Topic what's the square root of 28: Curious about what's the square root of 28? In this article, we explore the mathematical representation, calculation methods, and real-world applications of the square root of 28. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, you'll find valuable insights and easy-to-understand explanations. Let's dive into the world of square roots and uncover the mysteries of 28!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 28
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Mathematical Representation of Square Root of 28
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 28
- Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 28
- Radical Simplification of Square Root of 28
- Prime Factorization Approach
- Using a Calculator for Square Root of 28
- Applications of Square Root of 28
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 28 (Sqrt(28)). Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 28 một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Square Root of 28
The square root of 28 can be expressed in both its simplest radical form and its decimal form. Here's a detailed look at each representation:
Radical Form
The square root of 28 can be simplified by factoring out perfect squares:
\(\sqrt{28} = \sqrt{4 \times 7} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{7} = 2\sqrt{7}\)
So, the simplest radical form of the square root of 28 is \(2\sqrt{7}\).
Decimal Form
Using a calculator, we can find the approximate decimal value of the square root of 28:
Summary
- Radical Form: \(2\sqrt{7}\)
- Decimal Form: \(\sqrt{28} \approx 5.291502622\)
Thus, whether you need the exact form or a decimal approximation, the square root of 28 can be represented as \(2\sqrt{7}\) or approximately 5.291502622.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 28 is an important mathematical concept with various applications. Understanding the square root of a number helps in many areas of mathematics and real-life scenarios.
The square root of 28 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the product 28. Mathematically, this is represented as:
\[
\sqrt{28}
\]
Since 28 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. The decimal approximation of the square root of 28 is approximately 5.2915.
The exact form of the square root of 28 can be simplified using its prime factorization. The prime factors of 28 are 2 and 7, and we can express 28 as:
\[
28 = 2^2 \times 7
\]
Thus, the square root of 28 can be simplified to:
\[
\sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = 2\sqrt{7}
\]
This simplified form is often more convenient for mathematical calculations and problem-solving.
In summary, the square root of 28 is an interesting topic that combines elements of prime factorization, simplification of radicals, and understanding irrational numbers. This guide will explore various methods to calculate and simplify the square root of 28, as well as its applications and common misconceptions.
Understanding Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics and can be understood through several key points:
- Definition: The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Mathematically, if \(x^2 = a\), then \(x\) is the square root of \(a\).
- Notation: The square root of a number \(a\) is denoted as \(\sqrt{a}\). For example, the square root of 28 is written as \(\sqrt{28}\).
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For instance, \(\sqrt{28}\) and \(-\sqrt{28}\) are both square roots of 28.
- Principal Square Root: By convention, the term "square root" generally refers to the principal (positive) square root. Therefore, \(\sqrt{28}\) usually means the positive root.
- Perfect Squares: If a number is a perfect square, its square root is an integer. For example, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\). However, 28 is not a perfect square, so \(\sqrt{28}\) is an irrational number.
Understanding square roots also involves recognizing their properties and applications:
- Properties:
- \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\)
- \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
- \((\sqrt{a})^2 = a\)
- Applications: Square roots are used in various fields such as geometry (to find the side length of a square), physics (in formulas involving areas and volumes), and statistics (standard deviation calculations).
For example, to understand the square root of 28, we can start by recognizing that it lies between the perfect squares of 25 and 36. Hence, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) and \(\sqrt{36} = 6\), meaning \(\sqrt{28}\) is between 5 and 6. More precisely, \(\sqrt{28} \approx 5.2915\).
Mathematical Representation of Square Root of 28
The square root of 28 can be represented in several mathematical forms. Below, we explore the most common representations:
- Radical Form: The most straightforward representation of the square root of 28 is using the radical symbol. This is written as:
\[ \sqrt{28} \]
- Simplified Radical Form: To simplify \(\sqrt{28}\), we factorize 28 into its prime factors:
\[ 28 = 2^2 \times 7 \]
Applying the product rule for radicals, we get:\[ \sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{7} = 2\sqrt{7} \]
- Decimal Form: The square root of 28 can also be expressed as a decimal approximation. Calculating this value, we get:
\[ \sqrt{28} \approx 5.2915 \]
- Exponent Form: Another way to represent the square root of 28 is using exponent notation, which expresses the square root as a power of 1/2:
\[ 28^{\frac{1}{2}} \]
Each of these representations is useful in different mathematical contexts, providing flexibility in how we work with the square root of 28.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 28
Finding the square root of 28 can be approached using various methods, each with its own steps and level of precision. Here, we will explore some of the most common methods:
1. Calculator Method
Using a digital calculator is the simplest way to find the square root of 28. Enter the number 28 and press the square root button, which will give you an approximate value of 5.291502622.
2. Estimation Method
This method involves a bit of guesswork:
- Identify the nearest perfect squares around 28, which are 25 (52) and 36 (62).
- Since 28 is closer to 25, the square root of 28 will be slightly more than 5.
- A reasonable estimate would be around 5.3.
3. Long Division Method
The long division method is a traditional technique that provides a more precise result:
- Set up 28 inside the division symbol.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 28. In this case, it is 5 because 52 = 25.
- Subtract 25 from 28, leaving 3. Add a decimal point and bring down pairs of zeros.
- Double the divisor (5) to get 10, then find a digit X such that 10X * X is less than or equal to 300. Here, X = 2 because 102 * 2 = 204.
- Subtract 204 from 300 to get 96, and bring down the next pair of zeros (9600).
- Continue this process to achieve the desired precision.
4. Newton’s Method
Newton's Method (also known as the Newton-Raphson method) is an iterative approach:
- Start with an initial guess, say 5.3.
- Apply the formula: New guess = 0.5 * (Old guess + 28 / Old guess).
- Repeat the process with the new guess until the value stabilizes.
Conclusion
These methods provide different levels of precision and are suitable for various applications. Whether you use a calculator for a quick answer, estimation for an approximate value, or long division and Newton’s Method for more precision, understanding these techniques can enhance your mathematical skills.
Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 28
The square root of a number that is not a perfect square, like 28, is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. To find the decimal approximation of the square root of 28, we can use various methods.
One common method is to use a calculator, which provides a quick and accurate approximation. For example:
\[
\sqrt{28} \approx 5.2915026221
\]
Another way to approximate the square root manually is by using the method of successive averaging. Here's a step-by-step outline:
Choose two consecutive whole numbers between which the square root lies. Since \(5^2 = 25\) and \(6^2 = 36\), we know:
\[
5 < \sqrt{28} < 6
\]Averaging 5 and 6 gives us a better approximation:
\[
x = \frac{5 + 6}{2} = 5.5
\]Square the result and compare it to 28:
\[
5.5^2 = 30.25
\]Since 30.25 is greater than 28, choose a smaller number, say 5.4, and try again:
\[
5.4^2 = 29.16
\]Continue this process iteratively to narrow down the approximation. With more iterations, the value gets closer to the actual square root.
For practical purposes, especially in everyday calculations or when using a calculator, the square root of 28 can be approximated to a few decimal places. Commonly, it is rounded to:
\[
\sqrt{28} \approx 5.29
\]
This approximation is sufficiently accurate for most uses.
Radical Simplification of Square Root of 28
To simplify the square root of 28, we look for factors of 28 that are perfect squares. The goal is to express the square root in its simplest radical form.
- Identify the prime factors of 28:
- 28 can be factored into \(2^2 \times 7\).
- Rewrite the square root of 28 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7}\)
- Apply the property of square roots that states \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\):
\(\sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{7}\)
- Simplify the square root of the perfect square:
\(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\)
- Combine the simplified terms:
Thus, \(\sqrt{28} = 2\sqrt{7}\).
So, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{28}\) is \(2\sqrt{7}\).
Prime Factorization Approach
Prime factorization is a method used to express a number as the product of its prime factors. This approach can be helpful in simplifying the square root of a number.
To find the square root of 28 using the prime factorization approach, follow these steps:
- First, find the prime factors of 28.
- Start by dividing 28 by the smallest prime number, which is 2:
- 28 ÷ 2 = 14
- Next, divide the result by 2 again:
- 14 ÷ 2 = 7
- Now, 7 is a prime number and cannot be divided further by any prime number other than 7 itself.
- Therefore, the prime factorization of 28 is:
\(28 = 2 \times 2 \times 7\)
To find the square root, group the prime factors into pairs:
- Group the pairs of 2's together:
- \(2 \times 2\) forms one pair
- The remaining factor is 7, which does not form a pair.
Write the square root of 28 using the paired and unpaired factors:
\(\sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 7}\)
Since \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\), simplify the expression:
\(\sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{7}\)
Calculate the square root of the pairs:
\(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\)
Thus, the simplified form is:
\(\sqrt{28} = 2 \times \sqrt{7}\)
So, the square root of 28 in its simplest radical form is \(2\sqrt{7}\).
Using a Calculator for Square Root of 28
Calculating the square root of 28 using a calculator is a straightforward process. Here are the detailed steps:
- Power On the Calculator:
Begin by turning on your calculator. Ensure it is in the standard mode, not in any specialized mode like statistics or programming.
- Input the Number:
Enter the number 28 using the numeric keypad.
- Locate the Square Root Function:
Find the square root button on your calculator. This is usually denoted by a radical symbol (√) or sometimes as "sqrt".
- Calculate the Square Root:
Press the square root button after entering 28. The calculator will display the square root of 28. Depending on the calculator, you might need to press "=" after the square root button to get the result.
- View the Result:
The calculator will show the result. The square root of 28 is approximately 5.291502622.
Using a calculator not only simplifies the process but also ensures accuracy. This method is useful for quick calculations and for verifying results obtained through manual methods.
Additionally, online square root calculators are available for convenience. You can use these by simply entering the number 28 into the provided field and clicking the calculate button to get the result instantly.

Applications of Square Root of 28
The square root of 28, approximately 5.29, has several practical applications in various fields such as geometry, physics, and engineering. Here are some detailed examples:
-
Geometry
In geometry, the square root of 28 can be used to calculate the diagonal of a square or rectangle. For instance, if you have a square with an area of 28 square units, the length of each side of the square can be found by taking the square root of the area:
\[ \text{Side length} = \sqrt{28} \approx 5.29 \text{ units} \] -
Physics
In physics, the square root of 28 might be used in formulas involving kinetic energy or gravitational potential energy, where the need to take square roots arises frequently. For example, the time it takes for an object to fall a certain distance under gravity can be calculated using the square root function:
\[ t = \sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}} \] If the height \( h \) is 28 meters and \( g \) (acceleration due to gravity) is 9.8 m/s²:
\[ t = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 28}{9.8}} \approx 2.39 \text{ seconds} \] -
Engineering
In engineering, the square root of 28 can be applied in calculations for designing structures and systems. For instance, determining the necessary length of diagonal supports in a truss or framework:
\[ \text{Diagonal length} = \sqrt{(\text{Length}^2 + \text{Width}^2)} \] If both length and width are equal to 7 units:
\[ \text{Diagonal length} = \sqrt{(7^2 + 7^2)} = \sqrt{49 + 49} = \sqrt{98} \approx 9.90 \text{ units} \] -
Everyday Use
Square roots are often used in everyday calculations, such as determining the size of TV screens or any diagonal measurement. For a screen with an area of 28 square inches, the diagonal can be calculated:
\[ \text{Diagonal} = \sqrt{28} \approx 5.29 \text{ inches} \]
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Understanding and calculating the square root of 28 can sometimes lead to common mistakes and misconceptions. Here are some of the frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Simplification:
One common mistake is to incorrectly simplify the square root of 28. Some may assume it simplifies to an integer, but it is an irrational number. The correct simplified radical form is \( \sqrt{28} = 2\sqrt{7} \).
- Misunderstanding the Nature of Square Roots:
Another misconception is that square roots always result in neat, whole numbers. In reality, many square roots, including \(\sqrt{28}\), are irrational and cannot be expressed as a simple fraction or integer.
- Errors in Prime Factorization:
When using prime factorization to simplify \(\sqrt{28}\), it's crucial to correctly factorize the number. The correct factorization is \( 28 = 2^2 \times 7 \), leading to \( \sqrt{28} = 2\sqrt{7} \). Incorrect factorization will lead to wrong results.
- Confusion with Decimal Approximations:
While \(\sqrt{28} \approx 5.291\), rounding errors can occur if not careful. Always ensure to use enough decimal places for accuracy, especially in scientific or engineering contexts.
- Misapplying Properties of Square Roots:
Some may incorrectly apply properties such as \(\sqrt{a + b} = \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\). For example, \(\sqrt{28}\) should not be split into \(\sqrt{20 + 8}\) and then simplified incorrectly. The correct approach is recognizing \(\sqrt{28} \) cannot be split this way.
- Calculation Errors:
Simple arithmetic mistakes during calculation can lead to wrong answers. Always double-check your steps and ensure the correct operations are applied.
By being aware of these common pitfalls, you can avoid mistakes and accurately work with the square root of 28.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you understand and master the square root of 28:
-
Calculate the square root of 28 using the prime factorization method.
Solution: The prime factors of 28 are 2 and 7. Therefore, \( \sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = 2\sqrt{7} \).
-
Estimate the square root of 28 to two decimal places without using a calculator.
Solution: Using the method of approximations, \( \sqrt{28} \approx 5.29 \).
-
Simplify the radical expression \( \sqrt{112} \).
Solution: \( \sqrt{112} = \sqrt{4 \times 28} = 2\sqrt{28} = 2 \times 2\sqrt{7} = 4\sqrt{7} \).
-
Verify the square root of 28 using a calculator. What is the result?
Solution: The calculator result is approximately \( 5.291502622 \).
-
Compare the square roots: \( \sqrt{28} \) and \( \sqrt{25} \). Which is greater and by how much?
Solution: \( \sqrt{28} \approx 5.29 \) and \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \). \( \sqrt{28} \) is greater by approximately 0.29.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{28} \) in simplest radical form | \( 2\sqrt{7} \) |
| Decimal approximation of \( \sqrt{28} \) | Approximately \( 5.29 \) |
| Prime factorization of 28 | \( 2^2 \times 7 \) |
Practice these problems to enhance your understanding of square roots, specifically the square root of 28.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of 28?
The square root of 28 is approximately \( \sqrt{28} \approx 5.291502622 \). In its simplest radical form, it is \( 2\sqrt{7} \).
-
How do you simplify \( \sqrt{28} \) using prime factorization?
To simplify \( \sqrt{28} \) using prime factorization:
- Find the prime factors of 28: \( 28 = 2^2 \times 7 \).
- Express the square root using these factors: \( \sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} \).
- Simplify the expression: \( \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = 2\sqrt{7} \).
-
What is the decimal approximation of \( \sqrt{28} \) and how is it calculated?
The decimal approximation of \( \sqrt{28} \) is approximately 5.29. This can be calculated using a calculator or by using the method of successive approximations.
-
Can \( \sqrt{28} \) be simplified further?
No, \( 2\sqrt{7} \) is the simplest radical form of \( \sqrt{28} \). There is no further simplification possible.
-
Is \( \sqrt{28} \) a rational number?
No, \( \sqrt{28} \) is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
-
How can you verify the square root of 28 using a calculator?
To verify the square root of 28 using a calculator, enter 28 and press the square root (√) button. The calculator will display approximately 5.291502622.
-
How does \( \sqrt{28} \) compare to other square roots, like \( \sqrt{25} \) or \( \sqrt{30} \)?
Comparing square roots:
- \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
- \( \sqrt{28} \approx 5.29 \)
- \( \sqrt{30} \approx 5.48 \)
\( \sqrt{28} \) is slightly greater than \( \sqrt{25} \) and slightly less than \( \sqrt{30} \).
Why is \( \sqrt{28} \) considered an important concept?
Understanding \( \sqrt{28} \) is important for grasping the properties of square roots, simplifying radical expressions, and solving mathematical problems involving irrational numbers.
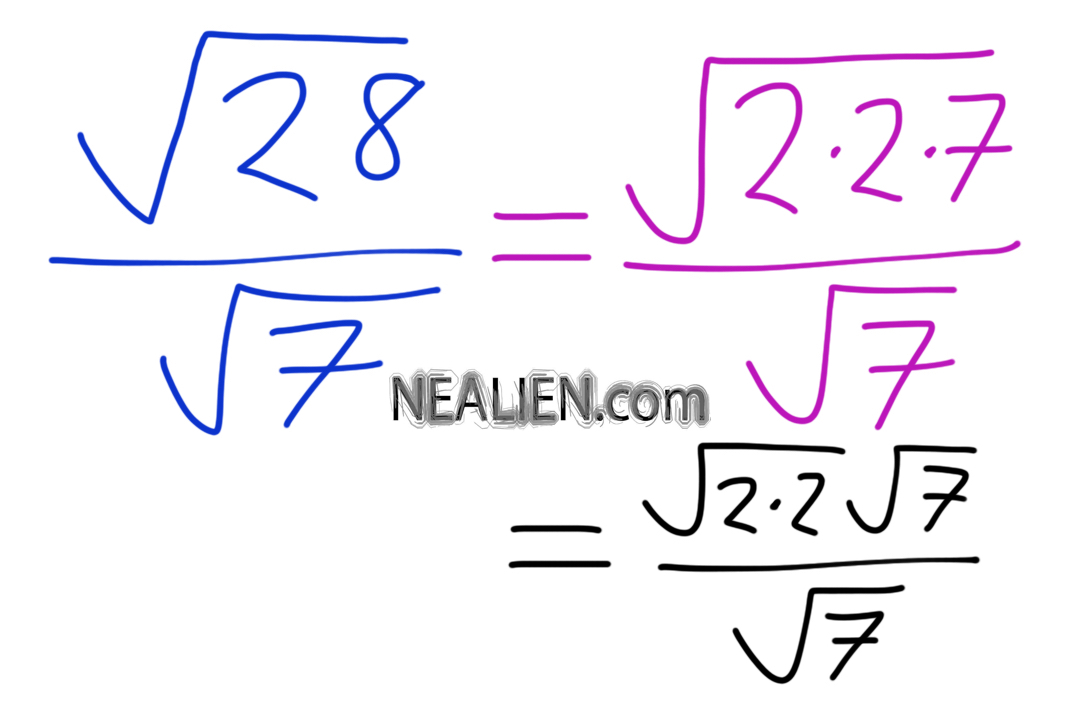
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 28 provides valuable insights into both basic and advanced mathematical concepts. The square root of 28, represented as \( \sqrt{28} \) or in its simplified form \( 2\sqrt{7} \), is an irrational number approximately equal to 5.291502622. Here's a summary of key points:
- Simplification: The square root of 28 simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{7} \), helping to understand how to handle and simplify radical expressions.
- Decimal Approximation: Using methods of successive approximations or a calculator, \( \sqrt{28} \) is approximately 5.29, demonstrating how irrational numbers can be represented as decimals.
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down 28 into its prime factors (2 and 7) and using these to simplify \( \sqrt{28} \) aids in grasping the fundamental principles of factorization and radical simplification.
- Applications: The knowledge of square roots is widely applicable in various fields such as geometry, algebra, engineering, and physics, highlighting the practical importance of understanding these concepts.
- Comparison: Comparing \( \sqrt{28} \) to other square roots like \( \sqrt{25} \) and \( \sqrt{30} \) helps contextualize its value and understand the relationships between different square roots.
- Common Mistakes: Being aware of common mistakes, such as incorrectly simplifying or approximating, ensures a more accurate and thorough understanding.
By mastering the concept of the square root of 28, you enhance your mathematical skills and build a solid foundation for tackling more complex problems. Practice regularly, use the methods discussed, and apply these concepts in various scenarios to gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of mathematics.
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 28 (Sqrt(28)). Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 28 một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 28: Sqrt(28)
READ MORE:
Video giải thích cách tính căn bậc hai của 28. Khám phá phương pháp đơn giản và chi tiết để tính toán căn bậc hai của số 28.
Căn Bậc Hai của 28