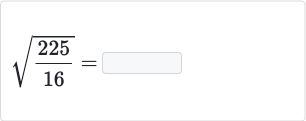
Topic is the square root of 16 rational: The square root of 16 is indeed rational. This article explores the concept, methods to find the square root, and why it qualifies as a rational number. By understanding the properties of square roots, you'll gain insights into mathematical reasoning and problem-solving. Join us as we delve into the intriguing world of square roots!
Table of Content
- Is the Square Root of 16 Rational?
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Perfect Square Verification
- Rationality of the Square Root of 16
- Calculation Methods
- What is the Value of the Square Root of 16?
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
- Is 16 a Perfect Square?
- Is the Square Root of 16 Rational or Irrational?
- Applications and Examples
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 16, tại sao nó là một số hợp lý và cách tính toán. Video này cung cấp thông tin chi tiết và dễ hiểu về chủ đề này.
Is the Square Root of 16 Rational?
The square root of 16 is indeed a rational number. This can be understood through various mathematical methods and principles.
Methods to Determine the Square Root of 16
-
Guess and Check Method:
By guessing a number that when squared gives 16, we find that 4 squared equals 16. Hence, √16 = 4.
-
Prime Factorization Method:
The prime factorization of 16 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2. Pairing the factors gives (2 × 2) × (2 × 2), and taking one element from each pair gives 2 × 2 = 4. Thus, √16 = 4.
-
Long Division Method:
Using the long division method, we find that 4 is the quotient when 16 is divided by 4. Therefore, √16 = 4.
Mathematical Explanation
In mathematical terms, a number is considered rational if it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. The number 4 can be expressed as 4/1, thus making it a rational number. Therefore, since √16 = 4, and 4 is a rational number, the square root of 16 is rational.
Radical and Exponential Form
The square root of 16 can also be expressed in radical form as √16 and in exponential form as 16^(1/2). Both forms confirm that the square root of 16 equals 4, which is a rational number.
Examples and Applications
Here are some practical examples demonstrating the concept:
-
Example 1: If you have a square table with an area of 16 square inches, each side of the table would measure √16 = 4 inches.
-
Example 2: If you arrange 16 flower plants in a square formation, each side of the square would have √16 = 4 plants.
-
Example 3: Simplifying the expression (7√16) + 15, given √16 = 4, results in (7×4) + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43.
Conclusion
The square root of 16 is a rational number, and its value is 4. This conclusion is supported by various mathematical methods and practical applications.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with various applications across fields such as geometry, engineering, and everyday calculations. Understanding whether the square root of 16 is rational helps in grasping basic mathematical properties and problem-solving techniques.
In this section, we will explore the definition of a square root, verify if 16 is a perfect square, determine the rationality of the square root of 16, and discuss methods to calculate it. These methods include guess and check, prime factorization, and the long division method.
- Definition of Square Root
- Perfect Square Verification
- Rationality of the Square Root of 16
- Calculation Methods
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16, denoted as √16, equals 4 because 4 × 4 = 16. Mathematically, this is represented as:
\(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
Perfect Square Verification
A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the square of another integer. Since 4 is an integer and \(4^2 = 16\), 16 is a perfect square. This can be visualized as:
\(16 = 4^2\)
Rationality of the Square Root of 16
A rational number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Since the square root of 16 is 4, which can be written as \(4/1\), it is a rational number. Therefore, the square root of 16 is rational.

Calculation Methods
- Guess and Check Method: Guess a number that, when squared, equals 16. Here, \(4^2 = 16\), so \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Prime Factorization: Factor 16 into prime factors: \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\). Pair the factors: \((2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)\). Take one element from each pair: \(2 \times 2 = 4\), so \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Long Division Method: Use long division to find the square root of 16 step-by-step, confirming that \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
What is the Value of the Square Root of 16?
The square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics. The value of the square root of 16 is 4. This is because 4 multiplied by itself (4 × 4) equals 16. We can express this mathematically as:
\[
\sqrt{16} = 4
\]
Here are some different ways to understand and calculate the square root of 16:
- Perfect Square Method: Since 16 is a perfect square, we know it can be written as 4 squared (42 = 16). Thus, \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Prime Factorization: The prime factors of 16 are 2 × 2 × 2 × 2. Pairing these factors gives us (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) = 4, so \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Using a Calculator: Simply input 16 and press the square root function to get \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Long Division Method: This method involves grouping digits in pairs and finding the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the given number. For 16, this process also leads to \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Understanding the square root of 16 is essential as it is a common example of a perfect square, which appears frequently in various fields such as geometry, algebra, and real-life applications.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 16, each offering a different approach. Below, we detail four common methods: the guess and check method, prime factorization, division method, and using a calculator.
- Guess and Check Method:
- Guess a number that, when squared, gives 16. For example, you might guess 4.
- Since 4 squared (4 × 4) equals 16, the square root of 16 is 4.
- Prime Factorization:
- Factorize 16 into its prime factors: 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
- Pair the factors: (2 × 2) × (2 × 2).
- Take one element from each pair: 2 × 2 = 4.
- Thus, the square root of 16 is 4.
- Division Method:
- Divide 16 by an initial guess (e.g., 4).
- Average the guess and the quotient: (4 + 4) / 2 = 4.
- Since the average does not change, the square root of 16 is 4.
- Using a Calculator:
- Enter 16 into the calculator and press the square root (√) function.
- The result will be 4.
By using any of these methods, we consistently find that the square root of 16 is 4, demonstrating that 16 is a perfect square.
Is 16 a Perfect Square?
Understanding whether 16 is a perfect square requires knowing what a perfect square is. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In other words, if you can find a whole number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number, then that number is a perfect square.
For example, consider the number 16. To determine if 16 is a perfect square, we need to find if there is an integer that can be multiplied by itself to yield 16.
- Step 1: Identify possible integer factors of 16. Common factors include 1, 2, 4, and 8.
- Step 2: Check if any of these factors, when squared, equal 16. This involves simple multiplication.
- Step 3: Calculate:
- \(1 \times 1 = 1\)
- \(2 \times 2 = 4\)
- \(4 \times 4 = 16\)
- \(8 \times 8 = 64\)
- Step 4: Observe that \(4 \times 4 = 16\). Thus, 4 is the integer that satisfies this condition, proving that 16 is a perfect square.
Additionally, the square root of 16 is 4, a whole number, which further confirms that 16 is a perfect square.
In summary, 16 is indeed a perfect square because it can be written as \(4^2\) or \(4 \times 4\).
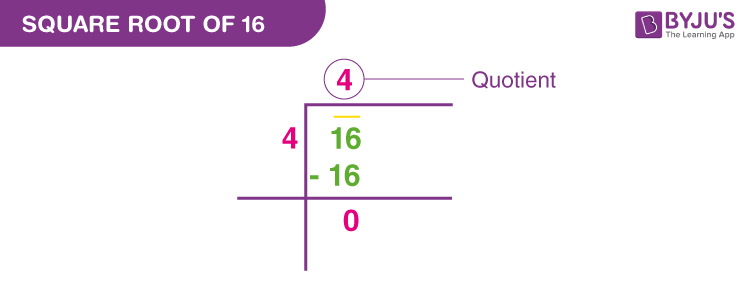
Is the Square Root of 16 Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 16 is rational. To understand why, let's delve into the properties of rational numbers and perfect squares:
- Rational Numbers: A number is rational if it can be expressed as a fraction where both the numerator and the denominator are integers. For example, 4/1 is a rational number because 4 and 1 are integers.
- Perfect Squares: A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In the case of 16, it can be written as 4 × 4.
Since 16 is a perfect square, its square root must be an integer. Specifically, the square root of 16 is 4. Given that 4 is an integer, it can be represented as a rational number (4/1). Thus, the square root of 16 is rational by definition.
To summarize, because 16 is a perfect square and its square root is an integer, the square root of 16 is rational.
Applications and Examples
The square root of 16, which is 4, has various applications and examples in real life. Understanding these applications can help us appreciate the significance of square roots in practical scenarios.
-
Geometry and Construction:
In geometry, square roots are used to find the lengths of sides in right triangles. For example, in a 3-4-5 right triangle, the square root of 16 (4) is one of the legs.
-
Physics:
Square roots are used in formulas to calculate physical properties. For instance, the distance formula in physics often involves square roots to determine distances between two points in space.
-
Engineering:
Engineers use square roots in various calculations, such as determining the dimensions of components and analyzing forces in structures.
-
Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics, square roots are used to calculate distances and render images accurately, ensuring realistic simulations and animations.
-
Finance:
In finance, square roots are used in statistical formulas, such as standard deviation, to measure volatility and risk.
By understanding these applications, we can see how the square root of 16, a simple mathematical concept, plays a crucial role in various fields, enhancing our problem-solving skills and practical knowledge.
Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 16, tại sao nó là một số hợp lý và cách tính toán. Video này cung cấp thông tin chi tiết và dễ hiểu về chủ đề này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 16
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của một số hợp lý trong video này. Video giải thích chi tiết và dễ hiểu về quá trình và phương pháp thực hiện.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của Một Số Hợp Lý