Topic semi circle perimeter formula: Unlock the secrets of geometry with our comprehensive guide to the semi circle perimeter formula, a key concept for students and enthusiasts alike, simplifying complex mathematics into accessible, practical knowledge.
Table of Content
- What is the formula for finding the perimeter of a semicircle?
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Basic Formula for Semicircle Perimeter
- Variations of the Formula Based on Given Parameters
- Derivation of the Semicircle Perimeter Formula
- Practical Examples and Problem Solving
- YOUTUBE: How To Calculate The Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Comparison: Perimeter of a Semicircle vs. Full Circle
- Applications of the Semicircle Perimeter in Real Life
- Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
- Further Resources and Learning Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions About Semicircle Perimeter
What is the formula for finding the perimeter of a semicircle?
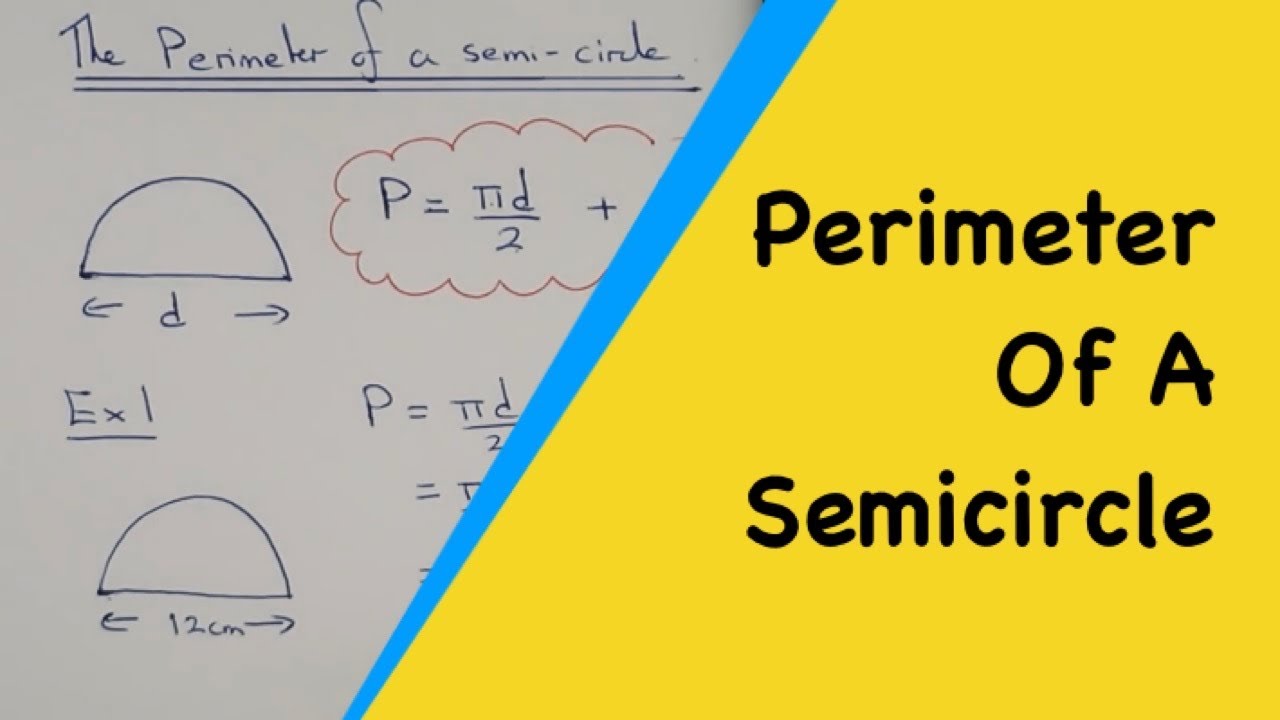
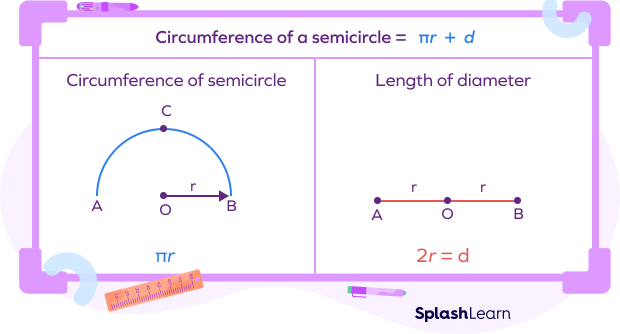
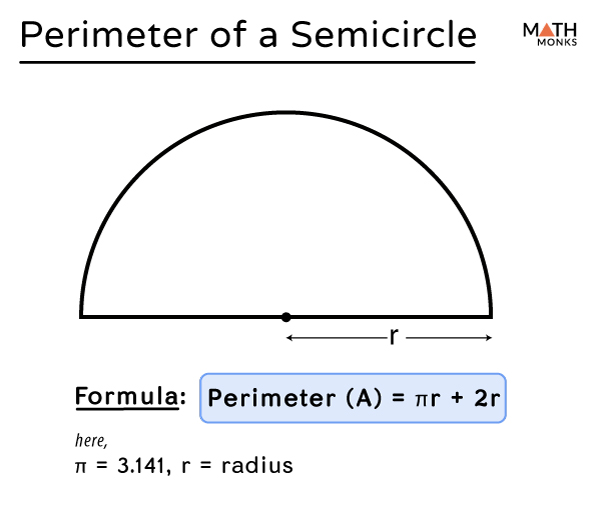
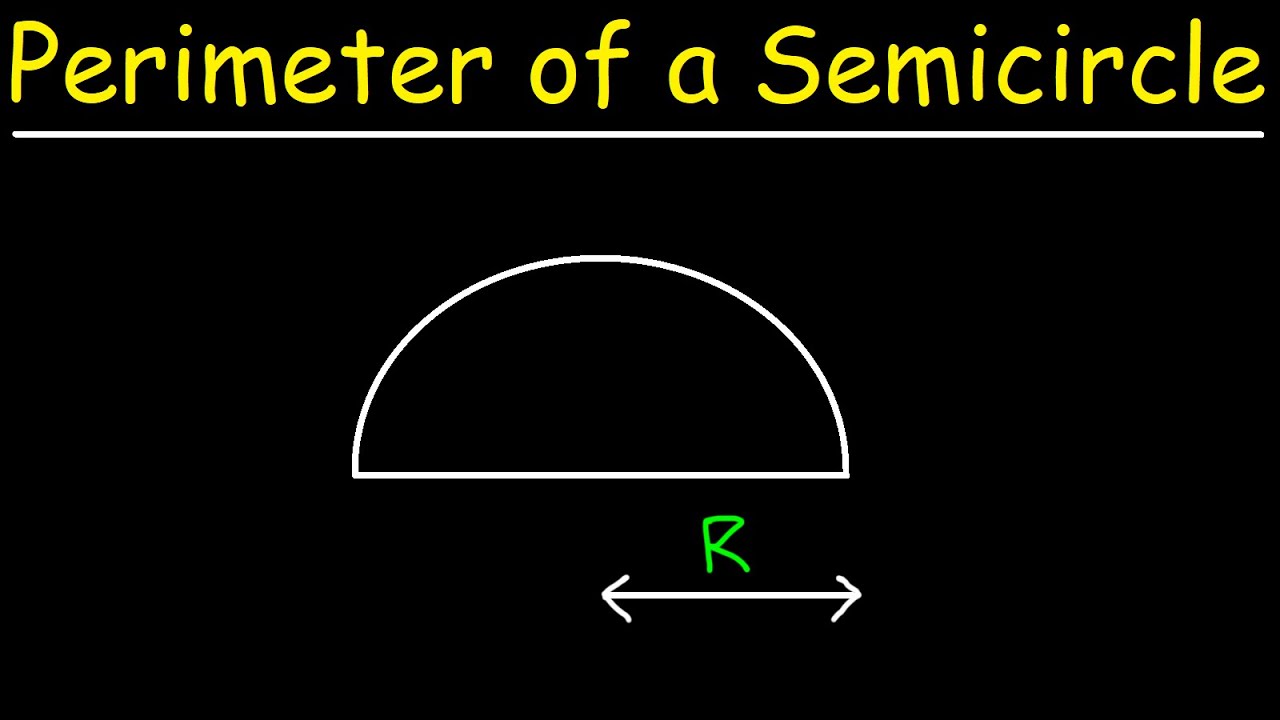
The formula for finding the perimeter of a semicircle is P = πr + 2r, where P is the perimeter and r is the radius of the semicircle.
To understand this formula better, let\'s break it down:
- P represents the perimeter of the semicircle, which is the total length of the curved boundary.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. It is used to relate the circumference of a circle to its diameter or radius.
- r is the radius of the semicircle, which is the distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on its curved boundary. The radius is half the distance of the diameter (d = 2r).
- 2r represents the straight line segment that completes the semicircle to form a full circle. It is equal to twice the value of the radius.
By summing the curved portion (πr) and the straight line segment (2r), we obtain the total perimeter of the semicircle.
An example calculation:
| Semicircle Radius (r) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 5 units | π(5) + 2(5) = 15.71 + 10 = 25.71 units |
So, for a semicircle with a radius of 5 units, the perimeter would be approximately 25.71 units.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is a fundamental geometric concept that combines the length of a semicircle\"s arc with its straight diameter. It\"s crucial in various applications ranging from architectural designs to academic problems. Let\"s break down its components and calculation.
- Basic Components: The perimeter of a semicircle consists of two parts - the curved arc (half of a circle\"s circumference) and the straight line (the diameter of the circle).
- Radius and Diameter: The radius is the distance from the center to any point on the semicircle. The diameter is twice the radius, spanning from one end of the semicircle to the other through the center.
- Perimeter Formula: The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is P = πr + 2r, where P is the perimeter, π approximates to 3.14, and r is the radius. This formula is derived by adding half the circle\"s circumference (πr) to the diameter (2r).
- Calculating with Different Parameters: Depending on the given values, the perimeter can also be calculated using the diameter directly with the formula P = π(d/2) + d.
- Applying the Formula: To calculate the perimeter, first determine the radius (or diameter), then substitute it into the formula and solve.
- Real-World Application: This concept is widely used in fields such as engineering, architecture, and design, where the precise measurements of curved shapes are essential.
Understanding and applying the semicircle perimeter formula is a skill that enhances both practical problem-solving abilities and theoretical mathematical knowledge.

Basic Formula for Semicircle Perimeter
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a semicircle is essential for solving various geometrical problems. This formula combines the concepts of a circle\"s circumference and diameter to measure the boundary length of a semicircle.
- Formula Components: The formula includes π (Pi), a constant approximately equal to 3.14, which represents the ratio of a circle\"s circumference to its diameter, and \"r\", the radius of the semicircle.
- Perimeter Formula: The standard formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle is P = πr + 2r, where r is the radius of the semicircle. This formula is derived by adding the length of the curved arc (half the circumference of a full circle, πr) and the diameter (2r).
- Alternative Formula with Diameter: When the diameter (d) is known instead of the radius, the formula adjusts to P = π(d/2) + d. Here, d/2 represents the radius, as the diameter is twice the radius.
- Understanding Pi (π): Pi (π) is a crucial element in circle-related formulas. It\"s a constant value that can be approximated as 22/7 or 3.14 for most practical purposes.
- Practical Application: This formula is widely applied in fields that require geometric measurements, such as architecture, engineering, and various design disciplines.
- Example Calculation: For a semicircle with a radius of 5 units, the perimeter would be calculated as P = 3.14 * 5 + 2 * 5, yielding a perimeter value.
Understanding and accurately applying the basic formula for semicircle perimeter is a fundamental skill in mathematics, offering a gateway to more complex geometrical concepts and applications.
Variations of the Formula Based on Given Parameters
The perimeter formula for a semicircle can vary depending on the parameters given, such as radius or diameter. Understanding these variations ensures accurate calculations in different scenarios.
- Using Radius: The basic formula, P = πr + 2r, is used when the radius of the semicircle is known. The term πr calculates the half-circumference, while 2r accounts for the diameter.
- Using Diameter: If the diameter is provided instead of the radius, the formula becomes P = π(d/2) + d. Here, d/2 is used to find the radius from the diameter, ensuring the formula remains accurate.
- Approximating Pi (π): The value of π (pi) can be approximated to 3.14 or 22/7, depending on the level of precision required. This approximation is essential in manual calculations.
- Adjusting for Units: It\"s crucial to maintain consistent units throughout the calculation. Whether measuring in inches, centimeters, or meters, the units of radius or diameter must align with the final perimeter units.
- Example with Radius: For a semicircle with a radius of 4 units, the perimeter is calculated as P = π*4 + 2*4.
- Example with Diameter: For a semicircle with a diameter of 8 units, the formula adjusts to P = π*(8/2) + 8.
By understanding these formula variations, one can adeptly navigate through problems involving the perimeter of semicircles, regardless of the initial set of parameters provided.
Derivation of the Semicircle Perimeter Formula
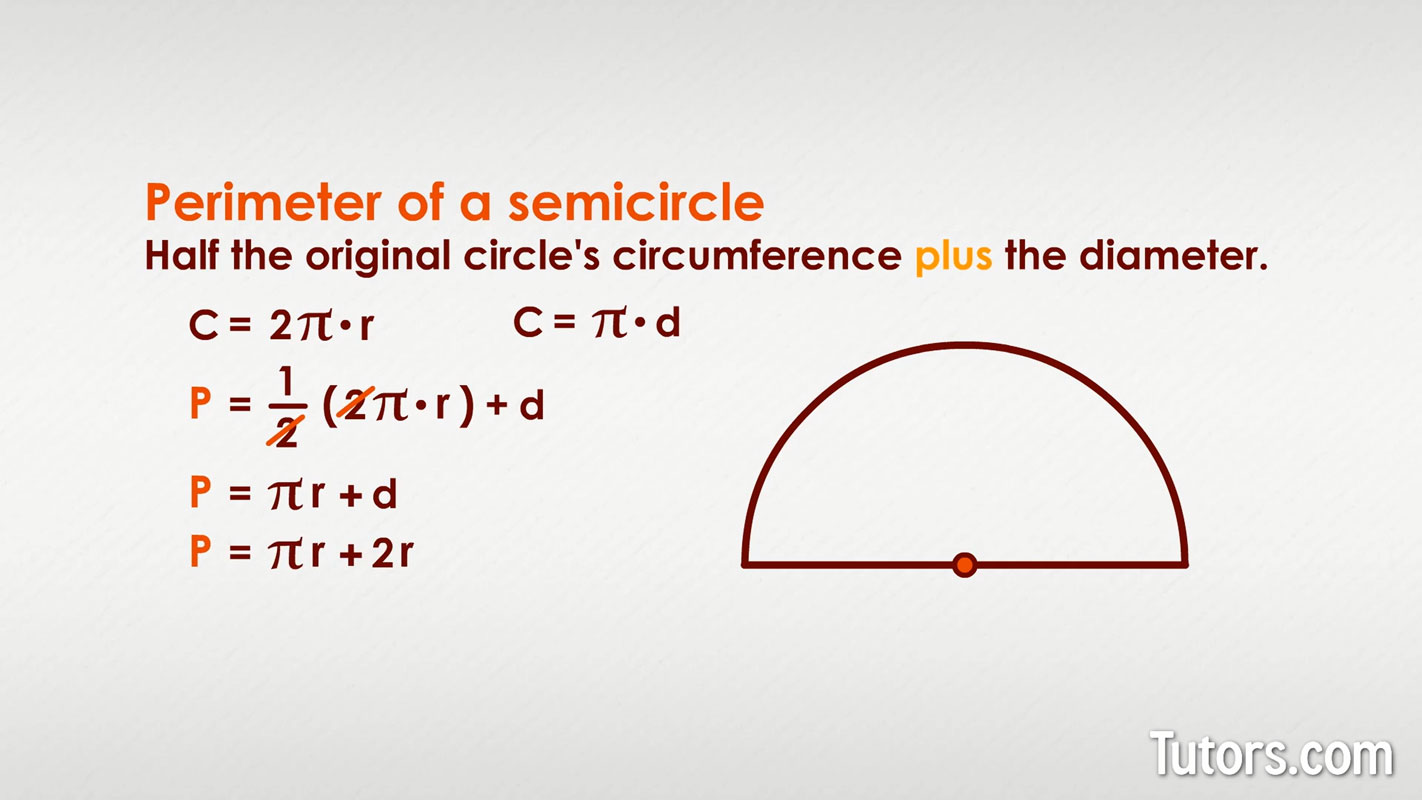
The perimeter of a semicircle is calculated by adding the length of the diameter to the length of the half-circle\"s arc. The formula can be expressed in two ways, depending on whether the radius or diameter is known.
- When the radius is known:
- The formula for the circumference of a full circle is ( C = 2pi r ).
- Since a semicircle is half of a circle, its arc length is half the circumference of the full circle, which is ( frac{1}{2} imes 2pi r = pi r ).
- Adding the diameter, which is ( 2r ), gives the total perimeter of the semicircle: ( pi r + 2r ) or simplified as ( r(pi + 2) ).
- When the diameter is known:
- The radius is half the diameter, so ( r = frac{d}{2} ).
- Using the formula for the radius, the perimeter becomes ( pi(frac{d}{2}) + d ).
These formulas are essential for calculating the perimeter of a semicircle in various practical applications.
_HOOK_
Practical Examples and Problem Solving
This section provides practical examples to understand the application of the formulas for the perimeter and area of a semicircle. Each problem is solved step-by-step to help grasp these concepts better.
Example Problems on Perimeter of a Semicircle
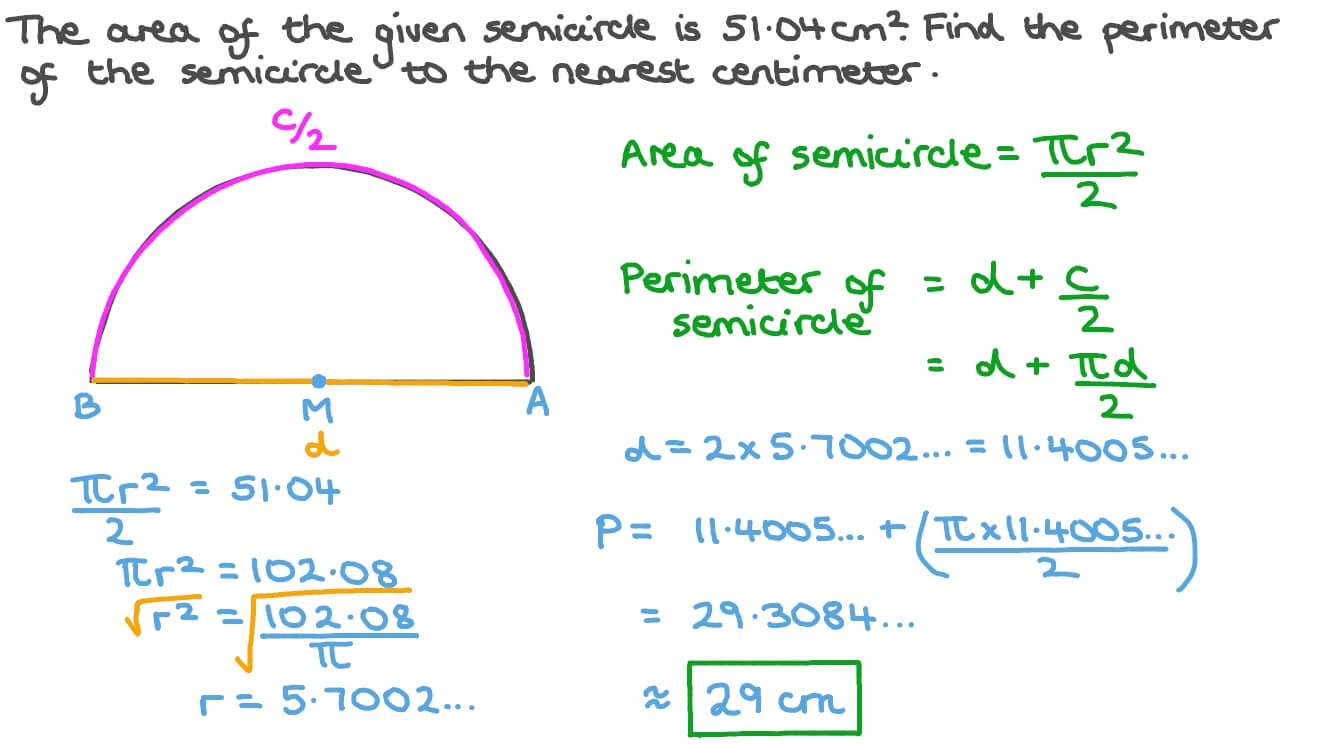
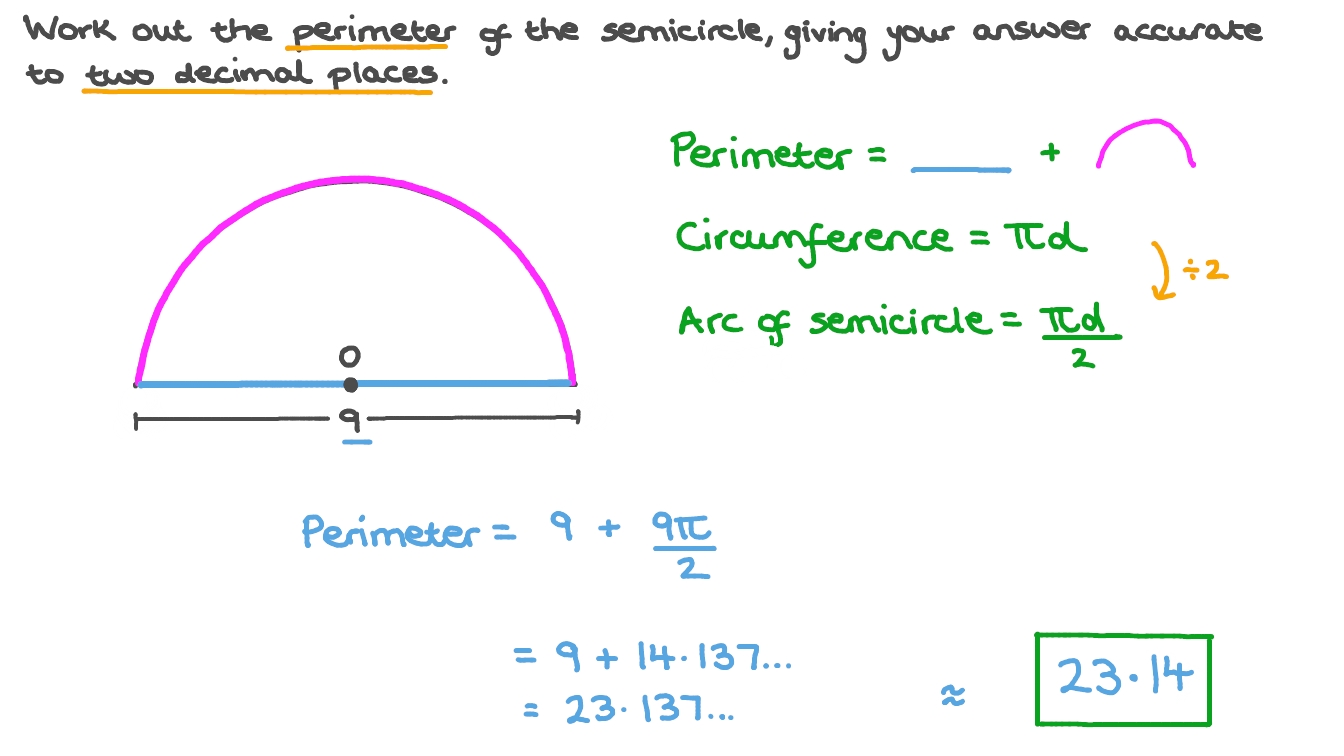
- Problem: Calculate the perimeter of a semicircular disc with a radius of 4 cm.
- Solution: Use the formula ( P = r imes (pi + 2) ). With ( r = 4 ) cm and ( pi approx 3.14 ), the perimeter is ( 4 imes (3.14 + 2) = 20.56 ) cm.
- Problem: A semicircular glass pane has a straight edge of 15 inches. Find its perimeter.
- Solution: The diameter is 15 inches. Use ( P = frac{d}{2} imes (pi + 2) ) to find the perimeter. Substituting ( d = 15 ) inches and ( pi = 3.14 ), the perimeter is ( 38.55 ) inches.
- Problem: Find the string length needed to decorate a semicircular protractor with a radius of 2 inches.
- Solution: Using ( P = r imes (pi + 2) ), and with ( r = 2 ) inches, the string length needed is ( 2 imes (3.14 + 2) = 10.28 ) inches.
Example Problems on Area of a Semicircle
- Problem: Find the area of a semicircular cake with a diameter of 12 cm.
- Solution: Use the formula ( Area = frac{1}{2} imes pi imes r^2 ). Here, ( r = frac{12}{2} = 6 ) cm. Thus, the area is ( frac{1}{2} imes 3.14 imes 6^2 = 56.52 ) cm².
- Problem: Calculate the area of a semicircular garden with a radius of 7 yards for planting flowers.
- Solution: Using ( Area = frac{1}{2} imes pi imes r^2 ), and with ( r = 7 ) yards, the area for planting is ( frac{1}{2} imes 22/7 imes 7^2 = 77 ) yard².
- Problem: Determine the area of a semicircular protractor with a 2-inch radius.
- Solution: Apply ( Area = frac{1}{2} imes pi imes r^2 ). With ( r = 2 ) inches, the area is ( frac{1}{2} imes 3.14 imes 2^2 = 6.28 ) in².
How To Calculate The Perimeter of a Semicircle
Calculate: Discover the fascinating world of calculations! Watch our video to learn clever tips and tricks on how to quickly calculate complex problems. Master the art of mental math and impress your friends with your lightning-fast arithmetic skills!
Perimeter of a Semicircle
Perimeter: Ready to unlock the secrets of perimeters? Join us in our video as we delve into the world of shapes and measurements. Learn how to find the perimeter of various objects, from simple squares to intricate polygons. Get ready to become a perimeter pro!
Comparison: Perimeter of a Semicircle vs. Full Circle
Understanding the difference between the perimeter of a semicircle and a full circle is crucial in geometry. The perimeter of a full circle, commonly known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle. In contrast, the perimeter of a semicircle is not simply half the circumference of the full circle. The semicircle\"s perimeter includes the straight edge (diameter) in addition to the curved edge.
The formula for the semicircle\"s perimeter is P = πr + 2r. Here, πr represents the half-length of the circle\"s circumference, and 2r is the length of the diameter. Thus, the perimeter of the semicircle comprises both the curved part (half the circle\"s circumference) and the straight line (the diameter).
| Shape | Formula | Description |
| Full Circle (Circumference) | C = 2πr | Only the curved edge, equal to two times π times the radius. |
| Semicircle (Perimeter) | P = πr + 2r | Includes the half-length of the circle\"s circumference plus the diameter. |
This distinction is important in various applications, such as in engineering and architecture, where the precise measurement of perimeters is required for accurate design and construction.