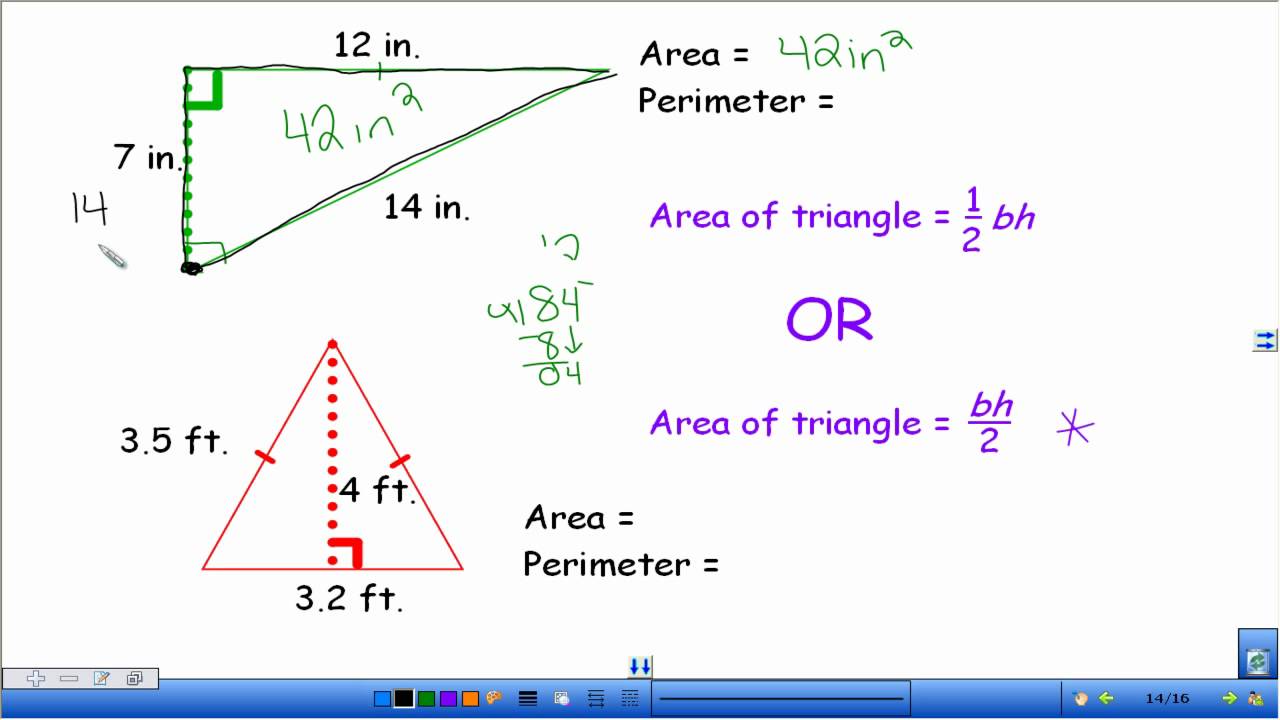
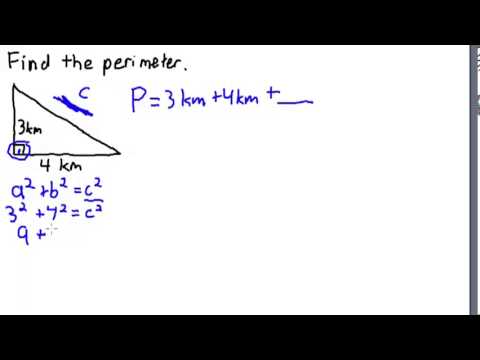
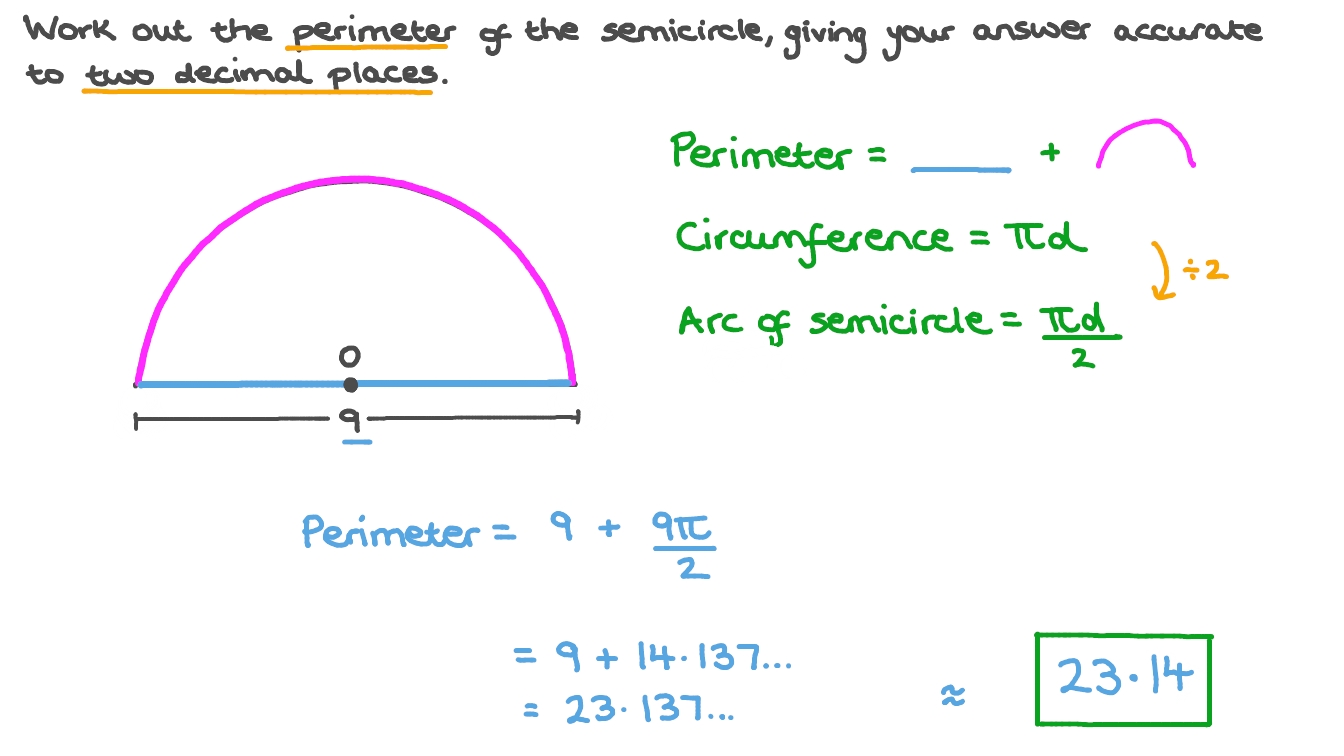
Topic area and perimeter word problems 4th grade: Dive into the fascinating world of "Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade," where young learners explore and master essential mathematical concepts through engaging and practical problems, laying a strong foundation for future math success.
Table of Content
- Are there any interactive activities or games available to practice area and perimeter word problems for 4th grade students?
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter Concepts
- Types of Shapes: Rectangles, Squares, and More
- Understanding Perimeter: The Basics
- Exploring Area: Calculation Methods
- Step-by-Step Word Problem Solving Strategies
- Practice Problems: Rectangular Shapes
- YOUTUBE: Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade Common Core
- Real-World Applications of Area and Perimeter
- Interactive Learning: Online Exercises and Worksheets
- Challenges and Advanced Problems
- Using Formulas in Word Problems
- Visual Learning Aids and Examples
- Review and Recap: Key Concepts
Are there any interactive activities or games available to practice area and perimeter word problems for 4th grade students?
Yes, there are several interactive activities and games available to practice area and perimeter word problems for 4th grade students. Some of these resources include:
- Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers a variety of interactive tutorials and practice exercises for 4th grade students to learn about area and perimeter.
- Math Playground: Math Playground provides interactive games and activities that allow students to practice solving area and perimeter word problems through fun and engaging gameplay.
- SplashLearn: SplashLearn offers educational math games specifically designed for 4th graders. They have interactive activities that help reinforce understanding of area and perimeter word problems.
These resources provide an interactive and engaging way for 4th grade students to practice and reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter word problems.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter Concepts
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, especially relevant for 4th-grade students. The area is the space contained within a shape, typically measured in square units like square inches or square meters. The perimeter is the total distance around the edges of a shape. Understanding these concepts is crucial for solving real-world problems and for further mathematical learning.
- Basic Definitions:
- Area: The amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape.
- Perimeter: The total distance around a shape.
- Formulas:
- For rectangles and squares, area is calculated as Length × Width.
- The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding all its sides (2 × Length + 2 × Width), while for a square, it is 4 times the length of one side.
- Real-World Applications:
- Calculating the area and perimeter has practical applications in daily life, such as determining the amount of material needed for a project or the distance around a garden.
- Problem-Solving Strategies:
- Understanding the shape and dimensions given in the problem.
- Applying the correct formulas and calculating systematically.
These concepts not only aid in solving mathematical problems but also enhance spatial understanding and reasoning skills, which are valuable in many aspects of life and further education in geometry and beyond.

Types of Shapes: Rectangles, Squares, and More
Fourth-grade math introduces various geometrical shapes, each with unique area and perimeter calculations. Understanding these shapes is essential for solving word problems effectively.
- Rectangles and Squares:
- Rectangles have opposite sides equal and four right angles.
- Squares are special rectangles with all sides equal.
- Area is calculated as Length × Width.
- Perimeter of a rectangle: 2 × (Length + Width); for a square, it is 4 × Side.
- Quadrilaterals:
- Includes shapes like parallelograms, rhombus, and trapezium.
- Each has four sides, but with different properties and formulas for area and perimeter.
- Circles:
- Unlike straight-edged shapes, circles have a continuous curve.
- Area is calculated using πr² (where r is the radius).
- Circumference (circle\"s perimeter) formula is 2πr.
- Polygons:
- Include shapes with more than four sides.
- Regular polygons have equal sides and angles, whereas irregular polygons do not.
- Perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
Through engaging activities and practical examples, students in 4th grade can explore these various shapes, understanding their properties and how they relate to real-life scenarios. Area and perimeter word problems often use these shapes, challenging students to apply formulas and critical thinking skills.

Understanding Perimeter: The Basics
Perimeter is a key concept in geometry, especially relevant for 4th-grade students. It represents the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. Learning to calculate perimeter equips students with a fundamental skill used in everyday problem solving and advanced mathematical concepts.
- Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares:
- The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding together the lengths of all its sides. The formula is 2 times the sum of its length and width (2 × (Length + Width)).
- For squares, all sides are equal, so the perimeter is 4 times the length of one side (4 × Side).
- Perimeter of Other Shapes:
- For other polygons, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides.
- In the case of a circle, the term used is \"circumference,\" which is the distance around the circle, calculated as 2π times the radius (2πr).
- Practical Applications:
- Understanding perimeter is essential in real-life scenarios such as determining the amount of fencing required to enclose a garden or calculating the border length of a craft project.
- Strategies for Learning:
- Students can practice by measuring and calculating the perimeter of various objects in their environment.
- Word problems enhance comprehension by applying perimeter concepts to everyday situations.
Mastering the concept of perimeter lays the groundwork for more advanced studies in geometry and helps students develop a practical skill set for solving a wide range of mathematical problems.

Exploring Area: Calculation Methods
Understanding the concept of area is vital for 4th-grade students as it plays a crucial role in geometry and everyday problem solving. The area is defined as the space within the boundaries of a flat object or figure, and is usually measured in square units.
- Area of Rectangles and Squares:
- For rectangles, the area is calculated by multiplying the length by the width (Area = Length × Width).
- In squares, where all sides are equal, the area is the side length squared (Area = Side²).
- Area of Triangles:
- The area of a triangle is found by using the formula: Area = ½ × base × height.
- Area of Circles:
- The area of a circle is determined by the formula: Area = π × radius².
- Complex Shapes:
- For more complex shapes, such as parallelograms or trapezoids, specific formulas are used that take into account their unique properties.
- Real-World Applications:
- Calculating area is not just a theoretical exercise; it has practical applications like determining the amount of paint needed for a wall or the amount of carpet for flooring.
- Problem-Solving Techniques:
- Using diagrams and labeling dimensions clearly can be helpful in visualizing and solving area problems.
- Practicing with real-life word problems enhances understanding and application of area calculation methods.
Grasping these area calculation methods allows students to tackle a variety of geometrical problems and apply these skills in practical scenarios, laying a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.

_HOOK_
Step-by-Step Word Problem Solving Strategies
Solving area and perimeter word problems in 4th-grade math involves a structured approach. These problems help students apply mathematical concepts to real-world situations, enhancing their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Understand the Problem:
- Read the problem carefully and identify what is being asked.
- Determine if the problem is about area, perimeter, or both.
- Identify the Shape:
- Recognize the shape involved in the problem (e.g., rectangle, square, circle).
- Understand the properties of the shape as they relate to area and perimeter.
- Gather Information:
- Identify and write down the given measurements (e.g., length, width, radius).
- Mark unknown values that need to be found.
- Choose the Correct Formula:
- Select the appropriate formula based on the shape and what you need to find (area or perimeter).
- Perform Calculations:
- Substitute the known values into the formula.
- Calculate carefully, following mathematical operations.
- Check Your Work:
- Review the calculations and ensure they make sense in the context of the problem.
- Double-check that the units of measurement are consistent and correct.
- Write the Answer:
- Provide the solution with the appropriate units (e.g., square meters for area).
- Ensure the answer addresses the question asked in the problem.
Through these steps, students can systematically approach and solve area and perimeter word problems, building confidence and competence in applying mathematical concepts to various scenarios.

Practice Problems: Rectangular Shapes
Practicing with rectangular shapes is a great way for 4th-grade students to enhance their understanding of area and perimeter. These problems often involve calculating the dimensions of rectangles and require students to apply their knowledge of the formulas for area and perimeter.
- Basic Problems:
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with given length and width.
- Find the area of a square when the length of one side is known.
- Intermediate Challenges:
- Determine the length of a rectangle when its area and width are given.
- Calculate the area of a rectangle when its perimeter and the length of one side are known.
- Advanced Scenarios:
- Solve word problems involving real-life scenarios, such as fencing a garden or covering a floor with tiles, where dimensions need to be calculated for rectangles.
- Work on problems that involve finding missing measurements using the area and perimeter formulas.
- Applying Concepts:
- Use visual aids and diagrams to better understand and solve problems.
- Engage in activities that require measuring actual objects and spaces to find area and perimeter.
These practice problems are designed to enhance problem-solving skills, improve understanding of geometric concepts, and apply mathematical knowledge to practical situations. Working through a variety of problems helps solidify students\" grasp on the concepts of area and perimeter in rectangular shapes.
Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade Common Core
\"Are you struggling with solving word problems? Look no further! This video is here to help you master word problems and boost your math skills. Watch it now and become a word problem-solving pro!\"
4th Grade Math: Area and Perimeter Word Problems
\"Want to sharpen your math skills and ace those tough equations? Look no further than this amazing math video. With step-by-step explanations and helpful tips, you\'ll become a math master in no time. Don\'t miss out!\"
Real-World Applications of Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for solving real-world problems. In this section, we explore how these mathematical concepts are applied in everyday life, enhancing the learning experience for 4th-grade students.
- Home Design: When planning room layouts or buying new carpets, calculating the area of a room helps in selecting the right amount of materials.
- Gardening: Understanding area helps in planning a garden space, determining how many plants can fit in a specified area.
- Sports: Knowing the perimeter is useful in sports, for example, determining the length of a race track or the border of a soccer field.
- Art Projects: Calculating area and perimeter can be used in designing art projects or creating murals, ensuring the right size and fit.
Let\"s delve into some specific examples:
- Room Decoration: Suppose you want to paint one wall in your room. To know how much paint to buy, calculate the area of the wall by multiplying its height and width.
- Building a Fence: If you need to build a fence around your backyard, calculate the perimeter to determine how much fencing material is required.
- Creating a Vegetable Patch: Planning to start a vegetable garden? Calculate the area to decide how many vegetable plants you can grow.
These practical applications not only make learning more enjoyable but also show the relevance of area and perimeter in everyday life. Through these examples, students can see the importance of mathematics in their daily activities.
| Activity | Concept Used | Real-World Application |
| Room Layout | Area | Calculating floor space for furniture arrangement |
| Garden Planning | Area | Determining the number of plants per square foot |
| Sport Field Setup | Perimeter | Marking the boundaries of a game area |
By applying these concepts to familiar and fun activities, students can better understand and appreciate the importance of area and perimeter in their world.

Interactive Learning: Online Exercises and Worksheets
Engaging with interactive learning tools enhances the understanding of area and perimeter for 4th-grade students. Below, we present a variety of online resources and worksheets that make learning these concepts both fun and effective.
- Interactive Word Problems: Students can practice solving word problems related to area and perimeter. These problems often involve real-life scenarios, making the learning process more relatable and interesting.
- Online Quizzes: Quizzes with instant feedback help students assess their understanding and mastery of the topic.
- Worksheet Downloads: Printable worksheets are available for offline practice, allowing students to work through problems at their own pace.
- Animated Lessons: Animated lessons and tutorials provide visual and engaging explanations of concepts, aiding in better comprehension.
These resources cover various aspects of area and perimeter, including:
- Calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles and other shapes.
- Understanding the application of formulas in real-world scenarios.
- Challenging exercises to enhance problem-solving skills.
Additionally, some platforms offer:
- Guided lesson explanations.
- Practice worksheets with real-world tasks.
- Math skill quizzes to test understanding and application.
- Interactive exercises for engaging practice sessions.
These interactive and diverse learning tools ensure a comprehensive understanding of area and perimeter, setting a strong foundation for future mathematical learning.

Challenges and Advanced Problems
For students ready to tackle more challenging problems, this section provides advanced word problems that test their understanding of area and perimeter in more complex scenarios.
- Complex Shapes: Problems involving the calculation of area and perimeter for irregular shapes, such as complex polygons and composite figures.
- Real-World Scenarios: Advanced problems that simulate real-life situations, like planning a garden layout or designing a park, requiring the application of area and perimeter concepts.
- Problem-Solving Strategies: Encourage the use of multiple approaches to solve problems, such as breaking down complex shapes into simpler ones.
- Math Puzzles: Introduce mathematical puzzles that require a deep understanding of area and perimeter to solve.
Example Challenges:
- Determining the cost of materials needed for a construction project, given the dimensions of various components.
- Finding the length of fencing required to enclose a garden with a given area.
- Calculating the amount of paint needed to cover a specific design on a wall, taking into account different shapes and sizes.
These advanced problems help students deepen their understanding of the concepts of area and perimeter, and how they apply in various contexts beyond the classroom.

_HOOK_
Using Formulas in Word Problems
Mastering the use of formulas in word problems is a key skill for 4th graders. This section will guide students through applying area and perimeter formulas in various scenarios, helping them to enhance their problem-solving abilities.
- Rectangle and Square Formulas: Introducing the basic formulas for calculating the area (length × width) and perimeter (2 × (length + width)) of rectangles and squares.
- Problem-Solving Techniques: Teaching students how to identify which formula to use in different word problems and how to apply these formulas correctly.
- Real-World Applications: Using word problems that relate to real-life scenarios, such as calculating the amount of fencing needed for a garden or the amount of paint required for a wall.
- Exploring Complex Shapes: Encouraging students to tackle more advanced problems involving irregular shapes and composite figures, using the knowledge of basic shapes.
Example Exercises:
- Calculating the area and perimeter of a garden plot given in a word problem.
- Using the perimeter to find the missing side of a rectangle when other dimensions are known.
- Breaking down complex figures into basic shapes to calculate the total area or perimeter.
Through these exercises, students will become proficient in applying area and perimeter formulas in various contexts, preparing them for more advanced mathematical concepts.
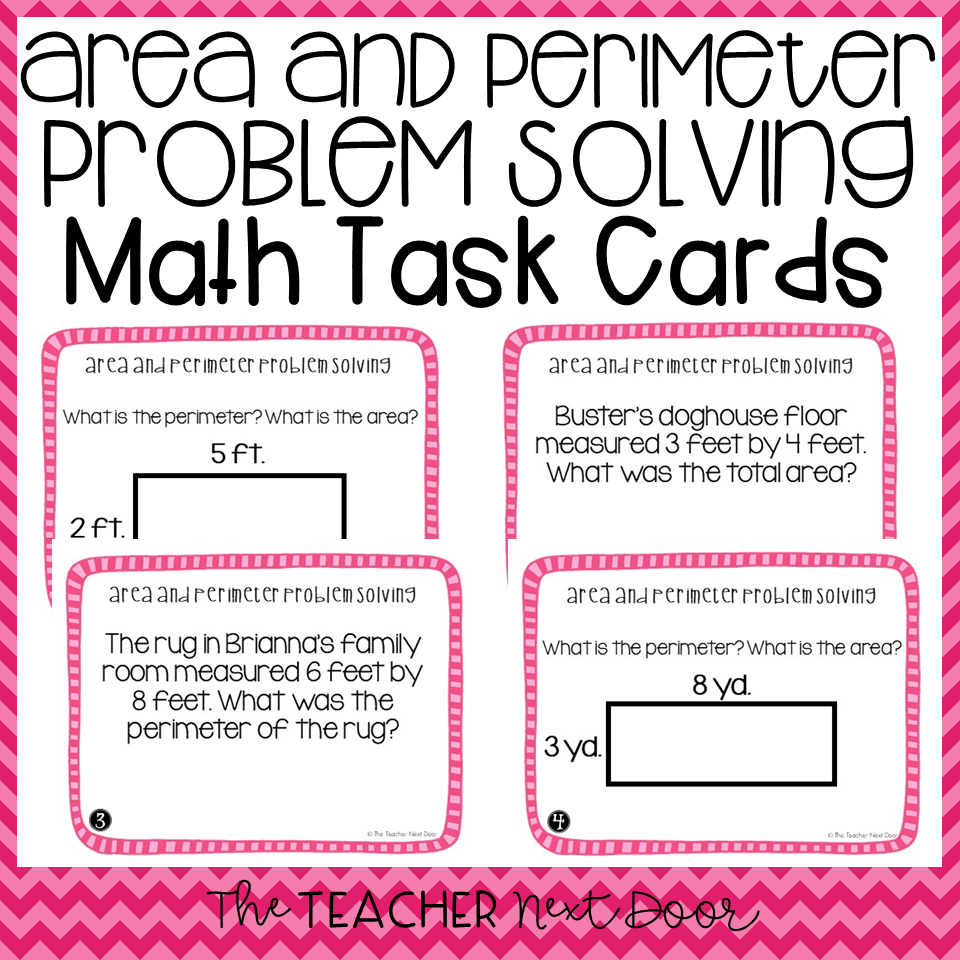
Visual Learning Aids and Examples
Visual aids are crucial in helping 4th-grade students understand the concepts of area and perimeter. This section provides a variety of visual learning tools and examples to enhance the students\" understanding of these mathematical concepts.
- Illustrated Word Problems: Using drawings and diagrams in word problems to visually represent the problem scenario. This helps in better understanding and solving the problems.
- Interactive Tools: Utilizing online interactive tools where students can manipulate shapes to understand how changes in dimensions affect area and perimeter.
- Graph Paper Exercises: Encouraging students to use graph paper for drawing shapes and calculating their area and perimeter. This provides a hands-on approach to learning.
- Real-World Object Measurement: Using everyday objects and spaces to measure and calculate area and perimeter, thereby connecting mathematical concepts to the real world.
Example Visual Aids:
- Diagrams of common shapes like rectangles and circles, with labeled sides and formulas for area and perimeter.
- Interactive simulations where students can change the dimensions of a shape and see the effect on its area and perimeter in real-time.
- Worksheets with grid-lined background, allowing students to draw shapes and calculate area and perimeter visually.
These visual learning aids not only make the concepts of area and perimeter more accessible but also more engaging for 4th-grade students.
READ MORE:
Review and Recap: Key Concepts
This section provides a summary of the essential concepts of area and perimeter that 4th-grade students have learned. It serves as a quick refresher to solidify their understanding and recall of these fundamental mathematical concepts.
- Area and Perimeter Basics: A review of the basic formulas - the area of a rectangle (length × width) and the perimeter of a rectangle (2 × (length + width)).
- Problem-Solving Techniques: Recalling strategies for solving word problems, including reading the problem carefully, identifying what is being asked, and deciding which formula to apply.
- Real-World Applications: Reminding students of how area and perimeter are used in everyday life, such as in building, gardening, or arranging furniture.
- Different Shapes: A recap on calculating area and perimeter for various shapes beyond rectangles, like squares, triangles, and circles.
Example Recap Exercises:
- Reviewing how to find the area of a rectangular park and the perimeter of its fence.
- Practicing with word problems that involve finding the length or width of a rectangle when given its area or perimeter.
- Exploring problems where students have to decompose complex shapes into simpler ones to calculate the total area or perimeter.
By revisiting these key concepts, students can strengthen their understanding and prepare for more advanced topics in mathematics.
Embark on a mathematical adventure with \"Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade,\" where learning meets fun, and every problem becomes a stepping stone to master these essential concepts. Join us in this journey to shape young minds!