Topic area perimeter volume: Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on "Area, Perimeter, and Volume", unlocking the secrets of these essential measurements in diverse applications, from everyday tasks to complex projects.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between area, perimeter, and volume?
- 1. Basic Definitions and Concepts
- 2. Formulas for Calculating Area
- 3. Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- 4. Volume Calculation Methods
- 5. Application of Formulas in Different Shapes
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter, Area, and Volume Explained | Math with Mr. J
- 6. Practical Examples and Problem Solving
- 7. Advanced Concepts in Area, Perimeter, and Volume
- 8. Tools and Resources for Learning
- 9. Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- 10. Real-world Applications of Area, Perimeter, and Volume
What is the relationship between area, perimeter, and volume?
The relationship between area, perimeter, and volume depends on the geometric shape being considered. Here is a breakdown:
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a two-dimensional shape refers to the length of its boundary or the sum of the lengths of all its sides. It is a measure of the distance around the shape. Perimeter is typically measured in units such as meters, centimeters, or feet.
- Area: The area of a two-dimensional shape is the measure of the space enclosed by the shape. It quantifies the amount of surface covered by the shape. Area is measured in square units, such as square meters or square feet.
- Volume: The volume of a three-dimensional shape refers to the amount of space enclosed by the shape. It is a measure of how much three-dimensional space the shape occupies. Volume is measured in cubic units, such as cubic meters or cubic feet.
The relationship between these three measurements can vary depending on the specific shape. Here are a few examples:
- In a rectangle:
- The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides: P = 2l + 2w, where l and w are the length and width of the rectangle.
- The area is calculated by multiplying the length and width: A = lw.
- In a circle:
- The perimeter is known as the circumference: C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
- The area is calculated using: A = πr^2.
- In a cube:
- The perimeter and area are not applicable to a cube, as it is a three-dimensional shape.
- The volume is calculated by raising the length of one side to the power of three: V = s^3, where s is the length of a side of the cube.
These are just a few examples, and the relationship between area, perimeter, and volume can vary depending on the specific shape.
READ MORE:
1. Basic Definitions and Concepts
Understanding the fundamental concepts of area, perimeter, and volume is crucial in various fields, including geometry, construction, and day-to-day measurements. Here\"s a detailed exploration of these concepts:
- Perimeter: It\"s the total distance around a two-dimensional shape. For polygons, it\"s the sum of the lengths of all sides. For instance, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated as twice the sum of its length and width (P = 2(l + b)).
- Area: This represents the space occupied within the boundary of a two-dimensional figure. The formula for area varies based on the shape. For example, the area of a rectangle is the product of its length and width (A = l × w), while the area of a triangle is half the product of its base and height (A = ½ × b × h).
- Volume: Volume measures the space a three-dimensional object occupies. It\"s calculated differently based on the shape of the object. For example, the volume of a rectangular solid is found by multiplying the area of the base by the height (V = B × h).
Each of these measurements has practical applications, such as in construction, where knowing the area is essential for flooring projects, or in packaging, where volume measurements determine how much space an object will occupy.
It\"s also important to understand the relationships and differences between these measurements. For instance, while perimeter and area both deal with two-dimensional figures, volume is concerned with three-dimensional space. Perimeter is a linear measure, whereas area and volume are measures of space covered.

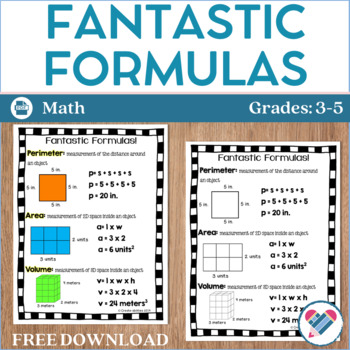
2. Formulas for Calculating Area
Area calculation is essential in various fields like geometry, architecture, and land surveying. It\"s the measure of space within a shape\"s boundaries. Here, we present formulas for calculating the area of common geometric shapes:
- Square: For a square, the area is calculated as the side length squared (A = side²).
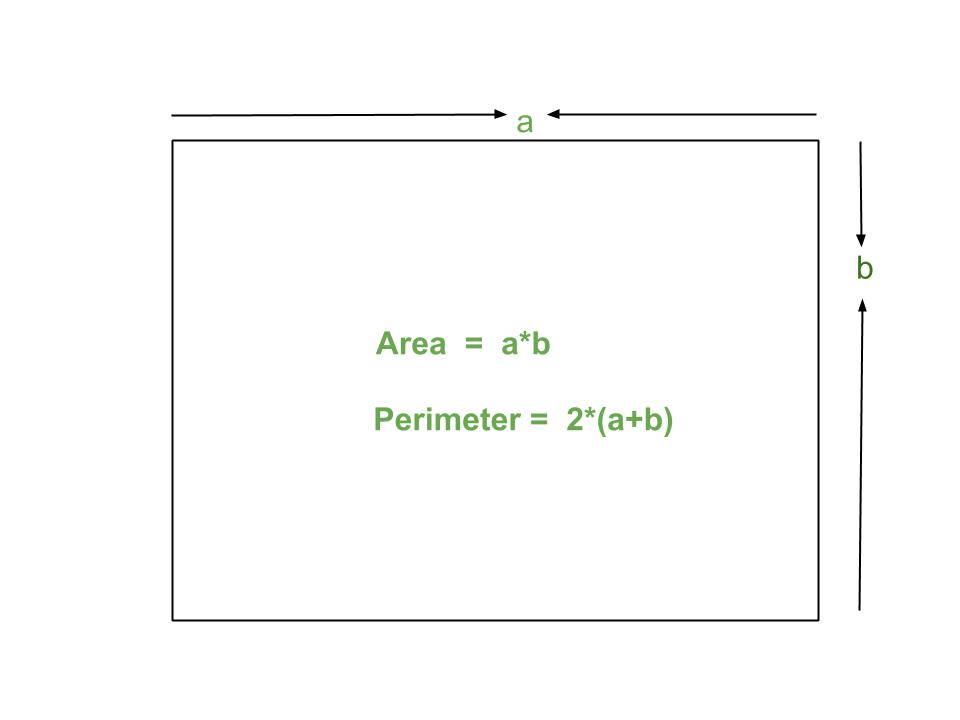
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length and width (A = length × width).
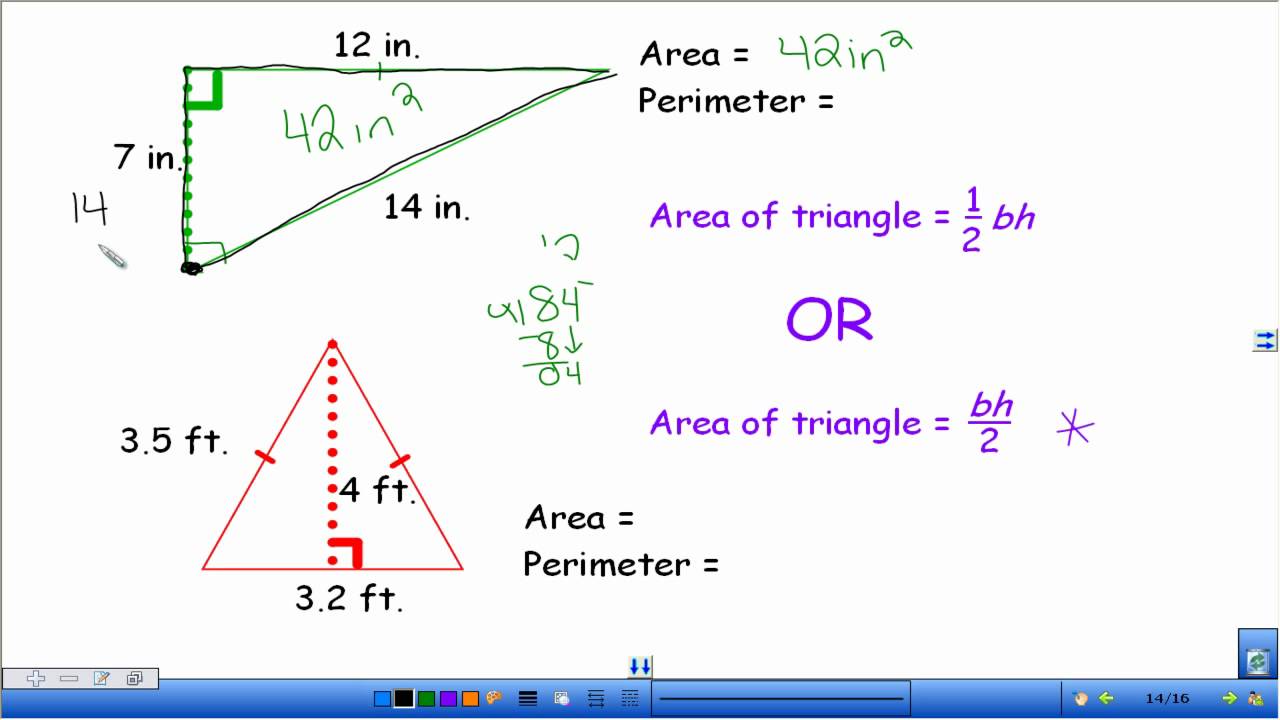
- Triangle: To find a triangle\"s area, multiply its base by its height and then divide by 2 (A = ½ × base × height).
- Parallelogram: The area of a parallelogram is calculated as the product of its base and height (A = base × height).
- Trapezoid: For a trapezoid, the area is half the sum of the two parallel sides multiplied by the height (A = ½ × (base1 + base2) × height).
- Circle: The area of a circle is calculated using the radius and π (pi), with the formula A = π × radius².
Understanding these formulas is crucial for accurate measurement and application in various practical scenarios. Remember, the units of measurement for area are always in square units, like square meters or square feet, depending on the length units used.

3. Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Calculating the perimeter involves summing the lengths of all sides of a shape. It’s a linear measure, representing the total distance around a two-dimensional figure. Here, we outline techniques to calculate the perimeter for common shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side (P = 4 × side).
- Rectangle: To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides, or use the formula P = 2 × (length + width).
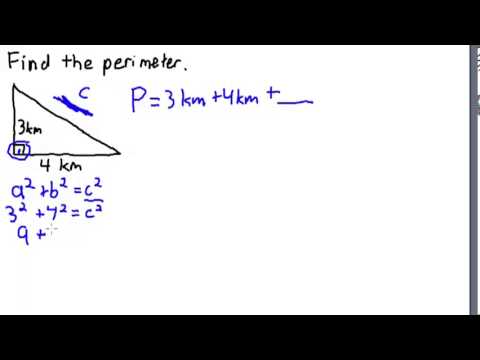
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides (P = side1 + side2 + side3).
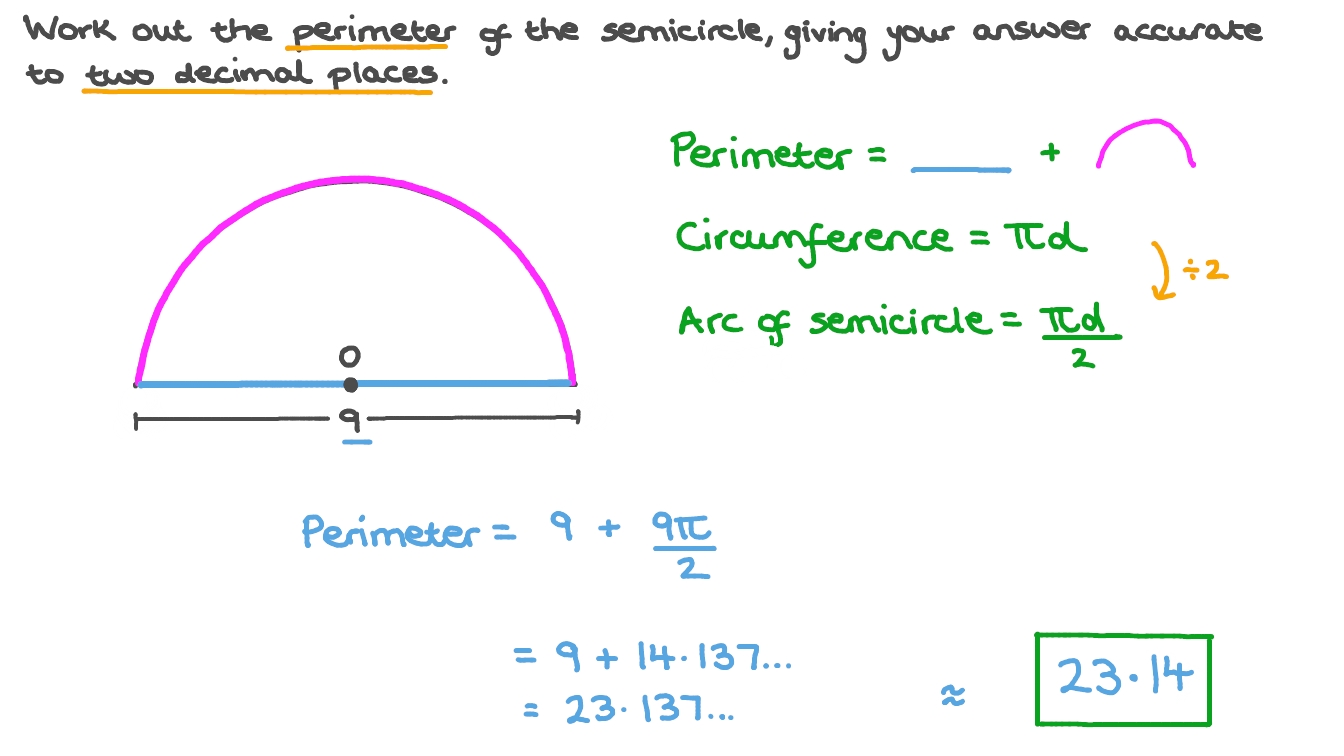
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius and π (pi), with the formula C = 2 × π × radius.
- Parallelogram: The perimeter of a parallelogram is twice the sum of its base and side lengths (P = 2 × (base + side)).
Understanding these perimeter calculation techniques is essential for various practical applications, such as determining the amount of materials needed for borders or fences around properties or gardens.

4. Volume Calculation Methods
Calculating the volume of a three-dimensional object involves determining the amount of space it occupies. Here, we provide methods for calculating the volume of various common shapes:
- Rectangular Solid (or Cube): For a rectangular solid, the volume is calculated as the product of its length, width, and height (V = length × width × height). In the case of a cube, since all sides are equal, it\"s the cube of the side length (V = side³).
- Cylinder: The volume of a cylinder is calculated using the area of its circular base and its height. The formula is V = π × radius² × height.
- Cone: To find the volume of a cone, use one-third of the product of the base\"s area (which is a circle) and the height (V = ⅓ × π × radius² × height).
- Sphere: The volume of a sphere is calculated by four-thirds times pi times the cube of the radius (V = ⁴⁄₃ × π × radius³).
- Pyramid: For a pyramid, the volume is one-third the product of the area of the base and the height (V = ⅓ × base area × height).
These formulas are essential in various fields, from engineering to everyday life, where understanding the volume of objects can be critical.

_HOOK_
5. Application of Formulas in Different Shapes
Applying area, perimeter, and volume formulas to different shapes is crucial in fields like geometry, construction, and design. Let’s explore how these formulas are used for various shapes:
- Squares and Rectangles: In real-world applications, calculating the area of squares and rectangles can help in determining the amount of material needed for flooring or carpeting a room. Perimeter calculations are useful in finding the amount of material needed for borders or fencing.
- Circles: Circumference and area calculations for circles are essential in designing anything from architectural elements to everyday items like plates and containers.
- Triangles: Understanding the area of triangles is vital in fields like architecture, especially in roof construction and other structural designs.
- 3D Shapes (Cylinders, Cones, Spheres, etc.): Volume calculations are fundamental in determining the capacity of containers, like water tanks and silos. In architecture and design, understanding the volume of various shapes helps in creating efficient and usable spaces.
- Composite Shapes: In more complex scenarios, like landscaping or advanced architectural design, understanding how to calculate area and perimeter for composite shapes becomes essential for accurate planning and resource allocation.
These applications highlight the importance of accurately applying geometric formulas to different shapes in practical scenarios.
Perimeter, Area, and Volume Explained | Math with Mr. J
Math: Unlock the mysteries of math and discover the beauty behind numbers! Dive into this fascinating video that uncovers the magic of math and how it shapes our everyday lives. Prepare to be amazed and entertained as you embark on an extraordinary journey of logic and problem-solving!
6. Practical Examples and Problem Solving
Understanding area, perimeter, and volume is not just a mathematical exercise; these concepts have practical applications in everyday life and various professional fields. Here are some examples and problem-solving scenarios where these concepts are crucial:
- Home Renovation: When renovating or decorating a home, calculating the area of rooms is necessary to purchase the right amount of paint or flooring. Similarly, understanding the volume of a space can help in heating and cooling considerations.
- Gardening: For a garden layout, the perimeter of garden beds is calculated to determine the amount of fencing required. The area measurement is crucial for knowing how much soil or mulch to buy.
- Construction Projects: In construction, area and volume calculations are essential for estimating materials like concrete, gravel, or tiles. Understanding the volume of a space is also critical for ensuring that buildings meet specific size regulations.
- Packaging and Manufacturing: In packaging, the volume of a box or container must be calculated to determine how much it can hold. Similarly, manufacturers often need to calculate the area and volume of materials for product design and quality control.
- Education and Problem-Solving: In educational settings, understanding these concepts is vital for problem-solving in geometry, physics, and engineering projects. For instance, calculating the area of a circle is fundamental in designing anything circular, like wheels or plates.
These practical examples show how area, perimeter, and volume are not just theoretical concepts but are integral to solving real-world problems.
Perimeter and Area: The Basics | Geometry | Khan Academy
Geometry: Step into the mesmerizing world of geometry and explore the wonders it beholds! This captivating video will transport you to a realm of shapes, angles, and patterns that will stretch your imagination. Join us on a visual adventure as we unravel the secrets of geometry and its significance in art, architecture, and nature. Get ready to see the world from a whole new perspective!
7. Advanced Concepts in Area, Perimeter, and Volume
Delving into advanced concepts in area, perimeter, and volume unveils a more intricate understanding of geometry and its applications. These concepts are vital in higher-level mathematics, physics, and engineering. Some of the advanced topics include:
- Integral Calculus: Integral calculus is used to calculate the area under a curve, providing a more dynamic way to assess areas in irregular shapes.
- Surface Area of Complex Shapes: Understanding surface areas of complex three-dimensional shapes like spheres, cones, and cylinders, which are fundamental in fields like architecture and engineering.
- Geometric Transformations: Exploring how area and perimeter change under various transformations such as rotation, reflection, and scaling.
- Applications in Physics: Utilizing concepts of volume and area in physics to calculate properties like density, pressure, and force.
- Higher-Dimensional Geometry: Extending the concepts of area and volume to higher dimensions, which is a key aspect in advanced mathematics and theoretical physics.
- Optimization Problems: Using calculus and algebra to solve optimization problems involving area and volume in various real-world scenarios.
- Non-Euclidean Geometry: Studying areas and perimeters in non-Euclidean spaces, which has implications in advanced geometry and cosmology.
These advanced concepts open new vistas in understanding the geometry of our world and beyond, stretching from practical engineering applications to theoretical explorations in the cosmos.
8. Tools and Resources for Learning
There are numerous tools and resources available for learning and understanding the concepts of area, perimeter, and volume. These resources cater to different learning styles and needs, providing a variety of methods to study these geometric concepts:
- Educational Websites: Websites like Khan Academy offer in-depth lessons and practice problems on geometry, including area, perimeter, and volume. They provide interactive lessons and quizzes to test knowledge and understanding.
- Online Calculators: There are many online calculators and tools, such as Omni Calculator, that can help students and professionals calculate area, perimeter, and volume quickly and accurately.
- YouTube Tutorials: Educational channels like Math with Mr. J offer comprehensive video tutorials explaining these concepts in an engaging and easy-to-understand manner.
- Textbooks and eBooks: Many educational textbooks and eBooks cover the fundamentals of geometry, offering detailed explanations, examples, and exercises.
- Interactive Games and Apps: Interactive games and mobile applications provide a fun way to learn and practice these concepts, making them ideal for younger students.
- Worksheets and Practice Problems: Printable worksheets and practice problems available on educational websites like SmartClass4Kids are great for hands-on practice and reinforcement of learned concepts.
- Academic Forums: Online forums and communities, such as those on Khan Academy, allow learners to discuss problems, share insights, and seek help from peers and educators.
These resources are invaluable for students, educators, and professionals alike, providing varied approaches to mastering area, perimeter, and volume.

9. Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
When learning about area, perimeter, and volume, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes and misconceptions that can arise. Understanding these can help avoid errors in calculations and deepen comprehension:
- Confusing Perimeter and Area: One common mistake is confusing the concepts of perimeter and area. Perimeter refers to the distance around a shape, while area measures the space within a shape.
- Mixing Units: Mixing units during calculations (e.g., using meters for length and centimeters for width) can lead to incorrect results. It\"s crucial to use consistent units throughout a calculation.
- Volume Calculation Errors: When calculating volume, a common error is to neglect the three-dimensional nature of objects, leading to incorrect volume measurements.
- Area of Irregular Shapes: Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be challenging, and a frequent mistake is to oversimplify these shapes, resulting in inaccurate area calculations.
- Application in Real-Life Scenarios: Misunderstanding the practical application of these concepts, such as not recognizing how to apply them in real-world scenarios like construction or design, is another common issue.
- Formula Misapplication: Using the wrong formulas or misapplying the correct formulas can lead to errors, especially in complex shapes and composite figures.
Being aware of these common mistakes and misconceptions can significantly enhance the learning process in geometry, particularly in the areas of area, perimeter, and volume.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
10. Real-world Applications of Area, Perimeter, and Volume
Area, perimeter, and volume are fundamental concepts in geometry with a wide range of real-world applications. Their practical usage spans various fields, emphasizing their importance beyond academic contexts:
- Architecture and Construction: In these fields, understanding the area and volume is crucial for designing buildings and structures, ensuring efficient use of space, and calculating materials needed for construction.
- Land Surveying and Urban Planning: Calculating the area and perimeter of land parcels is essential in land surveying, urban planning, and landscape design for effective land use and planning.
- Manufacturing and Engineering: In manufacturing, area and volume calculations are vital for material estimation, designing parts, and optimizing the use of materials to reduce waste.
- Education: These concepts are fundamental in teaching mathematics and physics, helping students understand spatial relationships and problem-solving.
- Environmental Science: Calculating the volume of bodies of water or the area of forest cover is crucial in environmental studies and conservation efforts.
- Interior Design: Area and volume calculations assist in effective space management, furniture arrangement, and interior decoration.
- Geography and Meteorology: Understanding these concepts is important for geographic information systems (GIS) and predicting weather patterns.
These examples showcase the extensive utility of area, perimeter, and volume calculations in various practical and professional realms.
In conclusion, mastering the concepts of area, perimeter, and volume opens doors to a world of practical applications and problem-solving in everyday life, architecture, engineering, and beyond. Embracing these fundamental geometrical principles enhances our understanding and interaction with the space around us.