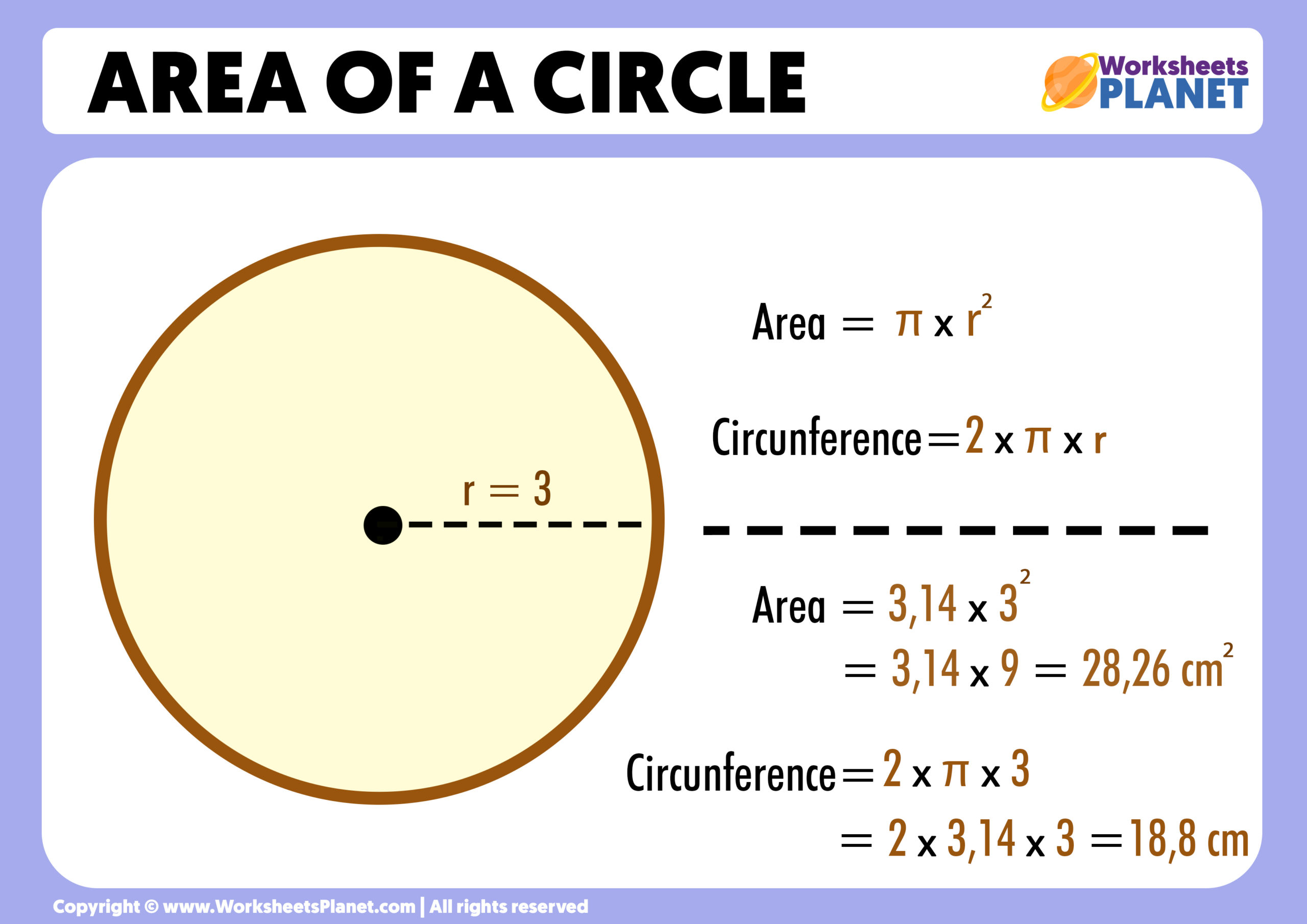
Topic polygon perimeter: Discover the fascinating world of polygons as we embark on a journey to explore the intricacies of their perimeters, a key concept in geometry that shapes our understanding of space and measurement.
Table of Content
- Definition and Basic Concept of Polygon Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Calculating the Perimeter of Polygons
- Calculating Perimeter for Different Types of Polygons
- Perimeter Formulas for Common Polygons
- Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
- Real-world Applications of Polygon Perimeters
- Solved Examples and Practice Problems
Definition and Basic Concept of Polygon Perimeter
The perimeter of a polygon is a fundamental concept in geometry, referring to the total length of the edges or sides of a polygon. It is a linear measurement, representing the distance around the polygon, much like the boundary line of a piece of land. This concept is crucial in various fields, from architecture to mathematics, offering a practical approach to understanding and manipulating space and shape.
- A regular polygon is one where all sides and angles are equal. The perimeter of such polygons can be easily calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides.
- An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter of an irregular polygon, one must add the lengths of each individual side.
Understanding the perimeter of polygons is not just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in everyday life. From planning the layout of a garden to designing a sports field, the perimeter of polygons plays a crucial role. It\"s a concept that helps us make sense of the space around us and optimizes it for various uses.
Moreover, in the world of design and art, the perimeter of polygons influences aesthetic decisions, enabling artists and designers to create pleasing and functional spaces. In summary, the perimeter of polygons is a versatile and indispensable tool in both theoretical and practical aspects of geometry.

READ MORE:
Calculating the Perimeter of Polygons
Get ready to unleash your inner math whiz! Discover the fascinating world of calculating in this mind-bending video that will make numbers dance and equations come alive before your eyes.
Math Antics - Perimeter
Dive into the exciting world of Math Antics and prepare to have your mind blown. This captivating video will simplify complex mathematical concepts, making learning fun and accessible for everyone.
Calculating Perimeter for Different Types of Polygons
The calculation of a polygon\"s perimeter depends on the type of polygon. Polygons can be broadly classified into two categories: regular and irregular. The approach to calculating their perimeters varies accordingly.
Regular Polygons
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure. To calculate the perimeter of a regular polygon, the formula is simple: multiply the length of one side by the total number of sides.
- Identify the length of one side of the polygon (s).
- Count the number of sides (n) the polygon has.
- Calculate the perimeter (P) using the formula: P = n × s.
Irregular Polygons
In the case of irregular polygons, where sides are not of equal length, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the individual sides together.
- Measure the length of each side of the polygon.
- Add these lengths together to get the total perimeter.
For example, if an irregular polygon has five sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 2 cm, and 6 cm, its perimeter would be the sum of these lengths, which equals 20 cm.
Application in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a polygon can be calculated by finding the distance between each pair of adjacent vertices. This involves using the distance formula between two points on a coordinate plane.
Whether regular or irregular, understanding how to calculate the perimeter of different types of polygons is essential for a variety of real-world applications, including construction, land measurement, and creative design. The perimeter serves as a fundamental metric in the practical application of geometric concepts.

Perimeter - Find the Perimeter of Any Polygon
Are you ready to find the answer to that perplexing math problem? Look no further! This video will guide you step-by-step through the process, revealing the secrets to finding solutions with ease and confidence.
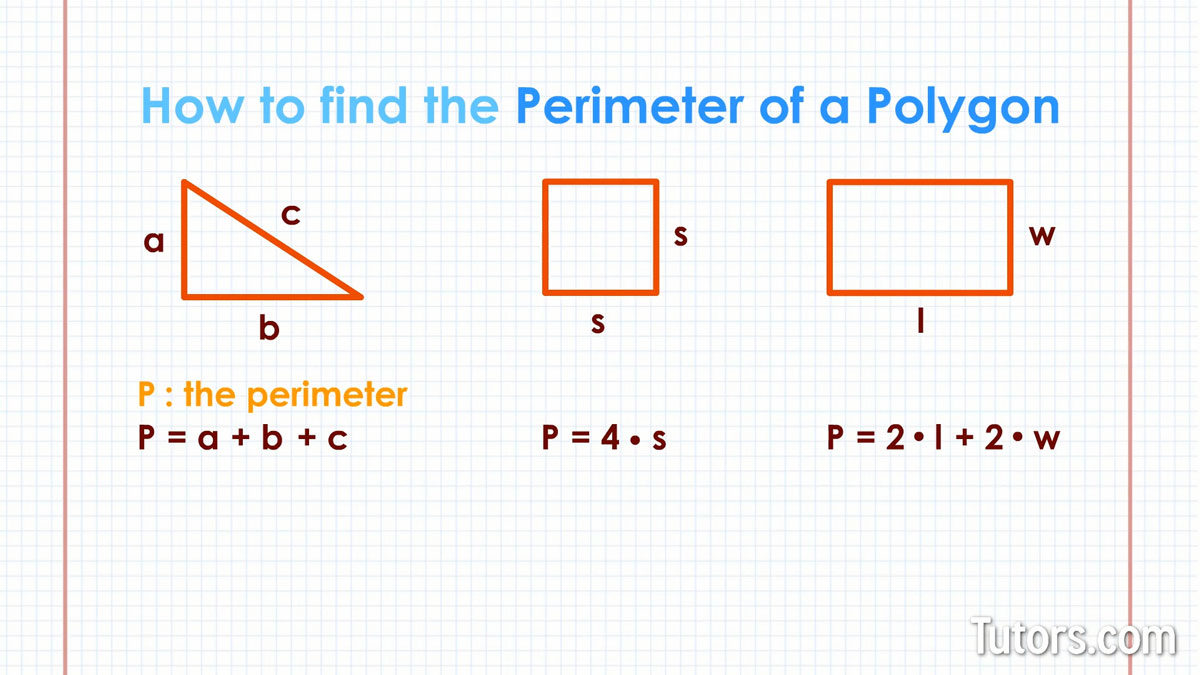
Perimeter Formulas for Common Polygons
Each type of polygon has a specific formula for calculating its perimeter. These formulas are straightforward for regular polygons, where all sides are equal, but can vary for irregular polygons. Below are the perimeter formulas for some common polygons.
| Polygon Type | Perimeter Formula |
| Triangle | Sum of all three sides (a + b + c) |
| Square | 4 times one side (4 × a) |
| Rectangle | 2 times the sum of length and width (2 × (l + w)) |
| Regular Pentagon | 5 times one side (5 × a) |
| Regular Hexagon | 6 times one side (6 × a) |
| Regular Octagon | 8 times one side (8 × a) |
For irregular polygons, where each side can be of a different length, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. As an example, an irregular quadrilateral with sides of lengths 4, 5, 6, and 7 units would have a perimeter of 22 units (4 + 5 + 6 + 7).
These formulas provide a quick and easy way to calculate the perimeter of common polygons, a fundamental aspect in fields like geometry, architecture, and land surveying.

Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
The concept of calculating the perimeter of a polygon in coordinate geometry involves using the coordinates of the vertices of the polygon. This approach is particularly useful for determining the length of the boundary of a polygon when it is plotted on a coordinate plane.
Identifying the Vertices
The process begins with identifying the vertices of the polygon. Each vertex of a polygon in coordinate geometry is defined by a pair of coordinates (x, y) in a Cartesian plane. Plotting these vertices accurately is essential for the correct calculation of the perimeter.
Calculating the Distance Between Vertices
Once the vertices are identified and plotted, the next step is to calculate the distance between consecutive vertices. This is done using the distance formula:
Distance = √[(x₂ – x₁)² + (y₂ – y₁)²]
This formula helps in determining the length of each side of the polygon by calculating the distance between two adjacent vertices.
Summing Up the Lengths
The perimeter of the polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. After calculating the lengths of each side using the distance formula, these lengths are added together to find the total perimeter of the polygon.
Example Calculation
- For a polygon with vertices A(2, 4), B(5, 7), C(8, 4), and D(5, 1), first calculate the distance between each pair of consecutive vertices.
- Then, add these distances to find the total perimeter.
Understanding the perimeter in coordinate geometry is not only crucial for academic purposes but also has practical applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and computer graphics, where precise measurements and spatial understanding are key.
Real-world Applications of Polygon Perimeters
The concept of polygon perimeters is not confined to the realm of mathematics but extends into various practical applications in everyday life. Understanding these applications emphasizes the significance of this geometric concept.
Construction and Architecture
In the fields of construction and architecture, the perimeter of polygons is crucial for designing and building structures. This includes determining the lengths of walls, fencing areas, and planning layouts for buildings, rooms, and other architectural elements.
Land Surveying and Property Planning
Perimeter measurements play a vital role in land surveying, property planning, and the demarcation of land boundaries. It helps in calculating the fencing required for a particular area, whether for residential plots, agricultural lands, or commercial properties.
Gardening and Landscaping
In gardening and landscaping, knowing the perimeter of an area assists in planning the layout, determining the length of fencing needed for gardens, and organizing the placement of plants, pathways, and decorative elements.
Art and Design
In art and design, understanding perimeters is essential for creating and framing artworks, designing fashion and apparel, and other creative endeavors where dimensions and spatial planning are key.
Science and Astronomy
Astronomers use the concept of perimeters to study planetary orbits and distances in space, which is fundamental in the field of astrophysics and space exploration.
Computer Graphics and Gaming
In computer graphics and the gaming industry, perimeter calculations are used for rendering objects, creating virtual environments, and ensuring that visual representations are geometrically accurate.
Everyday Practical Uses
From installing Christmas lights around a house to setting up tents, the concept of perimeter finds its application in many everyday scenarios, helping in practical tasks like estimating the amount of materials needed for various projects.
Understanding the real-world applications of polygon perimeters not only enhances practical skills but also underlines the importance of geometric concepts in our daily lives.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
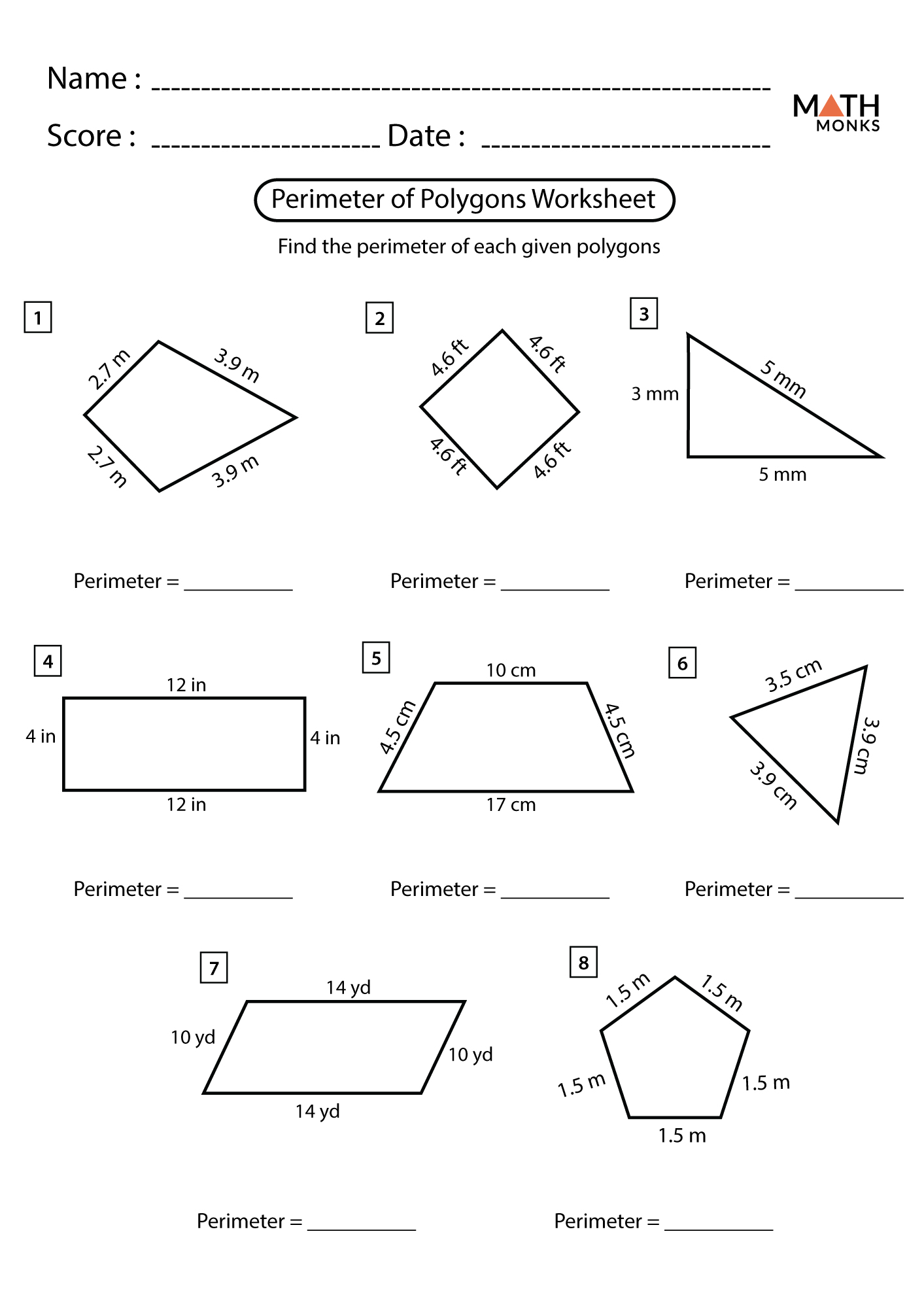
Solved Examples and Practice Problems
The concept of polygon perimeters can be better understood with solved examples and practice problems. These examples illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of various types of polygons using their side lengths or coordinates.
Solved Examples
- Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Given a triangle with side lengths of 5 cm, 9 cm, and 11 cm, the perimeter can be found by adding these lengths together.
- Solution: Perimeter = 5 cm + 9 cm + 11 cm = 25 cm.
- Example 2: Perimeter of a Rectangle
- A rectangle has a length of 8 cm and a width of 3 cm. To find the perimeter, add up all the side lengths or use the formula: Perimeter = 2 x (Length + Width).
- Solution: Perimeter = 2(8 cm + 3 cm) = 22 cm.
- Example 3: Perimeter of a Square
- For a square with each side measuring 2 inches, the perimeter is found by multiplying the side length by 4.
- Solution: Perimeter = 4 x 2 in = 8 in.
- Example 4: Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
- Calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 3 inches.
- Solution: Perimeter = 5 x 3 in = 15 in.
- Example 5: Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
- Given a polygon with sides measuring 3 units, 4 units, 6 units, 2 units, 1.5 units, and an unknown side x, where the total perimeter is 18.5 units, find the length of x.
- Solution: x = 18.5 - (3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 1.5) = 2 units.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 10 inches, 14 inches, and 15 inches.
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle whose length is 12 cm and width is 4 cm.
- Determine the perimeter of a regular hexagon where each side measures 8 meters.
- If the perimeter of a square is 20 feet, what is the length of each side?
- Given a regular pentagon with a perimeter of 100 cm, find the length of each side.
These examples and practice problems help in reinforcing the understanding of how to calculate perimeters for different polygons, whether they are regular or irregular in shape.
Discover the fascinating world of polygon perimeters, where geometry meets real life, enhancing your understanding and appreciation of the shapes that surround us every day. Join this intriguing journey through mathematics!