Topic how do you simplify the square root of 40: Understanding how to simplify the square root of 40 can enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities. This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into easy-to-follow steps, ensuring you grasp the concept quickly and effectively. Whether you're a student or math enthusiast, you'll find this guide invaluable in mastering square root simplification.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 40
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 40
- Prime Factorization of 40
- Identifying Perfect Square Factors
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Breaking Down the Factors
- Rewriting the Square Root Expression
- Simplifying the Expression
- Final Simplified Form
- Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications in Mathematics
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 40.
Simplifying the Square Root of 40
To simplify the square root of 40, we need to find the factors of 40 and look for perfect squares among them. Here's the step-by-step process:
Step-by-Step Process
- Find the prime factorization of 40.
- 40 = 2 × 20
- 20 = 2 × 10
- 10 = 2 × 5
- Identify the perfect square factors.
- \(2^2 \times 2 \times 5\)
- Simplify the square root using the perfect square factor.
40 can be factored into prime numbers as follows:
So, the prime factorization of 40 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 or \(2^3 \times 5\).
The prime factorization \(2^3 \times 5\) can be grouped as follows:
Here, \(2^2\) (which is 4) is a perfect square.
The square root of 40 can be expressed as:
\(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{2 \times 5}\)
Simplify further:
\(\sqrt{40} = 2 \times \sqrt{10}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is:
\(\sqrt{40} = 2\sqrt{10}\)

READ MORE:
Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is a fundamental skill in mathematics that involves expressing a square root in its simplest form. This process makes it easier to work with and understand the value of the square root. Let's explore how to simplify the square root of 40 step by step.
- Identify the Factors: Begin by identifying the factors of the number under the square root. For 40, these factors are 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, and 40.
- Prime Factorization: Break down 40 into its prime factors:
- 40 = 2 × 20
- 20 = 2 × 10
- 10 = 2 × 5
So, the prime factorization of 40 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 or \(2^3 \times 5\).
- Group the Factors: Group the prime factors into pairs of perfect squares:
- \(2^3 \times 5\) can be grouped as \(2^2 \times 2 \times 5\).
Here, \(2^2\) (which equals 4) is a perfect square.
- Simplify the Square Root: Simplify the expression by taking the square root of the perfect square and multiplying it by the remaining factors under the square root:
- \(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{2 \times 5}\)
- \(\sqrt{40} = 2 \times \sqrt{10}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is \(2\sqrt{10}\). This method can be applied to simplify any square root, making calculations more manageable and results more precise.
Understanding the Square Root of 40
The square root of 40 can be understood by breaking it down into its prime factors and then simplifying it step by step.
- First, identify the prime factors of 40:
- 40 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5
- Next, group the prime factors into pairs:
- \(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5}\)
- This can be written as \(\sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 5)}\)
- Simplify the expression by taking the square root of the pairs:
- \(\sqrt{(2 \times 2)} \times \sqrt{(2 \times 5)}\)
- \(\sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{10}\)
- Since the square root of 22 is 2:
- 2 \(\times \sqrt{10}\)
- Thus, \(\sqrt{40} = 2\sqrt{10}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is \(2\sqrt{10}\).
Prime Factorization of 40
To simplify the square root of 40, we begin with its prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of breaking down a number into its basic building blocks, which are prime numbers.
The number 40 can be factored into:
- 40 ÷ 2 = 20
- 20 ÷ 2 = 10
- 10 ÷ 2 = 5
- 5 is a prime number and cannot be divided further
Therefore, the prime factorization of 40 is:
\(40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5\)
This can also be written as:
\(40 = 2^3 \times 5\)
In terms of its prime factors, 40 is composed of three 2's and one 5. This factorization is essential for simplifying the square root, as it allows us to group the prime factors and extract them from under the square root symbol.
Identifying Perfect Square Factors
To simplify the square root of 40, the first step is to identify the perfect square factors of 40. Perfect squares are numbers that are the square of an integer. Here are the detailed steps to identify these factors:
-
List the Factors of 40:
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 8
- 10
- 20
- 40
-
Identify the Perfect Squares:
From the list of factors, we identify the perfect squares:
- 1 (since 1 × 1 = 1)
- 4 (since 2 × 2 = 4)
-
Select the Largest Perfect Square:
The largest perfect square factor of 40 is 4.
-
Divide 40 by the Largest Perfect Square:
40 ÷ 4 = 10
-
Write the Square Root Expression:
The square root of 40 can now be expressed as:
\(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{4 \times 10} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{10}\)
-
Simplify the Expression:
Since \(\sqrt{4} = 2\), we can simplify the expression further:
\(\sqrt{40} = 2\sqrt{10}\)
Thus, the square root of 40 simplifies to \(2\sqrt{10}\).
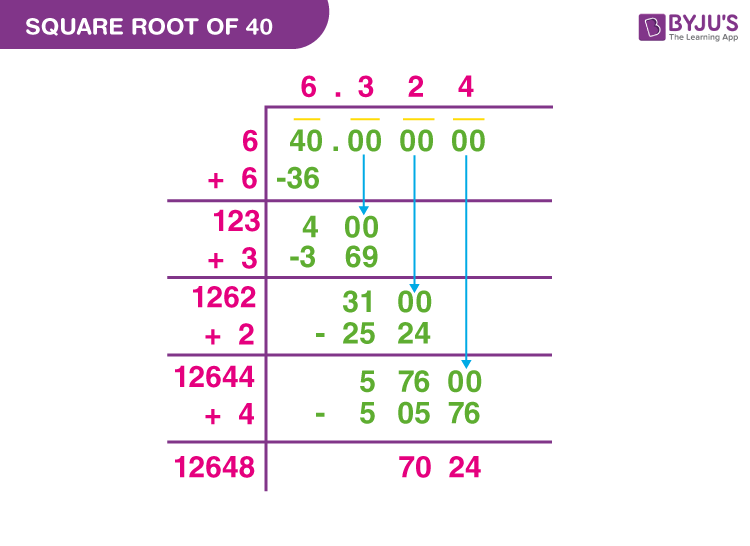
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
To simplify the square root of 40, follow these detailed steps:
-
Prime Factorization:
First, write the prime factorization of 40:
\[ 40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \]
-
Group Factors:
Group the same prime factors into pairs:
\[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5} \]
-
Extract Perfect Squares:
Rewrite the grouped pairs as squares:
\[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 10} \]
Apply the square root to the perfect square:
\[ \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \]
-
Simplify:
Simplify the expression by taking the square root of the perfect square out of the radical:
\[ \sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{10} \]
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is \( 2 \sqrt{10} \).
Breaking Down the Factors
To simplify the square root of 40, we need to break down the number into its prime factors. This helps in identifying the perfect square factors, making the simplification process easier. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
List the factors: Start by listing the factors of 40:
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 8
- 10
- 20
- 40
-
Identify the perfect squares: From the list of factors, identify the perfect squares. For 40, the perfect squares are:
- 1
- 4
-
Choose the largest perfect square factor: Out of the identified perfect squares, the largest is 4. This will be used to simplify the square root of 40.
-
Divide the original number: Divide 40 by the largest perfect square factor:
\[ \frac{40}{4} = 10 \]
-
Rewrite the square root expression: Express the square root of 40 in terms of the perfect square factor and the result from the division:
\[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{4 \times 10} \]
By breaking down the factors of 40, we have set the stage for simplifying the expression further. The next steps will involve rewriting and simplifying the square root expression using these factors.
Rewriting the Square Root Expression
To rewrite the square root expression for the square root of 40, we can use the prime factorization method to simplify it. Follow these steps:
- First, factor the number 40 into its prime factors: \( 40 = 2^3 \times 5 \).
- Express the square root of 40 using these prime factors: \( \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 5} \).
- Separate the factors under the square root: \( \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5} \).
- Since the square root of a product is the product of the square roots, we can write: \( \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{2 \times 5} \).
- Simplify the perfect square factor: \( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \).
- Combine the simplified term with the remaining square root: \( \sqrt{40} = 2 \times \sqrt{10} \).
Therefore, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{40} \) is \( 2\sqrt{10} \).
Simplifying the Expression
To simplify the expression for the square root of 40, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Prime Factors: The prime factorization of 40 is given by:
\( 40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \)
-
Group the Factors: Identify pairs of the same factors:
\( 40 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5 \)
-
Take Out the Square Root of the Perfect Squares: For the pair of 2's, the square root is:
\( \sqrt{(2 \times 2)} = 2 \)
Thus, we have:
\( \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5} = 2 \sqrt{2 \times 5} \)
-
Simplify the Remaining Expression: Multiply the remaining factors under the square root:
\( \sqrt{10} \)
Therefore, we have:
\( \sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{10} \)
The simplified form of the square root of 40 is \( 2 \sqrt{10} \).

Final Simplified Form
After breaking down the factors and rewriting the square root expression, we arrive at the final step of simplification. Here's how the final simplified form of the square root of 40 is determined:
Recall the rewritten expression from the previous steps:
\(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{4 \times 10}\)
Apply the property of square roots which states that \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\):
\(\sqrt{4 \times 10} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{10}\)
Calculate the square root of the perfect square factor (4):
\(\sqrt{4} = 2\)
Combine the results to obtain the simplified form:
\(\sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{10} = 2 \times \sqrt{10}\)
Therefore, the final simplified form of \(\sqrt{40}\) is:
\(2\sqrt{10}\)
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you master the simplification of square roots, particularly focusing on the square root of 40:
-
Problem 1: Simplify the square root of 50.
Solution:
- Prime factorize 50: \(50 = 2 \times 5^2\)
- Identify the perfect squares: \(5^2\) is a perfect square.
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
- Final answer: \(5\sqrt{2}\)
-
Problem 2: Simplify the square root of 72.
Solution:
- Prime factorize 72: \(72 = 2^3 \times 3^2\)
- Identify the perfect squares: \(2^2\) and \(3^2\) are perfect squares.
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = 6\sqrt{2}\)
- Final answer: \(6\sqrt{2}\)
-
Problem 3: Simplify the square root of 98.
Solution:
- Prime factorize 98: \(98 = 2 \times 7^2\)
- Identify the perfect squares: \(7^2\) is a perfect square.
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{98} = \sqrt{2 \times 7^2} = 7\sqrt{2}\)
- Final answer: \(7\sqrt{2}\)
-
Problem 4: Simplify the square root of 45.
Solution:
- Prime factorize 45: \(45 = 3^2 \times 5\)
- Identify the perfect squares: \(3^2\) is a perfect square.
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 5} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
- Final answer: \(3\sqrt{5}\)
Use these practice problems to test your understanding of simplifying square roots. Make sure to follow each step carefully to ensure accuracy in your final answers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying the square root of 40, there are several common mistakes that students often make. Here are some key points to keep in mind to avoid these errors:
- Incorrect Prime Factorization: Ensure that you correctly identify the prime factors of 40. The prime factorization of 40 is \(2^3 \times 5\). Some students mistakenly identify the factors, which leads to incorrect simplification.
- Grouping Factors Incorrectly: Remember to group the factors correctly when simplifying. For example, in \(\sqrt{40}\), you can group \(4\) (which is a perfect square) and \(10\) as follows:
\[\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{4 \times 10} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{10} = 2\sqrt{10}\]
- Ignoring Perfect Squares: Do not overlook perfect square factors within the radicand (the number inside the square root). In this case, 4 is a perfect square. Simplifying this way helps reduce the radicand efficiently.
- Incorrect Use of Properties: Apply the properties of square roots correctly. For example, \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\). Misapplying this property can lead to errors.
- Forgetting to Simplify Fully: Make sure to simplify the square root as much as possible. For \(\sqrt{40}\), simplify it to \(2\sqrt{10}\), and don't leave it as \(\sqrt{4 \times 10}\).
- Mistakes in Calculation: Double-check your calculations. Small arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect simplification.
By keeping these common mistakes in mind, you can ensure that you simplify square roots correctly and efficiently.
Applications in Mathematics
The simplification of square roots, such as the square root of 40, has various applications in mathematics. Understanding how to simplify these roots is fundamental in solving complex mathematical problems. Here are some key areas where simplified square roots are applied:
- Geometry: Simplified square roots are essential in calculating distances, areas, and volumes. For example, the Pythagorean theorem often requires simplification of square roots to determine the lengths of sides in right triangles.
- Algebra: In algebraic expressions and equations, simplifying square roots helps in solving for variables and simplifying expressions. For example, solving quadratic equations may involve the simplification of square roots to find the roots of the equation.
- Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions and identities sometimes require the simplification of square roots. For instance, when working with sine, cosine, and tangent functions, simplified square roots can make calculations more manageable.
- Calculus: In calculus, simplifying square roots is necessary when dealing with limits, derivatives, and integrals. For example, simplifying the square root of a function can make differentiation and integration processes more straightforward.
- Physics: Many physical formulas involve square roots. Simplifying these roots can help in solving problems related to motion, force, energy, and other physical concepts.
Here are some practical examples to illustrate these applications:
| Application | Example |
|---|---|
| Geometry | Finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of lengths 6 and 8 requires calculating , which simplifies to |
| Algebra | Solving simplifies to |
| Trigonometry | Simplifying |
| Calculus | Simplifying |
| Physics | Simplifying the equation for the period of a pendulum |
In conclusion, mastering the simplification of square roots not only enhances your mathematical skills but also equips you with the tools to solve a wide range of problems across various scientific disciplines.

Conclusion
In conclusion, simplifying the square root of 40 is a process that involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and identifying the perfect square factors. By following these steps, you can achieve the simplest form of the square root expression. Here's a recap of the steps:
- Identify the Factors: The factors of 40 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, and 40.
- Find the Perfect Squares: From these factors, the perfect square is 4.
- Divide by the Largest Perfect Square: Divide 40 by 4, which gives you 10.
- Calculate the Square Root: The square root of 4 is 2.
- Simplify: Combine these results to get the simplified form: \(2\sqrt{10}\).
Thus, the square root of 40 simplifies to \(2\sqrt{10}\). This method not only makes complex expressions easier to handle but also aids in solving various mathematical problems more efficiently.
By mastering the simplification process, you enhance your problem-solving skills and deepen your understanding of mathematical concepts, paving the way for more advanced studies.
- Remember to always look for the largest perfect square factor.
- Practice with different numbers to become more proficient in simplifying square roots.
We hope this guide has been helpful in understanding how to simplify the square root of 40 and similar problems. Keep practicing and applying these steps to improve your mathematical abilities.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 40.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 40: √40
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn chi tiết cách phân tích và đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 40, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách làm.
Phân tích căn bậc hai của bốn mươi, sqrt(40)