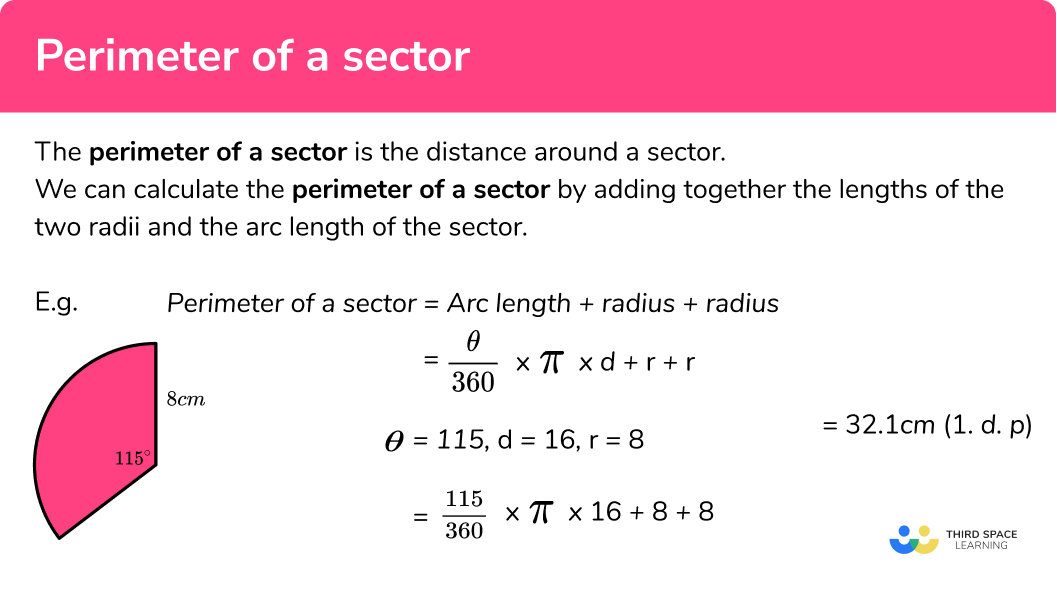
Topic how do we find the perimeter of a square: Discover the easy method to find the perimeter of a square with our straightforward guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, learning how to calculate the perimeter of a square is a valuable and practical skill. Let's explore the steps to master this essential mathematical concept!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Square Perimeter
- Understanding the Concept of Perimeter
- Perimeter Formula for a Square
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Visual Representations and Diagrams
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- FAQs on Square Perimeter
- Additional Resources and Practice Problems
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi của hình vuông, phù hợp cho học sinh và người mới bắt đầu học toán.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
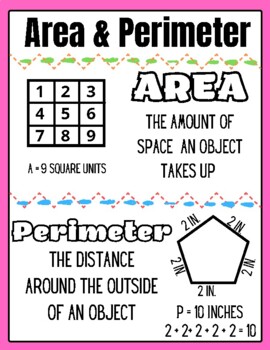
The perimeter of a square is the total distance around the outside of the square. To find the perimeter, you can use a simple mathematical formula based on the length of one side of the square.
Formula to Calculate Perimeter
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a square is:
Perimeter (P) = 4 × side length (s)
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the square.
- s is the length of one side of the square.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the length of one side of the square. This is denoted as s.
- Multiply the side length by 4. This accounts for all four sides of the square being equal in length.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
Example
If a square has a side length of 5 units, the perimeter can be calculated as follows:
\[ P = 4 \times s \]
\[ P = 4 \times 5 \]
\[ P = 20 \text{ units} \]
Using the Perimeter Formula
This formula works universally for any unit of length, whether it be centimeters, meters, inches, or feet. As long as the side length is known, the perimeter can be quickly and easily calculated.
Additional Notes
The simplicity of a square's geometry makes calculating its perimeter straightforward. Ensure that all side lengths are equal, as this is a defining property of squares.
Visual Representation
To better understand, consider the following diagram:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
| 3 units | 12 units |
| 7 units | 28 units |
| 10 units | 40 units |
By following these steps and understanding the formula, you can easily determine the perimeter of any square.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Perimeter
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental geometric concept that measures the total distance around the square's boundary. It's a crucial element in various fields, from architecture to everyday problem-solving. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is straightforward and involves a simple formula.
A square is a special type of polygon where all four sides are equal in length and every angle is a right angle. The perimeter of a square is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Because all sides are of equal length, finding the perimeter is simplified to multiplying one side length by four.
- Start by measuring the length of one side of the square. This measurement is denoted as s.
- Use the formula to find the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Multiply the side length by four. This accounts for the total distance around all four equal sides of the square.
For example, if a square has a side length of 6 units, its perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ units}
\]
This straightforward calculation shows how the uniformity of a square's sides simplifies perimeter calculations. By mastering this basic concept, you can apply it to a variety of practical and theoretical problems involving squares.
Understanding the perimeter of a square is not only foundational in geometry but also essential in many real-world applications, such as designing square-shaped objects, planning spaces, and even in crafting and construction projects.
Understanding the Concept of Perimeter
The concept of perimeter is a fundamental aspect of geometry that describes the continuous line forming the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. In simple terms, the perimeter is the total length of the edges or sides of a polygon. For any shape, whether regular or irregular, the perimeter is calculated by summing up the lengths of all its sides.
Perimeter plays a crucial role in various practical applications, such as fencing a yard, framing a picture, or any scenario where determining the boundary length is necessary. It's an essential concept not only in mathematics but also in everyday life and different professions.
Steps to Understand and Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the Shape: First, determine the type of polygon you are dealing with. For example, squares, rectangles, triangles, and more complex shapes each have unique perimeter calculations.
- Measure the Sides: Measure the lengths of all the sides of the polygon. Ensure that each side length is recorded in the same unit of measurement.
- Sum the Sides: Add the lengths of all the sides together to find the perimeter. For regular polygons (where all sides are equal), you can use a simplified formula.
For a square, which is a regular polygon with equal sides, the perimeter can be easily calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. For example, if each side of a square is 8 units, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ units}
\]
Perimeter in Different Shapes
The method to find the perimeter varies with different shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated as: \[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of all three side lengths: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Circle (Circumference): Though not a polygon, the perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference and is calculated as: \[ C = 2 \pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
Understanding the concept of perimeter is a key stepping stone in mastering more advanced geometric calculations and is applicable in a wide range of everyday and professional contexts.
Perimeter Formula for a Square
The perimeter of a square is a straightforward calculation due to the square's unique properties. Each of the four sides of a square is equal in length, making the calculation of the perimeter simple and direct. The perimeter can be found by using a basic formula that multiplies the length of one side by four.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a square with side length \( s \) is:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the Side Length: Determine the length of one side of the square. This value is denoted as \( s \).
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula \( P = 4 \times s \) to calculate the perimeter.
- Multiply: Multiply the side length by 4 to account for all four sides of the square.
For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Let's explore a few more examples to reinforce this concept:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 3 units | \[ P = 4 \times 3 = 12 \text{ units} \] |
| 7 units | \[ P = 4 \times 7 = 28 \text{ units} \] |
| 10 units | \[ P = 4 \times 10 = 40 \text{ units} \] |
This formula is not only simple but also universally applicable to any square, regardless of the units used to measure the side lengths. Whether you're dealing with centimeters, meters, inches, or feet, the process remains the same.
In practical applications, this formula helps in situations like determining the amount of material needed to frame a square object, the length of fencing required for a square garden, or any scenario where you need to know the boundary length of a square.
By mastering the perimeter formula for a square, you can easily solve a variety of problems involving squares in both academic and real-world contexts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a fundamental and straightforward task in geometry. By following these clear steps, you can easily determine the perimeter of any square. The process is simple and involves measuring one side of the square and applying a basic formula.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Identify and Measure the Side Length:
- Locate one side of the square. Because all sides of a square are equal, measuring one side is sufficient.
- Use a ruler or measuring tool to determine the length of this side. Denote this length as \( s \).
- Understand the Perimeter Formula:
The perimeter \( P \) of a square is calculated by multiplying the side length by 4:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\] - Apply the Formula:
- Insert the measured side length \( s \) into the formula.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to calculate the perimeter.
- Calculate the Result:
- Perform the multiplication to find the total perimeter.
- Express the perimeter in the same units used to measure the side length.
Example Calculations
Let's walk through a few examples to illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a square:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter Calculation | Resulting Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 units | \[ P = 4 \times 4 \] | 16 units |
| 6 units | \[ P = 4 \times 6 \] | 24 units |
| 8 units | \[ P = 4 \times 8 \] | 32 units |
Following these steps ensures that you can quickly and accurately calculate the perimeter of any square. This basic skill is useful in numerous practical scenarios, such as designing, planning, and measuring spaces or objects.
Remember, the key to success is to consistently apply the formula \( P = 4 \times s \), making sure to measure accurately and use the correct units throughout your calculations.

Examples of Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square can be greatly enhanced by examining specific examples. Here, we will walk through several scenarios to illustrate how the formula is applied in different contexts. Each example will demonstrate the step-by-step process of finding the perimeter.
Example 1: Simple Square
Consider a square with a side length of 5 units. To find the perimeter:
- Measure the side length: \( s = 5 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Example 2: Larger Square
Now, let's take a square with a side length of 12 units. The steps are as follows:
- Measure the side length: \( s = 12 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times 12 = 48 \text{ units} \]
Example 3: Square with Decimals
Consider a square where the side length is a decimal, for example, 7.5 units. Here's how you calculate the perimeter:
- Measure the side length: \( s = 7.5 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times 7.5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Example 4: Large Unit Measurements
In another scenario, let's calculate the perimeter for a large square with a side length of 100 meters:
- Measure the side length: \( s = 100 \) meters.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times 100 = 400 \text{ meters} \]
Example 5: Practical Application
Imagine you need to find the perimeter of a square garden that has sides of 15.5 feet each:
- Measure the side length: \( s = 15.5 \) feet.
- Apply the formula: \[ P = 4 \times s \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ P = 4 \times 15.5 = 62 \text{ feet} \]
Summary Table of Examples
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter Calculation | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 units | \[ P = 4 \times 5 \] | 20 units |
| 12 units | \[ P = 4 \times 12 \] | 48 units |
| 7.5 units | \[ P = 4 \times 7.5 \] | 30 units |
| 100 meters | \[ P = 4 \times 100 \] | 400 meters |
| 15.5 feet | \[ P = 4 \times 15.5 \] | 62 feet |
These examples demonstrate how versatile and straightforward it is to calculate the perimeter of a square, regardless of the unit of measurement or size.
Visual Representations and Diagrams
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square can be significantly enhanced by using visual aids and diagrams. These tools help to illustrate the concept clearly and provide a step-by-step visual guide to the calculation process. Let's explore how diagrams can simplify the understanding of finding the perimeter of a square.
Diagram of a Square
Consider a square labeled with side lengths:
| Side \( s \) | ||||||||||
| Side \( s \) | ||||||||||
In this diagram, each side of the square is represented as \( s \). To calculate the perimeter, we sum the lengths of all four sides:
\[
P = s + s + s + s = 4 \times s
\]
Example with a Specific Side Length
Let's consider a square with a side length of 6 units:
| Side \( s = 6 \) units | ||||||||||
| Side \( s = 6 \) units | ||||||||||
Using the formula, we calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ units}
\]
Interactive Understanding
Visual tools such as diagrams and interactive models allow for a deeper understanding of perimeter calculations. Here’s how a step-by-step illustration can help:
- Step 1: Identify the Square
Begin by recognizing the square and its properties, where all sides are equal in length.
- Step 2: Measure the Side
Determine the length of one side using a ruler or other measuring tool.
- Step 3: Apply the Formula
Use the perimeter formula \( P = 4 \times s \) to find the total perimeter by multiplying the side length by 4.
- Step 4: Visualize the Perimeter
Think of the perimeter as the continuous boundary around the square. The diagram helps to visualize how adding up all four equal sides gives the total perimeter.
These visual representations make the concept of perimeter tangible and easier to grasp, especially for visual learners. By seeing how each side contributes to the total boundary, the process of calculating the perimeter becomes clearer and more intuitive.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of a square is essential in various real-life situations. Here are some practical applications:
-
Fencing a Property:
When planning to fence a square garden or property, knowing the perimeter helps determine the total length of the fence needed. For example, if each side of the garden is 10 meters, the total perimeter is \(4 \times 10 = 40\) meters.
-
Construction Projects:
In construction, calculating the perimeter is crucial for laying out foundations, borders, and frameworks. For instance, when constructing a square-shaped patio, the perimeter measurement ensures precise material estimates.
-
Interior Design and Furniture Layout:
Designers often use perimeter calculations to plan the layout of furniture and decor within a square room. This helps in optimizing space and ensuring a balanced arrangement.
-
Painting and Wallpapering:
When painting a square room or applying wallpaper, knowing the perimeter allows for accurate calculation of materials needed. For example, to add a border around the room, you need to measure the perimeter to buy the right length of the border material.
-
Sports and Recreation:
In sports like basketball or tennis, calculating the perimeter of the court is essential for setting up boundaries and ensuring the playing area meets official dimensions.
-
Gardening:
Gardeners use perimeter measurements to create planting beds and pathways. For example, creating a square flower bed with a side length of 5 meters will have a perimeter of \(4 \times 5 = 20\) meters, guiding the placement of plants and decorations.
-
Crafting and DIY Projects:
For DIY enthusiasts, knowing the perimeter helps in various projects such as making square frames, quilts, or crafts that require precise measurements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a square, there are several common mistakes that learners often make. Here are some of them and tips on how to avoid these errors:
-
Confusing Perimeter with Area:
One common mistake is confusing the perimeter of a square with its area. The perimeter is the total length around the square, while the area measures the surface inside. The formula for perimeter is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length, while the area is \( A = s^2 \).
-
Incorrect Side Length Measurement:
Ensure that the side length \( s \) is measured accurately. Any error in measuring the side length will directly affect the perimeter calculation. Use a reliable ruler or measuring tape for precise measurements.
-
Arithmetic Errors:
Simple arithmetic mistakes can lead to incorrect perimeter values. Always double-check your multiplication and addition. For example, if the side length is 7 units, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 7 = 28 \) units. Verify each step to avoid errors.
-
Using the Wrong Formula:
Sometimes, learners might mistakenly use the formula for the perimeter of a different shape, such as a rectangle or triangle. Remember, the perimeter of a square is calculated as \( P = 4s \), not using other formulas like \( P = 2(l + w) \) for a rectangle.
-
Forgetting Units:
Another common mistake is forgetting to include units in the final answer. If the side length is measured in meters, the perimeter should also be in meters. Consistently use units throughout your calculations.
-
Misinterpreting the Problem:
Carefully read the problem to ensure you understand what is being asked. Sometimes problems may provide the area or a diagonal instead of the side length. Make sure to use the appropriate steps to find the side length first if necessary.
-
Rounding Errors:
When dealing with measurements that require rounding, be cautious. Rounding too early in the process can lead to inaccurate results. It's best to keep numbers in their exact form until the final step.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and carefully following each step, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a square and avoid potential pitfalls.
FAQs on Square Perimeter
Here are some frequently asked questions about the perimeter of a square:
-
What is the perimeter of a square in math?
The perimeter of a square is the total length around its boundary. The formula to calculate the perimeter is \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \), where the side is the length of one side of the square.
-
How do you calculate the perimeter of a square?
To calculate the perimeter of a square, you simply multiply the length of one side by 4. If each side of the square is \( a \) units long, then the perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 4a \).
-
What is the difference between the area and perimeter of a square?
The area of a square measures the space within its boundary and is calculated as \( \text{Area} = \text{side} \times \text{side} \) or \( \text{side}^2 \). The perimeter measures the total distance around the boundary and is calculated as \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \).
-
How can you find the side length of a square if the perimeter is given?
If the perimeter \( P \) of a square is known, the side length \( a \) can be found by rearranging the perimeter formula: \( a = \frac{P}{4} \).
-
How can you find the perimeter of a square if the area is given?
If the area \( A \) of a square is known, you can find the side length by taking the square root of the area: \( \text{side} = \sqrt{A} \). Then, use the perimeter formula: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
-
What units are used for measuring the perimeter of a square?
The perimeter of a square is measured in linear units such as inches, feet, centimeters, or meters, depending on the units used for the side length.
-
How do you find the perimeter of a square using its diagonal?
The diagonal of a square is related to the side length by the formula \( \text{diagonal} = \sqrt{2} \times \text{side} \). To find the perimeter when the diagonal is given, use the formula \( P = 2\sqrt{2} \times \text{diagonal} \).
Additional Resources and Practice Problems
To deepen your understanding of finding the perimeter of a square, here are some additional resources and practice problems:
Online Resources
- - Detailed explanations, derivations, and interactive games to learn the concept of square perimeter.
- - Step-by-step tutorials and examples for calculating the perimeter of a square.
- - Comprehensive guide with formulas, examples, and practice problems.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Solution: \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm
- A square has a perimeter of 36 inches. What is the length of each side?
Solution: \( 36 = 4s \Rightarrow s = 36 / 4 = 9 \) inches
- If a square's area is 64 square meters, what is its perimeter?
Solution:
\[
\text{Side length} = \sqrt{64} = 8 \text{ meters}
\]
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ meters}
\] - Calculate the perimeter of a square whose side is reduced by 2 cm from its original length of 10 cm.
Solution:
\[
\text{New side length} = 10 - 2 = 8 \text{ cm}
\]
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ cm}
\] - A square garden has a side length of 15 feet. How much fencing material is needed to enclose the garden?
Solution: \( P = 4 \times 15 = 60 \) feet
Additional Practice
Try to solve these additional problems on your own:
- What is the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7.5 meters?
- If the perimeter of a square is 48 inches, what is the side length?
- A square has an area of 49 square feet. Calculate its perimeter.
- Find the perimeter of a square that has a side length of 22 cm.
- If the side length of a square is increased by 3 cm and the new side length is 12 cm, what is the new perimeter?
Use the resources and practice problems to strengthen your understanding and ensure you can accurately find the perimeter of any square!
Conclusion and Summary
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that measures the total distance around the edges of the square. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for various real-life applications, from construction and design to everyday problem-solving.
To summarize:
- Definition: The perimeter of a square is the sum of all four sides of the square.
- Formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a square with side length \( a \) is given by \( P = 4a \).
- Calculation Steps:
- Identify the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
- Common Mistakes: Ensure not to confuse perimeter with area, and always use consistent units for measurement.
- Applications: Perimeter calculations are used in fencing, framing, and various other fields requiring measurements of boundaries.
- Practice: Regular practice with different examples helps reinforce the concept and prevents errors.
By mastering the concept of perimeter, students can build a strong foundation for more advanced topics in mathematics and its applications. Practice problems, visual aids, and real-life examples are great tools to aid in learning and understanding this basic yet crucial geometric concept.
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi của hình vuông, phù hợp cho học sinh và người mới bắt đầu học toán.
Làm Thế Nào Để Tìm Chu Vi Của Hình Vuông | Toán Học với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình vuông, phù hợp cho học sinh và người mới bắt đầu học toán.
Làm Thế Nào Để Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Của Hình Vuông