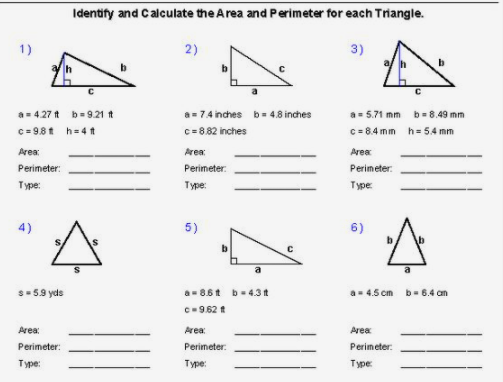
Topic what is the perimeter of rectangle efgh: Discover how to easily calculate the perimeter of rectangle EFGH using simple steps and formulas. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the concept, apply the formula, and solve practical examples. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone looking to enhance their math skills with clear explanations and real-world applications.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of Rectangle EFGH
- Understanding the Perimeter of Rectangle EFGH
- Introduction to Rectangle Perimeter
- Introduction to Rectangle Perimeter
- Understanding the Rectangle
- Understanding the Rectangle
- Definition of Perimeter
- Definition of Perimeter
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter
- Example Calculations
- Example Calculations
- Real-World Applications
- Real-World Applications
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video 'Chu vi của hình chữ nhật EFGH là gì?' giới thiệu cách tính chu vi của hình chữ nhật EFGH một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Hãy xem để nắm vững công thức và cách áp dụng vào thực tế!
Understanding the Perimeter of Rectangle EFGH
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the edges of the rectangle. To find the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of the rectangle's sides.
Formula for Perimeter
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( \text{length} + \text{width} ) \]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the length \( l \) and the width \( w \) of the rectangle.
- Add the length and the width:
- Multiply the sum by 2:
\[ l + w \]
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Example Calculation
Suppose rectangle EFGH has a length of 10 units and a width of 5 units. The perimeter can be calculated as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 10 units
- Width \( w \) = 5 units
- Calculate the sum of length and width:
- Multiply the sum by 2 to get the perimeter:
\[ 10 + 5 = 15 \]
\[ P = 2 \times 15 = 30 \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 30 units.

READ MORE:
Understanding the Perimeter of Rectangle EFGH
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the edges of the rectangle. To find the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of the rectangle's sides.
Formula for Perimeter
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( \text{length} + \text{width} ) \]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the length \( l \) and the width \( w \) of the rectangle.
- Add the length and the width:
- Multiply the sum by 2:
\[ l + w \]
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Example Calculation
Suppose rectangle EFGH has a length of 10 units and a width of 5 units. The perimeter can be calculated as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 10 units
- Width \( w \) = 5 units
- Calculate the sum of length and width:
- Multiply the sum by 2 to get the perimeter:
\[ 10 + 5 = 15 \]
\[ P = 2 \times 15 = 30 \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 30 units.

Introduction to Rectangle Perimeter
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the shape. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for various real-world applications, from simple measurements to complex architectural designs. This section will guide you through the basics of perimeter calculation for rectangle EFGH.
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you need to know the lengths of its sides. A rectangle has two pairs of equal opposite sides: the length (denoted as \( l \)) and the width (denoted as \( w \)).
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Where:
- \( l \) is the length of the rectangle
- \( w \) is the width of the rectangle
This formula is derived from adding the lengths of all four sides of the rectangle. Since opposite sides are equal, you can simplify the addition by multiplying the sum of the length and the width by 2.
- Identify the length (\( l \)) and the width (\( w \)) of rectangle EFGH.
- Sum the length and the width.
- Multiply the result by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if rectangle EFGH has a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter calculation would be as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 8 units
- Width \( w \) = 3 units
- Sum of length and width = \( 8 + 3 = 11 \)
- Perimeter \( P = 2 \times 11 = 22 \) units
Thus, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 22 units. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for solving more complex geometry problems and for practical applications in various fields.
Introduction to Rectangle Perimeter
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the shape. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for various real-world applications, from simple measurements to complex architectural designs. This section will guide you through the basics of perimeter calculation for rectangle EFGH.
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you need to know the lengths of its sides. A rectangle has two pairs of equal opposite sides: the length (denoted as \( l \)) and the width (denoted as \( w \)).
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Where:
- \( l \) is the length of the rectangle
- \( w \) is the width of the rectangle
This formula is derived from adding the lengths of all four sides of the rectangle. Since opposite sides are equal, you can simplify the addition by multiplying the sum of the length and the width by 2.
- Identify the length (\( l \)) and the width (\( w \)) of rectangle EFGH.
- Sum the length and the width.
- Multiply the result by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if rectangle EFGH has a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter calculation would be as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 8 units
- Width \( w \) = 3 units
- Sum of length and width = \( 8 + 3 = 11 \)
- Perimeter \( P = 2 \times 11 = 22 \) units
Thus, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 22 units. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for solving more complex geometry problems and for practical applications in various fields.
Understanding the Rectangle
A rectangle is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, with opposite sides that are equal in length and four right angles (90 degrees). Rectangles are a fundamental shape in geometry and are widely used in various fields, from mathematics to engineering.
Key properties of a rectangle include:
- Opposite Sides are Equal: The lengths of opposite sides are equal. If one pair of opposite sides is labeled as \( l \) (length) and the other pair as \( w \) (width), then both lengths are equal to \( l \) and both widths are equal to \( w \).
- Right Angles: All four interior angles of a rectangle are right angles, meaning they each measure 90 degrees.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length. Each diagonal divides the rectangle into two congruent right triangles.
Mathematically, if we denote the vertices of the rectangle as E, F, G, and H, then the opposite sides EF and GH will be equal in length, and the other pair of opposite sides EG and FH will also be equal in length.
The perimeter of rectangle EFGH, as discussed earlier, is given by:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Understanding these properties helps in comprehending the structure and calculation related to rectangles. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of identifying and working with these properties:
- Identify the Length and Width: Measure or note the lengths of two adjacent sides. One will be the length (\( l \)) and the other will be the width (\( w \)).
- Verify the Right Angles: Ensure that all interior angles are right angles, confirming the shape is a rectangle.
- Calculate the Diagonals: Use the Pythagorean theorem if necessary to verify the length of the diagonals, where the diagonal \( d \) can be found using: \[ d = \sqrt{ l^2 + w^2 } \]
For example, consider rectangle EFGH with \( l = 6 \) units and \( w = 4 \) units:
- Length \( l \) = 6 units
- Width \( w \) = 4 units
- Calculate the diagonal: \[ d = \sqrt{ 6^2 + 4^2 } = \sqrt{ 36 + 16 } = \sqrt{ 52 } \approx 7.21 \text{ units} \]
By understanding these fundamental properties and calculations, you can confidently work with rectangles in various mathematical and practical contexts.
Understanding the Rectangle
A rectangle is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, with opposite sides that are equal in length and four right angles (90 degrees). Rectangles are a fundamental shape in geometry and are widely used in various fields, from mathematics to engineering.
Key properties of a rectangle include:
- Opposite Sides are Equal: The lengths of opposite sides are equal. If one pair of opposite sides is labeled as \( l \) (length) and the other pair as \( w \) (width), then both lengths are equal to \( l \) and both widths are equal to \( w \).
- Right Angles: All four interior angles of a rectangle are right angles, meaning they each measure 90 degrees.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length. Each diagonal divides the rectangle into two congruent right triangles.
Mathematically, if we denote the vertices of the rectangle as E, F, G, and H, then the opposite sides EF and GH will be equal in length, and the other pair of opposite sides EG and FH will also be equal in length.
The perimeter of rectangle EFGH, as discussed earlier, is given by:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Understanding these properties helps in comprehending the structure and calculation related to rectangles. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of identifying and working with these properties:
- Identify the Length and Width: Measure or note the lengths of two adjacent sides. One will be the length (\( l \)) and the other will be the width (\( w \)).
- Verify the Right Angles: Ensure that all interior angles are right angles, confirming the shape is a rectangle.
- Calculate the Diagonals: Use the Pythagorean theorem if necessary to verify the length of the diagonals, where the diagonal \( d \) can be found using: \[ d = \sqrt{ l^2 + w^2 } \]
For example, consider rectangle EFGH with \( l = 6 \) units and \( w = 4 \) units:
- Length \( l \) = 6 units
- Width \( w \) = 4 units
- Calculate the diagonal: \[ d = \sqrt{ 6^2 + 4^2 } = \sqrt{ 36 + 16 } = \sqrt{ 52 } \approx 7.21 \text{ units} \]
By understanding these fundamental properties and calculations, you can confidently work with rectangles in various mathematical and practical contexts.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. For any polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. When dealing with rectangles, the perimeter is specifically the sum of twice the length and twice the width of the rectangle.
To understand the perimeter more clearly, let's break it down step by step:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the shape you are dealing with. In this context, it is a rectangle labeled EFGH.
- Measure the Sides: Measure or identify the lengths of the two distinct pairs of opposite sides. Label one pair as the length (\( l \)) and the other as the width (\( w \)).
- Apply the Formula: Use the perimeter formula for a rectangle, which is: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Here’s how the formula works:
- The term \( l \) represents the length of the rectangle.
- The term \( w \) represents the width of the rectangle.
- First, add the length and the width together: \[ l + w \]
- Then, multiply the result by 2 to account for both pairs of opposite sides: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
For example, if rectangle EFGH has a length of 7 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter calculation would be as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 7 units
- Width \( w \) = 3 units
- Add the length and width: \[ 7 + 3 = 10 \]
- Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times 10 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 20 units. This straightforward formula makes it easy to calculate the perimeter of any rectangle, ensuring you can determine the total distance around the shape efficiently.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. For any polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. When dealing with rectangles, the perimeter is specifically the sum of twice the length and twice the width of the rectangle.
To understand the perimeter more clearly, let's break it down step by step:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the shape you are dealing with. In this context, it is a rectangle labeled EFGH.
- Measure the Sides: Measure or identify the lengths of the two distinct pairs of opposite sides. Label one pair as the length (\( l \)) and the other as the width (\( w \)).
- Apply the Formula: Use the perimeter formula for a rectangle, which is: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Here’s how the formula works:
- The term \( l \) represents the length of the rectangle.
- The term \( w \) represents the width of the rectangle.
- First, add the length and the width together: \[ l + w \]
- Then, multiply the result by 2 to account for both pairs of opposite sides: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
For example, if rectangle EFGH has a length of 7 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter calculation would be as follows:
- Length \( l \) = 7 units
- Width \( w \) = 3 units
- Add the length and width: \[ 7 + 3 = 10 \]
- Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times 10 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 20 units. This straightforward formula makes it easy to calculate the perimeter of any rectangle, ensuring you can determine the total distance around the shape efficiently.
Formula for Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated using a simple and intuitive formula that takes into account the lengths of its sides. This section will guide you through the formula and the steps involved in calculating the perimeter of rectangle EFGH.
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Where:
- \( l \) is the length of the rectangle
- \( w \) is the width of the rectangle
This formula works because a rectangle has two pairs of equal opposite sides. Therefore, the perimeter is the sum of all four sides, which simplifies to twice the sum of the length and the width.
Here are the steps to use the formula:
- Identify the Length and Width: Measure or note the lengths of the rectangle's length (\( l \)) and width (\( w \)).
- Add the Length and Width: Calculate the sum of the length and the width: \[ l + w \]
- Multiply by 2: Multiply the sum by 2 to get the total perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Let’s go through an example to illustrate this:
Assume rectangle EFGH has a length of 12 units and a width of 8 units. Follow these steps to find the perimeter:
- Length \( l \) = 12 units
- Width \( w \) = 8 units
- Calculate the sum of the length and the width: \[ 12 + 8 = 20 \]
- Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times 20 = 40 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 40 units. This formula is versatile and can be applied to any rectangle, making it a fundamental tool in geometry and various practical applications.
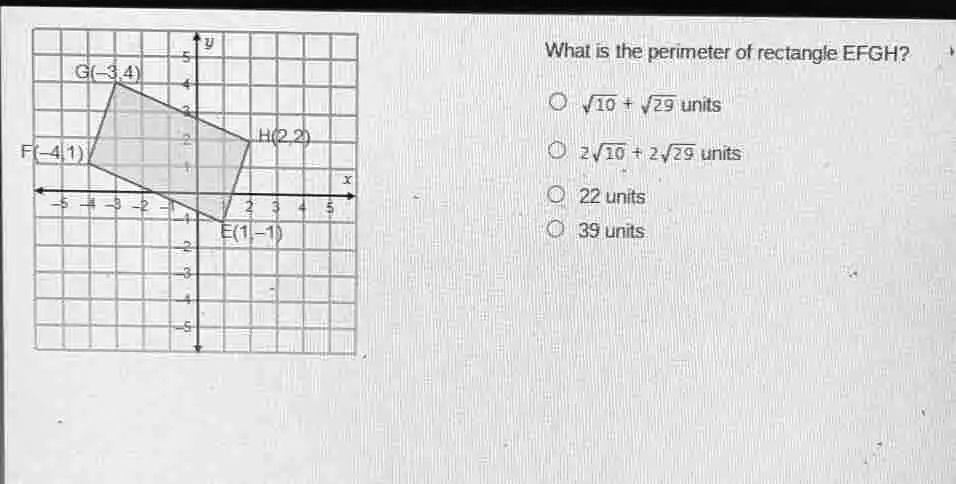
Formula for Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated using a simple and intuitive formula that takes into account the lengths of its sides. This section will guide you through the formula and the steps involved in calculating the perimeter of rectangle EFGH.
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Where:
- \( l \) is the length of the rectangle
- \( w \) is the width of the rectangle
This formula works because a rectangle has two pairs of equal opposite sides. Therefore, the perimeter is the sum of all four sides, which simplifies to twice the sum of the length and the width.
Here are the steps to use the formula:
- Identify the Length and Width: Measure or note the lengths of the rectangle's length (\( l \)) and width (\( w \)).
- Add the Length and Width: Calculate the sum of the length and the width: \[ l + w \]
- Multiply by 2: Multiply the sum by 2 to get the total perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Let’s go through an example to illustrate this:
Assume rectangle EFGH has a length of 12 units and a width of 8 units. Follow these steps to find the perimeter:
- Length \( l \) = 12 units
- Width \( w \) = 8 units
- Calculate the sum of the length and the width: \[ 12 + 8 = 20 \]
- Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times 20 = 40 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH is 40 units. This formula is versatile and can be applied to any rectangle, making it a fundamental tool in geometry and various practical applications.

Example Calculations
To fully understand how to calculate the perimeter of rectangle EFGH, let’s look at some example calculations. These examples will demonstrate the step-by-step process using the formula:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Example 1:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 10 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 5 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 10 + 5 = 15 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 15 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 30 units.
Example 2:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 7 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 3 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 7 + 3 = 10 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 10 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 20 units.
Example 3:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 15 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 8 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 15 + 8 = 23 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 23 = 46 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 46 units.
These examples illustrate the simplicity and effectiveness of the perimeter formula for rectangles. By identifying the length and width and applying the formula, you can quickly and accurately calculate the perimeter of any rectangle.
Example Calculations
To fully understand how to calculate the perimeter of rectangle EFGH, let’s look at some example calculations. These examples will demonstrate the step-by-step process using the formula:
\[ P = 2 \times ( l + w ) \]
Example 1:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 10 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 5 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 10 + 5 = 15 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 15 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 30 units.
Example 2:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 7 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 3 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 7 + 3 = 10 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 10 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 20 units.
Example 3:
- Identify the Length and Width:
- Length (\( l \)) = 15 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 8 units
- Calculate the Sum of Length and Width:
\[ 15 + 8 = 23 \] - Multiply by 2 to Find the Perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 23 = 46 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of rectangle EFGH in this example is 46 units.
These examples illustrate the simplicity and effectiveness of the perimeter formula for rectangles. By identifying the length and width and applying the formula, you can quickly and accurately calculate the perimeter of any rectangle.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, such as rectangle EFGH, has numerous real-world applications. This knowledge is vital in various fields, including construction, landscaping, interior design, and more. Here are some examples of how perimeter calculations are applied in real-life scenarios:
- Construction and Architecture:
Builders and architects use perimeter calculations to determine the amount of materials needed for building foundations, walls, and fencing. For example, knowing the perimeter of a plot of land helps in planning the boundary walls or fences.
- Landscaping:
Gardeners and landscapers calculate the perimeter of garden beds, lawns, and other outdoor areas to plan irrigation systems, edging, and walkways. This ensures efficient use of materials and proper planning of outdoor spaces.
- Interior Design:
Interior designers use perimeter calculations to determine the lengths of baseboards, crown molding, and other decorative elements. Accurate measurements ensure a precise fit and a professional finish.
- Sports Fields:
In sports, the perimeter of fields and courts is calculated to plan boundary lines and seating arrangements. For instance, understanding the perimeter of a basketball court helps in laying out the court markings accurately.
- Manufacturing:
Manufacturers calculate the perimeter of materials to estimate the amount of raw material required for production. This is crucial for minimizing waste and optimizing material usage in manufacturing processes.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter calculations in designing parks, playgrounds, and public spaces. Accurate perimeter measurements help in planning pathways, fencing, and placement of amenities within these spaces.
Example Application:
Consider a scenario where you need to install a fence around a rectangular garden with dimensions 20 units by 15 units. To determine the length of the fence required, calculate the perimeter as follows:
- Identify the length (\( l \)) and the width (\( w \)) of the garden:
- Length (\( l \)) = 20 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 15 units
- Calculate the sum of the length and the width:
\[ 20 + 15 = 35 \] - Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 35 = 70 \text{ units} \]
Thus, you would need 70 units of fencing material to enclose the garden completely. Understanding and applying perimeter calculations in such scenarios ensure precise planning and efficient resource management.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, such as rectangle EFGH, has numerous real-world applications. This knowledge is vital in various fields, including construction, landscaping, interior design, and more. Here are some examples of how perimeter calculations are applied in real-life scenarios:
- Construction and Architecture:
Builders and architects use perimeter calculations to determine the amount of materials needed for building foundations, walls, and fencing. For example, knowing the perimeter of a plot of land helps in planning the boundary walls or fences.
- Landscaping:
Gardeners and landscapers calculate the perimeter of garden beds, lawns, and other outdoor areas to plan irrigation systems, edging, and walkways. This ensures efficient use of materials and proper planning of outdoor spaces.
- Interior Design:
Interior designers use perimeter calculations to determine the lengths of baseboards, crown molding, and other decorative elements. Accurate measurements ensure a precise fit and a professional finish.
- Sports Fields:
In sports, the perimeter of fields and courts is calculated to plan boundary lines and seating arrangements. For instance, understanding the perimeter of a basketball court helps in laying out the court markings accurately.
- Manufacturing:
Manufacturers calculate the perimeter of materials to estimate the amount of raw material required for production. This is crucial for minimizing waste and optimizing material usage in manufacturing processes.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter calculations in designing parks, playgrounds, and public spaces. Accurate perimeter measurements help in planning pathways, fencing, and placement of amenities within these spaces.
Example Application:
Consider a scenario where you need to install a fence around a rectangular garden with dimensions 20 units by 15 units. To determine the length of the fence required, calculate the perimeter as follows:
- Identify the length (\( l \)) and the width (\( w \)) of the garden:
- Length (\( l \)) = 20 units
- Width (\( w \)) = 15 units
- Calculate the sum of the length and the width:
\[ 20 + 15 = 35 \] - Multiply by 2 to find the perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times 35 = 70 \text{ units} \]
Thus, you would need 70 units of fencing material to enclose the garden completely. Understanding and applying perimeter calculations in such scenarios ensure precise planning and efficient resource management.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a rectangle, there are several common mistakes that students and even experienced individuals can make. Understanding and avoiding these errors will ensure accurate results. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
-
Incorrectly Identifying Length and Width:
Ensure that you correctly identify the length and width of the rectangle. The length is typically the longer side, and the width is the shorter side. Confusing these can lead to incorrect calculations.
-
Forgetting to Double the Length and Width:
The formula for the perimeter is
2(l + w), wherelis the length andwis the width. A common error is to add the length and width without doubling the result.For example, if the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
, which simplifies to 16 units.
-
Misinterpreting Units:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit. If the length and width are given in different units, convert them to the same unit before calculating the perimeter.
For example, if the length is given as 5 meters and the width as 300 centimeters, convert the width to meters (3 meters) before using the formula.
-
Using an Incorrect Formula:
The perimeter of a rectangle is not calculated by multiplying length by width. This is a common confusion with the area formula. Remember, the perimeter involves adding the sides, not multiplying them.
-
Neglecting to Add Both Pairs of Sides:
Some might forget to add all four sides of the rectangle. The perimeter involves both pairs of opposite sides, so always add the length twice and the width twice.
-
Errors in Measurement:
Double-check your measurements before calculating. Accurate measurement is crucial to ensure that the computed perimeter is correct.
By keeping these common mistakes in mind and double-checking your work, you can avoid errors and accurately calculate the perimeter of any rectangle.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a rectangle, there are several common mistakes that students and even experienced individuals can make. Understanding and avoiding these errors will ensure accurate results. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
-
Incorrectly Identifying Length and Width:
Ensure that you correctly identify the length and width of the rectangle. The length is typically the longer side, and the width is the shorter side. Confusing these can lead to incorrect calculations.
-
Forgetting to Double the Length and Width:
The formula for the perimeter is
2(l + w), wherelis the length andwis the width. A common error is to add the length and width without doubling the result.For example, if the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
, which simplifies to 16 units.
-
Misinterpreting Units:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit. If the length and width are given in different units, convert them to the same unit before calculating the perimeter.
For example, if the length is given as 5 meters and the width as 300 centimeters, convert the width to meters (3 meters) before using the formula.
-
Using an Incorrect Formula:
The perimeter of a rectangle is not calculated by multiplying length by width. This is a common confusion with the area formula. Remember, the perimeter involves adding the sides, not multiplying them.
-
Neglecting to Add Both Pairs of Sides:
Some might forget to add all four sides of the rectangle. The perimeter involves both pairs of opposite sides, so always add the length twice and the width twice.
-
Errors in Measurement:
Double-check your measurements before calculating. Accurate measurement is crucial to ensure that the computed perimeter is correct.
By keeping these common mistakes in mind and double-checking your work, you can avoid errors and accurately calculate the perimeter of any rectangle.
Advanced Perimeter Problems
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle can extend beyond simple formulas and involve more complex scenarios. Here are some advanced perimeter problems and their solutions:
-
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle with Algebraic Expressions
Given a rectangle where the length is represented by \( l = 2x + 3 \) and the width by \( w = x - 1 \), find the perimeter in terms of \( x \).
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter is:
Substitute the given expressions:
Simplify the expression:
The perimeter is \( 6x + 4 \) units.
-
Problem 2: Perimeter with Diagonal Given
Given a rectangle where the diagonal is \( d = 13 \) units, and the width is \( w = 5 \) units, find the perimeter.
Solution:
Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length:
Substitute the known values:
Solve for \( l \):
Now use the perimeter formula:
Substitute \( l = 12 \) and \( w = 5 \):
The perimeter is 34 units.
-
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Composite Shape
Find the perimeter of a composite shape consisting of a rectangle with dimensions \( l = 8 \) units and \( w = 4 \) units attached to a semicircle with diameter equal to the rectangle's width.
Solution:
Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle:
Calculate the perimeter of the semicircle:
The circumference of the full circle is \( \pi \times d \). For a semicircle:
Substitute \( d = 4 \):
Add the straight edge of the semicircle (the diameter):
The total perimeter of the composite shape is:
These problems illustrate that the basic perimeter formula can be applied in various complex scenarios, requiring deeper mathematical understanding and sometimes integrating different geometric principles.

Advanced Perimeter Problems
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle can extend beyond simple formulas and involve more complex scenarios. Here are some advanced perimeter problems and their solutions:
-
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle with Algebraic Expressions
Given a rectangle where the length is represented by \( l = 2x + 3 \) and the width by \( w = x - 1 \), find the perimeter in terms of \( x \).
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter is:
Substitute the given expressions:
Simplify the expression:
The perimeter is \( 6x + 4 \) units.
-
Problem 2: Perimeter with Diagonal Given
Given a rectangle where the diagonal is \( d = 13 \) units, and the width is \( w = 5 \) units, find the perimeter.
Solution:
Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length:
Substitute the known values:
Solve for \( l \):
Now use the perimeter formula:
Substitute \( l = 12 \) and \( w = 5 \):
The perimeter is 34 units.
-
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Composite Shape
Find the perimeter of a composite shape consisting of a rectangle with dimensions \( l = 8 \) units and \( w = 4 \) units attached to a semicircle with diameter equal to the rectangle's width.
Solution:
Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle:
Calculate the perimeter of the semicircle:
The circumference of the full circle is \( \pi \times d \). For a semicircle:
Substitute \( d = 4 \):
Add the straight edge of the semicircle (the diameter):
The total perimeter of the composite shape is:
These problems illustrate that the basic perimeter formula can be applied in various complex scenarios, requiring deeper mathematical understanding and sometimes integrating different geometric principles.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a rectangle?
A: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula:
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
-
Q: How do I find the length and width if I only know the perimeter and one side?
A: If you know the perimeter \( P \) and one side (say the width \( w \)), you can rearrange the formula to find the length \( l \):
Substitute the known values to solve for \( l \).
-
Q: Can the perimeter be a decimal or a fraction?
A: Yes, the perimeter can be a decimal or a fraction, especially when the length and width are given in such forms. For instance, if the length is \( 5.5 \) units and the width is \( 3.2 \) units, the perimeter would be:
units
-
Q: What if the rectangle has different units for length and width?
A: Convert all measurements to the same unit before calculating the perimeter. For example, if the length is \( 5 \) meters and the width is \( 200 \) centimeters, convert the width to meters (\( 2 \) meters) and then calculate:
-
Q: How can the perimeter formula be used in real-world applications?
A: The perimeter formula is useful in various applications such as:
- Determining the amount of material needed to build a fence around a rectangular yard.
- Calculating the trim required to go around the edges of a rectangular picture frame.
- Planning the border of a garden bed or the edging for a rectangular area.
-
Q: How do you find the perimeter if a rectangle is part of a composite shape?
A: For a composite shape involving a rectangle, calculate the perimeter of each individual shape first. Then add or subtract the shared sides depending on the arrangement of the shapes. For example, if a rectangle is joined with a semicircle, add the perimeter of the rectangle and the semicircle minus the shared side (the diameter).
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a rectangle?
A: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula:
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
-
Q: How do I find the length and width if I only know the perimeter and one side?
A: If you know the perimeter \( P \) and one side (say the width \( w \)), you can rearrange the formula to find the length \( l \):
Substitute the known values to solve for \( l \).
-
Q: Can the perimeter be a decimal or a fraction?
A: Yes, the perimeter can be a decimal or a fraction, especially when the length and width are given in such forms. For instance, if the length is \( 5.5 \) units and the width is \( 3.2 \) units, the perimeter would be:
units
-
Q: What if the rectangle has different units for length and width?
A: Convert all measurements to the same unit before calculating the perimeter. For example, if the length is \( 5 \) meters and the width is \( 200 \) centimeters, convert the width to meters (\( 2 \) meters) and then calculate:
-
Q: How can the perimeter formula be used in real-world applications?
A: The perimeter formula is useful in various applications such as:
- Determining the amount of material needed to build a fence around a rectangular yard.
- Calculating the trim required to go around the edges of a rectangular picture frame.
- Planning the border of a garden bed or the edging for a rectangular area.
-
Q: How do you find the perimeter if a rectangle is part of a composite shape?
A: For a composite shape involving a rectangle, calculate the perimeter of each individual shape first. Then add or subtract the shared sides depending on the arrangement of the shapes. For example, if a rectangle is joined with a semicircle, add the perimeter of the rectangle and the semicircle minus the shared side (the diameter).
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter of a rectangle is fundamental in both mathematics and real-world applications. The formula for the perimeter, , where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width, is straightforward yet powerful. It allows us to calculate the total boundary distance of any rectangular shape, whether it be a garden, a room, or a piece of land.
Throughout this guide, we've explored various aspects of rectangle perimeter calculations, from basic definitions to advanced problems involving algebraic expressions and composite shapes. Here are the key takeaways:
- Basic Formula: Always start with the perimeter formula . Ensure all measurements are in the same units.
- Advanced Problems: For complex shapes or algebraic expressions, break down the problem into smaller parts and apply the basic perimeter principles step by step.
- Practical Applications: The perimeter is crucial for planning and resource estimation in fields like construction, interior design, and landscaping.
- Common Pitfalls: Avoid mixing up units and ensure you differentiate between perimeter and area, which have different formulas and units.
By mastering the calculation of a rectangle's perimeter, you equip yourself with a valuable tool that simplifies many real-world tasks. Whether solving academic problems or tackling practical projects, the knowledge of perimeter calculation is indispensable.
Continue to practice and apply these concepts to build a solid mathematical foundation. Remember, each step taken in learning mathematics enhances your problem-solving skills and opens up new opportunities.
Thank you for exploring the perimeter of rectangles with us. Keep learning and applying these concepts to see their practical benefits in everyday life!
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter of a rectangle is fundamental in both mathematics and real-world applications. The formula for the perimeter, , where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width, is straightforward yet powerful. It allows us to calculate the total boundary distance of any rectangular shape, whether it be a garden, a room, or a piece of land.
Throughout this guide, we've explored various aspects of rectangle perimeter calculations, from basic definitions to advanced problems involving algebraic expressions and composite shapes. Here are the key takeaways:
- Basic Formula: Always start with the perimeter formula . Ensure all measurements are in the same units.
- Advanced Problems: For complex shapes or algebraic expressions, break down the problem into smaller parts and apply the basic perimeter principles step by step.
- Practical Applications: The perimeter is crucial for planning and resource estimation in fields like construction, interior design, and landscaping.
- Common Pitfalls: Avoid mixing up units and ensure you differentiate between perimeter and area, which have different formulas and units.
By mastering the calculation of a rectangle's perimeter, you equip yourself with a valuable tool that simplifies many real-world tasks. Whether solving academic problems or tackling practical projects, the knowledge of perimeter calculation is indispensable.
Continue to practice and apply these concepts to build a solid mathematical foundation. Remember, each step taken in learning mathematics enhances your problem-solving skills and opens up new opportunities.
Thank you for exploring the perimeter of rectangles with us. Keep learning and applying these concepts to see their practical benefits in everyday life!
READ MORE:
Video 'Chu vi của hình chữ nhật EFGH là gì?' giới thiệu cách tính chu vi của hình chữ nhật EFGH một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Hãy xem để nắm vững công thức và cách áp dụng vào thực tế!
Chu vi của hình chữ nhật EFGH là gì? | Hướng dẫn tính chu vi