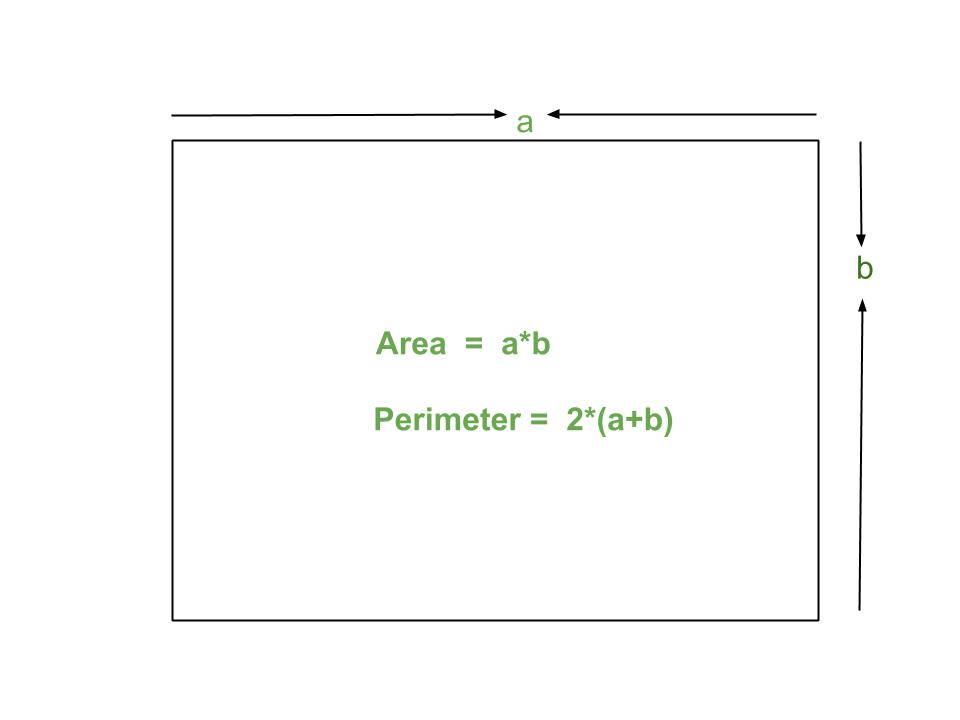
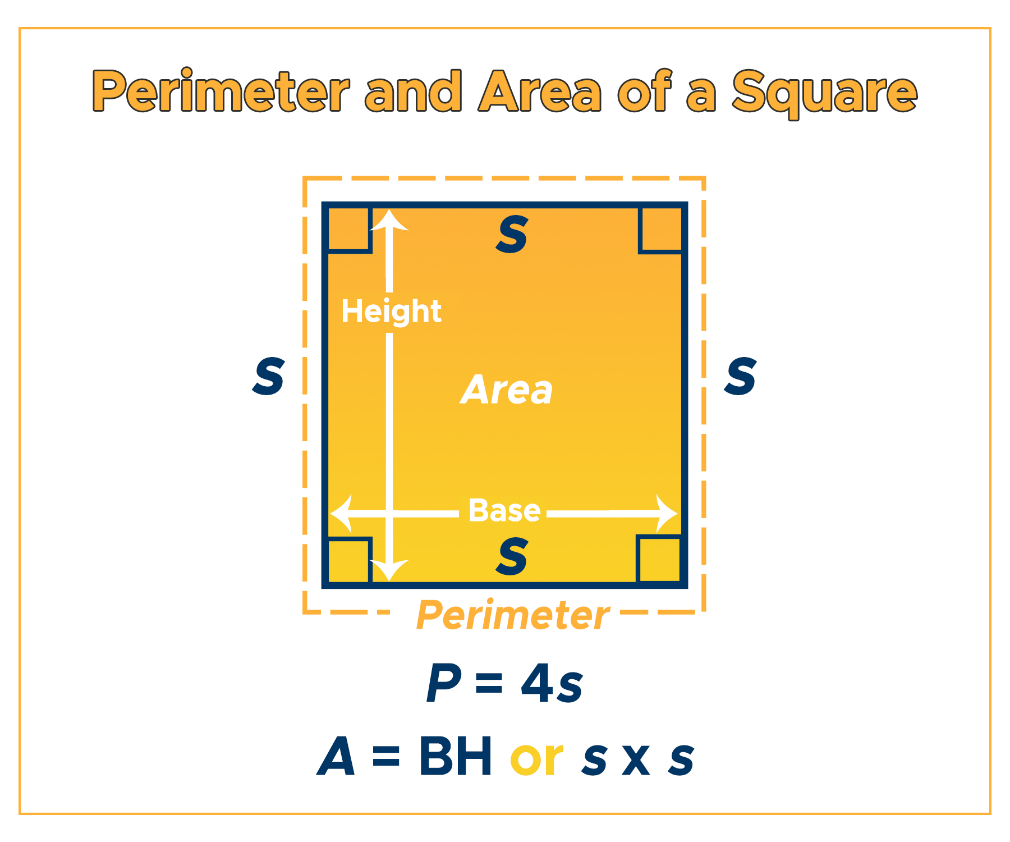
Topic perimeter area square: Dive into the world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on "Perimeter Area Square", unlocking the secrets of these fundamental concepts in a simple, engaging way.
Table of Content
- What is the formula to find the perimeter and area of a square?
- Definition of a Square
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Square
- Formula for the Area of a Square
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Square
- Calculating Perimeter: Step-by-Step Guide
- Calculating Area: Step-by-Step Guide
- Real-World Applications of Square Perimeter and Area
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Tools and Calculators for Square Measurements
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Teaching Resources and Strategies for Educators
- Frequently Asked Questions About Square Perimeter and Area
What is the formula to find the perimeter and area of a square?
The formula to find the perimeter of a square is:
- Multiply the length of one side of the square by 4.
The formula to find the area of a square is:
- Square the length of one side of the square.
Using these formulas, you can calculate the perimeter and area of a square.
READ MORE:
Definition of a Square
A square is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, characterized by four equal sides and four right angles. Each angle in a square measures 90 degrees, making it a regular polygon with symmetrical properties. The uniqueness of a square lies in its equal sides and angles, distinguishing it from other quadrilaterals like rectangles or rhombuses.
- Equal Sides: All four sides of a square have the same length.
- Equal Angles: Each of the four angles in a square is a right angle (90 degrees).
- Symmetrical: A square has two lines of symmetry, dividing it into mirror-image halves.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
In geometry, the properties of a square are often used to solve problems related to area and perimeter, where the area is the space contained within the square and the perimeter is the total length of its boundaries. A square\"s simplicity and symmetry make it a fundamental shape in both mathematics and real-world applications.

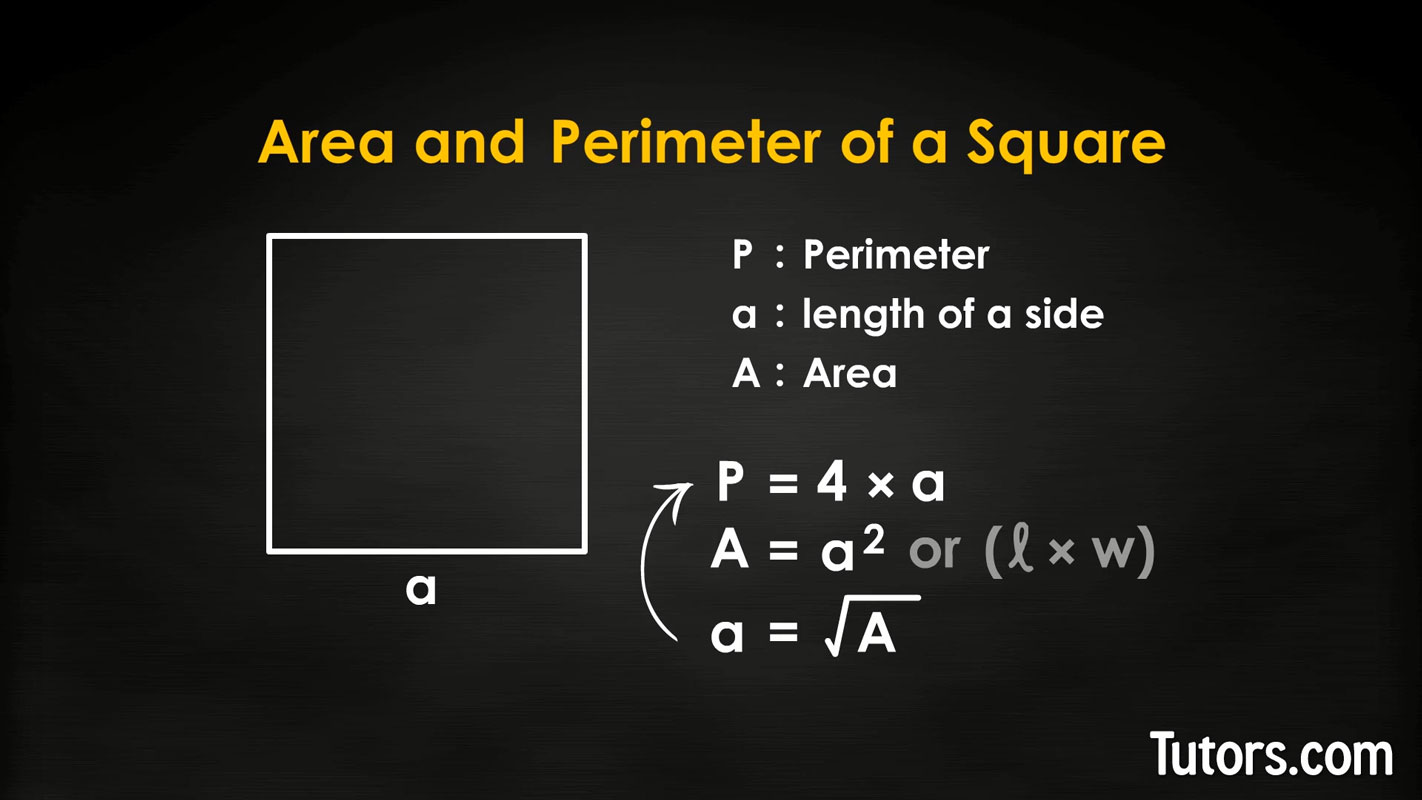
Formula for the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is defined as the total distance around the square. It\"s calculated based on the length of the square\"s sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, the formula to calculate the perimeter is quite straightforward.
Using Side Length
If the length of a side (denoted as \"s\") of the square is known, the perimeter (P) is calculated as:
Perimeter (P) = 4 × s
For instance, if each side of a square is 5 cm, its perimeter is 4 × 5 cm = 20 cm.
Using Diagonal
In cases where the diagonal (d) of the square is known, the side length can be found using the formula:
Side (s) = diagonal / √2
Then, use the side length to calculate the perimeter as before.
Using Area
If the area (A) of the square is known, the side length can be determined by:
Side (s) = √Area
Then, calculate the perimeter using the side length.
It\"s important to remember that the units of measurement for perimeter include meters, centimeters, inches, feet, etc., depending on the context or requirement.

Formula for the Area of a Square
The area of a square refers to the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries. This measure is crucial in numerous practical applications, from architecture to land measurement.
Basic Formula
When you know the length of the side of a square (denoted as \"s\"), the area (A) can be calculated using the formula:
Area (A) = s × s = s²
For example, if each side of a square is 6 cm, the area would be 6 cm × 6 cm = 36 cm².
Using the Diagonal
In cases where the length of the diagonal (d) is known, the area can be calculated using the formula:
Area = ½ × d²
This formula is derived from the properties of a square and the Pythagorean theorem.
Alternative Methods
There are other ways to determine the area of a square, such as:
- If the perimeter (P) is known, then Area = P² / 16.
- Using the circumradius (R), Area = 2 × R².
- With the inradius (r), Area = 4 × r².
Remember, the units of measurement for area are always in square units, such as square meters (m²), square centimeters (cm²), square inches (in²), etc.
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Square
Get ready to dive into the captivating world of squares! This video will unveil the secrets and beauty of this geometric shape, showcasing its symmetry and versatility in a way that will leave you amazed and inspired.
Perimeter and Area: The Basics | Geometry | Khan Academy
Prepare to have your mind blown by the wonders of geometry! In this video, you\'ll explore the fascinating relationship between shapes and angles, and discover how geometry plays a crucial role in everyday life. Get ready for a mind-expanding journey!
Calculating Perimeter: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a straightforward process, but it can be done using different methods depending on the information available. Here\"s a step-by-step guide for each method:
Using Side Length
- Measure the length of one side of the square (denoted as \"s\").
- Multiply the side length by 4. The formula is: Perimeter = 4 × s.
- Express the result in the appropriate unit (like cm, m, inches).
Using Diagonal
- Measure the length of the diagonal (denoted as \"d\").
- Calculate the side length using the formula: Side = diagonal / √2.
- Find the perimeter by multiplying the calculated side length by 4. The formula is: Perimeter = 4 × (diagonal / √2).
Using Area
- Identify the area of the square (denoted as \"A\").
- Calculate the side length using the formula: Side = √Area.
- Find the perimeter by multiplying the calculated side length by 4. The formula is: Perimeter = 4 × √Area.
Remember, the perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of the square, and it\"s expressed in linear units like centimeters, meters, or inches.
_HOOK_
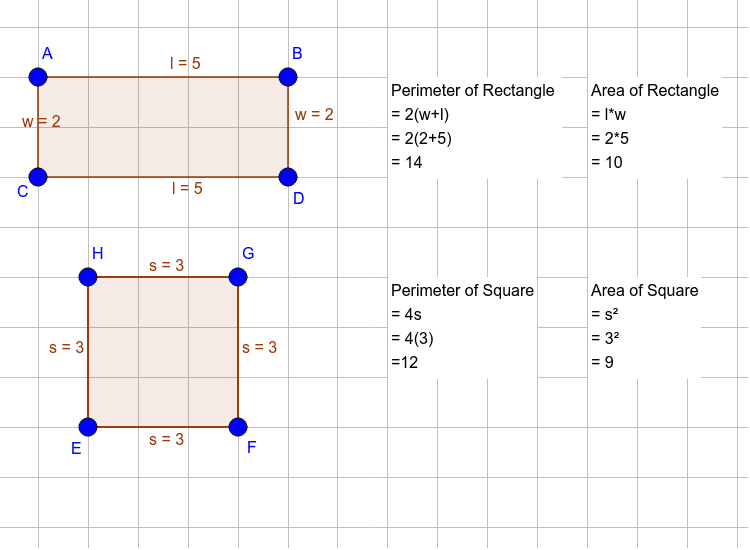
Calculating Area: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the area of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry. The area represents the space occupied by the square. Here is a step-by-step guide to calculate it:
Using Side Length
If you know the length of a side of the square (denoted as \"s\"), use the formula:
Area = s²
Simply multiply the length of the side by itself.
Using Diagonal
If the diagonal (d) of the square is known, the area can be calculated using the formula:
Area = ½ × d²
This formula arises from the properties of the square and its diagonal.
Using Perimeter
When the perimeter (P) is known, the area can be found using the formula:
Area = (P²) / 16
First, find the side length by dividing the perimeter by 4, then use the side length to calculate the area.
The units of area are typically square units, like square meters (m²), square centimeters (cm²), or square inches (in²).
Real-World Applications of Square Perimeter and Area
The concepts of perimeter and area are not just academic; they play a crucial role in various real-world scenarios. Understanding these concepts can provide insights into everyday situations and professional fields alike.
- Land Management:
- Perimeter and area calculations are fundamental in real estate and agriculture, determining property boundaries and measuring land sizes for sale or development.
- Construction and Architecture:
- In the construction of homes, buildings, and infrastructure like roads and bridges, precise measurements of area and perimeter ensure efficient use of space and materials.
- Interior Design and Home Improvement:
- Calculating the area of rooms is essential for tasks like tiling floors or painting walls, while perimeter measurements help in installing fixtures like moldings and fences.
- Astronomy:
- Perimeter and area calculations aid in understanding celestial phenomena, such as measuring the orbits of planets and their motion within our solar system.
- Art and Fashion:
- Designers and artists frequently use these concepts to determine fabric sizes for clothing or to achieve precision in their artwork.
- Gaming and Computer Graphics:
- In the gaming industry, area and perimeter are used to create realistic and engaging environments and character designs.
- Gardening and Agriculture:
- Calculating the perimeter of gardens or agricultural fields is essential for fencing and efficient land use.
These applications highlight the practical importance of understanding the concepts of square perimeter and area, demonstrating their relevance beyond the classroom.

Examples and Practice Problems
Explore the fascinating world of geometry with these engaging examples and practice problems focused on the perimeter and area of a square. Each problem is designed to reinforce your understanding and application of these fundamental concepts.
- Calculating Perimeter of a Square:
- Find the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 8 inches. Remember, the perimeter of a square is the sum of all its sides.
- Area of a Square:
- Determine the area of a square whose sides are each 12 feet long. The area of a square is calculated as side × side.
- Perimeter with Given Length:
- If a square has sides each 12 inches long, what is its perimeter? Apply the formula P = 4 × side length.
- Area Calculation:
- Find the area of a square with sides measuring 15 yards. Use the formula Area = side².
- Perimeter of a Large Square:
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 25 inches. Remember, perimeter is four times the side length.
- Cost Calculation for Painting:
- A square wall has sides of 6 feet each. If painting costs $0.5 per square foot, calculate the total cost for painting the wall.
- Finding Side Length from Perimeter:
- Determine the length of the sides of a square that has a perimeter of 44 feet.
- Side Length from Area:
- Find the length of one side of a square that has an area of 121 square inches.
- Perimeter of a Square with Known Side:
- What is the length of the sides of a square that has a perimeter of 60 inches?
- Ceramic Tiles Calculation:
- A square floor with sides of 40 feet is to be covered with 2 feet square tiles. Calculate how many tiles are needed.
These problems will help solidify your grasp on the concepts of perimeter and area, essential for geometry understanding and applications.
Tools and Calculators for Square Measurements
Understanding the measurements of a square, such as its area and perimeter, is vital in various fields like geometry, construction, and design. To facilitate these calculations, several online tools and calculators are available. Here’s a guide to some useful tools:
- Symbolab’s Square Calculator:
- This calculator offers step-by-step solutions for calculating the area and perimeter of a square. It includes a variety of mathematical functions and tools, making it a comprehensive choice for both students and professionals.
- NCalculators’ Square Calculator:
- This tool provides an easy-to-use interface where you can enter the side length of a square to obtain its area, perimeter, and diagonal length. It\"s especially handy for quick calculations.
- GigaCalculator’s Perimeter of a Square Calculator:
- Designed for simplicity, this calculator assists in finding the perimeter of a square by multiplying the length of one side by four. It\"s useful for practical applications like fencing a square area.
- Symbolab’s Squares Calculator - Find Area, Given Perimeter:
- This unique tool is beneficial when you know the perimeter of a square and need to find its area. It’s a versatile calculator suitable for various geometrical calculations.
- Other Online Calculators:
- Various other calculators like Omni Calculator and Calculator Soup provide tools for calculating square measurements, each offering unique features and user-friendly interfaces.
These online tools are not only efficient but also provide educational value by illustrating the steps involved in the calculations, enhancing your understanding of square measurements.
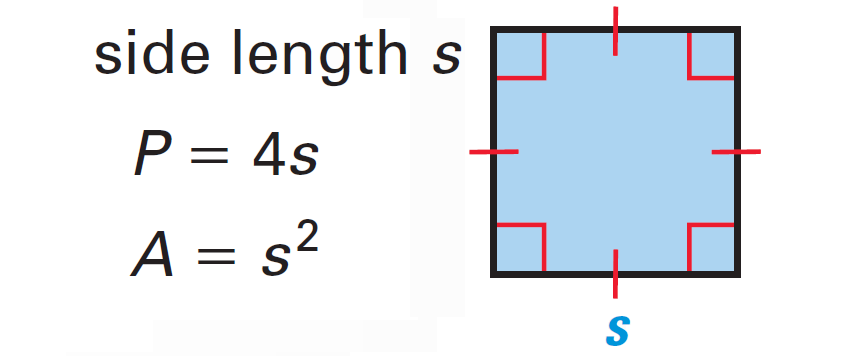
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Understanding the perimeter and area of a square is crucial in mathematics, yet several common mistakes and misconceptions often hinder students\" learning. This section aims to address these issues, providing clarity and guidance to avoid common errors.
Mistaking Area for Perimeter and Vice Versa
One common misconception is confusing area with perimeter. Area measures the space within a shape, expressed in square units like square meters or square inches. In contrast, perimeter refers to the length of the boundary surrounding a shape, measured in linear units like meters or feet. This confusion often arises due to the simultaneous teaching of both concepts.
Incorrect Use of Units
Another frequent error is the misuse of units. It\"s important to remember that area is measured in square units, while perimeter is in linear units. Forgetting to square the units when calculating area or using inappropriate units can lead to incorrect results.
Errors in Calculation
Calculation errors often occur due to a lack of understanding of the formulas. For a square, the area is found by squaring the length of one side (Area = side × side), and the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4 (Perimeter = 4 × side). Overlooking these simple formulas can lead to incorrect calculations.
Visual Misinterpretation
Students sometimes struggle with visualizing area and perimeter, especially when transitioning from concrete models (like counting squares on a grid) to more abstract concepts. Ensuring a strong foundation in visualizing and understanding these concepts is crucial for accurate calculations.
Lack of Real-world Connection
A lack of connection to real-world applications can make it harder for students to grasp the importance and practicality of understanding area and perimeter. Demonstrating real-life examples where these calculations are necessary can enhance understanding and interest.
Over-reliance on Memorization
Relying solely on memorization of formulas without understanding the underlying concepts can lead to mistakes. It\"s essential for learners to grasp why formulas are used and how they are derived to apply them correctly in different scenarios.
By being aware of these common mistakes and misconceptions, students can approach the calculation of square perimeter and area with greater confidence and accuracy.
_HOOK_
Teaching Resources and Strategies for Educators
Teaching the concepts of perimeter and area, especially of squares, can be made engaging and effective through a variety of creative strategies and resources. Here are some proven methods and activities to enhance learning in this area:
Hands-On Learning Activities
- Using Square Post-It Notes: These can be used for group discussions, anchor charts, and interactive learning. They are excellent for visually demonstrating area and perimeter concepts.
- Exploring with Tape and Floor Tiles: Utilizing floor tiles and tape can help bring the concept into the real world. Students can measure and calculate the area and perimeter of classroom sections or create their own spaces with specific measurements.
- Pattern Blocks: For a more advanced understanding, pattern blocks are useful. They come in various shapes but maintain a standard side length, aiding in perimeter exploration.
Creative and Engaging Activities
- Area and Perimeter Song: Creating a catchy tune can help students remember the formulas and applications of area and perimeter.
- Building a Kite: Students can make kites and measure their area and perimeter, followed by discussions on how these dimensions impact their flight.
- Interior Design Project: A real-life application where students arrange furniture in a room, taking into account area and perimeter constraints.
- City Building Activity: Students design a city, calculating area and perimeter for each building, integrating volume concepts as well.
- Island Conquer Game: A fun game where students plot rectangles on a grid, calculating area and perimeter to \"conquer\" islands.
Other Innovative Teaching Ideas
- Outdoor Shape Drawing: Drawing shapes with chalk outside and estimating their perimeter. Using strings for irregular shapes can add a challenge.
- Manipulatives: Using items like straws, play dough, and pasta noodles to create polygons and measure their perimeters.
- Interactive Notebooks: Incorporating interactive notebooks in lessons can engage students effectively. Differentiated activities ensure all students are included.
Teaching Strategies
- Visual Cues: Use visual aids to differentiate between perimeter (the outer \"rim\" of a shape) and area (the space inside a shape).
- Different Computations: Teach perimeter and area as distinct computations, using addition for perimeter and multiplication for area.
- Color Coding: Use color-coding to distinguish tasks - outlining shapes for perimeter and coloring in for area.
- Word Problems and Real-World Applications: Regularly incorporate complex word problems and real-life scenarios to deepen understanding and correct misconceptions.
By employing these diverse teaching methods, educators can make the concepts of perimeter and area accessible, memorable, and enjoyable for students.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions About Square Perimeter and Area
Understanding the perimeter and area of squares is essential in geometry. Here are some common questions and their answers:
1. How do you calculate the perimeter of a square?
The perimeter of a square is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is 4 times the length of one side. The formula is: Perimeter = 4 × side length.
2. How is the area of a square determined?
The area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one of its sides. The formula is: Area = side × side.
3. Can you determine the perimeter of a square if only the area is known?
Yes, you can determine the perimeter of a square if you know its area. First, find the length of one side by taking the square root of the area. Then, calculate the perimeter by multiplying the side length by 4.
4. What are the properties of a square?
- All four sides of the square are equal.
- The opposite sides of the square are parallel.
- Each interior angle of a square is 90 degrees.
- The diagonals of the square bisect each other at 90 degrees and are equal in length.
5. How can the perimeter of a square be found using its diagonal?
To find the perimeter using the diagonal, divide the length of the diagonal by the square root of 2 to get the side length, and then multiply this length by 4 to get the perimeter.
6. Are there any practical examples where the calculation of the perimeter and area of a square is used?
Yes, practical applications include calculating the fencing needed for a square park, the flooring required for a square room, and crafting items like photo frames or tiles.
These FAQs cover the fundamental aspects of understanding and calculating the perimeter and area of squares, which are key concepts in geometry.
Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the perimeter and area of a square, perfect for students, teachers, and math enthusiasts alike!