Topic how to get perimeter from area: Unlocking the secrets of geometry, "How to Get Perimeter from Area" guides you through the intriguing process of calculating perimeters using area measurements, a fundamental skill in both academic and real-world scenarios.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between the area and perimeter of a square?
- 1. Basic Concepts: Understanding Area and Perimeter
- 2. The Relationship Between Area and Perimeter
- 3. Calculating Perimeter from Area for Regular Shapes
- 4. Strategies for Irregular Shapes: Estimations and Approximations
- 5. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculations
- YOUTUBE: Finding Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle Guide
- 6. Real-World Applications: Practical Examples
- 7. Advanced Techniques: Using Algebra and Geometry
- 8. Tools and Resources for Effective Learning
- 9. Practice Problems and Solutions
- 10. Additional Reading and Educational Material
What is the relationship between the area and perimeter of a square?
The relationship between the area and perimeter of a square can be explained through the following steps:
- Step 1: Understand the formula for calculating the area and perimeter of a square.
- Step 2: Understanding the relationship between the area and perimeter of a square.
- The perimeter (P) = 4 times the length of one side (s).
- The area (A) = the square of the length of one side (s).
- Step 3: Analyzing the relationship further.
The area of a square is given by the formula A = s2, where \'s\' represents the length of one side of the square.
The perimeter of a square is given by the formula P = 4s, where \'s\' represents the length of one side of the square.
By analyzing the formulas, we can observe that the perimeter of a square is directly proportional to the length of its sides, while the area of a square is proportional to the square of its side length.
Mathematically, we can express this relationship as:
As the length of one side of a square increases, both the area and perimeter of the square increase.
For example, if we double the length of one side of a square, the perimeter will also double (it becomes 2P), while the area will quadruple (it becomes 4A).
Conversely, if we halve the length of one side of a square, the perimeter will also halve (it becomes P/2), while the area will decrease to one-fourth (it becomes A/4).
Thus, the relationship between the area and perimeter of a square is that the perimeter is directly proportional to the length of one side, while the area is proportional to the square of the length of one side.
READ MORE:
1. Basic Concepts: Understanding Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, each representing different properties of shapes. The area is the amount of space enclosed within a shape, typically measured in square units. In contrast, the perimeter refers to the total distance around the boundary of a shape, measured in linear units.
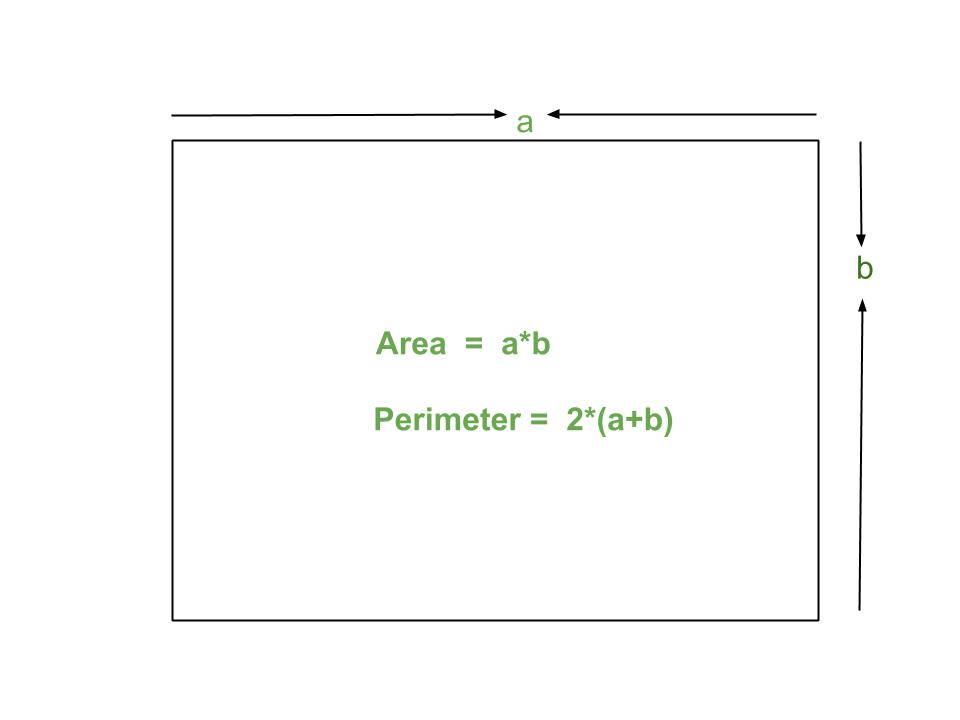
- Calculating Area: The method for calculating area varies based on the shape. For example, the area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width (Area = length × width).
- Calculating Perimeter: Perimeter calculation also differs by shape. For rectangles, it is the sum of all sides (Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)). For a circle, known as the circumference, it is calculated using the radius (Circumference = 2 × π × radius).
Understanding the formulas and relationships between area and perimeter is crucial for solving various geometric problems. Each shape, whether a rectangle, square, circle, or triangle, has specific formulas to calculate its area and perimeter.
- Rectangle Example: To find a rectangle\"s perimeter from its area, you would first determine one of the missing dimensions using the area formula, and then apply the perimeter formula.
- Circle Example: The perimeter (circumference) of a circle can be found from its area by applying the formula C = 2 × √(π × area).
- Square Example: For a square, the perimeter can be found from its area by first calculating the side length (side = √area) and then applying the perimeter formula (Perimeter = 4 × side).
This section sets the foundation for understanding how area and perimeter are interconnected and how they can be calculated from one another in various geometric shapes.

2. The Relationship Between Area and Perimeter
The relationship between area and perimeter is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Understanding this relationship is key to solving various mathematical problems and real-world applications. While area measures the space inside a shape, perimeter refers to the distance around it. Their calculation methods and units of measurement are distinct yet interconnected.
- Area: Area is the size of the surface enclosed within the boundaries of a shape, measured in square units (e.g., square meters).
- Perimeter: Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a shape, measured in linear units (e.g., meters).
The relationship between area and perimeter can be explored through different shapes:
- Squares and Rectangles: For these shapes, knowing the area can help deduce one of the dimensions if the other is known, which can then be used to calculate the perimeter.
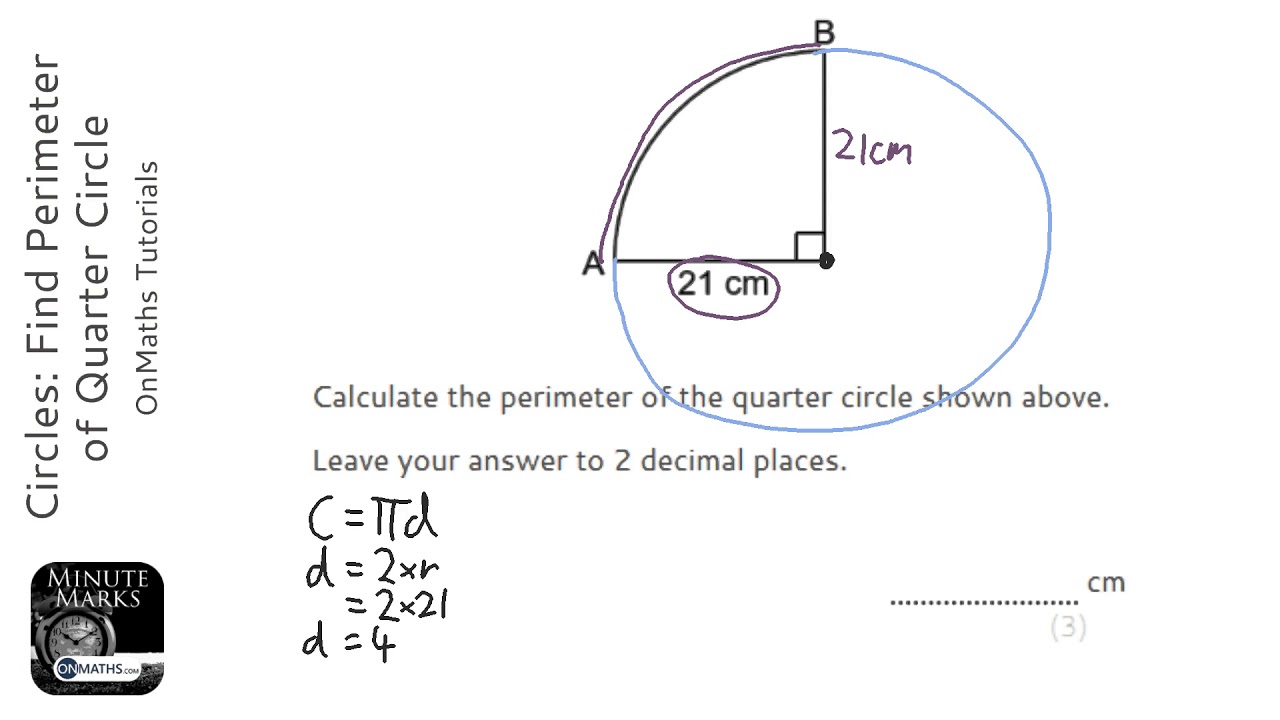
- Circles: The perimeter (circumference) of a circle can be calculated from its area using the formula C = 2 × √(π × area).
- Complex Shapes: In more complex shapes, the relationship between area and perimeter becomes less direct but still follows the principles of linear and square measurements.
Understanding the differences and connections between area and perimeter is crucial for deeper comprehension of geometry and its practical applications, from designing a garden to architecture and beyond.

3. Calculating Perimeter from Area for Regular Shapes
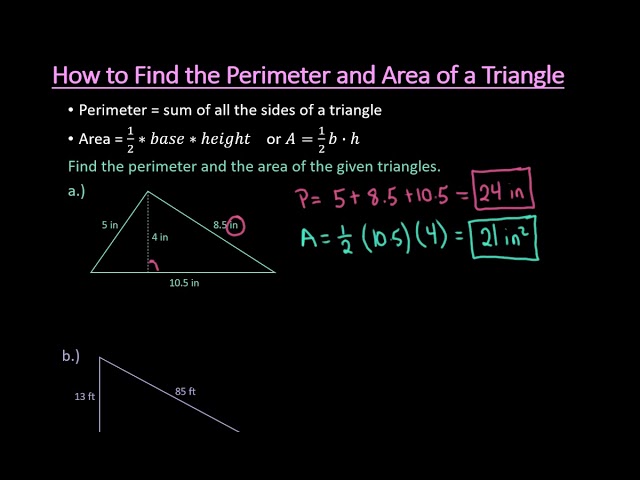
Calculating the perimeter from the area of regular shapes involves specific formulas depending on the shape in question. Regular shapes like squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles have set formulas that make this calculation straightforward.
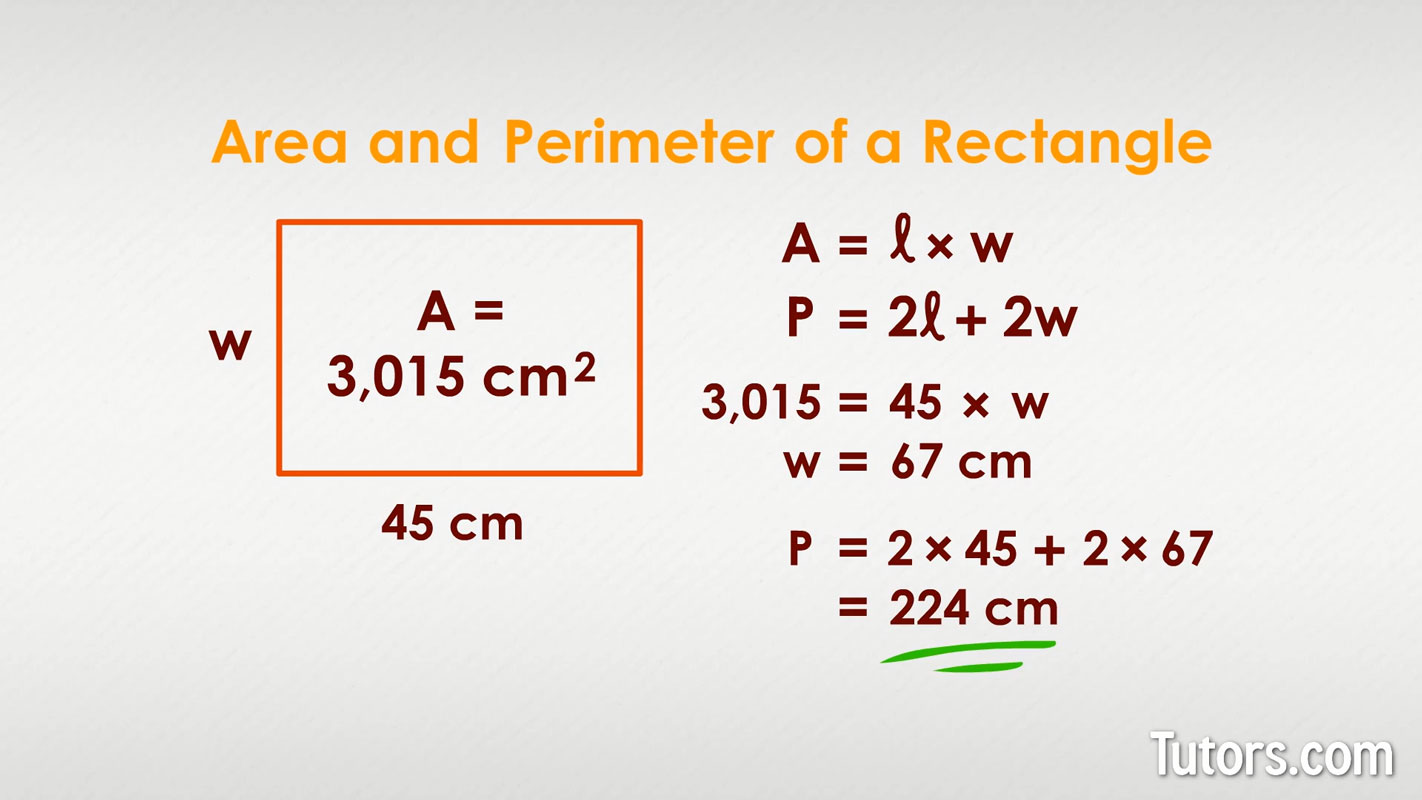
- Rectangles: For a rectangle, if you know one side and the area, you can find the other side (Area = width × length) and then calculate the perimeter (Perimeter = 2 × (width + length)).
- Circles: To find the circumference (perimeter) of a circle from its area, use the formula: C = 2 × √(π × area).
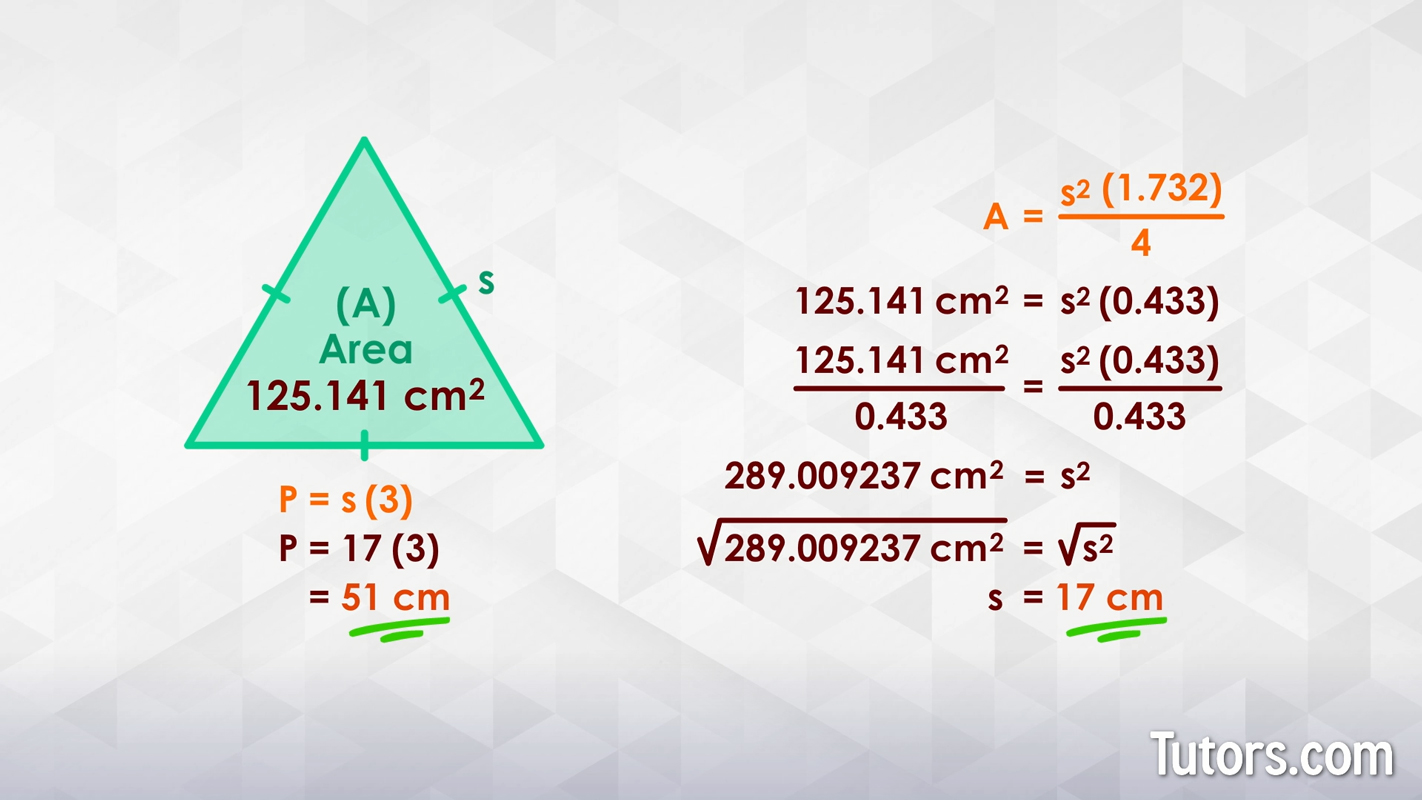
- Squares: Given the area of a square, the side can be found by taking the square root of the area (Side = √area). The perimeter is then calculated as 4 times the side length.
- Triangles: For equilateral triangles, if the area is known, the side can be determined using appropriate formulas, which then helps in calculating the perimeter.
These methods leverage the basic geometric properties of regular shapes, making it possible to derive one measurement from another. Understanding these relationships is key to solving a variety of geometric problems.
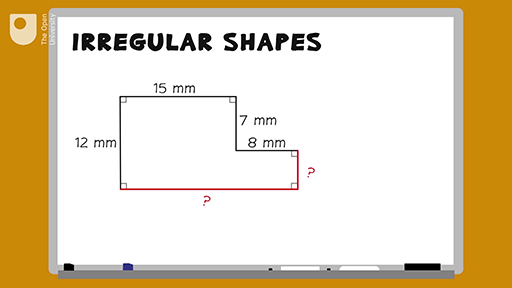
4. Strategies for Irregular Shapes: Estimations and Approximations
Calculating the perimeter from the area of irregular shapes often requires more complex strategies than those used for regular shapes. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes don\"t have standard formulas for directly calculating perimeter from area. Estimation and approximation techniques become crucial in these scenarios.
- Estimation Techniques: When dealing with irregular shapes, one common approach is to approximate the shape to the nearest regular shape. This involves simplifying the irregular shape into a series of regular shapes (like triangles, rectangles, or circles), calculating the area and perimeter for each, and then summing up these measurements to get an overall estimate.
- Grid Method: Another method involves overlaying a grid on the shape and counting the number of squares that approximately cover the shape. The perimeter can then be estimated based on the dimensions of the grid squares.
- Composite Shapes: For shapes that are a combination of regular shapes, breaking down the composite shape into its regular components and then calculating the area and perimeter of each component separately before adding them up is an effective strategy.
- Advanced Mathematical Methods: For more complex irregular shapes, using calculus or numerical methods to approximate the area and perimeter can be necessary. These methods are particularly useful in professional fields such as architecture and engineering.
While these methods may not provide exact values, they offer practical ways to approximate the perimeter of irregular shapes using their areas, especially when precision is not the primary concern.

_HOOK_
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry, but it\"s also prone to certain common mistakes, especially when dealing with area and perimeter. Being aware of these mistakes can help improve accuracy in mathematical problem-solving.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: A common mistake is confusing the concepts of perimeter and area. The perimeter is the distance around a shape, while the area is the space within it. Mixing these up can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Incorrect Unit Conversion: When calculating perimeter, ensure that all measurements are in the same unit. Inaccurate conversions between different units (like inches to feet) can lead to erroneous results.
- Overlooking Shape Properties: Each shape has specific properties that dictate how its perimeter should be calculated. For example, the perimeter of a square is 4 times one of its sides, but this formula cannot be applied to irregular shapes.
- Misapplying Formulas: Applying a formula meant for one shape to another different shape is a frequent error. For instance, using the formula for the circumference of a circle (C=2πr) for a square would give an incorrect perimeter.
- Miscalculating Dimensions: For complex shapes, like composite figures, miscalculating the dimensions of individual parts can lead to incorrect total perimeter calculations.
- Ignoring Scale: When working with diagrams or maps, it\"s essential to take the scale into account. Neglecting the scale factor can result in significant discrepancies in perimeter calculations.
Being mindful of these common errors and double-checking calculations can greatly enhance the accuracy of perimeter estimations and computations.

Finding Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle Guide
\"Discover the beauty and versatility of the rectangle in our captivating video! From elegant architecture to stunning artwork, this shape will amaze you with its endless possibilities. Come witness the enchanting world of rectangles.\"
Finding Perimeter of a Square with Known Area
\"Experience the perfect harmony and symmetry of the square in our mesmerizing video! Immerse yourself in the captivating symmetry of this shape, as it effortlessly blends beauty and balance. Dive into the world of squares and be amazed!\"
6. Real-World Applications: Practical Examples
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter from the area is not just a mathematical exercise; it has various practical applications in real life. These applications span across different fields, showcasing the versatility and importance of this aspect of geometry.
- Architecture and Construction: In architecture, knowing the perimeter of a building or land plot, derived from its area, is crucial for planning construction projects, fencing, and landscaping.
- Interior Design: Calculating the perimeter from the area is essential in interior design for determining the amount of materials needed for flooring, painting walls, or installing baseboards.
- Agriculture and Land Management: Farmers and land managers use these calculations to determine the fencing required for a plot of land, especially when only the area is known initially.
- Sports and Recreation: The perimeter calculation is useful in sports for designing tracks and fields. Knowing the area of a circular track, for instance, helps in determining its circumference, which is essential for track and field events.
- Education and Learning: These concepts are fundamental in education, helping students understand the relationship between different geometric properties through practical examples.
These examples show how the conversion of area to perimeter is not just theoretical but a necessary skill in various professional and everyday contexts.
7. Advanced Techniques: Using Algebra and Geometry
Advanced techniques in algebra and geometry significantly enhance the process of calculating perimeter from area. These techniques involve more sophisticated mathematical concepts and can be applied to a wide range of shapes, from basic to complex.
- Algebraic Manipulation: Algebra plays a crucial role in perimeter calculations, especially when dealing with unknown dimensions. For instance, in a rectangle, if the area is known and one dimension is given, algebra can be used to find the missing dimension, which then helps in calculating the perimeter.
- Geometric Properties: Understanding the geometric properties of shapes, such as the relationship between the sides of a rectangle or the radius of a circle, is essential. For circles, the perimeter (circumference) can be calculated from the area using the formula C=2π√(A/π).
- Use of Theorems: The application of geometric theorems, such as Pythagoras\" theorem in right-angled triangles, aids in finding missing lengths which are then used to calculate the perimeter.
- Calculus for Irregular Shapes: For more irregular and complex shapes, calculus might be required. This can involve integrating along a curve to find the perimeter.
These advanced techniques underscore the importance of a strong foundation in algebra and geometry for accurately calculating perimeters from given areas.

8. Tools and Resources for Effective Learning
For those looking to master the concepts of calculating perimeter from area, a variety of educational tools and resources are available. These resources cater to different learning styles, providing interactive and comprehensive approaches to understanding this fundamental aspect of geometry.
- Online Calculators: Websites like Omni Calculator offer specific calculators for different shapes, making it easier to understand the relationship between area and perimeter. These tools are particularly useful for visualizing how changes in dimensions affect area and perimeter.
- Educational Websites: Khan Academy provides in-depth lessons and practice exercises on perimeter and area. Their resources cover a wide range of shapes and include interactive problems to enhance understanding.
- YouTube Tutorials: Channels like The Organic Chemistry Tutor offer video tutorials that provide step-by-step instructions and examples, making complex concepts more accessible.
- Geometry Software: Tools like GeoGebra offer a dynamic way to explore geometric concepts, allowing users to manipulate shapes and immediately see the effects on area and perimeter.
- Textbooks and Workbooks: Traditional learning materials like textbooks and workbooks are still valuable resources, offering structured and detailed explanations of geometric principles.
By combining these tools and resources, learners can develop a strong, practical understanding of how to calculate the perimeter from area in various contexts.
9. Practice Problems and Solutions
Enhance your understanding of calculating perimeter from area with these practice problems and solutions. Engaging in practical examples helps consolidate learning and improve problem-solving skills.
- Rectangular Land Plot: A rectangular plot of land is 20 miles wide and covers an area of 500 square miles. Find its perimeter. Solution: Use the formula A = width × length to find the length, then apply P = 2 × (width + length) to get the perimeter.
- Circle Perimeter from Area: Determine the circumference of a circle with an area of 1,000 km². Solution: Apply the formula C = 2 × π × √(area/π).
- Quiz Question: Explore the relationship between the area and perimeter of a square. For example, if the area of a square is given, how can you find its perimeter?
- Rectangle with Known Area: Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with an area of 20 m² and a length of 4 m. Solution: First, find the width by dividing the area by the length, then use P = 2 × (width + length) to find the perimeter.
These problems are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to derive perimeter from area in different geometric scenarios.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
10. Additional Reading and Educational Material
To deepen your understanding of how to calculate perimeter from area, there are numerous educational resources and materials available. These can enhance your learning experience and provide further insight into various geometric concepts.
- Online Tutorials and Courses: Khan Academy offers comprehensive tutorials on perimeter and area, including interactive exercises and quizzes. Their material covers a wide range of topics, from basic to advanced levels.
- Practical Guides and Calculators: Websites like Tutors.com and Omni Calculator provide practical guides and easy-to-use calculators for calculating the perimeter from the area of various shapes, including rectangles, squares, and circles. These resources are particularly useful for quick calculations and understanding the application of formulas.
- Video Tutorials: YouTube channels such as The Organic Chemistry Tutor offer video tutorials that explain geometric concepts in an easy-to-understand manner. These videos can be especially helpful for visual learners.
- Books and Textbooks: Traditional textbooks and geometry books are invaluable resources for detailed explanations and structured learning. They often include practice problems with solutions, helping reinforce concepts learned online or in the classroom.
Combining these resources can provide a well-rounded understanding of geometry, particularly in the context of calculating perimeter from area.
Mastering the skill of calculating perimeter from area opens doors to a world of geometric understanding and practical application, enhancing both academic learning and real-world problem-solving abilities.