Topic perimeter of isosceles trapezoid: Explore the intriguing world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the perimeter of isosceles trapezoids, a key concept in mathematical understanding and real-world applications.
Table of Content
- How to find the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid?
- Definition and Basic Properties of an Isosceles Trapezoid
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of an Isosceles Trapezoid
- Step-by-Step Guide for Finding the Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations in Isosceles Trapezoids
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Calculating Perimeter
- Applications of Isosceles Trapezoids in Real Life
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of an Isosceles Trapezoid
- Tips for Remembering the Perimeter Formula
- Interactive Tools and Resources for Learning
- Comparison with Other Quadrilaterals
- Advanced Problems and Solutions
- FAQs on Perimeter of Isosceles Trapezoids
How to find the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid?
To find the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid, you need to know the lengths of its bases and its height. Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Identify the lengths of the bases of the isosceles trapezoid. Let\'s say the lengths are a and b.
- Determine the height of the trapezoid. We\'ll call it h.
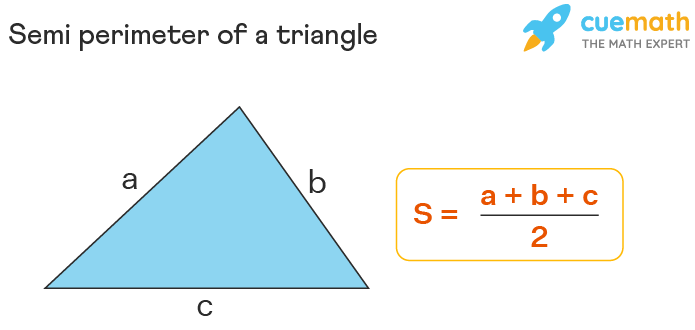
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: perimeter = a + b + 2h.
Let\'s illustrate these steps with an example:
Example: The perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid is 28 inches, and the ratio of lengths of its bases is 5:3. Find the lengths of the sides of the trapezoid if its height is 6 inches.
- Let the lengths of the bases be 5x and 3x, where x is a common factor.
- The height of the trapezoid is given as 6 inches.
- Substitute the values into the perimeter formula:
perimeter = (5x + 3x + 2 * 6) inches.
To solve for x, set up the equation:
28 = 8x + 12.
Now, solve for x:
| 28 - 12 | = 8x |
| 16 | = 8x |
| 16 / 8 | = x |
| 2 | = x |
Now that we have the value of x, we can calculate the lengths of the bases:
Length of the shorter base = 3x = 3 * 2 = 6 inches.
Length of the longer base = 5x = 5 * 2 = 10 inches.
Finally, plug in the values to find the perimeter:
Perimeter = 6 + 10 + 2 * 6 = 6 + 10 + 12 = 28 inches.
Therefore, the lengths of the sides of the isosceles trapezoid are 6 inches, 6 inches, 10 inches, and 10 inches. The perimeter of the trapezoid is 28 inches.
READ MORE:
Definition and Basic Properties of an Isosceles Trapezoid
An isosceles trapezoid is a fascinating quadrilateral with unique properties that distinguish it in geometry. This section outlines its definition and basic characteristics.
- Definition: An isosceles trapezoid is a four-sided figure with one pair of parallel sides, known as the bases, and non-parallel sides that are equal in length.
- Equal Angles: The angles adjacent to each base are congruent. This means that the angles at each base are equal in measure.
- Line of Symmetry: It has a line of symmetry that bisects it into two congruent right triangles.
- Base Lengths: The lengths of the parallel sides (bases) can vary, but they are not equal in length.
- Legs: The non-parallel sides (legs) are equal in length and angle.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent, which is a unique property distinguishing it from other trapezoids.
Understanding these properties is essential for comprehending how the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid is calculated, as well as its application in various mathematical and real-world contexts.

Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of an Isosceles Trapezoid
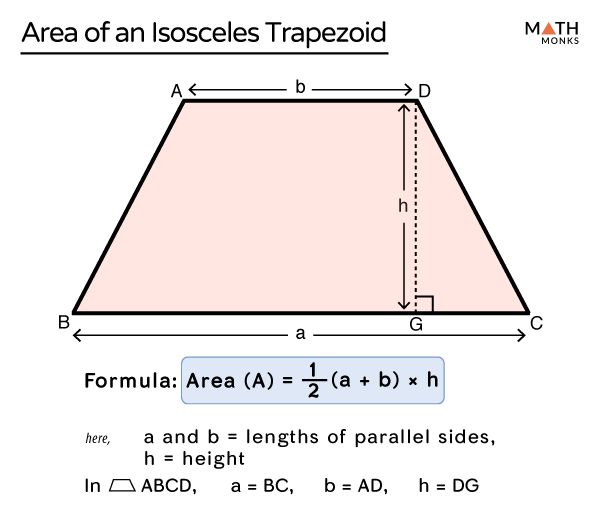
The perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid can be calculated by adding the lengths of all its four sides. The formula is straightforward, reflecting its symmetrical properties.
- Perimeter Formula: The perimeter (P) of an isosceles trapezoid is given by P = a + b + 2c, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the parallel sides, and \"c\" is the length of the non-parallel (equal) sides.
- Understanding the Components:
- a and b (Bases): These are the lengths of the two parallel sides of the trapezoid. They can be different in length.
- c (Legs): This represents the length of the non-parallel sides, which are equal in an isosceles trapezoid.
- Calculation Steps:
- Measure the lengths of the parallel sides (a and b).
- Measure the length of one of the non-parallel sides (c).
- Apply the formula: Add the lengths of the parallel sides and double the length of the non-parallel side.
This formula is crucial for solving various geometric problems and is especially useful in real-world applications where the shape of an isosceles trapezoid is encountered.

Step-by-Step Guide for Finding the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to accurately determine the perimeter:
- Identify the Sides: Recognize the parallel sides (bases) and the equal non-parallel sides (legs) of the isosceles trapezoid.
- Measure the Bases: Measure the lengths of the two bases (a and b). It\"s crucial to ensure accuracy in these measurements for a correct calculation.
- Measure the Legs: Measure the length of one of the non-parallel sides (c). Since the trapezoid is isosceles, both non-parallel sides are of equal length.
- Apply the Perimeter Formula: Use the formula P = a + b + 2c, where \"P\" is the perimeter, \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the bases, and \"c\" is the length of the non-parallel sides.
- Calculate the Perimeter: Add the measurements together as per the formula to find the total perimeter of the trapezoid.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid, a fundamental skill in geometry.

Examples of Perimeter Calculations in Isosceles Trapezoids
Understanding the perimeter calculation of an isosceles trapezoid is best illustrated through examples. Below are scenarios demonstrating how to apply the formula in practical situations:
- Example 1:
- Consider an isosceles trapezoid with bases 8 cm and 12 cm, and the length of the non-parallel sides (legs) is 5 cm each. Applying the formula P = a + b + 2c, we get P = 8 + 12 + 2(5) = 30 cm.
- Example 2:
- For an isosceles trapezoid with bases of 10 cm and 14 cm and legs measuring 7 cm, the perimeter is calculated as P = 10 + 14 + 2(7) = 38 cm.
- Example 3:
- If an isosceles trapezoid has equal bases of 6 cm and the length of each leg is 4 cm, its perimeter is P = 6 + 6 + 2(4) = 20 cm.
These examples showcase how to compute the perimeter of isosceles trapezoids with different dimensions, reinforcing the practical application of the perimeter formula.
_HOOK_
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid can sometimes be tricky. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Confusing Base and Side Lengths: Ensure you correctly identify which sides are the bases and which are the legs. The bases are parallel, while the legs are not.
- Incorrectly Adding Side Lengths: Remember to add both base lengths and double the length of one leg, as the legs are equal in an isosceles trapezoid.
- Neglecting Units of Measurement: Consistency in units (like cm, m) is crucial. Convert all measurements to the same unit before calculating.
- Forgetting the Properties of Isosceles Trapezoids: Recall that the non-parallel sides (legs) are equal. Mistaking this can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Overlooking Decimal Points: Pay attention to decimal points in measurements for precise calculations.
Avoiding these mistakes will help ensure accuracy in your perimeter calculations of isosceles trapezoids.

Applications of Isosceles Trapezoids in Real Life
Isosceles trapezoids are not just mathematical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields:
- Architecture and Construction: Isosceles trapezoids are used in architectural designs, particularly in trusses and bridges, where uniform strength and distribution of weight are crucial.
- Graphic Design: They are employed in graphic design and art for creating geometric patterns and shapes that are visually appealing and symmetrical.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, components with isosceles trapezoid shapes are common due to their stability and ease of assembly.
- Physics and Engineering: The principles of isosceles trapezoids apply in physics and engineering, especially in calculating forces and designing objects with specific stress distributions.
- Furniture Design: This shape is often seen in furniture design, particularly in tables and shelves, for both aesthetic and functional purposes.
These real-life applications show the relevance of understanding the properties of isosceles trapezoids, including their perimeter calculations.

Finding the Area and Perimeter of an Isosceles Trapezoid
\"Discover the fascinating world of trapezoids in this captivating video! You\'ll be amazed at their unique shape and the many ways they are used in architecture and mathematics. Join us as we explore the properties and applications of trapezoids in this educational and visually stunning presentation!\"
Finding the Lengths of an Isosceles Trapezoid with Base Angles and Side Lengths
\"Unlock the secrets of lengths with this engaging and informative video! From measuring the distance between two points to understanding the concept of scale, lengths play a crucial role in our daily lives. Join us as we delve into the significance and practical applications of lengths in this eye-opening exploration!\"
Tips for Remembering the Perimeter Formula
Remembering the perimeter formula for an isosceles trapezoid can be made easier with these tips:
- Visualize the Shape: Picture an isosceles trapezoid in your mind. Remember that it has two parallel sides and two equal non-parallel sides.
- Memorize the Basic Formula: Keep in mind the simple formula P = a + b + 2c, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the bases, and \"c\" is the length of the equal legs.
- Use Mnemonics: Create a mnemonic to remember the parts of the formula, such as \"All Bases Covered Twice\" (ABC2) to represent a + b + 2c.
- Relate to Real Objects: Associate the shape with objects you see daily, like certain tables or frames, to reinforce the concept.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with different examples will help solidify your understanding and recall of the formula.
With these strategies, recalling and applying the perimeter formula for isosceles trapezoids becomes more manageable and intuitive.

Interactive Tools and Resources for Learning
To enhance your understanding of the perimeter of isosceles trapezoids, various interactive tools and resources can be extremely helpful:
- Online Calculators: Websites that offer geometric calculators can help you quickly compute the perimeter of isosceles trapezoids with your inputted measurements.
- Educational Apps: Apps designed for geometry learning often include interactive modules focused on trapezoids, providing a hands-on approach to understanding concepts.
- Video Tutorials: Educational platforms like YouTube have numerous videos explaining the concept visually, which can be beneficial for visual learners.
- Geometry Software: Programs like GeoGebra offer interactive geometry tools that allow for dynamic manipulation of shapes, including isosceles trapezoids.
- Interactive Worksheets: Online worksheets or e-books often have exercises that provide immediate feedback, enhancing learning through practice.
These tools not only aid in understanding the perimeter formula but also offer a comprehensive approach to learning geometry.
Comparison with Other Quadrilaterals
Understanding the unique aspects of an isosceles trapezoid becomes clearer when compared with other quadrilaterals:
- Rectangle: Unlike a rectangle, which has two pairs of parallel sides, an isosceles trapezoid has only one pair of parallel sides.
- Square and Rhombus: Both squares and rhombuses have all sides equal in length, which is not the case in an isosceles trapezoid that has only its non-parallel sides equal.
- General Trapezoids: While general trapezoids also have a single pair of parallel sides, they lack the symmetry and equal leg lengths of isosceles trapezoids.
- Parallelogram: Parallelograms have opposite sides that are equal and parallel, which differentiates them from isosceles trapezoids where only one pair of sides is parallel.
This comparison highlights the distinct features of isosceles trapezoids and how they differ from other common quadrilaterals in geometry.

_HOOK_
Advanced Problems and Solutions
For those seeking a deeper understanding of isosceles trapezoids, here are some advanced problems and their solutions:
- Problem 1: If an isosceles trapezoid has a perimeter of 50 cm, one base of 18 cm, and a leg of 10 cm, find the length of the other base.
- Solution 1: Use the perimeter formula P = a + b + 2c. With P = 50, a = 18, and c = 10, solve for b.
- Problem 2: Determine the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid where the diagonal is 13 cm, one base is 10 cm, and the other base is 14 cm.
- Solution 2: Apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the legs and then use the perimeter formula.
These problems demonstrate more complex scenarios involving isosceles trapezoids, enhancing problem-solving skills.
READ MORE:
FAQs on Perimeter of Isosceles Trapezoids
- What is the formula for the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid?
- The perimeter formula is P = a + b + 2c, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the parallel sides and \"c\" is the length of the non-parallel sides.
- Can the bases of an isosceles trapezoid be of equal length?
- No, in an isosceles trapezoid, the bases (parallel sides) are of different lengths.
- How are the legs of an isosceles trapezoid unique?
- The non-parallel sides, or legs, of an isosceles trapezoid are equal in length.
- Is it possible to have a right-angled isosceles trapezoid?
- Yes, an isosceles trapezoid can have right angles where the legs meet the bases.
These frequently asked questions help clarify common queries about the perimeter and properties of isosceles trapezoids.
In summary, understanding the perimeter of an isosceles trapezoid enriches geometrical knowledge and has practical real-world applications, offering a fascinating glimpse into the world of shapes and measurements.