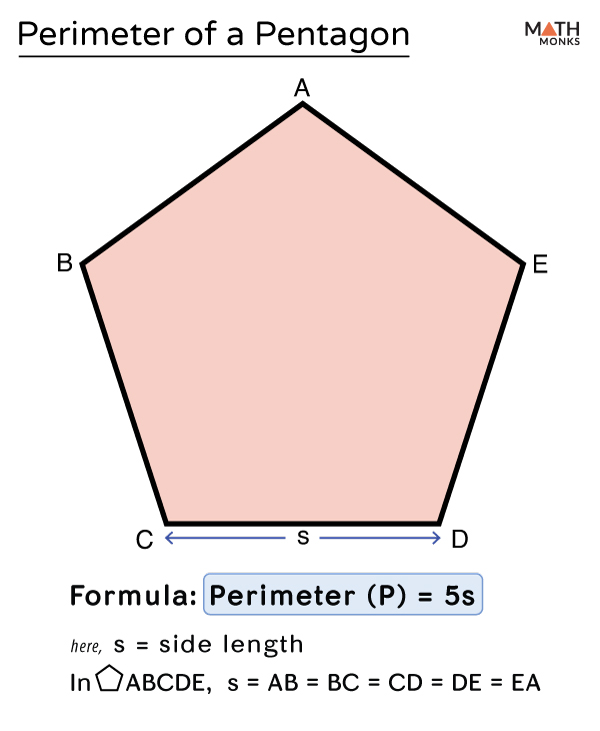
Applications of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
The calculation of the perimeter of a pentagon has numerous practical applications across various fields. Understanding how to determine the perimeter can help in diverse scenarios, from construction and architecture to recreational mathematics and educational purposes. Here are some key applications:
- Architecture and Construction:
Designing pentagonal structures or spaces requires precise perimeter calculations to ensure all sides fit together correctly. This can be seen in modern architectural designs where unique shapes are used for aesthetic and functional purposes.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners may use pentagonal layouts for parks, roundabouts, or other public spaces. Accurate perimeter measurements help in planning pathways, fencing, and other boundary-related features.
- Landscaping:
In landscaping, creating pentagon-shaped flower beds, ponds, or lawns requires knowing the perimeter to determine the amount of materials needed, such as edging, fencing, or irrigation systems.
- Educational Tools:
Teaching geometry often involves using polygons like pentagons to help students understand basic principles of shapes and measurements. Calculating perimeters is a fundamental exercise that aids in grasping broader mathematical concepts.
- Recreational Mathematics:
Pentagons are often used in puzzles and games, where calculating the perimeter can be part of the challenge. This helps in developing problem-solving skills and spatial awareness.
- Art and Design:
Artists and designers use geometric shapes, including pentagons, to create patterns and designs. Knowing the perimeter is crucial when planning the layout and dimensions of their artwork.
Overall, the ability to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon is a versatile skill that finds relevance in many practical and theoretical applications. Whether for professional projects or educational purposes, understanding how to determine the perimeter enhances one's ability to work with this unique geometric shape.
Practical Uses in Various Fields
The perimeter of a pentagon, like that of other polygons, has several practical applications across different fields. Understanding and applying the concept of perimeter can be crucial in various real-world scenarios:
-
Construction and Architecture:
In construction, knowing the perimeter of a site or structure is essential for planning and material estimation. For instance, determining the perimeter of a plot of land helps in laying foundations and planning boundaries. Similarly, architects use perimeter calculations to design the layout of buildings and other structures, ensuring the proper allocation of resources like fencing and wiring.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter calculations to design parks, recreational areas, and other public spaces. Calculating the perimeter helps in efficiently planning pathways, lighting, and other infrastructural elements to optimize the use of space and resources.
-
Art and Design:
In the field of art and fashion design, the perimeter is used to plan the layout of designs on various surfaces. Artists calculate the perimeter of canvases or other materials to ensure their designs fit perfectly within the space. Fashion designers use perimeter measurements for tailoring garments and creating intricate patterns on fabrics.
-
Sports and Recreation:
In sports, the perimeter of fields and courts is crucial for ensuring that the playing areas meet regulatory standards. For example, the perimeter of a running track or a basketball court must be precisely measured to adhere to official guidelines and ensure fair play.
-
Agriculture:
Farmers and agricultural planners use perimeter calculations to determine the boundaries of their fields. This helps in effective land management, planning irrigation systems, and installing fencing to protect crops from animals and pests.
-
Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics and game design, the perimeter of objects is often calculated to render shapes accurately. This ensures that visual representations in digital environments are precise, contributing to the overall aesthetics and functionality of the designs.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of perimeter calculations in various fields, highlighting the importance of understanding this fundamental geometric concept.
Tips and Tricks for Accurate Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, requires attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Here are some tips and tricks to help you achieve precise results:
- Use the Correct Formula:
- For a regular pentagon, use \( P = 5s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- For an irregular pentagon, sum the lengths of all sides: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Measure Accurately: Ensure all side lengths are measured with precision. Use a ruler or measuring tape for physical objects and double-check your measurements.
- Use Consistent Units: Always use the same units for all side lengths. Convert measurements to the same unit if necessary before performing calculations.
- Double-Check Calculations: After calculating the perimeter, review your work. Re-add the side lengths to confirm accuracy.
- Use Tools for Complex Shapes: For irregular pentagons or shapes with angles, consider using geometric software or tools for more precise measurements and calculations.
- Understand the Shape: Familiarize yourself with the properties of pentagons, both regular and irregular. Knowing that all sides of a regular pentagon are equal helps simplify the process.
- Apply Correct Significant Figures: When working with measurements, apply the appropriate number of significant figures to maintain accuracy, especially in scientific contexts.
- Check for Common Errors:
- Ensure no side lengths are omitted in calculations.
- Verify that all measurements are added correctly.
- Ensure you are not using the diameter or radius instead of the side length for regular pentagons inscribed in circles.
By following these tips and using a methodical approach, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations for both regular and irregular pentagons.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon can be straightforward if you follow the correct steps and avoid common pitfalls. Here are some typical mistakes and tips to avoid them:
- Incorrectly Identifying the Pentagon Type
One common error is not distinguishing between regular and irregular pentagons. A regular pentagon has all sides and angles equal, while an irregular pentagon does not. Use the correct formula for each type:
- For a regular pentagon: \( P = 5 \times s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- For an irregular pentagon: \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \), where \( s_1, s_2, \ldots, s_5 \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Incorrect Measurements
Ensure accurate measurement of sides. Even small errors can lead to significant discrepancies. Use precise tools and double-check measurements.
- Misusing Formulas for Derived Measurements
When using the radius or apothem to find the side length of a regular pentagon, apply the correct formulas:
- If using the radius (\( r \)): \( s = 2r \sin\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right) \)
- If using the apothem (\( a \)): \( s = 2a \tan\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right) \)
- Adding Side Lengths Incorrectly
For irregular pentagons, manually adding the side lengths can lead to errors. Write down each length and use a calculator to sum them accurately.
- Forgetting Units
Always include units in your final answer and ensure consistency throughout the calculation. Convert units if necessary to avoid confusion.
- Neglecting to Double-Check Work
Errors can be minimized by reviewing each step of the calculation. Double-check both the measurement and the arithmetic involved.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following these tips, you can ensure accurate perimeter calculations for any type of pentagon.

Conclusion and Summary
Understanding the perimeter formula for a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, is fundamental in various geometric applications. For a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is calculated using the simple formula:
\( P = 5a \)
Here, \( a \) is the length of one side of the pentagon.
For an irregular pentagon, where the sides have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
Calculating the perimeter is essential in many fields, such as architecture, land surveying, and various design and engineering applications. This knowledge ensures accurate measurements and helps in constructing geometric shapes accurately in practical scenarios.
To avoid common mistakes in these calculations, always ensure to:
- Double-check the length of each side.
- Use the correct formula based on whether the pentagon is regular or irregular.
- Accurately convert units if necessary to maintain consistency.
In summary, mastering the perimeter calculations for pentagons enhances your mathematical skills and provides practical benefits in diverse professional fields. Practice with real-world examples and varied problems to build a robust understanding and application of these geometric principles.
Tìm hiểu về chu vi của ngũ giác, bao gồm cả ngũ giác đều và không đều, cùng với công thức và ví dụ minh họa.
Chu vi của Ngũ giác, Chu vi cho Ngũ giác Đều và Không Đều cùng với Công thức & Ví dụ
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi của một hình ngũ giác một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Của Một Hình Ngũ Giác