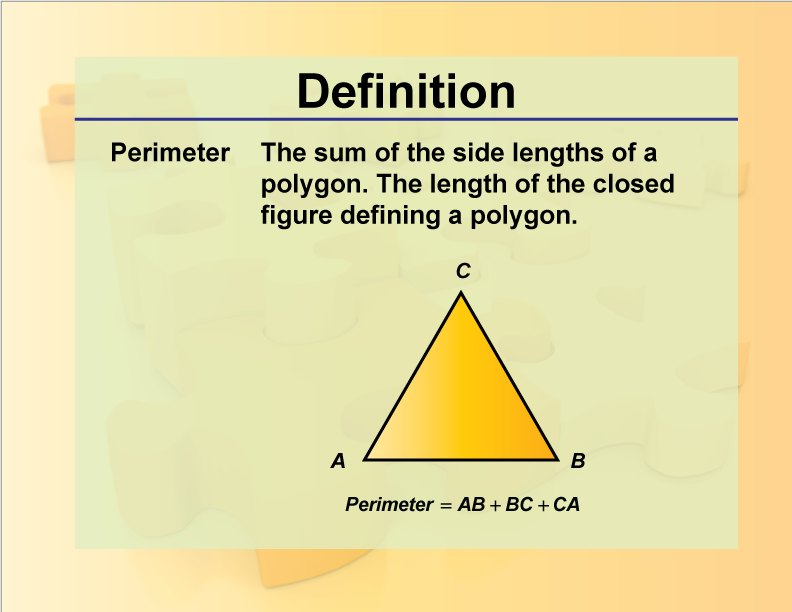
Topic perimeter problems: Understanding perimeter problems is essential for mastering geometry. This article will guide you through various perimeter problems, including practical examples and step-by-step solutions. Whether you're working with rectangles, triangles, or complex polygons, these problems will help you sharpen your skills and boost your confidence in solving perimeter-related questions.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter Problems
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Definition and Significance of Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
- Perimeter Word Problems
- Perimeter in Real-World Applications
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Interactive Perimeter Games and Activities
- YOUTUBE: Tìm Chu Vi | Toán Học với Thầy J. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi, phù hợp cho học sinh và người học muốn nắm vững khái niệm chu vi.
Understanding Perimeter Problems
Perimeter problems often involve calculating the total length around a 2D shape. This concept is essential in various real-world applications such as fencing, construction, and landscaping. Here, we will explore different types of perimeter problems and provide examples to enhance understanding.
Basic Perimeter Formulas
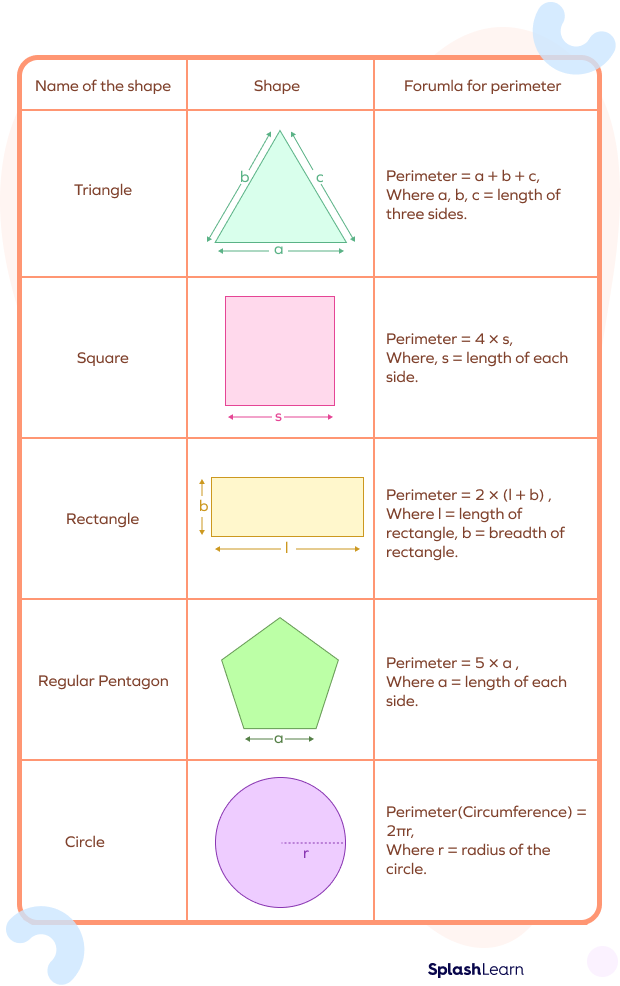
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
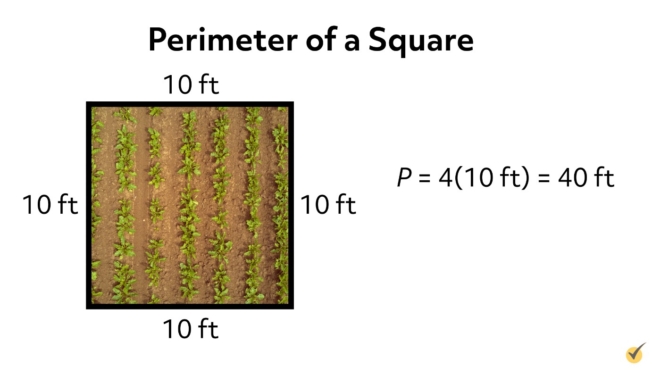
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the side length.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Trapezoid: \( P = a + b + c + d \) where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the side lengths.
Word Problems and Examples
- Manny fences in a rectangular area for his dog to play in the backyard. The area measures 35 yards by 45 yards. What is the total length of fence that Manny uses?
Solution: \( P = 2(35) + 2(45) = 70 + 90 = 160 \) yards.
- Tyler uses 6 craft sticks to make a hexagon. Each craft stick is 6 inches long. What is the perimeter of Tyler’s hexagon?
Solution: \( P = 6 \times 6 = 36 \) inches.
- Francis made a rectangular path from her driveway to the porch. The width of the path is 2 feet. The length is 28 feet longer than the width. What is the perimeter of the path?
Solution: Length \( l = 2 + 28 = 30 \) feet. \( P = 2(2) + 2(30) = 4 + 60 = 64 \) feet.
- A building at Elmira College has a room shaped like an octagon. The length of each side of the room is 30 feet. What is the perimeter of this room?
Solution: \( P = 8 \times 30 = 240 \) feet.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 26 cm. The first side is 6 cm shorter than the second side. The third side is 2 cm shorter than twice the length of the first side. What is the length of each side?
Solution: Let the second side be \( x \) cm. First side = \( x - 6 \). Third side = \( 2(x - 6) - 2 \).
Equation: \( (x - 6) + x + [2(x - 6) - 2] = 26 \). Solve for \( x \) to find the lengths.
Interactive Problems
To further practice, try solving these interactive problems:
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( P = 2l + 2w \) |
| Square | \( P = 4s \) |
| Circle | \( P = 2\pi r \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Trapezoid | \( P = a + b + c + d \) |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The concept of perimeter is fundamental in geometry, referring to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Calculating the perimeter involves summing the lengths of all sides or edges that enclose the shape. This concept applies to various shapes, including rectangles, squares, circles, and irregular polygons.
The significance of understanding perimeter extends beyond mathematics, with practical applications in fields such as construction, landscaping, and security. For example, knowing the perimeter of a plot of land can help in estimating the amount of fencing material required.
- For rectilinear shapes like rectangles and squares, finding the perimeter is straightforward. You simply add the lengths of all the sides. For instance, the perimeter of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is \( 2l + 2w \).
- Circular shapes use the concept of circumference to determine the perimeter. The circumference of a circle is calculated using the formula \( 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Irregular shapes require breaking down the shape into simpler components and summing the lengths of their respective sides to determine the perimeter.
Understanding perimeter helps in various real-world scenarios:
- In construction, perimeter measurements are essential for planning and building structures within specified dimensions.
- In landscaping, perimeter calculations help determine the material needed for pathways, garden beds, or retaining walls.
- For safety and security, defining boundaries and monitoring restricted areas relies heavily on accurate perimeter measurements.
Definition and Significance of Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is a linear measure, representing the distance around the edge of a shape. Understanding and calculating the perimeter is crucial for various practical applications, including construction, land measurement, and design.
Here are some key points about the perimeter:
- Definition: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of a polygon.
- Formula for Regular Shapes: For regular polygons, the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the total number of sides.
- Irregular Shapes: For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all individual sides.
- Units: Perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet.
Let's look at some examples:
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: For a square with side length \( a \), the perimeter is \( P = 4a \).
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is given by \( C = 2 \pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides, \( P = a + b + c \).
Understanding the concept of the perimeter helps in solving various real-life problems such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or wrapping a gift. It also forms the basis for more complex geometric and mathematical calculations.
Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves adding up the lengths of all its sides. The formula and method can vary depending on the type of shape you are working with. Here are the steps and formulas for calculating the perimeter of some common shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated as: \[ P = 2 \times (l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square is calculated as: \[ P = 4 \times a \] where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is calculated as: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle is calculated as: \[ C = 2 \pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
- Polygon: The perimeter \( P \) of a regular polygon is calculated as: \[ P = n \times s \] where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side. For irregular polygons, add up the lengths of all the sides.
Let's go through an example of calculating the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Identify the length (\( l \)) and width (\( w \)) of the rectangle. For instance, let \( l = 5 \) units and \( w = 3 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \text{ units} \]
By following these steps, you can calculate the perimeter of any given shape accurately. Understanding how to find the perimeter is essential for solving various real-world problems, such as determining the length of fencing needed to enclose a garden or the border length of a painting.
Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
Understanding the perimeter of various shapes is crucial in both mathematics and practical applications. Here are the perimeter formulas for some common shapes:
- Square
- Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Description: The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side.
- Rectangle
- Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Description: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
- Triangle
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Description: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- Circle
- Formula: \( P = 2 \pi r \) (Circumference)
- Description: The perimeter of a circle, called the circumference, is twice the product of pi and the radius.
- Parallelogram
- Formula: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Description: The perimeter of a parallelogram is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
- Trapezoid
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Description: The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Polygon
- Formula: \( P = a_1 + a_2 + \ldots + a_n \)
- Description: The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
These formulas provide a foundation for solving various perimeter problems. Whether you are working with simple shapes like squares and rectangles or more complex polygons, understanding these formulas is essential.
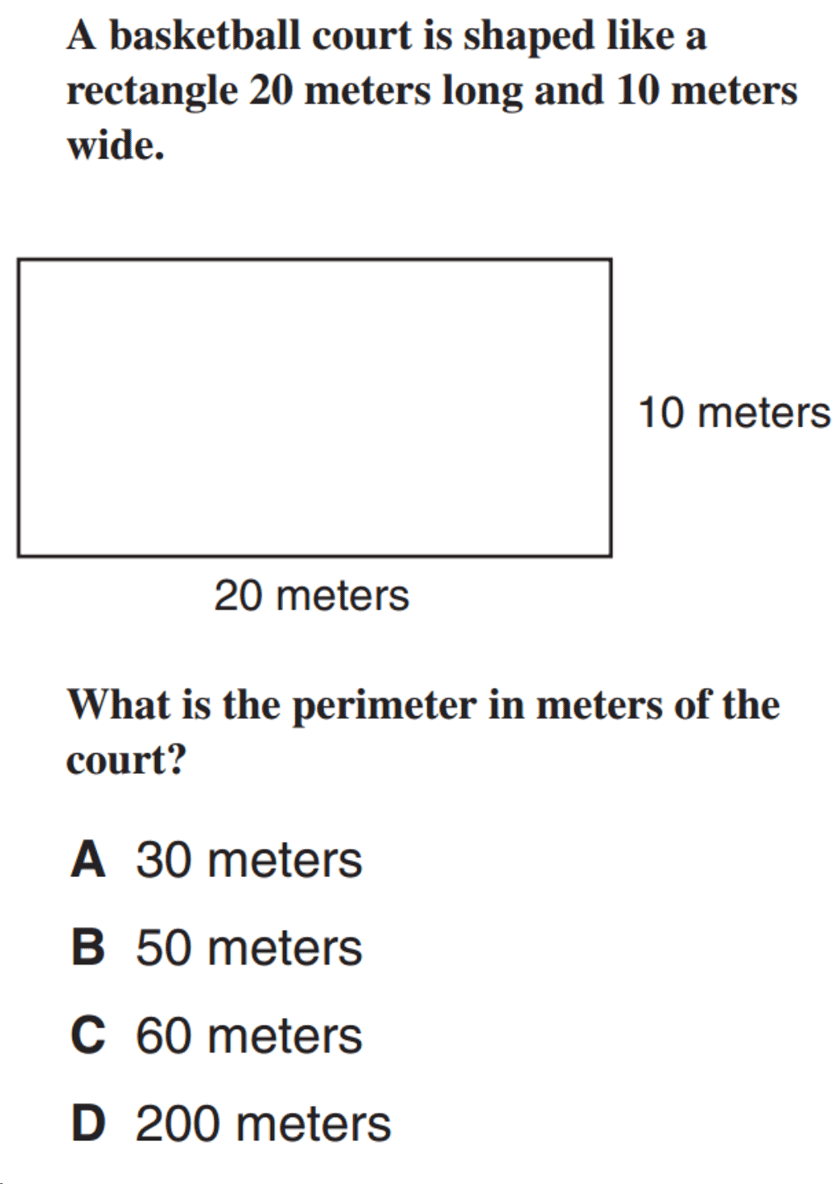
Perimeter Word Problems
Perimeter word problems often involve real-life scenarios where you need to determine the total distance around a given shape. These problems help enhance understanding of perimeter calculations and application of basic arithmetic and algebraic skills.
-
Example 1: Rectangular Garden
Margo wants to build a rectangular fence around her garden using 20 meters of wood. What dimensions will give Margo the largest area? This problem involves calculating the perimeter of the rectangle and exploring different length and width combinations.
-
Example 2: Triangular Path
Patrick’s bike ride follows a triangular path; two legs are equal, and the third is 8 miles longer than each of the other legs. If Patrick rides 30 miles total, what is the length of the longest leg? This problem requires setting up and solving equations based on the perimeter of the triangle.
-
Example 3: Equilateral Triangle
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 6 inches. What is the length of one side? This problem involves understanding that all sides of an equilateral triangle are equal and solving for the length of each side.
-
Example 4: Rectangle Dimensions
The perimeter of a rectangle is 42 inches. If the width is 8 inches, what is the length? This problem involves using the perimeter formula and solving for the unknown length.
-
Example 5: Regular Pentagon
When the perimeter of a regular pentagon is divided by 5, the length of a side is 25 inches. What is the perimeter of the pentagon? This problem requires understanding the properties of regular polygons and using multiplication to find the total perimeter.
Perimeter in Real-World Applications
The concept of perimeter is not just confined to theoretical mathematics; it has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. Understanding and calculating the perimeter is essential for various real-world tasks, from construction to art.
-
Construction of Roads and Bridges:
In the construction industry, accurate measurement of the perimeter is crucial for planning and surveying. For roads, the perimeter helps in determining the required materials and ensuring proper layout. Similarly, the perimeter is vital in maintaining the symmetry and structural integrity of bridges.
-
Interior Design and Decorating:
Whether adding tiles to a room or installing fences, knowing the perimeter allows for precise calculation of the materials needed. This ensures cost-effective and efficient use of resources in interior design projects.
-
Landscaping:
In landscaping, the perimeter of garden beds, lawns, and walkways must be calculated to outline the areas and plan the design effectively. This includes placing borders, laying out paths, and organizing planting areas.
-
Fashion and Apparel Design:
Designers use the concept of perimeter to measure and cut fabrics accurately, ensuring that pieces fit together perfectly in garments. This is essential for creating well-fitted clothing and intricate designs.
-
Computer Graphics:
In the realm of computer graphics, calculating the perimeter helps in creating precise and realistic shapes and models. This is particularly important in gaming and animation, where visual accuracy is key.
-
Astronomy:
Astronomers use the concept of perimeter to measure orbits and distances between celestial bodies. This helps in understanding planetary motions and mapping the vast expanse of space.
Overall, the application of perimeter in these areas highlights its significance beyond the classroom, making it an invaluable tool in various professional and everyday contexts.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Here are some practice problems to help you master the concept of perimeter. Each problem includes a step-by-step solution to guide you through the process.
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle
Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 10 cm and a width of 7 cm.
Solution:
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Substitute the given values into the formula: \( P = 2(10 + 7) \).
- Calculate the sum inside the parentheses: \( 10 + 7 = 17 \).
- Multiply by 2: \( 2 \times 17 = 34 \).
- So, the perimeter of the rectangle is 34 cm.
Problem 2: Perimeter of a Triangle
Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides of lengths 8 cm, 15 cm, and 17 cm.
Solution:
- Add the lengths of all the sides: \( 8 + 15 + 17 \).
- Calculate the total: \( 8 + 15 = 23 \) and \( 23 + 17 = 40 \).
- Thus, the perimeter of the triangle is 40 cm.
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has a side length of 6 cm. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon: \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length.
- Substitute the values: \( P = 5 \times 6 \).
- Multiply: \( 5 \times 6 = 30 \).
- Therefore, the perimeter of the pentagon is 30 cm.
Problem 4: Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference)
Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Solution:
- Use the formula for the circumference: \( C = 2 \pi r \).
- Substitute the given radius: \( C = 2 \pi \times 5 \).
- Calculate the circumference: \( C = 10 \pi \).
- Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \), approximate the circumference: \( C \approx 10 \times 3.14 = 31.4 \).
- Thus, the circumference of the circle is approximately 31.4 cm.
Problem 5: Perimeter of a Composite Shape
Find the perimeter of an L-shaped figure where the longer part has lengths 12 cm and 9 cm, and the shorter part has lengths 6 cm and 4 cm.
Solution:
- Identify the segments that form the perimeter: 12 cm, 9 cm, 6 cm, 4 cm, and two additional connecting segments (each equal to 4 cm).
- Add all these lengths: \( 12 + 9 + 6 + 4 + 4 + 4 \).
- Calculate the total: \( 12 + 9 = 21 \), \( 21 + 6 = 27 \), \( 27 + 4 = 31 \), \( 31 + 4 = 35 \), \( 35 + 4 = 39 \).
- So, the perimeter of the L-shaped figure is 39 cm.
Problem 6: Word Problem
Susan has a rectangular garden that measures 20 meters by 15 meters. She wants to put a fence around it. How many meters of fencing does she need?
Solution:
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Substitute the given dimensions: \( P = 2(20 + 15) \).
- Calculate the sum inside the parentheses: \( 20 + 15 = 35 \).
- Multiply by 2: \( 2 \times 35 = 70 \).
- Susan needs 70 meters of fencing.
Interactive Perimeter Games and Activities
Engage students with interactive games and activities to reinforce their understanding of perimeter. These activities encourage hands-on learning and make the concept of perimeter more enjoyable.
1. Perimeter Scavenger Hunt
Organize a scavenger hunt where students find objects around the classroom or playground and measure their perimeters. Provide a list of items and a worksheet for recording measurements.
- Objective: Identify objects and calculate their perimeters.
- Materials: Measuring tapes or rulers, worksheets.
- Instructions:
- Provide a list of objects (e.g., books, desks, doors).
- Students measure each object’s perimeter.
- Record measurements on the worksheet.
- Discuss findings as a group.
2. Perimeter Puzzle Pieces
Use perimeter puzzles to challenge students to fit together shapes that create specific perimeters.
- Objective: Combine shapes to form a target perimeter.
- Materials: Cut-out shapes with known side lengths, target perimeter cards.
- Instructions:
- Provide cut-out shapes and target perimeter cards.
- Students combine shapes to match the target perimeter.
- Verify solutions and discuss strategies.
3. Perimeter Relay Race
Turn perimeter calculations into a fun relay race. Students race to solve perimeter problems and pass the baton to the next teammate.
- Objective: Solve perimeter problems quickly and accurately in a relay format.
- Materials: Perimeter problem cards, batons.
- Instructions:
- Divide students into teams.
- Each team receives a set of perimeter problem cards.
- First team member solves a problem, then passes the baton.
- Next member solves the next problem, and so on.
- The team that finishes first with correct answers wins.
4. Interactive Online Games
Explore online games and activities that teach perimeter concepts through interactive play. Here are some suggested websites:
- - Offers perimeter games and challenges.
- - Provides perimeter games and printable activities.
- - Features engaging perimeter puzzles and games.
5. Create Your Own Perimeter Board Game
Students design a board game where players calculate perimeters to move forward. This activity combines creativity with math skills.
- Objective: Design and play a board game focused on perimeter calculations.
- Materials: Cardboard, markers, rulers, dice, game pieces.
- Instructions:
- Divide students into small groups.
- Each group designs a board game with spaces requiring perimeter calculations.
- Players roll dice to move and must solve perimeter problems to advance.
- Test and play the games within the groups.
6. Perimeter Art Projects
Incorporate art by having students create perimeter-based artwork. They calculate and use perimeter measurements in their designs.
- Objective: Apply perimeter calculations to create art pieces.
- Materials: Construction paper, rulers, scissors, glue.
- Instructions:
- Have students plan their artwork using specific perimeter measurements.
- Cut and assemble pieces according to their designs.
- Display and discuss how perimeter was used in the artwork.
7. Perimeter Jeopardy
Create a Jeopardy-style game with perimeter-related questions. Use categories such as “Shapes,” “Word Problems,” and “Formulas.”
- Objective: Reinforce perimeter knowledge through a quiz game.
- Materials: Jeopardy board or projector, question cards.
- Instructions:
- Set up a Jeopardy board with categories and point values.
- Teams take turns selecting questions and answering to earn points.
- The team with the most points wins.
These interactive games and activities are designed to make learning about perimeter fun and engaging, helping students to better understand and apply the concept in various contexts.
Tìm Chu Vi | Toán Học với Thầy J. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi, phù hợp cho học sinh và người học muốn nắm vững khái niệm chu vi.
Tìm Chu Vi | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, lý tưởng cho việc học hình học cơ bản.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán Học với Thầy J