Topic how to find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle: Discover the fascinating world of geometry with our guide on "How to Find the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle," simplifying this essential mathematical concept into easy-to-follow steps for learners of all levels.
Table of Content
- How do I calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle?
- Understanding an Isosceles Triangle
- Basic Formula for the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
- Calculating the Perimeter with Equal Sides Known
- Calculating the Perimeter with Base and Height Known
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem in Perimeter Calculation
- Practical Examples and Problem-Solving
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Calculation
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Tools and Resources for Learning More
How do I calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle?
To calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, follow these steps:
- Identify the length of the equal sides of the triangle. Let\'s call this length \"a\".
- Find the length of the remaining side. Let\'s call this length \"b\".
- Calculate the perimeter by adding the lengths of all three sides of the triangle: a + a + b = 2a + b.
So, the perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be found by adding the lengths of the two equal sides and the remaining side.
READ MORE:
Understanding an Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle is a distinct type of triangle characterized by having two sides of equal length. These equal sides are known as the \"legs\" of the triangle, while the third side is referred to as the \"base\". The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal, giving the isosceles triangle its unique symmetry.
- Equal Sides: In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of the same length. These are typically referred to as the legs of the triangle.
- Equal Angles: The angles opposite the equal sides are congruent. This means if one angle is known, the other can be easily determined as they are equal.
- Base: The third side of the triangle, which is not necessarily equal to the legs, is called the base.
- Base Angles: The angles adjacent to the base are called base angles, and they are equal in measure.
- Vertex Angle: The angle formed by the equal sides, opposite the base, is known as the vertex angle.
- Properties: Isosceles triangles maintain a line of symmetry along the altitude from the vertex angle to the midpoint of the base. This also means the altitude bisects the vertex angle and the base.
Understanding these fundamental properties of an isosceles triangle is crucial for calculating its perimeter and other geometric properties.

Basic Formula for the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be calculated using a simple formula. In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length (the legs), and the third side (the base) is of a different length. The basic formula for finding the perimeter (P) of an isosceles triangle is:
P = 2a + b
- a: Represents the length of the equal sides (legs) of the triangle.
- b: Denotes the length of the base of the triangle.
Using this formula, the sum of the lengths of all three sides gives the total perimeter of the triangle. For instance, if an isosceles triangle has two equal sides of length 5 cm each (a = 5 cm) and a base of 3 cm (b = 3 cm), the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
P = 2 * 5 cm + 3 cm = 10 cm + 3 cm = 13 cm
This formula simplifies the process of calculating the perimeter, especially when the lengths of the equal sides and the base are known.
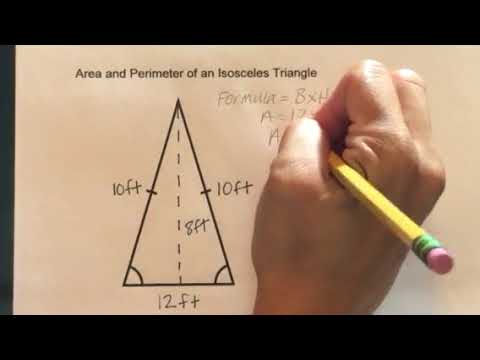
Calculating the Perimeter with Equal Sides Known
When the lengths of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle are known, calculating its perimeter is straightforward. The perimeter is the total distance around the triangle, which includes two equal sides and the base. Let\"s break down the steps for this calculation:
- Identify the Lengths: Determine the lengths of the equal sides (denoted as \"a\").
- Measure the Base: Measure the length of the base (denoted as \"b\").
- Apply the Formula: Use the perimeter formula for an isosceles triangle: P = 2a + b. This formula adds together the lengths of the two equal sides and the base.
- Calculate the Perimeter: Substitute the known values into the formula and calculate the sum to find the perimeter.
For example, if the lengths of the equal sides are 4 cm each, and the base is 6 cm, the calculation would be P = 2(4 cm) + 6 cm = 8 cm + 6 cm = 14 cm. Thus, the perimeter of the triangle is 14 cm.
Understanding this calculation is essential for many geometric problems and applications, especially in fields that require precise measurements like engineering and architecture.
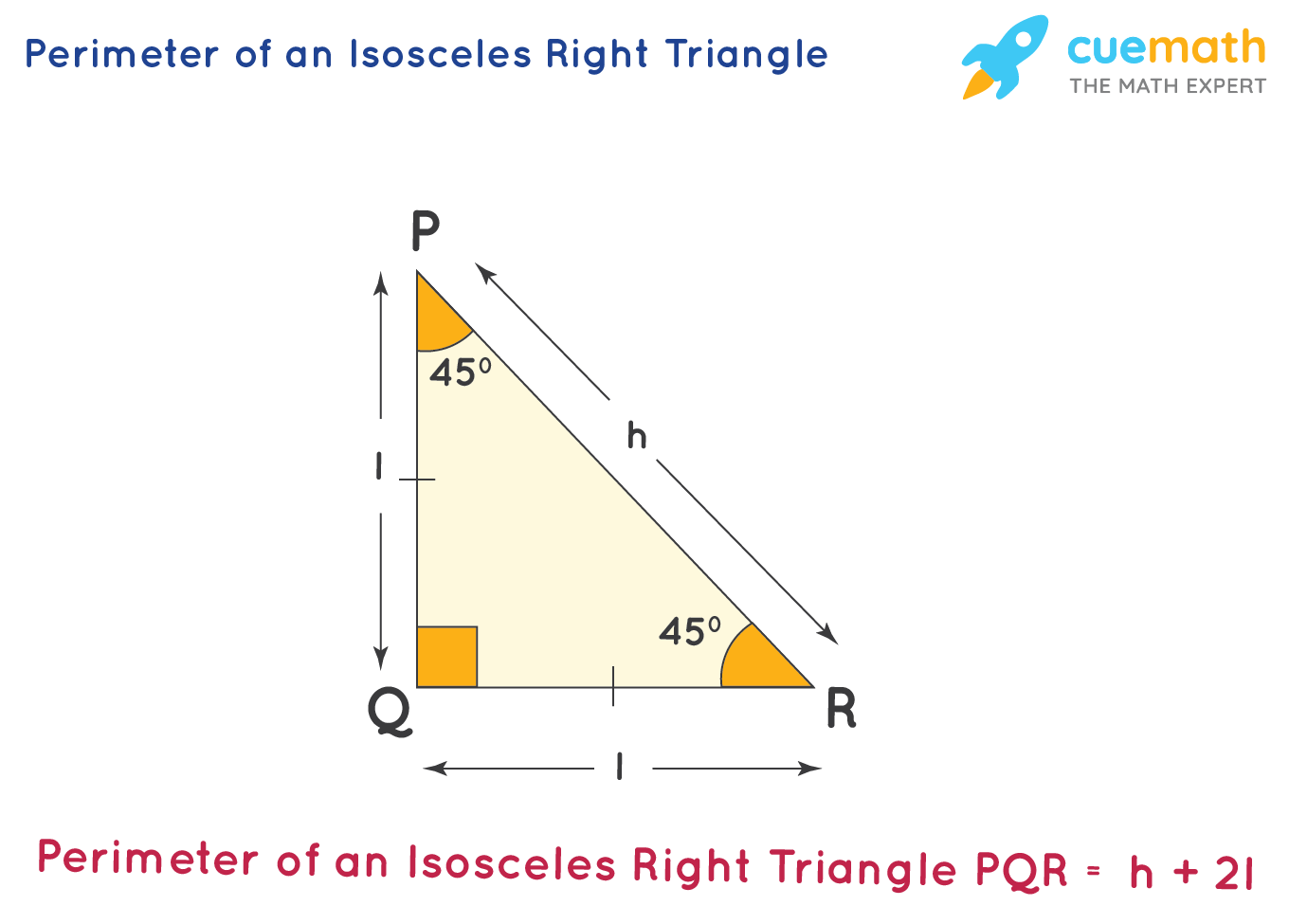
Calculating the Perimeter with Base and Height Known
Calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle when the base and height are known involves a few more steps than when the lengths of the sides are known. The process involves using the Pythagorean Theorem to first determine the lengths of the equal sides (legs) of the triangle. Here\"s how to do it:
- Identify Base and Height: Note the length of the base (b) and the height (h) of the triangle.
- Divide the Base: Divide the base into two equal halves. This is because the height in an isosceles triangle creates two right triangles. Each half of the base will be one side of these right triangles.
- Apply the Pythagorean Theorem: Use the theorem (a² + b² = c²) to find the length of the equal sides. In this case, the height is \"a\", half of the base is \"b\", and the length of the equal sides (c) is what we are trying to find.
- Calculate the Length of the Equal Sides: Rearrange the Pythagorean theorem to solve for c: c = √(a² + b²).
- Calculate the Perimeter: Once you have the length of the equal sides, use the perimeter formula P = 2a + b, where \"a\" is the length of the equal sides and \"b\" is the base.
For example, if the base (b) is 6 cm and the height (h) is 4 cm, the length of each half of the base is 3 cm. Using the Pythagorean theorem, the length of each equal side (c) is √(4² + 3²) = √(16 + 9) = √25 = 5 cm. Therefore, the perimeter would be 2 * 5 cm + 6 cm = 10 cm + 6 cm = 16 cm.
This method is particularly useful in scenarios where the side lengths are not readily available, but the base and height can be measured or calculated.
_HOOK_
Finding the Area and Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
\"Discover the hidden beauty of your surrounding area in this captivating video! From enchanting landscapes to bustling city streets, you\'ll be amazed by the diverse wonders that await you. Join us on this magical journey and fall in love with your area all over again!\"
Using the Pythagorean Theorem in Perimeter Calculation
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental tool in geometry, especially useful in calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle when the length of the base and the height are known. This theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Here\"s how to use it in the context of an isosceles triangle:
- Divide the Triangle: Draw a line from the vertex opposite the base to the midpoint of the base. This divides the isosceles triangle into two right triangles.
- Apply the Pythagorean Theorem: In each right triangle, the height of the isosceles triangle becomes one leg, and half of the base becomes the other leg. The Pythagorean Theorem can be applied here to find the length of the hypotenuse, which is equal to the length of the equal sides of the isosceles triangle.
- Calculate the Length of the Equal Sides: Use the formula c = √(a² + b²), where \"c\" is the length of the equal sides, \"a\" is the height, and \"b\" is half the length of the base.
- Find the Perimeter: Use the perimeter formula P = 2a + b, where \"a\" is the length of the equal sides (found using the Pythagorean Theorem) and \"b\" is the length of the base.
For example, if an isosceles triangle has a height of 4 cm and a base of 6 cm, each right triangle will have sides of 4 cm (height) and 3 cm (half the base). Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the length of the equal sides (c) is √(4² + 3²) = √(16 + 9) = √25 = 5 cm. The perimeter is therefore 2 * 5 cm + 6 cm = 16 cm.
This method demonstrates the versatility of the Pythagorean Theorem in geometry, providing a reliable way to calculate missing dimensions in various shapes, including isosceles triangles.

Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle.
\"Unlock the mathematical secrets of perimeter in this mind-boggling video! Explore the concept from basic shapes to intricate patterns, as we unravel the fascinating world of measurements. Get ready to be engrossed in a world of numbers and geometry that will leave you wanting more!\"
Practical Examples and Problem-Solving
Applying the concepts of perimeter calculation in isosceles triangles can be better understood through practical examples. Let\"s explore a few scenarios to illustrate how to apply these concepts effectively:
Example 1: Known Side Lengths
Suppose an isosceles triangle has two equal sides of 7 cm each, and the base measures 5 cm. To find the perimeter, simply apply the formula P = 2a + b:
- Equal sides (a): 7 cm
- Base (b): 5 cm
- Perimeter (P): 2 * 7 cm + 5 cm = 14 cm + 5 cm = 19 cm
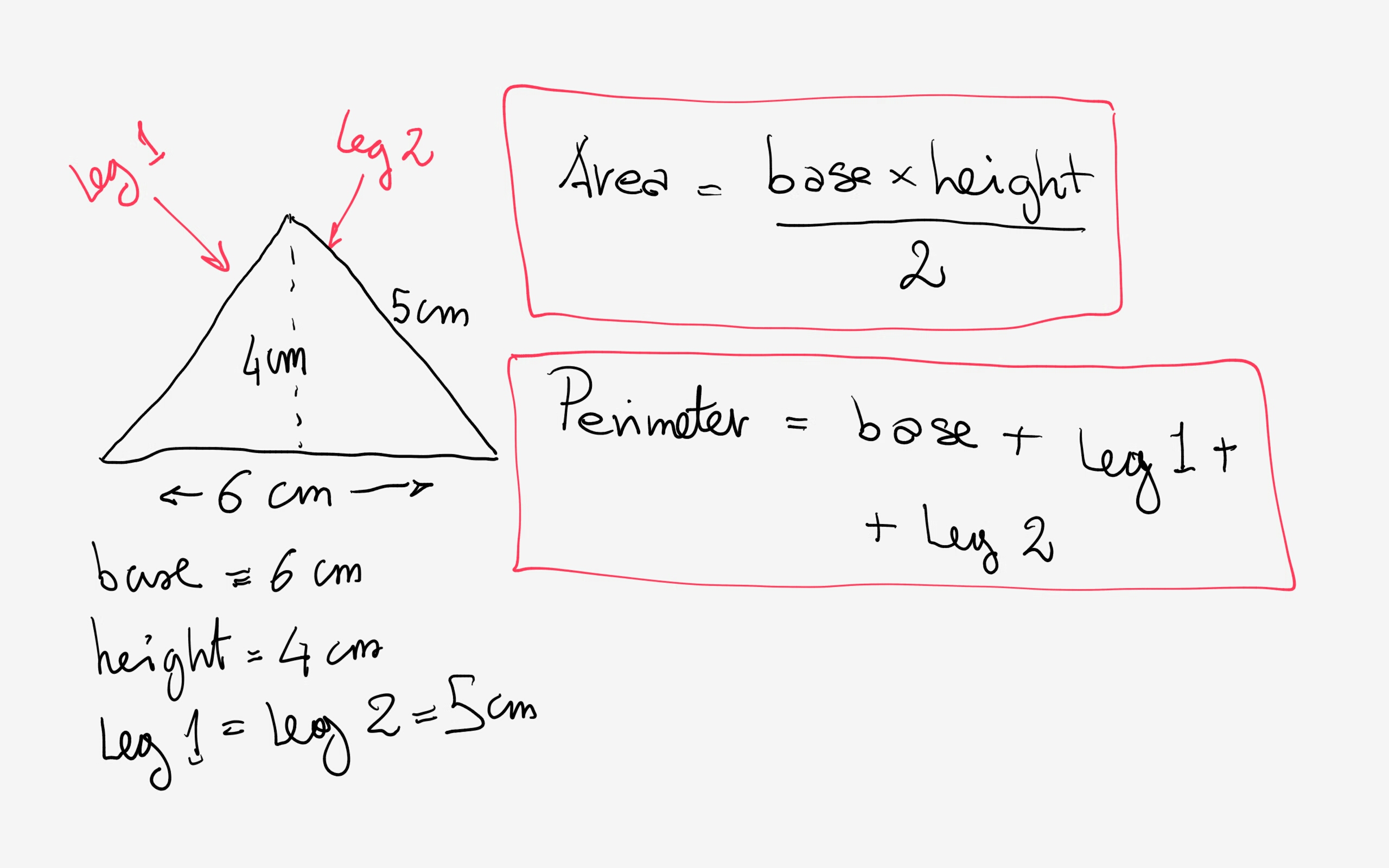
Example 2: Known Base and Height
Consider an isosceles triangle with a base of 8 cm and a height of 6 cm. First, use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the equal sides:
- Half of the base: 8 cm / 2 = 4 cm
- Applying Pythagorean Theorem: a² + b² = c², where a = 6 cm, b = 4 cm.
- Length of the equal sides: c = √(6² + 4²) = √(36 + 16) = √52 ≈ 7.21 cm
- Perimeter: 2 * 7.21 cm + 8 cm ≈ 14.42 cm + 8 cm = 22.42 cm
Problem-Solving Tips
- Verify Measurements: Always double-check the lengths provided. Accuracy is key in geometric calculations.
- Use Correct Formulas: Ensure you are using the appropriate formula based on the information given. The perimeter formula and Pythagorean Theorem are crucial in different scenarios.
- Round Appropriately: If dealing with decimal values, round off to a reasonable number of decimal places, usually two.
- Practice with Variety: Solve problems with different sets of known values (e.g., sides, base, height) to gain a better understanding of the calculations.
These practical examples and tips can help reinforce the understanding of perimeter calculations in isosceles triangles, making it easier to tackle various geometric problems.

Tips and Tricks for Accurate Calculation
Accuracy is key when calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle. Whether you are a student, a teacher, or just someone interested in geometry, here are some helpful tips and tricks to ensure precise calculations:
- Double-Check Measurements: Always verify the measurements of the sides, base, and height. Even a small error in measurement can lead to significant inaccuracies in the final calculation.
- Understand the Formulas: Be clear about which formula to use in different scenarios. The basic perimeter formula is P = 2a + b, but understanding when and how to apply the Pythagorean Theorem is also crucial.
- Use a Calculator: For more complex calculations, especially those involving square roots, use a calculator to ensure accuracy.
- Practice with Different Scenarios: Try calculating the perimeter with various sets of given values (only the sides, only the base and height, etc.) to build confidence and proficiency.
- Rounding Numbers: Be consistent in rounding off numbers, especially when dealing with irrational numbers. Decide on the number of decimal places you\"ll round to before starting your calculation.
- Check Units: Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit. Convert measurements to the same unit before beginning the calculation if necessary.
- Sketch the Triangle: Drawing a rough sketch of the triangle can help visualize the problem and reduce the likelihood of mistakes.
- Review Geometry Basics: A strong understanding of basic geometry can help avoid common errors in calculating perimeters, such as confusing different types of triangles or misapplying formulas.
By following these tips, you can enhance your accuracy in calculating the perimeter of isosceles triangles, making your geometric analysis more reliable and effective.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, certain common mistakes can lead to incorrect results. Being aware of these pitfalls can help in ensuring accurate calculations:
- Confusing Triangle Types: Ensure that the triangle is indeed isosceles. Mistaking it for an equilateral or scalene triangle can lead to using the wrong formula.
- Misapplying the Pythagorean Theorem: The Pythagorean Theorem is applicable only when the base and height are known, and it\"s used to find the length of the equal sides. Using it incorrectly or in the wrong context can result in errors.
- Incorrect Measurements: Errors in measuring the sides, base, or height of the triangle can significantly affect the outcome. Always double-check measurements.
- Mixing Units: Inconsistent units (like mixing centimeters and meters) can lead to incorrect calculations. Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before calculating the perimeter.
- Incorrect Formula Application: The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is calculated as P = 2a + b. Using the wrong values for \"a\" (the equal sides) and \"b\" (the base) is a common error.
- Rounding Errors: Be careful with rounding off numbers during calculations, as this can lead to slight inaccuracies, especially in more complex problems.
- Overlooking Triangle Properties: Remember that in an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the equal sides are also equal. This property can sometimes be useful in calculations.
Avoiding these mistakes will lead to more accurate and reliable results when working with the geometry of isosceles triangles.
READ MORE:
Tools and Resources for Learning More
For those interested in delving deeper into the world of isosceles triangles and their properties, including perimeter calculation, there are several useful tools and resources available:
- Online Calculators: Websites like Omni Calculator provide specialized tools for calculating the perimeter of isosceles triangles. These calculators can handle various inputs like side lengths, base, and height, making the calculation process more convenient and accurate.
- Educational Websites: Platforms such as Khan Academy, SplashLearn, and Cuemath offer comprehensive lessons and exercises on triangles, including isosceles triangles. These resources are great for learners of all levels, from beginners to advanced students.
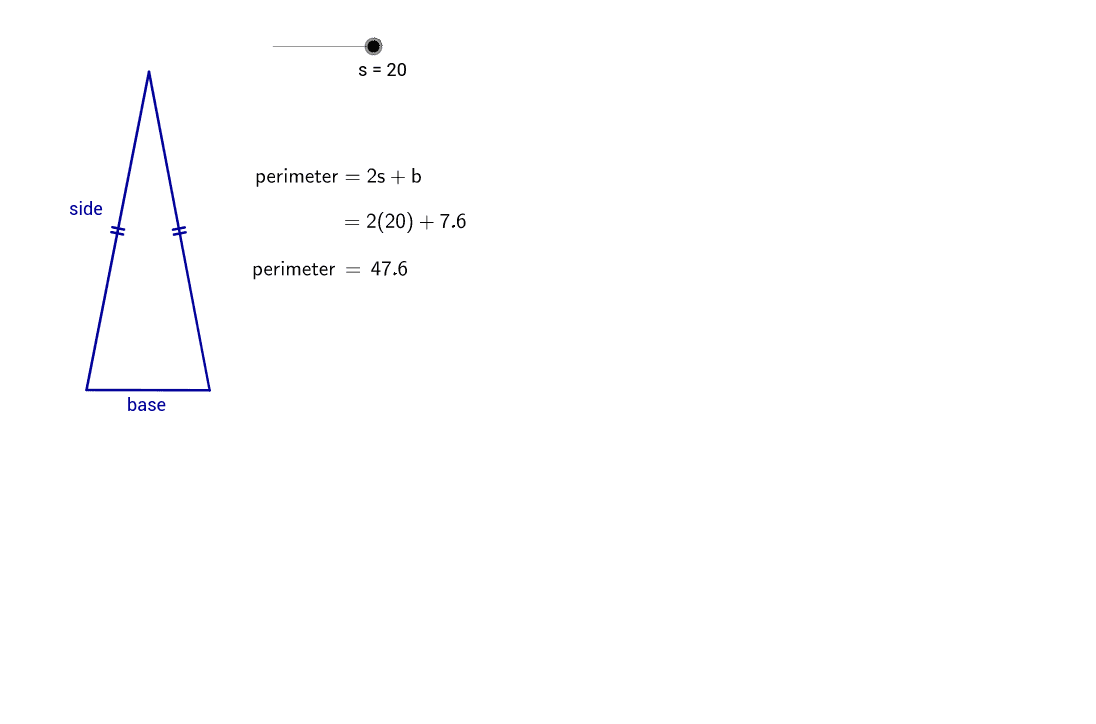
- Math Software: Software like GeoGebra provides interactive geometry tools, allowing users to visualize and manipulate shapes, including isosceles triangles. This can be a great way to understand geometric concepts more deeply.
- Textbooks and Reference Books: Traditional mathematics textbooks often have detailed sections on geometry, including the study of isosceles triangles. Reference books specifically focused on geometry can also provide more in-depth information.
- YouTube Tutorials: Many educators and math enthusiasts share tutorials on YouTube, offering step-by-step guides on how to calculate the perimeter of isosceles triangles and other geometric figures.
- Math Forums and Online Communities: Websites like Stack Exchange or Math Forums are places where you can ask specific questions and get answers from math enthusiasts and experts.
- Mobile Apps: There are various mobile apps available for learning geometry, which include modules or sections specifically dedicated to triangles, including isosceles triangles.
Utilizing these resources can greatly enhance understanding and proficiency in geometry, specifically in calculating the perimeter of isosceles triangles and other related concepts.
Discovering the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is a journey through intriguing geometry. Whether a beginner or an enthusiast, our comprehensive guide makes this exploration both educational and enjoyable, illuminating the fascinating world of triangles.

_HOOK_