Topic perimeter of a irregular shape: Discover the fascinating world of geometry as we delve into the "Perimeter of an Irregular Shape." This journey will unveil practical methods and intriguing insights, making measurement an accessible and enjoyable skill for all.
Table of Content
- How to calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape?
- Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Irregular Shapes
- Basic Methods for Calculating the Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Step-by-Step Guide to Measure Perimeter Using Grid Method
- Advanced Techniques: Perimeter Calculation for Complex Shapes
- Utilizing Technology: Software and Tools for Perimeter Calculation
- YOUTUBE: Calculating Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Practical Applications of Perimeter in Real-World Scenarios
- Common Mistakes and Tips to Avoid Them in Perimeter Calculation
- Interactive Examples and Exercises for Better Understanding
- Additional Resources and Further Reading
How to calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape?
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape, follow these steps:
- Break down the irregular shape into simpler shapes.
- Calculate the perimeter of each individual shape.
- Add up the perimeters of all the simpler shapes to find the total perimeter of the irregular shape.
Let\'s take an example to illustrate the process:
Example: Calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape
| Shape | Perimeter |
|---|---|
| Square | 16 units |
| Triangle | 12 units |
| Rectangle | 18 units |
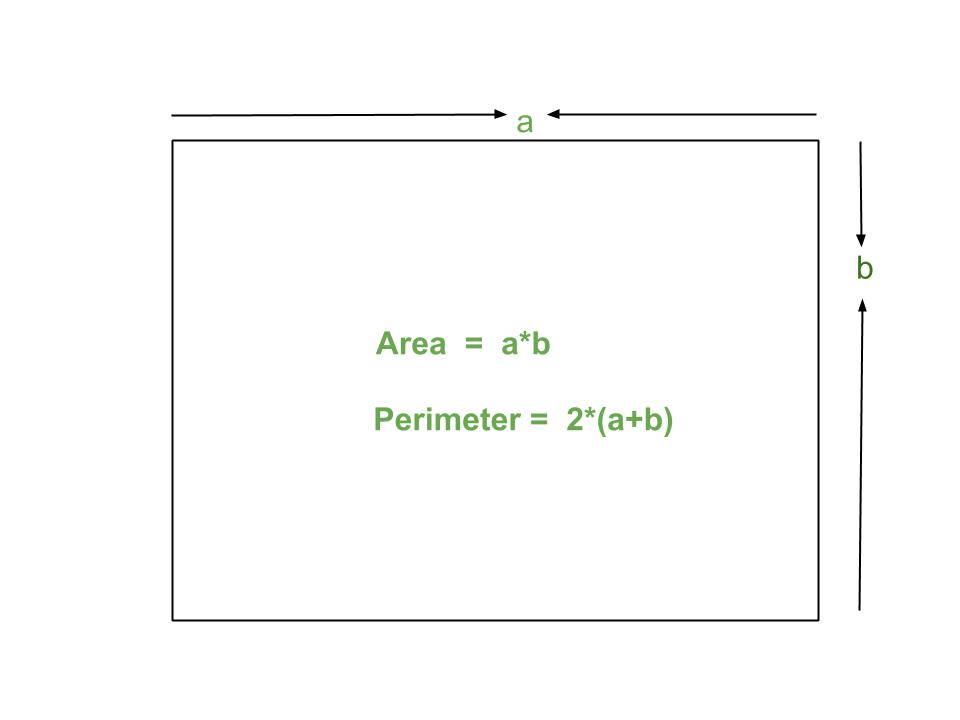
1. Break down the irregular shape into simpler shapes. In this example, we have a square, a triangle, and a rectangle.
- Square: Each side is 4 units in length, so the perimeter is 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 16 units.
- Triangle: The three sides have lengths of 4 units, 5 units, and 3 units, so the perimeter is 4 + 5 + 3 = 12 units.
- Rectangle: The lengths of the sides are 5 units and 4 units, so the perimeter is 2(5 + 4) = 18 units.
2. Calculate the perimeter of each individual shape.
3. Add up the perimeters of all the simpler shapes to find the total perimeter of the irregular shape. In this example, the total perimeter is 16 + 12 + 18 = 46 units.
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular shape is 46 units.
READ MORE:
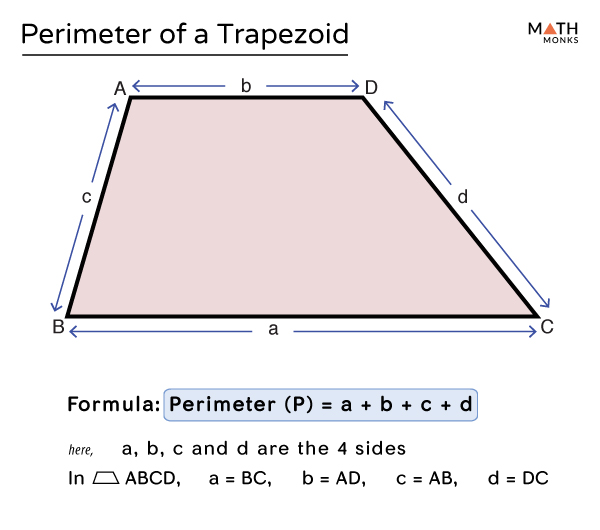
Definition and Importance of Perimeter in Irregular Shapes
The perimeter of an irregular shape is the total length of its boundaries. Unlike regular shapes with uniform sides, irregular shapes consist of various line segments, making their perimeter calculation unique and slightly complex.
Understanding the perimeter of irregular shapes is crucial in various fields. In architecture, it helps in designing spaces with non-standard layouts. In land surveying, it\"s key for accurately defining property boundaries. In education, it enhances geometrical comprehension, aiding students in grasping the diversity of shapes in real-world scenarios.
- Real Estate: Determining property lines and fencing requirements.
- Construction: Accurate material estimation for irregularly shaped structures.
- Landscaping: Planning garden layouts and irrigation systems.
- Mathematical Education: Teaching problem-solving and spatial reasoning.
Overall, the ability to calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes not only deepens one\"s understanding of geometry but also has practical applications in everyday life, highlighting its importance across multiple disciplines.
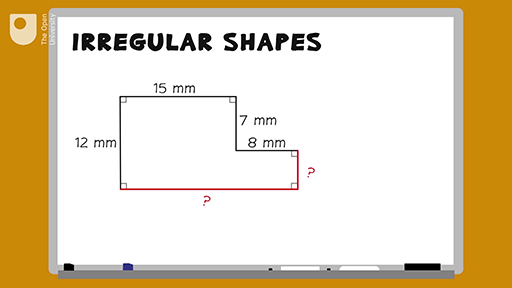
Basic Methods for Calculating the Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape can be a bit more challenging than a regular shape, but there are several basic methods to approach it:
- Summing Line Segments: Measure each side\"s length of the irregular shape and sum them up. This method is straightforward but requires precision in measurement, especially for shapes with many sides.
- Using a Grid: Place the shape on a grid and approximate the length of each side by counting grid squares. This method is less precise but useful for irregular shapes with curved boundaries.
- String and Ruler Method: Trace the perimeter with a string, then straighten the string and measure its length with a ruler. This approach works well for irregular shapes with smooth curves.
- Geometric Decomposition: Break down the irregular shape into a combination of regular shapes, calculate the perimeter of each, and sum them up. This method is effective for complex shapes but requires an understanding of geometry.
Each method has its advantages and suitability depending on the shape\"s complexity and the required precision level. Understanding these basic methods provides a solid foundation for accurately calculating the perimeters of various irregular shapes.
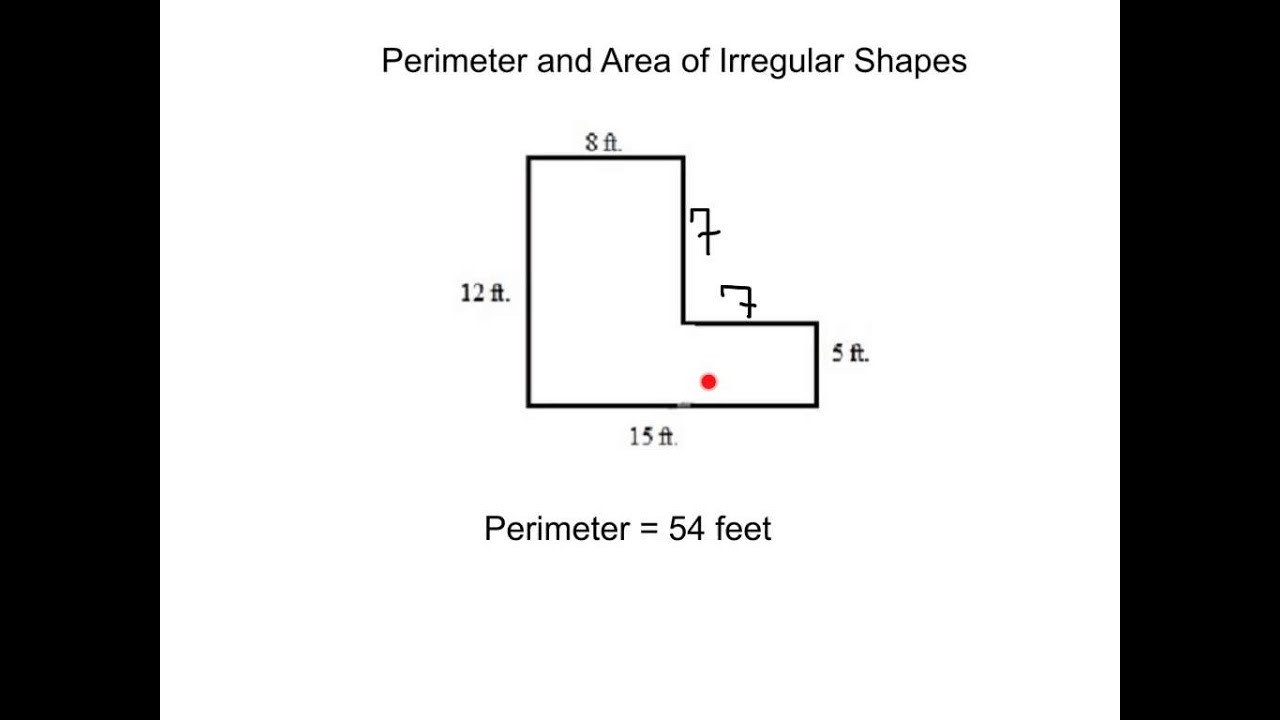
Step-by-Step Guide to Measure Perimeter Using Grid Method
The grid method is a practical approach for estimating the perimeter of irregular shapes, especially when precision measurement tools are unavailable. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using this method:
- Prepare a Grid: Place the irregular shape on a grid paper or draw a grid over it. Ensure the grid squares are of known dimensions (e.g., 1 cm x 1 cm).
- Trace the Shape: Carefully trace the outline of the shape onto the grid. If the shape is 3-dimensional, flatten it onto the grid as accurately as possible.
- Count Full Squares: Count the number of full grid squares inside the shape\"s perimeter. This provides a base measurement.
- Estimate Partial Squares: For squares that the shape partially covers, estimate their coverage. For example, if a square is approximately half-covered, count it as 0.5.
- Sum Up the Squares: Add the counts of full and partial squares. This gives the total number of square units that approximate the perimeter.
- Convert to Length: Multiply the total square units by the length of one side of a grid square. This converts the unit count into a linear measurement, giving an estimated perimeter.
While this method may not provide exact measurements, especially for shapes with curved edges, it offers a quick and reasonably accurate way to estimate the perimeter of irregular shapes.

Advanced Techniques: Perimeter Calculation for Complex Shapes
For complex or highly irregular shapes, advanced techniques are required to calculate the perimeter accurately. These methods often involve more sophisticated mathematical tools and technologies:
- Digital Imaging and Analysis: By using digital photographs or scans of the shape, software can analyze the image and accurately measure the perimeter. This method is especially useful for shapes with intricate or curved boundaries.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology is used for mapping and surveying land areas, and can be employed to calculate the perimeters of irregular shapes on a large scale, such as property boundaries or natural formations.
- Mathematical Algorithms: Certain algorithms, such as those using calculus or coordinate geometry, can provide precise measurements. These are particularly effective for shapes that can be mathematically defined or decomposed into simpler components.
- 3D Modeling Software: For three-dimensional irregular shapes, 3D modeling tools can be used to create a virtual model of the object, allowing for accurate measurement of its perimeter.
These advanced techniques require specialized knowledge and tools but offer a higher degree of accuracy and efficiency, particularly for shapes that are too complex for basic measurement methods.

_HOOK_
Utilizing Technology: Software and Tools for Perimeter Calculation
In the digital age, various software and tools have been developed to simplify and enhance the accuracy of calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes. These technologies range from simple applications to more complex systems:
- Graphing Software: Tools like GeoGebra or Desmos allow for the plotting of shapes and automatic calculation of their perimeters. They are user-friendly and ideal for educational purposes.
- Image Analysis Tools: Software such as ImageJ can analyze photographs or scanned images of shapes to calculate perimeters, especially useful for irregularly shaped objects in fields like biology or geography.
- CAD Software: Computer-Aided Design programs like AutoCAD provide precise tools for designing and measuring complex shapes, widely used in engineering and architecture.
- GIS Systems: Geographic Information Systems are powerful tools for large-scale mapping projects, capable of calculating perimeters of natural and man-made features on the earth\"s surface.
- Mobile Apps: There are various mobile applications available that can estimate the perimeter by allowing users to plot points along the shape’s boundary. These apps are convenient for quick estimations on the go.
These technological solutions not only provide more accurate measurements but also make the process of calculating perimeters faster and more efficient, catering to a wide range of professional and educational needs.

Calculating Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
\"Discover the secrets of your favorite tourist area in this captivating video! From stunning landscapes to hidden gems, get ready to be mesmerized by the beauty that awaits you.\"
Practical Applications of Perimeter in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of perimeter, especially for irregular shapes, finds numerous practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Architecture and Construction: Accurate perimeter measurements are crucial for designing building layouts, especially for non-standard, irregularly shaped structures.
- Landscaping and Gardening: Determining the perimeter of garden beds or lawns helps in planning the layout and calculating the materials needed, like fencing or edging.
- Geography and Environmental Science: Measuring the perimeter of natural features like lakes, forests, and islands is essential for ecological studies and resource management.
- Sports Fields and Playgrounds: Creating sports fields or playgrounds often requires calculating the perimeter for proper space allocation and safety planning.
- Fashion and Textile Design: In designing clothing or textiles, understanding the perimeter of irregular shapes aids in pattern making and fabric cutting.
- Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors frequently work with irregular shapes, and understanding their perimeters can influence the design and stability of their creations.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers use perimeter calculations to plan crop areas, irrigation systems, and fencing, particularly in irregularly shaped fields.
These applications demonstrate the significance of understanding and accurately calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes across diverse fields and industries.
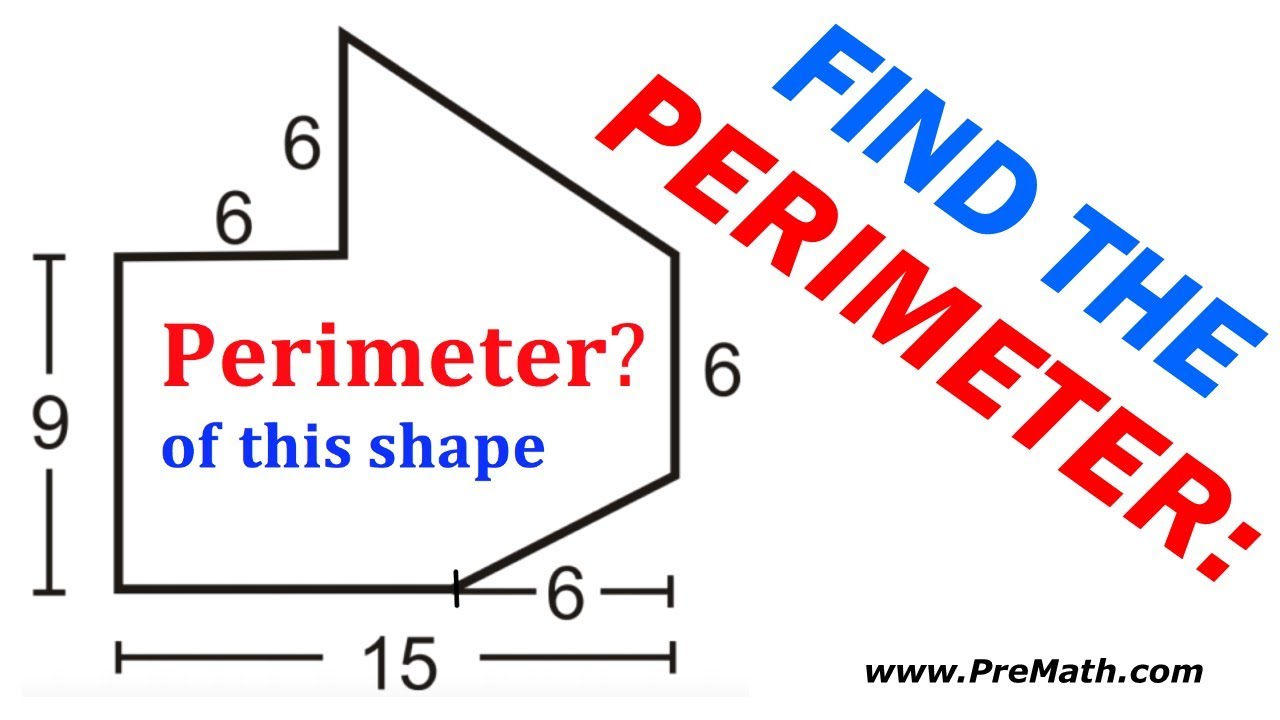
Junior Cert Maths: Finding the Perimeter of an Irregular Shape
\"Struggling with Junior Cert Maths? Look no further! This video is your ultimate guide to acing your exams. With step-by-step explanations and helpful tips, you\'ll increase your confidence in no time!\"
Common Mistakes and Tips to Avoid Them in Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes can be tricky, and common mistakes can lead to inaccurate measurements. Here are some typical errors and tips on how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Measurement: Using improper or imprecise measuring tools can lead to errors. Tip: Always use a well-calibrated measuring instrument and measure each side twice for accuracy.
- Overlooking Small Segments: In complex shapes, small segments can be easily missed. Tip: Break the shape down into smaller, manageable sections to ensure no side is overlooked.
- Rounding Errors: Excessive rounding off can accumulate significant errors. Tip: Keep decimal places consistent and only round off the final result.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: It\"s common to confuse these two measurements. Tip: Remember, perimeter is the measure of the boundary length, while area is the measure of the surface.
- Ignoring Units: Inconsistent units can lead to incorrect results. Tip: Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before adding them up.
- Assuming Regularity: Assuming irregular shapes have regular properties can lead to errors. Tip: Treat each side as unique and measure accordingly.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls and applying these tips, one can significantly improve the accuracy of perimeter calculations for irregular shapes.

Interactive Examples and Exercises for Better Understanding
Interactive exercises are a great way to enhance understanding of the concepts related to the perimeter of irregular shapes. Below are some examples and exercises that can be used in educational settings or for self-learning:
- Trace and Measure: Provide a set of irregular shapes on paper. Ask learners to trace each shape and then use a ruler to measure and calculate the perimeter.
- Online Simulations: Utilize online tools that allow manipulation of points to create irregular shapes. These tools can automatically calculate the perimeter, offering immediate feedback.
- Perimeter Hunt: Create a real-world scavenger hunt where students have to find objects of irregular shapes and estimate their perimeters using different methods.
- Group Projects: Assign a project where students design a garden or a playground, requiring them to calculate perimeters of various sections.
- Worksheet Challenges: Design worksheets with increasingly complex shapes. This step-by-step approach helps in gradually building the skill of perimeter calculation.
- Software Applications: Encourage the use of CAD or graphic design software for advanced students to create and measure irregular shapes, fostering a deeper understanding of the concept.
These interactive activities are designed to make the learning process engaging and hands-on, thereby improving comprehension and practical application of perimeter calculation for irregular shapes.

READ MORE:
Additional Resources and Further Reading
To deepen your understanding of calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes, the following resources and reading materials are highly recommended:
- Geometry Textbooks: Look for chapters on perimeter and irregular shapes in standard geometry textbooks. These often provide detailed explanations and examples.
- Online Educational Platforms: Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera offer courses and tutorials focused on geometry and measurement, including perimeter calculations.
- Mathematical Journals: Articles and papers in mathematical journals often explore complex concepts related to geometry and can provide advanced insights into perimeter calculations.
- Educational Software: Geometry software tools like GeoGebra offer interactive ways to explore and understand the perimeter of various shapes.
- YouTube Tutorials: Numerous educators and mathematicians share tutorials on geometry topics, which can be a visually engaging way to learn about perimeter calculations.
- Workbooks and Practice Sheets: Practice is key to mastering geometry concepts. Look for workbooks or online worksheets that focus on perimeter problems.
These resources provide a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical exercises, catering to different learning styles and advancing your understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
In conclusion, mastering the calculation of the perimeter of irregular shapes opens a world of practical applications and enriches our understanding of geometry, making it a valuable skill in various professional and everyday contexts.

_HOOK_