Topic perimeter of a half circle formula: Discover the easy steps to calculate the perimeter of a half circle with our comprehensive guide. Learn the formula, understand the components, and see practical examples to master this essential mathematical concept. Whether you're a student or a professional, this article will simplify the process and enhance your understanding.
Table of Content
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Introduction
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples of Calculating the Perimeter
- Applications in Real Life
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
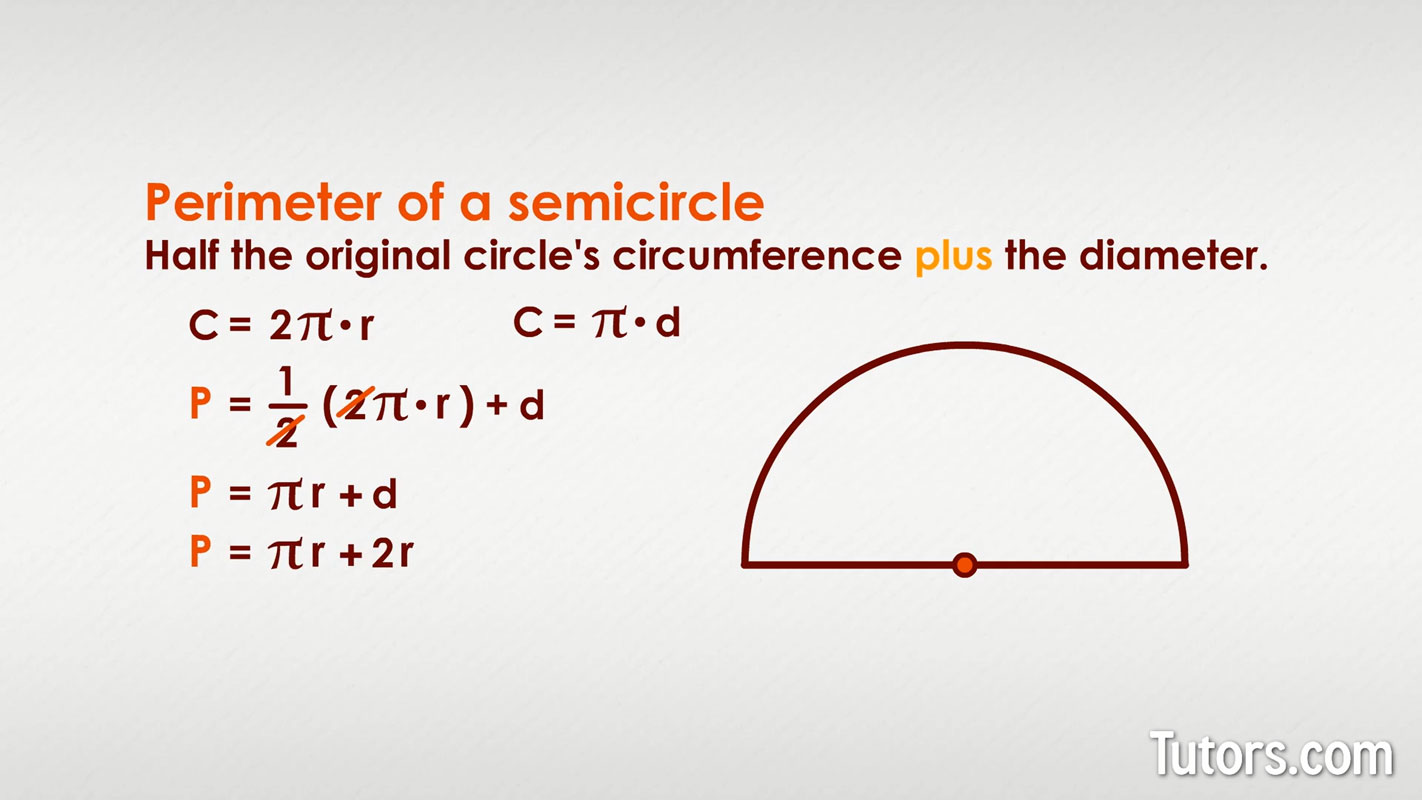
The perimeter of a half circle is calculated by adding the straight edge (diameter) to the curved edge (semicircular arc). The formula is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the half circle
- \( r \) is the radius of the half circle
- \( \pi \) is approximately 3.14159
The formula can also be expressed as:
\[ P = r (\pi + 2) \]
Example Calculation
For a half circle with a radius of 5 units, the perimeter can be calculated as follows:
\[ P = 5 (\pi + 2) \]
Plugging in the value of \(\pi\):
\[ P = 5 (3.14159 + 2) \]
\[ P = 5 \times 5.14159 \]
\[ P \approx 25.70795 \, \text{units} \]

Introduction
The perimeter of a half circle is an essential concept in geometry, combining both linear and curved measurements. Understanding how to calculate this perimeter is crucial for various practical applications, from engineering to everyday tasks.
In this guide, we will explore:
- The formula for the perimeter of a half circle
- Step-by-step calculation process
- Examples to illustrate the concept
- Common mistakes to avoid
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how to determine the perimeter of a half circle accurately and efficiently.
Let's start by examining the formula and the components involved.
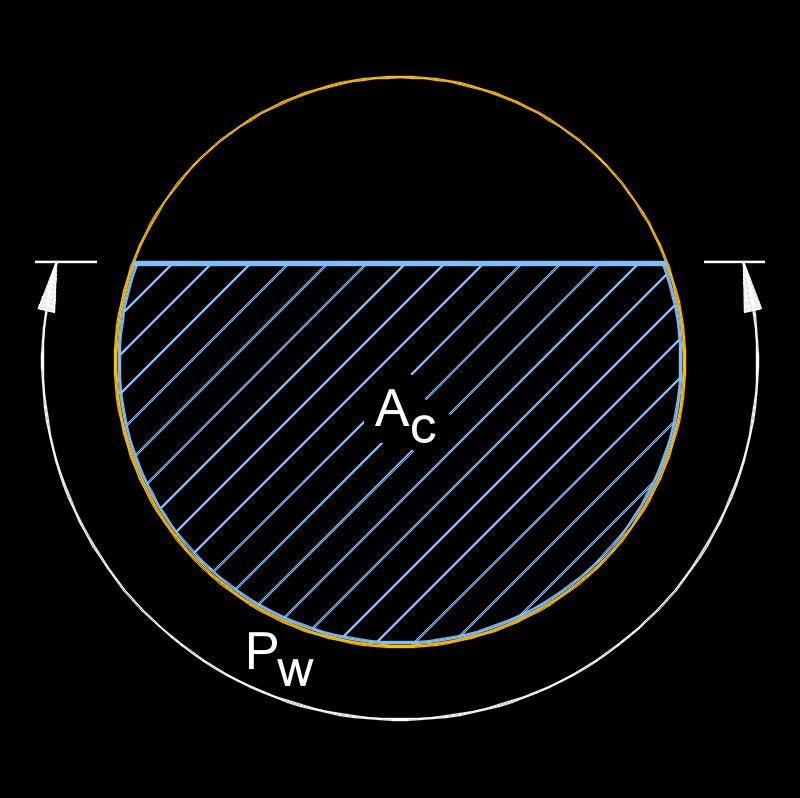
Understanding the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle, also known as the semicircle, is the total length around the half circle's edge. This perimeter includes both the straight edge (the diameter) and the curved edge (the semicircular arc).
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a half circle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the half circle
- \( r \) is the radius of the half circle
- \( \pi \) is approximately 3.14159
To understand this formula better, let's break it down into its components:
- Semicircular Arc Length: The length of the curved part of the half circle is given by the formula \( \pi r \). This is derived from the circumference formula of a full circle \( 2\pi r \), divided by 2.
- Diameter: The straight edge of the half circle is the diameter, which is \( 2r \).
Therefore, the total perimeter of the half circle is the sum of the semicircular arc length and the diameter, expressed as:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r = r (\pi + 2) \]
This formula helps in calculating the perimeter easily and accurately. Understanding each component's role ensures a clear grasp of the overall concept.
Next, we will delve into a step-by-step calculation to demonstrate the use of this formula in practical scenarios.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle is the sum of the straight edge (diameter) and the curved edge (half the circumference of a full circle). To derive the formula, we need to understand the components:
- Diameter (d) of the circle
- Radius (r) of the circle, which is half of the diameter: \( r = \frac{d}{2} \)
- Circumference (C) of a full circle, which is \( C = 2\pi r \)
Since we are dealing with a half circle, we take half of the circumference:
Half Circumference \( = \pi r \)
Now, we add the length of the diameter to the half circumference to get the perimeter (P) of the half circle:
Perimeter (P) of a half circle \( = \pi r + d \)
Substituting \( r = \frac{d}{2} \), we get:
Perimeter (P) of a half circle \( = \pi \left(\frac{d}{2}\right) + d \)
Which simplifies to:
\[
P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d
\]
To further simplify, we factor out the diameter (d):
\[
P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right)
\]
Thus, the final formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
\[
P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right)
\]
Or, using the radius (r):
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]
This formula provides a straightforward way to calculate the perimeter of any half circle given its diameter or radius.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a half circle, follow these detailed steps:
- Identify the diameter (d) or the radius (r) of the circle:
- If you have the diameter, the radius is calculated as \( r = \frac{d}{2} \).
- If you have the radius, the diameter is calculated as \( d = 2r \).
- Calculate the half circumference of the circle:
The circumference (C) of a full circle is given by \( C = 2\pi r \). For a half circle, the half circumference is:
\[
\text{Half Circumference} = \pi r
\] - Add the diameter to the half circumference:
The perimeter (P) of a half circle is the sum of the half circumference and the diameter:
\[
P = \pi r + d
\]Substitute \( r = \frac{d}{2} \) into the formula:
\[
P = \pi \left(\frac{d}{2}\right) + d
\] - Simplify the formula:
Combine the terms to get the final simplified formula:
\[
P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d
\]Factor out the diameter (d):
\[
P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right)
\] - Use the formula to calculate the perimeter:
Plug in the given diameter or radius into the formula to find the perimeter. For example, if the diameter (d) is 10 units:
\[
P = 10 \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right) \approx 10 \left(1.57 + 1\right) = 10 \times 2.57 = 25.7 \, \text{units}
\]
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any half circle.
Examples of Calculating the Perimeter
Here are some examples to illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a half circle:
Example 1: Given Diameter
- Given: Diameter (d) = 8 units
- Find the radius (r):
\[
r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{8}{2} = 4 \, \text{units}
\] - Calculate the half circumference:
\[
\text{Half Circumference} = \pi r = \pi \times 4 \approx 3.14 \times 4 = 12.56 \, \text{units}
\] - Calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = \pi r + d = 12.56 + 8 = 20.56 \, \text{units}
\]
Example 2: Given Radius
- Given: Radius (r) = 5 units
- Calculate the diameter (d):
\[
d = 2r = 2 \times 5 = 10 \, \text{units}
\] - Calculate the half circumference:
\[
\text{Half Circumference} = \pi r = \pi \times 5 \approx 3.14 \times 5 = 15.7 \, \text{units}
\] - Calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = \pi r + d = 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \, \text{units}
\]
Example 3: Using the Simplified Formula
- Given: Diameter (d) = 12 units
- Use the simplified formula:
\[
P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right)
\]Substitute \( d = 12 \):
\[
P = 12 \left(\frac{3.14}{2} + 1\right) = 12 \left(1.57 + 1\right) = 12 \times 2.57 = 30.84 \, \text{units}
\]
These examples demonstrate how to use both the step-by-step method and the simplified formula to calculate the perimeter of a half circle given different initial measurements.
Applications in Real Life
The concept of the perimeter of a half circle is used in various real-life scenarios. Here are some practical applications:
1. Architecture and Construction
In architecture and construction, the perimeter of a half circle is crucial when designing arches, domes, and curved structures. Accurate calculations ensure stability and aesthetic appeal.
- Arched Doorways and Windows: Knowing the perimeter helps in framing and fitting materials correctly.
- Bridges: Semi-circular arches are common in bridge design, and their perimeter aids in determining the length of materials needed.
2. Landscaping and Garden Design
Designers use the perimeter of half circles to create aesthetically pleasing garden layouts and structures.
- Pathways: Curved pathways often incorporate half circles, requiring precise perimeter calculations for paving and edging.
- Water Features: Semi-circular ponds or fountains use perimeter measurements for layout and construction.
3. Interior Design
In interior design, the perimeter of half circles is used to create unique and functional spaces.
- Furniture Design: Tables or seating areas with semi-circular designs need accurate perimeter measurements for material cutting and assembly.
- Decorative Elements: Wall art, mirrors, and other decorative pieces with semi-circular shapes require perimeter calculations for placement and mounting.
4. Event Planning
Event planners use half circle perimeters to design stages, seating arrangements, and decorative elements.
- Stages: Semi-circular stages provide better visibility for audiences, and accurate perimeter measurements are essential for setup.
- Seating Arrangements: Curved seating plans, often seen in theaters and arenas, rely on half circle perimeter calculations.
5. Engineering and Manufacturing
In engineering and manufacturing, understanding the perimeter of half circles is vital for creating parts and components.
- Machinery Parts: Semi-circular components, such as gears and pulleys, require precise perimeter measurements for functionality.
- Product Design: Many products, from containers to tools, incorporate semi-circular designs, necessitating accurate perimeter calculations.
By understanding and applying the formula for the perimeter of a half circle, professionals in various fields can ensure precision and efficiency in their work.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a half circle can sometimes lead to errors. Here are common mistakes and tips on how to avoid them:
1. Incorrectly Adding the Radius Instead of the Diameter
Mistake: Using the radius (r) instead of the diameter (d) in the formula.
Solution: Remember that the formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
\[
P = \pi r + d
\]
Ensure you use the diameter, not the radius, for the straight edge component.
2. Forgetting to Add the Straight Edge
Mistake: Calculating only the curved part (half circumference) and forgetting to add the diameter.
Solution: Always include both the half circumference and the diameter:
\[
P = \pi r + d
\]
3. Misinterpreting the Formula
Mistake: Confusing the formula for the perimeter of a half circle with that of a full circle or another shape.
Solution: Memorize the specific formula for a half circle and its components:
- Half Circumference: \( \pi r \)
- Diameter: \( d \)
Combine them correctly.
4. Incorrect Calculation of \(\pi\)
Mistake: Using an incorrect value for \(\pi\), such as 3.14 instead of a more accurate value.
Solution: Use a more precise value of \(\pi\) (e.g., 3.14159) or the \(\pi\) function on a calculator for better accuracy.
5. Rounding Errors
Mistake: Rounding intermediate steps too early, leading to inaccuracies in the final result.
Solution: Keep intermediate values as precise as possible and only round the final answer if necessary.
6. Misidentifying the Radius and Diameter
Mistake: Confusing the radius with the diameter.
Solution: Clearly distinguish between the radius (half of the diameter) and the diameter (twice the radius) before starting calculations.
- Radius: \( r \)
- Diameter: \( d = 2r \)
7. Incorrect Units
Mistake: Using inconsistent units, leading to errors in the final perimeter calculation.
Solution: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before performing calculations. Convert units if necessary.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following the suggested solutions, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a half circle and avoid errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a half circle?
The formula for the perimeter (or circumference) of a half circle is given by:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
- Why is there an additional \(2r\) in the formula?
The term \( \pi r \) represents the curved part of the half circle, which is half of the full circle's circumference. The additional \( 2r \) accounts for the straight-line diameter at the base of the half circle.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a half circle with a given diameter?
First, find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2. Then use the formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
For example, if the diameter is 10 units, the radius \( r \) is 5 units. The perimeter would be:
\[ P = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 = 5\pi + 10 \]
- Can the formula be applied to real-life situations?
Yes, the formula for the perimeter of a half circle can be applied in various real-life contexts, such as calculating the length of a semi-circular garden bed edging, the border of a semi-circular window, or any design element featuring a half circle shape.
- What are common mistakes when calculating the perimeter of a half circle?
- Forgetting to add the diameter (2r) to the curved part (\(\pi r\)).
- Using the diameter instead of the radius in the formula.
- Incorrectly approximating the value of \(\pi\).
- How accurate should the value of \(\pi\) be for practical calculations?
For most practical purposes, using \(\pi \approx 3.14\) is sufficient. For more precision, \(\pi \approx 3.14159\) can be used. For highly accurate scientific calculations, more decimal places of \(\pi\) may be necessary.

Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle is crucial for various practical applications, from engineering to everyday problem-solving. The formula for the perimeter of a half circle combines the curved part of the circle and the diameter, represented as:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \]
Here, \( r \) stands for the radius of the circle. This formula can be broken down as follows:
- Calculate the curved part of the half circle, which is half the circumference of the full circle: \( \pi r \).
- Add the length of the diameter, which is twice the radius: \( 2r \).
Thus, the complete perimeter of the half circle is the sum of these two components, yielding \( \pi r + 2r \). This formula is derived from the basic principles of circle geometry, ensuring that you account for both the curved and straight parts of the half circle's boundary.
In practical terms, knowing how to calculate this perimeter helps in various fields such as architecture, construction, and design, where precise measurements are necessary. By applying the formula correctly, one can efficiently determine the necessary dimensions for materials, spaces, and designs involving semicircular shapes.
To conclude, mastering the calculation of the perimeter of a half circle is a fundamental skill that extends beyond academic exercises and into real-world applications, demonstrating the importance of geometric knowledge in everyday life.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn
Video hướng dẫn tìm chu vi của hình bán nguyệt kết hợp với hình vuông. Hãy khám phá cách tính chu vi một cách dễ dàng và chính xác!
Tìm Chu Vi Của Hình Bán Nguyệt Kết Hợp Với Hình Vuông!