Topic perimeter of cube formula: Discover the simplicity behind the "Perimeter of Cube Formula" and unlock the secrets of this fundamental geometric concept, essential for students and enthusiasts alike.
Table of Content
- What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a cube?
- Basic Concept and Formula of Cube Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter from Cube\"s Side Length
- Determining Perimeter from Cube\"s Volume
- Perimeter Derived from Surface Area
- YOUTUBE: How to Find the Area, Perimeter, and Volume of a Cube
- Figuring Out Perimeter Using Interior Diagonal
- Perimeter Calculation from the Face Diagonal
- Real-life Applications of Cube Perimeter
- Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a cube?
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a cube can be derived by considering that a cube has 6 identical square faces and 12 identical edges.
Since each face of a cube is a square, the perimeter of each square face is 4 times its side length.
Therefore, the perimeter of one face of the cube is given by the formula:
Perimeter of one face = 4 * (side length)
Since all the faces of a cube are identical, the perimeter of the cube is equal to the perimeter of one face multiplied by the number of faces (6).
So the formula for the perimeter of a cube is:
Perimeter of cube = 6 * (Perimeter of one face)
Substituting the formula for the perimeter of one face, we get:
Perimeter of cube = 6 * (4 * side length)
Simplifying further:
Perimeter of cube = 24 * side length
Therefore, the formula for calculating the perimeter of a cube is Perimeter = 24 * side length.
READ MORE:
Basic Concept and Formula of Cube Perimeter
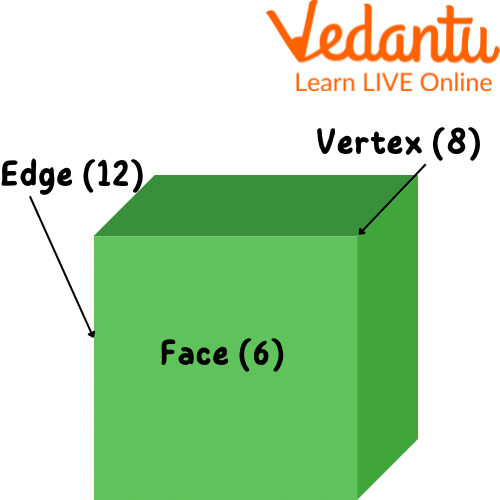
The perimeter of a cube, a fundamental geometric concept, can be easily understood and calculated. A cube, a three-dimensional shape, comprises six square faces, each sharing its edges with adjacent faces. These edges, crucial to the cube\"s structure, are equal in length due to the cube\"s uniformity.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a cube is straightforward: Perimeter (P) = 12 x a, where \"a\" represents the length of each side of the cube. This formula stems from the fact that a cube has 12 edges in total, and by multiplying the length of one edge by 12, we get the total perimeter.
- Basic Perimeter Calculation: Simply multiply the length of one side of the cube by 12.
- Perimeter from Volume: To find the perimeter from the cube\"s volume, first determine the side length by cube rooting the volume, and then apply the basic perimeter formula.
- Perimeter from Surface Area: For perimeter calculation using surface area, find the side length by square rooting the surface area divided by 6, and then use the basic perimeter formula.
These methods provide versatile approaches to calculating the cube\"s perimeter in various scenarios, be it in academic studies or practical applications in fields like architecture and design. Understanding this concept enhances one\"s geometric and spatial comprehension, crucial for many scientific and engineering disciplines.

Calculating Perimeter from Cube\"s Side Length
The calculation of a cube\"s perimeter using its side length is a straightforward process. The key lies in understanding that a cube has 12 equal edges. Thus, to find the perimeter, we simply multiply the length of one edge by 12.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Determine the length of one edge of the cube (denoted as \"a\").
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a cube: Perimeter (P) = 12 × a.
- Substitute the value of \"a\" into the formula and calculate.
Example Calculations:
- If a cube\"s edge is 5 meters long, the perimeter is calculated as 12 × 5 = 60 meters.
- For an edge length of 8 meters, the perimeter would be 12 × 8 = 96 meters.
- In case the edge is 15 meters, the perimeter is 12 × 15 = 180 meters.
This formula provides a quick and efficient way to determine the perimeter of a cube, which is essential in various mathematical and real-world applications.

Determining Perimeter from Cube\"s Volume
Calculating the perimeter of a cube using its volume involves two primary steps. First, you need to find the length of one side of the cube from its volume. This is done by taking the cube root of the volume. Once you have the side length, the perimeter can be calculated using the standard formula for the perimeter of a cube.
Steps to Follow:
- Calculate the side length (a) by cube rooting the volume: Side = ^{3}√Volume.
- Once the side length is obtained, calculate the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x Side.
Example: For a cube with a volume of 1000 cubic units:
- First, find the side length: Side = ^{3}√1000 = 10 units.
- Then, calculate the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x 10 = 120 units.
This method is particularly useful in scenarios where the volume is known, but the side length is not directly given.
Perimeter Derived from Surface Area
To determine the perimeter of a cube from its surface area, we follow a two-step process. First, we need to find the length of one side of the cube. This is achieved by dividing the surface area by 6 and then taking the square root of the result. Once we have the length of a side, we can use it to calculate the perimeter.
Procedure:
- Find the length of a side (a) by calculating: Side = √(Surface Area ÷ 6).
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: Perimeter = 12 x Side.
Example: For a cube with a surface area of 600 square units:
- First, determine the side length: Side = √(600 ÷ 6) = √100 = 10 units.
- Then, calculate the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x 10 = 120 units.
This method provides an effective way to find the perimeter when the surface area is known, a common scenario in geometric applications.

_HOOK_
How to Find the Area, Perimeter, and Volume of a Cube
Looking for a mind-bending challenge? Watch this video and prepare to have your mind blown by the endless possibilities of the cube. Get ready for a world of creativity and problem-solving that will leave you wanting more!
Geometry Basic Formulas: Perimeter, Area, Volume of Triangle, Rectangle, Square, Cuboid, and Cube
Dive into the fascinating world of geometry with this captivating video. Explore the intricate patterns and shapes that make up our surroundings, and discover how geometry holds the key to unlocking a deeper understanding of the universe. Prepare to be amazed by the beauty and complexity of this ancient mathematical art form.
Figuring Out Perimeter Using Interior Diagonal
To determine the perimeter of a cube using its interior diagonal, the process involves two main steps. First, you calculate the length of one side of the cube from its interior diagonal. This is done by dividing the diagonal length by the square root of 3. After finding the side length, you can easily compute the perimeter by applying the cube\"s perimeter formula.
Steps for Calculation:
- Calculate the side length (a) from the interior diagonal: Side = Diagonal ÷ √3.
- Use the side length to find the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x Side.
Example: For a cube with an interior diagonal of 170 units:
- Determine the side length: Side = 170 ÷ √3 ≈ 98.18 units.
- Calculate the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x 98.18 ≈ 1177.74 units.
This method is particularly useful in geometrical problems where the interior diagonal is known, and the perimeter needs to be found.

Perimeter Calculation from the Face Diagonal
To calculate the perimeter of a cube using its face diagonal, we begin by finding the length of one side of the cube from the diagonal measurement. The side length is determined by dividing the square of the diagonal by 2 and then taking the square root of that value. After obtaining the side length, the perimeter can be easily calculated using the formula for the perimeter of a cube.
Procedure:
- Find the side length (a) by calculating: Side = √(Diagonal² ÷ 2).
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: Perimeter = 12 x Side.
Example: If a cube\"s face diagonal measures 14 units:
- First, determine the side length: Side = √(14² ÷ 2) = √98 ≈ 9.90 units.
- Then, calculate the perimeter: Perimeter = 12 x 9.90 ≈ 118.8 units.
This method is useful in situations where the cube\"s face diagonal is known, and the perimeter is required.

Real-life Applications of Cube Perimeter
Understanding the perimeter of a cube has various practical applications in different fields. Below are some real-life scenarios where cube perimeter calculations are crucial:
- Construction and Architecture: In construction, the perimeter of cube-shaped structures is vital for planning and material estimation. For example, calculating the amount of materials needed for borders, fences, or decorative elements around cube-shaped rooms or buildings.
- Land Measurement: Perimeter calculations are used in agriculture and land surveying. Farmers might calculate the perimeter of their cubic plots to determine fencing requirements or layout of crops.
- Computer-Aided Design: In graphic design, especially in gaming, designers use the concept of perimeter to create accurate models and environments, enhancing visual appeal and gameplay experience.
- Fashion and Art: The principles of perimeter are applied in fashion for fabric cutting and in art for precise brush strokes and framing.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use perimeter calculations to measure orbits and movements of celestial bodies, aiding in our understanding of the universe.
- Everyday Construction Tasks: Whether it\"s building a shed or installing a fence around a garden, understanding the perimeter helps in determining the quantity of materials needed.
- Interior Decoration: Perimeter measurements assist in determining the amount of molding required for windows and doors, as well as the quantity of paint or wallpaper for room decoration.
- Sports: In athletics, knowing the perimeter of tracks helps athletes understand the distance covered per lap, aiding in training and competition strategies.
These applications show the importance of understanding the perimeter of a cube in various professional and personal contexts, demonstrating its practicality beyond theoretical mathematics.
Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
Mastering the concept of the cube\"s perimeter is easier with hands-on examples and exercises. Let\"s dive into some interactive problems to enhance your understanding.
Practice Problem Set 1
- Problem: If a cube has edges of length 4 units, what is its perimeter?
- Hint: Remember, the perimeter of a cube is 12 times the length of one side.
- Problem: Find the perimeter of a cube whose each edge measures 7 meters.
- Problem: Determine the edge length of a cube if its perimeter is known to be 96 cm.
- Hint: Use the perimeter formula in reverse to find the edge length.
Practice Problem Set 2
- Given a cube with an edge length of 5.5 cm, calculate its perimeter.
- What would be the perimeter of a cube with each side measuring 12 mm?
- For a cube with a perimeter of 144 units, find the length of a single edge.
After attempting these problems, compare your answers with the formula: Perimeter of a cube = 12 x edge length. Practicing these problems will solidify your understanding of how to calculate the perimeter of a cube in various scenarios.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a cube?
- The perimeter of a cube is calculated using the formula: Perimeter = 12 x side length. This formula multiplies the length of one edge of the cube by 12, as a cube has 12 edges in total.
- How can you determine the side length of a cube from its perimeter?
- To find the side length of a cube from its perimeter, divide the perimeter by 12. For example, if the perimeter is 120 units, the side length would be 120/12 = 10 units.
- Can the perimeter of a cube be calculated from its volume or surface area?
- Yes, the perimeter can be derived from the cube\"s volume or surface area. For the volume, find the cube root of the volume and then multiply by 12. For the surface area, find the square root of the surface area divided by 6, and then multiply the result by 12.
- Is the perimeter of a cube different from that of a cuboid?
- Yes, the perimeter of a cube, which is 12 times one side, is different from that of a cuboid. The perimeter of a cuboid is calculated as 4 times the sum of its length, breadth, and height.
- Why is the perimeter of a cube considered a linear measure?
- Although a cube is a three-dimensional object, its perimeter is a linear measure because it sums the lengths of its 12 edges, each of which is a one-dimensional line segment.
Discovering the perimeter of a cube unlocks a world of geometric understanding, blending simplicity with mathematical elegance. This exploration journey enhances practical insights and deepens our appreciation for this fundamental shape\"s role in various applications.
_HOOK_