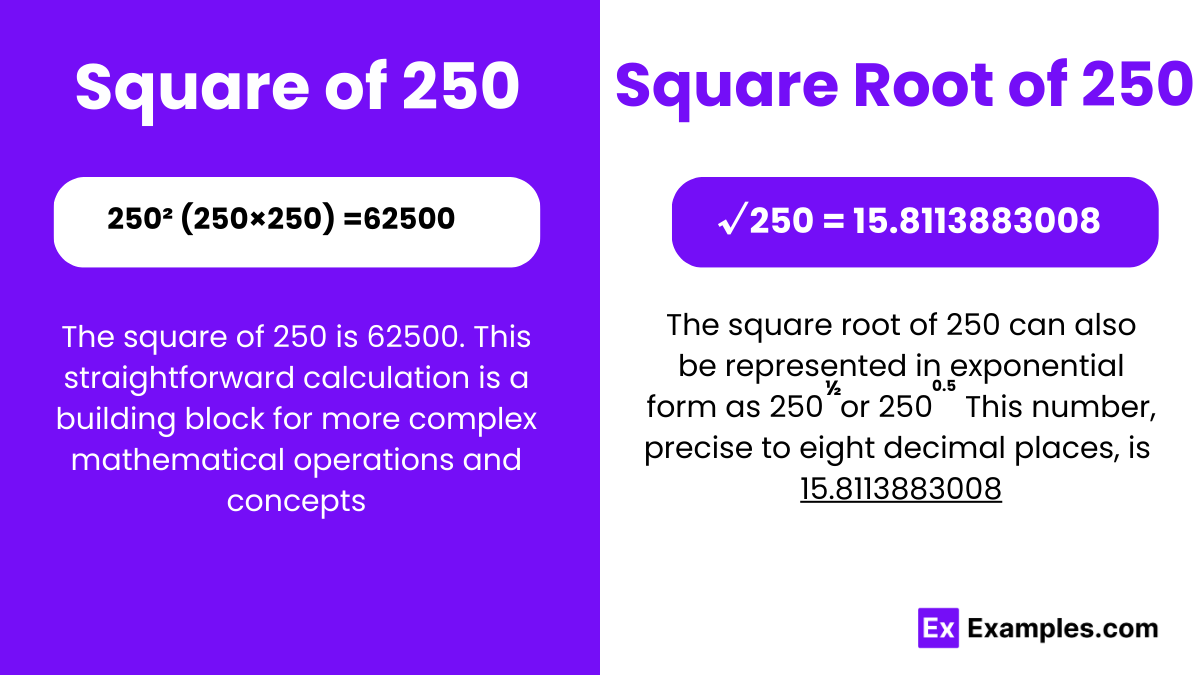
Topic 62500 square root: The square root of 62500 is a fascinating mathematical calculation. In this article, we explore how to find the square root of 62500, its significance, and practical applications. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, understanding this concept can enhance your mathematical skills and knowledge.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 62500
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 62500?
- Properties of Square Roots
- Methods to Calculate Square Roots
- The Babylonian Method
- Using a Square Root Calculator
- Simplifying Square Roots
- Square Root Table 1-100
- Examples of Simplified Square Roots
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 62500
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 62500 can be expressed as:
\[ \sqrt{62500} = 250 \]
Key Concepts
- Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The principal square root is the positive root.
- The notation for the square root of 62500 is \( \sqrt{62500} \) or \( 62500^{1/2} \).
Calculation
The square root of 62500 can be calculated as follows:
\[ 250 \times 250 = 62500 \]
Therefore:
\[ \sqrt{62500} = 250 \]
Properties
In general, for any positive number \( x \):
- The square root of \( x \) is denoted \( \sqrt{x} \).
- \( \sqrt{x} \times \sqrt{x} = x \).
Examples of Other Square Roots
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 81 | ±9 |
| 25 | ±5 |
| 100 | ±10 |
| 144 | ±12 |
How to Simplify Square Roots
To simplify the square root of a non-perfect square, look for factors that are perfect squares:
- For example, to simplify \( \sqrt{45} \): \[ \sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5} \]
- To simplify \( \sqrt{8} \): \[ \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{2} = 2\sqrt{2} \]
Understanding how to simplify square roots can make calculations easier, especially when dealing with large numbers or variables.
For further exploration and tools to calculate square roots, you can visit various online calculators and resources:

READ MORE:
Introduction
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, providing a foundation for more complex mathematical operations and theories. Understanding square roots can help in various fields such as engineering, physics, and finance, among others. This guide will specifically delve into the square root of 62500, exploring its properties, calculation methods, and practical applications.
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, since 3 multiplied by 3 equals 9. In mathematical notation, the square root is often represented by the radical symbol (√) or as an exponent of 1/2.
The square root of 62500 is a perfect square, meaning it has an integer value. By understanding how to calculate and simplify this square root, one can gain a better grasp of both basic and advanced mathematical concepts. In this guide, we will explore the methods to find the square root of 62500, including manual calculations and using tools like calculators.
Additionally, we will discuss the properties of square roots and how they can be applied in various mathematical problems. From simplifying square roots to understanding their geometric interpretations, this comprehensive guide aims to equip you with all the necessary knowledge about the square root of 62500.
Understanding Square Roots
The concept of a square root is fundamental in mathematics. It involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 62500 is the number which, when squared, equals 62500.
In mathematical notation, the square root of a number \( a \) is represented as \( \sqrt{a} \). This can also be written as \( a^{1/2} \). For example:
\( \sqrt{62500} = 250 \)
To understand square roots better, consider the following properties:
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number actually has two square roots, one positive and one negative. For 62500, these roots are \( 250 \) and \( -250 \).
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root is the non-negative root. Hence, for 62500, the principal square root is \( 250 \).
Properties of Square Roots
- For any non-negative number \( a \), \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{a} = a \).
- The square root of a product is the product of the square roots: \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \).
- The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots: \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
These properties are useful in simplifying expressions and solving equations involving square roots.
Examples
- \( \sqrt{62500} = 250 \), because \( 250 \times 250 = 62500 \).
- \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \), because \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \).
Understanding these concepts is crucial for delving into more advanced topics in mathematics, including algebra and calculus.
What is the Square Root of 62500?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Mathematically, the square root of a number x is denoted as √x. For 62500, we find that its square root is a whole number.
To calculate the square root of 62500, we look for a number that, when squared, equals 62500. Using this approach, we can determine:
√62500 = 250
This means that 250 × 250 = 62500.
The concept can be understood better with the following points:
- Square root: The square root of a number is a value that produces the original number when multiplied by itself. In this case, 250 is the square root of 62500.
- Mathematical representation: √62500 = 250. This can also be written as 62500^(1/2) = 250.
- Positive and negative roots: Typically, the square root function returns the principal (positive) root. However, -250 is also a square root of 62500 because (-250) × (-250) = 62500.
In summary, the square root of 62500 is 250. This calculation is straightforward since 62500 is a perfect square, making it easy to find its square root without any remainder.
Properties of Square Roots
The square root of a number has several interesting and useful properties. Understanding these properties helps in simplifying and working with square roots in various mathematical contexts. Here are some key properties:
- Perfect Squares: If a number is a perfect square, its square root is an integer. For example, \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \).
- Radical Symbol: The square root is denoted by the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \). If \( x \) is not a perfect square, \( \sqrt{x} \) is an irrational number.
- Exponential Form: The square root of a number \( x \) can be expressed as \( x^{1/2} \) or \( x^{0.5} \). For example, \( 5^{1/2} = \sqrt{5} \).
- Last Digit Patterns:
- If a number has the last digit 0, its square root also ends in 0.
- If a number ends in 1, its square root ends in 1 or 9.
- If a number ends in 4, its square root ends in 2 or 8.
- If a number ends in 5, its square root ends in 5.
- If a number ends in 6, its square root ends in 4 or 6.
- If a number ends in 9, its square root ends in 3 or 7.
- Even and Odd Numbers:
- The square root of an even number is always even. For example, \( \sqrt{64} = 8 \).
- The square root of an odd number is always odd. For example, \( \sqrt{121} = 11 \).
- Zeros at the End:
- If a number ends with an even number of zeros, its square root is an integer. For example, \( \sqrt{10000} = 100 \).
- If a number ends with an odd number of zeros, its square root is not a whole number. For example, \( \sqrt{1000} \) is not an integer.
- Positive and Negative Roots: If \( x \) is a square root of a number \( X \), then \( -x \) is also a square root of \( X \). For example, \( \sqrt{X} = \pm x \).
- Negative Numbers: The square root of a negative number does not exist in the set of real numbers. Instead, it exists in the set of complex numbers. For example, \( \sqrt{-7} = 7i \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \).
- Sum of Odd Numbers: For a natural number \( n \), the square \( n^2 \) is equal to the sum of the first \( n \) odd numbers. For example, \( 25 = 5^2 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 \).
- Multiplication Rule: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots. For example, \( \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Division Rule: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots. For example, \( 2 = \sqrt{\frac{8}{2}} = \frac{\sqrt{8}}{\sqrt{2}} \).

Methods to Calculate Square Roots
Calculating square roots can be approached through various methods, each with its own advantages. Below are some common methods used to determine square roots:
-
Using a Calculator
The simplest method is using a calculator. Just enter the number and press the square root (√) button to get the result.
-
Prime Factorization Method
- Write the prime factorization of the number.
- Group the prime factors into pairs.
- Take one factor from each pair and multiply them to find the square root.
- Prime factorization: \( 62500 = 2^2 \times 5^4 \times 5^2 \)
- Group into pairs: \( (2^2) \times (5^4) \times (5^2) \)
- Square root: \( 2 \times 5^2 \times 5 = 250 \)
For example, to find the square root of 62500:
-
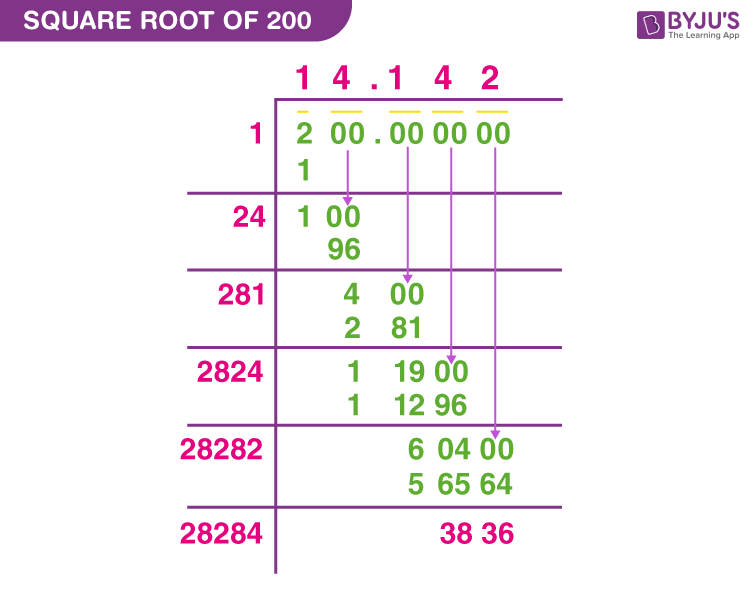
Long Division Method
This method is useful for finding square roots of larger numbers or numbers that do not have a simple factorization:
- Pair the digits from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair of digits.
- Subtract the square and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Double the quotient and determine the next digit by trial and error.
- Repeat the steps to find each digit of the square root.
-
Approximation Method
- Identify perfect squares close to the given number.
- Estimate the square root based on proximity to these perfect squares.
- The closest perfect squares are 62500 (2502) and 63001.
- The square root is approximately 250 since 62500 is a perfect square.
For example, to estimate the square root of 62500:
Each of these methods provides a different way to approach the problem, allowing for flexibility depending on the context and tools available.
The Babylonian Method
The Babylonian method, also known as Heron's method, is an ancient algorithm for finding the square root of a number. This method is based on the principle of averaging and can be understood through the following steps:
- Choose an initial guess, \( x_0 \), for the square root of the number \( S \).
- Calculate a new estimate, \( x_1 \), using the formula: \[ x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_0 + \frac{S}{x_0} \right) \]
- Repeat the process with \( x_1 \) as the new guess: \[ x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{S}{x_n} \right) \]
- Continue iterating until the difference between successive estimates is less than a small predefined value, \( \epsilon \), indicating convergence to the true square root.
Let's illustrate this method with an example to find the square root of 62500:
- Choose an initial guess. For simplicity, we can start with \( x_0 = 100 \).
- Calculate the first iteration: \[ x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 100 + \frac{62500}{100} \right) = \frac{1}{2} \left( 100 + 625 \right) = 362.5 \]
- Perform the second iteration using \( x_1 \): \[ x_2 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 362.5 + \frac{62500}{362.5} \right) \approx 250.69 \]
- Continue this process: \[ x_3 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 250.69 + \frac{62500}{250.69} \right) \approx 250.00 \]
- Iterate until the change is negligible, indicating that the estimate has converged to the actual square root. For this example, after a few more iterations, the estimate stabilizes around 250, which is the square root of 62500.
This iterative approach provides a highly accurate estimate of square roots and is a fundamental example of numerical methods used in computational mathematics today.
Using a Square Root Calculator
A square root calculator is a convenient tool for quickly determining the square root of a number. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use one:
-
Access a Square Root Calculator:
Navigate to a website that offers a square root calculator. Many online calculators, such as those on CalculatorSoup or OmniCalculator, provide easy-to-use interfaces.
-
Enter the Number:
Input the number for which you need to find the square root. For instance, to find the square root of 62500, you would enter "62500" in the designated field.
-
Calculate:
Press the calculate button. The calculator will process the input and display the square root. For 62500, the calculator will show the result as 250.
Square root calculators often provide additional features, such as determining whether the input number is a perfect square or showing the principal (positive) and negative square roots.
Here are some common features found in square root calculators:
- Perfect Square Identification: Indicates if the input number is a perfect square.
- Complex Solutions: Provides solutions for the square roots of negative numbers, including imaginary numbers.
- Fractional and Decimal Results: Outputs the square root in both fractional and decimal forms, if applicable.
Using a square root calculator can simplify many mathematical tasks, saving time and reducing the potential for errors in manual calculations.
Simplifying Square Roots
When dealing with square roots of large numbers like 62500, simplification can be helpful in various mathematical contexts. Here’s how you can simplify the square root of 62500:
- Identify the prime factors of 62500: \( 62500 = 5^4 \times 10^2 \).
- Express the square root in terms of its prime factors: \( \sqrt{62500} = \sqrt{5^4 \times 10^2} \).
- Split the square root: \( \sqrt{5^4 \times 10^2} = \sqrt{5^4} \times \sqrt{10^2} \).
- Calculate each square root individually: \( \sqrt{5^4} = 5^2 = 25 \) and \( \sqrt{10^2} = 10 \).
- Combine the results: \( \sqrt{62500} = 25 \times 10 = 250 \).
Therefore, the simplified square root of 62500 is \( \sqrt{62500} = 250 \).
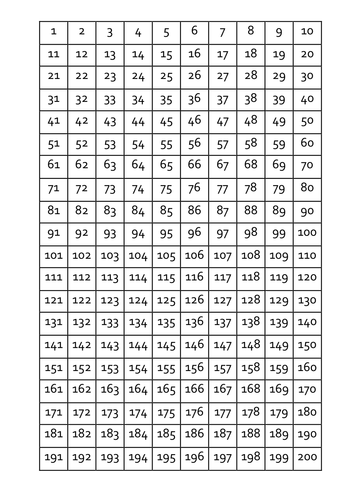
Square Root Table 1-100
| Number | Square Root |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1.414 |
| 3 | 1.732 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 2.236 |
| 6 | 2.449 |
| 7 | 2.646 |
| 8 | 2.828 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 10 | 3.162 |
| 11 | 3.317 |
| 12 | 3.464 |
| 13 | 3.606 |
| 14 | 3.742 |
| 15 | 3.873 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 17 | 4.123 |
| 18 | 4.243 |
| 19 | 4.359 |
| 20 | 4.472 |
| 21 | 4.583 |
| 22 | 4.690 |
| 23 | 4.796 |
| 24 | 4.899 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 26 | 5.099 |
| 27 | 5.196 |
| 28 | 5.291 |
| 29 | 5.385 |
| 30 | 5.477 |
| 31 | 5.568 |
| 32 | 5.657 |
| 33 | 5.745 |
| 34 | 5.831 |
| 35 | 5.916 |
| 36 | 6 |
| 37 | 6.083 |
| 38 | 6.164 |
| 39 | 6.245 |
| 40 | 6.324 |
| 41 | 6.403 |
| 42 | 6.481 |
| 43 | 6.557 |
| 44 | 6.633 |
| 45 | 6.708 |
| 46 | 6.782 |
| 47 | 6.855 |
| 48 | 6.928 |
| 49 | 7 |
| 50 | 7.071 |
| 51 | 7.141 |
| 52 | 7.211 |
| 53 | 7.280 |
| 54 | 7.348 |
| 55 | 7.416 |
| 56 | 7.483 |
| 57 | 7.550 |
| 58 | 7.616 |
| 59 | 7.681 |
| 60 | 7.746 |
| 61 | 7.810 |
| 62 | 7.874 |
| 63 | 7.937 |
| 64 | 8 |
| 65 | 8.062 |
| 66 | 8.124 |
| 67 | 8.185 |
| 68 | 8.246 |
| 69 | 8.307 |
| 70 | 8.367 |
| 71 | 8.426 |
| 72 | 8.485 |
| 73 | 8.544 |
| 74 | 8.602 |
| 75 | 8.660 |
| 76 | 8.718 |
| 77 | 8.775 |
| 78 | 8.832 |
| 79 | 8.888 |
| 80 | 8.944 |
| 81 | 9 |
| 82 | 9.055 |
| 83 | 9.110 |
| 84 | 9.165 |
| 85 | 9.220 |
| 86 | 9.273 |
| 87 | 9.327 |
| 88 | 9.380 |
| 89 | 9.434 |
| 90 | 9.487 |
| 91 | 9.539 |
| 92 | 9.591 |
| 93 | 9.643 |
| 94 | 9.695 |
| 95 | 9.746 |
| 96 | 9.798 |
| 97 | 9.848 |
| 98 | 9.899 |
| 99 | 9.950 |
| 100 | 10 |
Examples of Simplified Square Roots
Here are some examples of simplified square roots:
- √62500 = 250
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 62500 offers valuable insights into the nature of square roots and their applications in various fields. By exploring the methods to calculate square roots, such as the Babylonian method, and utilizing tools like square root calculators, we gain a deeper appreciation for mathematical concepts.
The square root of 62500 is 250, a number that signifies the ease of breaking down large numbers into their simpler components. This exploration has not only provided us with the specific value but also a comprehensive understanding of square roots in general.
To summarize:
- The square root of 62500 is .
- Square roots are fundamental in mathematics and have numerous applications in science, engineering, and everyday calculations.
- Various methods can be used to calculate square roots, including traditional algorithms like the Babylonian method and modern computational tools.
- Simplifying square roots can make complex calculations more manageable and reveal underlying patterns in numbers.
- Learning and practicing these concepts strengthens our mathematical skills and enhances our problem-solving abilities.
In conclusion, the journey through the square root of 62500 and related concepts highlights the beauty and utility of mathematics. Embracing these principles empowers us to tackle challenges with confidence and precision.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 62500
READ MORE:
Phương Pháp Tính Căn Bậc Hai Của 62500 và So Sánh Kết Quả