Topic trapezoid perimeter calculator: Discover how to effortlessly calculate the perimeter of any trapezoid with our comprehensive trapezoid perimeter calculator. Whether for academic purposes or practical applications, our guide simplifies the process, ensuring accurate results every time. Explore the key properties, detailed steps, and handy tips to master trapezoid perimeter calculations with ease.
Table of Content
- Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator
- Introduction to Trapezoid Perimeter Calculation
- Understanding Trapezoids
- Key Properties of a Trapezoid
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
- Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Example Calculations
- Interactive Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Applications of Trapezoid Perimeter in Real Life
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách xác định chu vi và diện tích của hình thang. Video này giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách tính toán các yếu tố của hình thang.
Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator
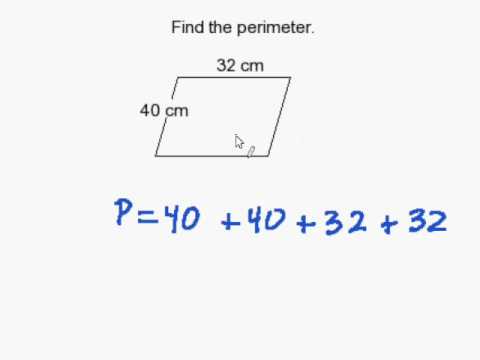
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. To find the perimeter of a trapezoid, you need to know the lengths of all four sides. The formula for calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid is:
\[
P = a + b + c + d
\]
Where:
- \( a \) is the length of the first non-parallel side
- \( b \) is the length of the first parallel side
- \( c \) is the length of the second non-parallel side
- \( d \) is the length of the second parallel side
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
- Measure the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid.
- Identify the lengths of the parallel sides (\( b \) and \( d \)).
- Identify the lengths of the non-parallel sides (\( a \) and \( c \)).
- Sum the lengths of all four sides using the formula: \[ P = a + b + c + d \]
Example Calculation
Consider a trapezoid with sides \( a = 3 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 7 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \), and \( d = 9 \, \text{cm} \). Using the perimeter formula:
\[
P = 3 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm}
\]
The perimeter of the trapezoid is 24 cm.
Interactive Calculator
Use the following tool to quickly calculate the perimeter of your trapezoid:

READ MORE:
Introduction to Trapezoid Perimeter Calculation
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium in some regions, is a four-sided figure with at least one pair of parallel sides. Calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Understanding how to determine the perimeter is essential for various applications in geometry, design, and real-world problem-solving. This section will guide you through the basics and the step-by-step process to find the perimeter of any trapezoid.
In a trapezoid, the parallel sides are referred to as the "bases," and the non-parallel sides are called the "legs." To calculate the perimeter, you simply need to add up the lengths of these four sides. Here's how you can approach it:
- Identify the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid. Let these sides be denoted as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \).
- Recognize which sides are parallel. These are typically the longer sides and are often labeled as \( b \) and \( d \).
- The other two sides, \( a \) and \( c \), are the non-parallel sides.
- Apply the perimeter formula: \[ P = a + b + c + d \]
- Sum the lengths of all four sides to get the perimeter.
For example, if you have a trapezoid with side lengths \( a = 4 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \), and \( d = 7 \, \text{cm} \), the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 4 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} = 22 \, \text{cm}
\]
The formula and method apply regardless of the specific measurements of the trapezoid, making it a versatile approach to solve various geometric problems. In the following sections, we will explore more detailed examples, common mistakes, and practical applications of trapezoid perimeter calculations.
Understanding Trapezoids
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium in some regions, is a type of quadrilateral characterized by having at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called the "bases" of the trapezoid, while the other two sides are referred to as the "legs." Trapezoids can vary greatly in their appearance and properties, but their defining feature remains the pair of parallel sides.
To understand trapezoids better, consider the following key aspects:
- Bases: The two parallel sides of a trapezoid are known as the bases. These are typically denoted as \( b_1 \) and \( b_2 \).
- Legs: The non-parallel sides of a trapezoid are called the legs, often labeled as \( a \) and \( c \).
- Height: The height (or altitude) of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance between the two bases.
- Angles: The angles adjacent to each base can vary, leading to different types of trapezoids. For example:
- Right Trapezoid: At least one pair of adjacent angles is a right angle (90 degrees).
- Isosceles Trapezoid: The legs (non-parallel sides) are of equal length, and the base angles are equal.
- Scalene Trapezoid: All sides and angles are of different lengths and measures.
Trapezoids can be classified into several types based on their properties:
| Type of Trapezoid | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Right Trapezoid | One pair of adjacent angles is 90 degrees. |
| Isosceles Trapezoid | The legs are equal in length, and the base angles are equal. |
| Scalene Trapezoid | No sides or angles are equal. |
The different types of trapezoids exhibit unique properties and applications. Understanding these variations is crucial for correctly calculating dimensions such as the perimeter and area. For example, isosceles trapezoids are often seen in architectural designs due to their symmetry, while right trapezoids are commonly used in constructing ramps and slides.
By familiarizing yourself with these fundamental aspects of trapezoids, you can better appreciate their geometric properties and apply this knowledge to solve practical problems involving their measurements.
Key Properties of a Trapezoid
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium, is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. Here are the key properties of a trapezoid:
- Parallel Sides: A trapezoid has two parallel sides, referred to as the bases. The other two sides are called the legs.
- Angles: The angles adjacent to each base are supplementary, meaning their sum is 180 degrees.
- Height: The perpendicular distance between the bases is known as the height (or altitude) of the trapezoid.
- Area: The area \(A\) of a trapezoid can be calculated using the formula:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h \] where \(b_1\) and \(b_2\) are the lengths of the bases, and \(h\) is the height. - Midsegment: The segment that connects the midpoints of the legs is parallel to the bases and its length is the average of the lengths of the bases:
\[ \text{Midsegment} = \frac{b_1 + b_2}{2} \] - Symmetry: An isosceles trapezoid, a special type of trapezoid, has non-parallel sides (legs) that are equal in length, and its diagonals are also equal in length.
| Property | Description |
| Parallel Sides | Two sides (bases) are parallel. |
| Supplementary Angles | Angles adjacent to each base add up to 180 degrees. |
| Height | Perpendicular distance between the bases. |
| Area Formula | \[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h \] |
| Midsegment | \[ \frac{b_1 + b_2}{2} \], connects midpoints of legs. |
| Symmetry | Isosceles trapezoids have equal legs and equal diagonals. |
Formula for Calculating the Perimeter
To calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid, you need to know the lengths of all four of its sides. The formula for the perimeter (P) is straightforward and is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
where:
- \( a \) is the length of the first parallel side (base)
- \( b \) is the length of the second parallel side (base)
- \( c \) is the length of the first non-parallel side (leg)
- \( d \) is the length of the second non-parallel side (leg)
This formula simply adds up the lengths of all the sides of the trapezoid to find its perimeter.
Example Calculation
Let's consider an example where the side lengths of the trapezoid are as follows:
- \( a = 5 \) units
- \( b = 7 \) units
- \( c = 3 \) units
- \( d = 4 \) units
Using the perimeter formula, we get:
\[ P = 5 + 7 + 3 + 4 = 19 \text{ units} \]
So, the perimeter of the trapezoid in this example is 19 units.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure and record the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid.
- Plug these measurements into the perimeter formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \).
- Add the four side lengths together to get the perimeter.
Using an Online Calculator
For quick and accurate results, you can use an online trapezoid perimeter calculator. These tools typically require you to input the lengths of the sides and will compute the perimeter for you. This method is especially useful for complex or irregular trapezoids.
Common Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding the perimeter calculation of a trapezoid:
- What units should I use? You can use any units (e.g., meters, centimeters, inches) as long as all sides are measured in the same unit.
- Can this formula be used for any trapezoid? Yes, the formula applies to all trapezoids, regardless of their specific shape or side lengths.
- Why is calculating the perimeter important? Knowing the perimeter is useful in various practical applications such as construction, fencing, and material estimation.
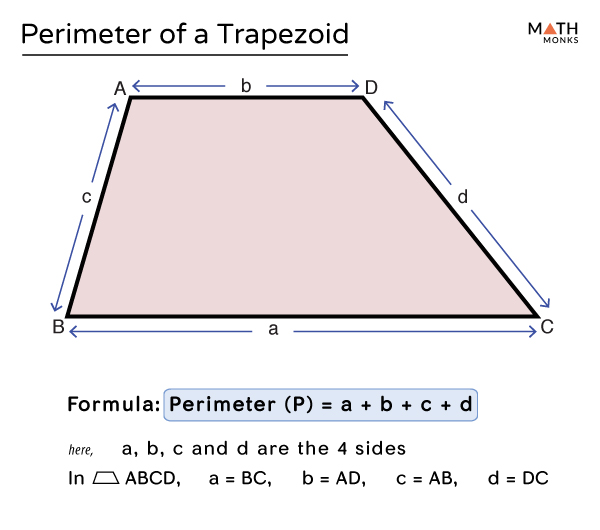
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Follow these steps to find the perimeter:
- Identify the lengths of the four sides of the trapezoid. Label them as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \).
- \( a \): Length of the first parallel side
- \( b \): Length of the second parallel side
- \( c \): Length of the first non-parallel side
- \( d \): Length of the second non-parallel side
- Use the perimeter formula for a trapezoid:
\[
P = a + b + c + d
\] - Sum the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter:
\[
P = a + b + c + d
\]
Let's look at an example:
Suppose you have a trapezoid with the following side lengths:
- \( a = 5 \) units
- \( b = 10 \) units
- \( c = 3 \) units
- \( d = 7 \) units
To find the perimeter, sum these lengths:
\[
P = 5 + 10 + 3 + 7 = 25 \text{ units}
\]
Thus, the perimeter of this trapezoid is 25 units.
Example Calculations
Here are some example calculations to illustrate how to find the perimeter of a trapezoid:
Example 1:
Consider a trapezoid with the following side lengths:
- Base \(a\) = 8 units
- Base \(b\) = 12 units
- Leg \(c\) = 5 units
- Leg \(d\) = 7 units
To find the perimeter, use the formula:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
Substituting the given values:
\[ P = 8 + 12 + 5 + 7 = 32 \text{ units} \]
Example 2:
Consider another trapezoid with the following side lengths:
- Base \(a\) = 5 units
- Base \(b\) = 10 units
- Leg \(c\) = 3 units
- Leg \(d\) = 7 units
To find the perimeter, use the formula:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
Substituting the given values:
\[ P = 5 + 10 + 3 + 7 = 25 \text{ units} \]
Example 3:
Let's calculate the perimeter for a trapezoid with the following dimensions:
- Base \(a\) = 6 units
- Base \(b\) = 9 units
- Leg \(c\) = 4 units
- Leg \(d\) = 8 units
Using the perimeter formula:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
Substituting the values:
\[ P = 6 + 9 + 4 + 8 = 27 \text{ units} \]
Interactive Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator
Welcome to the Interactive Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator! Use this tool to easily compute the perimeter of any trapezoid by inputting the lengths of its sides. Follow the steps below to get started:
- Enter the lengths of the sides of the trapezoid:
- Base 1 (a): The length of the first parallel side.
- Base 2 (b): The length of the second parallel side.
- Leg 1 (c): The length of the first non-parallel side.
- Leg 2 (d): The length of the second non-parallel side.
- Click the "Calculate" button to compute the perimeter.
- The calculator will display the perimeter based on the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d
\]
Common Mistakes and Tips
When calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid, it's essential to avoid common mistakes and follow useful tips to ensure accuracy. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Common Mistakes
- Incorrect Base Identification: Confusing the longer base with the shorter base can lead to incorrect calculations. Make sure to identify and input them correctly.
- Mislabeling Angles: Ensure the angles entered correspond to the correct vertices as per the diagram you are using. Mislabeling can lead to incorrect height calculations and overall errors.
- Ignoring Units: Mixing units of measurement (e.g., inches and centimeters) can result in incorrect calculations. Consistently use one unit throughout your calculations.
- Incomplete Data: Providing incomplete data may lead to errors or incomplete calculations. Ensure all required fields are filled out.
- Overlooking Decimal Precision: Selecting an inappropriate number of decimal places can affect the accuracy of your results. Choose precision that aligns with your needs.
Tips for Accurate Calculations
- Measure Precisely: Ensure that all lengths and angles are measured accurately to get precise results.
- Double-Check Values: Before calculating, double-check the input values to avoid any errors.
- Use Correct Units: Make sure all input values are in the same unit of measurement (e.g., all in centimeters or all in inches).
- Consistent Angles: When inputting angles, ensure they are in degrees unless specified otherwise.
- Refer to Diagrams: Use the provided diagrams and visual aids to understand the placement of each input value correctly.
Applications of Trapezoid Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of a trapezoid has practical applications in various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Architecture and Construction: Trapezoids are often used in roof designs and structural elements. Knowing the perimeter helps in calculating materials needed for edging and framing.
- Engineering: In bridge and truss design, trapezoids help distribute loads effectively. The perimeter calculation aids in material estimation and structural analysis.
- Surveying and Land Measurement: Surveyors use trapezoidal shapes to approximate areas of irregular plots of land. The perimeter helps in fencing and boundary marking.
- Graphics and Computer Modeling: In computer graphics, trapezoids are used in rendering algorithms and simulations. Calculating the perimeter is essential for texture mapping and object scaling.
- Agriculture: Farmers use trapezoidal plots to optimize land use. The perimeter calculation is crucial for planning irrigation systems and fencing.
- Product Design: Items like handbags, buckets, and bathtubs often have trapezoidal shapes. Knowing the perimeter helps in material selection and manufacturing processes.
- Physics and Mechanics: Trapezoidal configurations are used in mechanical systems like pulley arrangements. The perimeter aids in designing belts and chains for efficient power transmission.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of trapezoid perimeter calculations in real life, highlighting its importance across various domains.
Additional Resources
For further reading and tools to help you understand and calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid, consider the following resources:
-
Online Calculators
- - This tool allows you to input the lengths of the sides of a trapezoid and calculates the perimeter for you.
- - An easy-to-use calculator that provides quick results for the perimeter of a trapezoid.
-
Educational Websites
- - A comprehensive guide on trapezoids, including how to calculate their perimeter and area.
- - Detailed explanations and interactive tools to help you understand the properties and calculations related to trapezoids.
-
Math Forums and Communities
- - A Q&A site where you can ask questions about trapezoid perimeter calculations and get answers from math experts.
- - A community where you can discuss and seek help on various math topics, including trapezoid perimeter.
-
Books and Publications
- Geometry for Dummies by Mark Ryan - A beginner-friendly book that covers a wide range of geometry topics, including trapezoids.
- The Complete Book of Trapezoid Problems by Ann X. Carter - A specialized book focused on trapezoids, offering various problems and solutions.
Hướng dẫn cách xác định chu vi và diện tích của hình thang. Video này giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách tính toán các yếu tố của hình thang.
Xác Định Chu Vi và Diện Tích Hình Thang
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách xác định diện tích và chu vi ướt của mặt cắt kênh hình thang. Video này giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách tính toán các yếu tố của kênh hình thang.
Xác Định Diện Tích và Chu Vi Ướt của Mặt Cắt Kênh Hình Thang