Topic how to find the perimeter of quadrilateral: Discover the essentials of geometry with our guide on "How to Find the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral", simplifying complex calculations into easy-to-understand steps for learners and enthusiasts alike.
Table of Content
- How do I find the perimeter of a quadrilateral?
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Basic Formula for Quadrilateral Perimeter
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Special Cases: Square, Rectangle, and Rhombus
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
- YOUTUBE: Determining the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral with the Distance Formula
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Perimeter of Irregular Quadrilaterals
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Practical Applications and Examples
- ... [Other Sections] ...
- Calculating Perimeter with an Inscribed Circle
- Interactive Tools and Calculators for Quadrilaterals
- Frequently Asked Questions About Quadrilateral Perimeters
How do I find the perimeter of a quadrilateral?
To find the perimeter of a quadrilateral, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the lengths of all four sides of the quadrilateral.
- Add up the lengths of all four sides to calculate the perimeter.
Let\'s see an example:
Suppose we have a quadrilateral with side lengths of 5 cm, 7 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm.
- The lengths of the sides are: 5 cm, 7 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm.
- To calculate the perimeter, add up all four side lengths:
| Side Length |
|---|
| 5 cm |
| 7 cm |
| 4 cm |
| 6 cm |
Now, add all the side lengths:
- 5 cm + 7 cm + 4 cm + 6 cm = 22 cm
So, the perimeter of the given quadrilateral is 22 cm.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
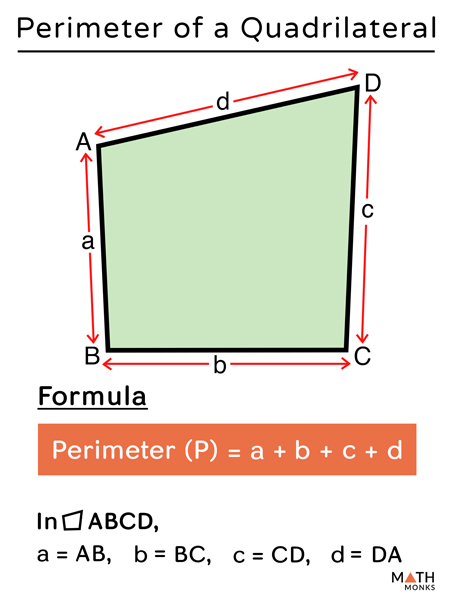
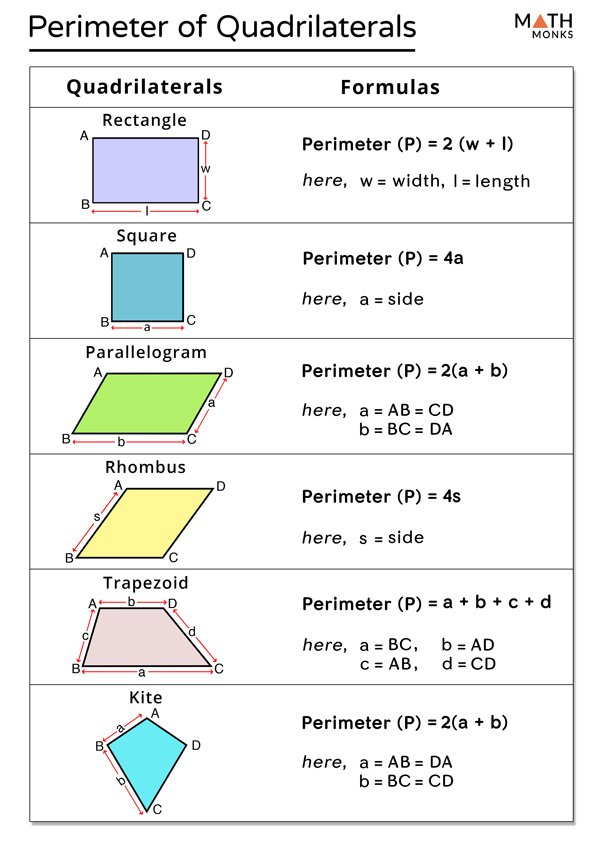
The perimeter of a quadrilateral, a four-sided polygon, is the total length of its boundary. To calculate this, one must add the lengths of all four sides. This fundamental concept applies to all quadrilaterals, regardless of their shape or dimensions. The formula for the perimeter of a quadrilateral is P = a + b + c + d, where \"P\" represents the perimeter, and \"a\", \"b\", \"c\", and \"d\" are the lengths of the four sides.
For specific types of quadrilaterals like squares and rectangles, where sides are equal or opposites are equal, the formula can be simplified. In squares, all four sides are equal, making the formula 4a (a being the length of one side). For rectangles, the formula becomes 2(length + width) due to the equality of opposite sides. However, in irregular quadrilaterals where the sides are not of equal length, the perimeter is the sum of all its distinct sides.
Understanding the concept of perimeter is crucial in various fields, including architecture, design, and even everyday situations like fencing a garden. It’s a fundamental aspect of geometry that helps in understanding the properties and measurements of different shapes.
In special cases, such as a quadrilateral with an inscribed circle, the perimeter can be determined using properties of tangents drawn to the circle. This requires understanding that tangents drawn from a single point to a circle are equal in length, allowing for the calculation of missing sides if necessary.
Another interesting application is in the calculation of the perimeter of irregular quadrilaterals, where side lengths might not be directly given. In such cases, additional geometric principles or measurements are used to deduce the unknown lengths.

... [Other Sections] ...
![... [Other Sections] ...](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/formula-to-find-the-perimeter-of-quadrilateral-1621938225.png)
Basic Formula for Quadrilateral Perimeter
The basic formula to calculate the perimeter of a quadrilateral, which is a four-sided polygon, is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Mathematically, this is represented as P = a + b + c + d, where P stands for the perimeter and a, b, c, d are the lengths of the four sides.
This formula is universally applicable, regardless of the type of quadrilateral. Whether the quadrilateral is a rectangle, square, rhombus, trapezoid, or any irregular shape, the formula remains consistent: simply add the lengths of all four sides.
In special cases of quadrilaterals like squares and rectangles, this formula can be simplified. For a square, where all four sides are equal, the formula becomes P = 4a (a being the length of one side). In a rectangle, where opposite sides are equal, the formula can be rewritten as P = 2(l + w), with l representing the length and w the width.
For irregular quadrilaterals or those with an inscribed circle, special consideration is needed to determine the lengths of the sides before applying the perimeter formula. In cases where the quadrilateral encloses a circle, tangent properties are used to find the lengths of the sides.
Understanding this formula is crucial in various real-world applications, such as in architecture, land surveying, and crafting, where precise measurements are essential.
... [Other Sections] ...
![... [Other Sections] ...](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/problem_question_image/image/2790/Quad.gif)
_HOOK_
Special Cases: Square, Rectangle, and Rhombus
Calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral varies slightly in special cases like squares, rectangles, and rhombuses. These shapes have unique properties that allow for simplified formulas.
- Square: All sides of a square are equal. The formula for the perimeter of a square is P = 4a, where \"a\" is the length of one side.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides of a rectangle are equal. The perimeter formula for a rectangle is P = 2(l + w), where \"l\" is the length and \"w\" is the width.
- Rhombus: All sides of a rhombus are equal, similar to a square. The formula for its perimeter is P = 4s, where \"s\" is the length of one side.
These formulas take advantage of the properties of each shape. For instance, knowing just one side length of a square or rhombus is enough to calculate the perimeter, and knowing the length and width is sufficient for a rectangle.
It\"s interesting to note that while these shapes have these specific formulas, the general formula for the perimeter of a quadrilateral, P = a + b + c + d, still applies. The special formulas are just simplified versions tailored to the properties of these shapes.
... [Other Sections] ...
![... [Other Sections] ...](https://study.com/cimages/multimages/16/geogebra-export_23163667637492648769.png)
Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
Calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral when one or more sides are missing involves using the properties of specific quadrilaterals and geometric principles. The approach varies depending on the type of quadrilateral and the available information.
- Using Properties of Special Quadrilaterals: For quadrilaterals like squares, rectangles, and parallelograms, knowing the properties can help. For example, in a rectangle, knowing the length and width is enough as opposite sides are equal. The formula becomes P = 2(length + width).
- Quadrilaterals with Equal Sides: In shapes like squares and rhombuses, all sides are equal. Therefore, knowing one side length allows you to calculate the perimeter. For a square, if one side is \"a\", the perimeter is 4a.
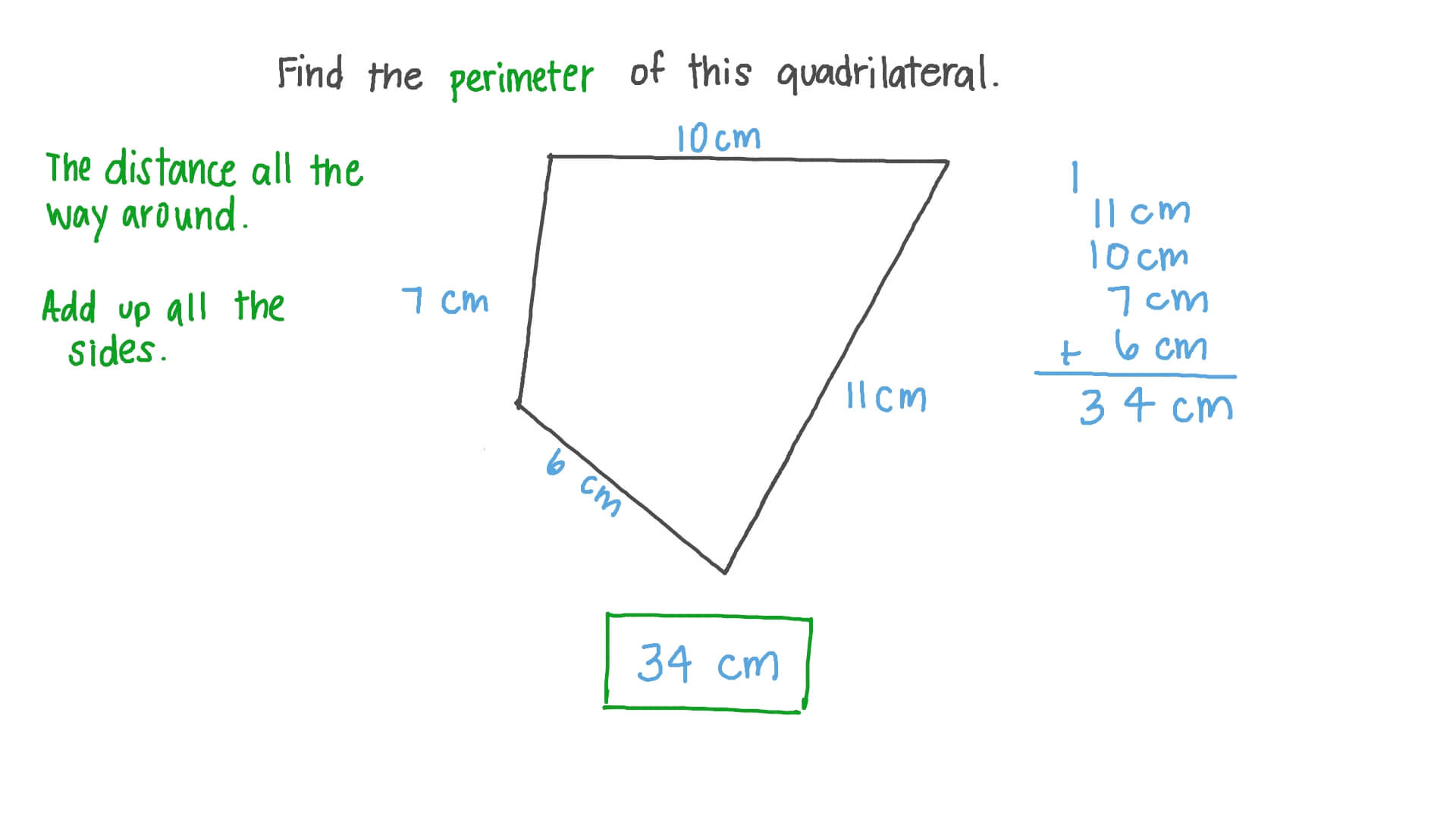
- Irregular Quadrilaterals: If a side is missing in an irregular quadrilateral, other methods like using the total perimeter and subtracting the lengths of the known sides can be used. For example, if the total perimeter is known along with three sides, the missing side can be found by subtracting the sum of the three known sides from the total perimeter.
- Quadrilaterals with Inscribed Circles: In cases where a quadrilateral has an inscribed circle, the properties of tangents (equal lengths of tangents from the same external point) can be used to find missing sides.
These methods demonstrate the application of geometric principles and properties of special quadrilaterals to solve for missing sides and calculate the perimeter effectively.

Determining the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral with the Distance Formula
Explore the fascinating world of geometry as we dive into the concept of perimeter! In this video, you\'ll discover the secrets to calculating the total distance around various shapes, unlocking the true beauty and intricacy of this mathematical concept.
Finding the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
Uncover the hidden properties of quadrilaterals in this captivating video! Join us on an exciting journey where we unravel the mysteries of these four-sided figures, giving you a unique understanding of their angles, sides, and diverse classifications. Don\'t miss out on this opportunity to expand your knowledge in geometry!
... [Other Sections] ...
![... [Other Sections] ...](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/zcdWrutFkco/hqdefault.jpg)
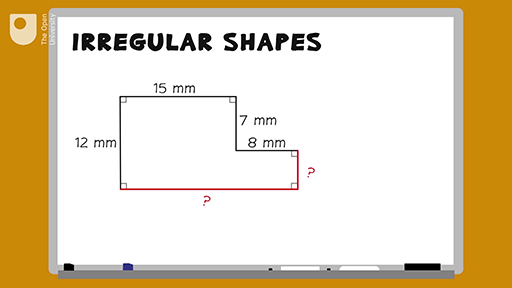
Perimeter of Irregular Quadrilaterals
Calculating the perimeter of irregular quadrilaterals, which do not have equal sides or angles, involves summing the lengths of all four sides. The general formula for the perimeter, P, of any quadrilateral is P = s1 + s2 + s3 + s4, where s1, s2, s3, and s4 are the lengths of the four sides.
For irregular quadrilaterals where not all side lengths are known, different methods might be employed:
- If three sides and the total perimeter are known, the fourth side can be calculated by subtracting the sum of the three known sides from the total perimeter.
- In cases where the quadrilateral has an inscribed circle, the properties of tangents (equal lengths from a single point) can be used to determine missing side lengths.
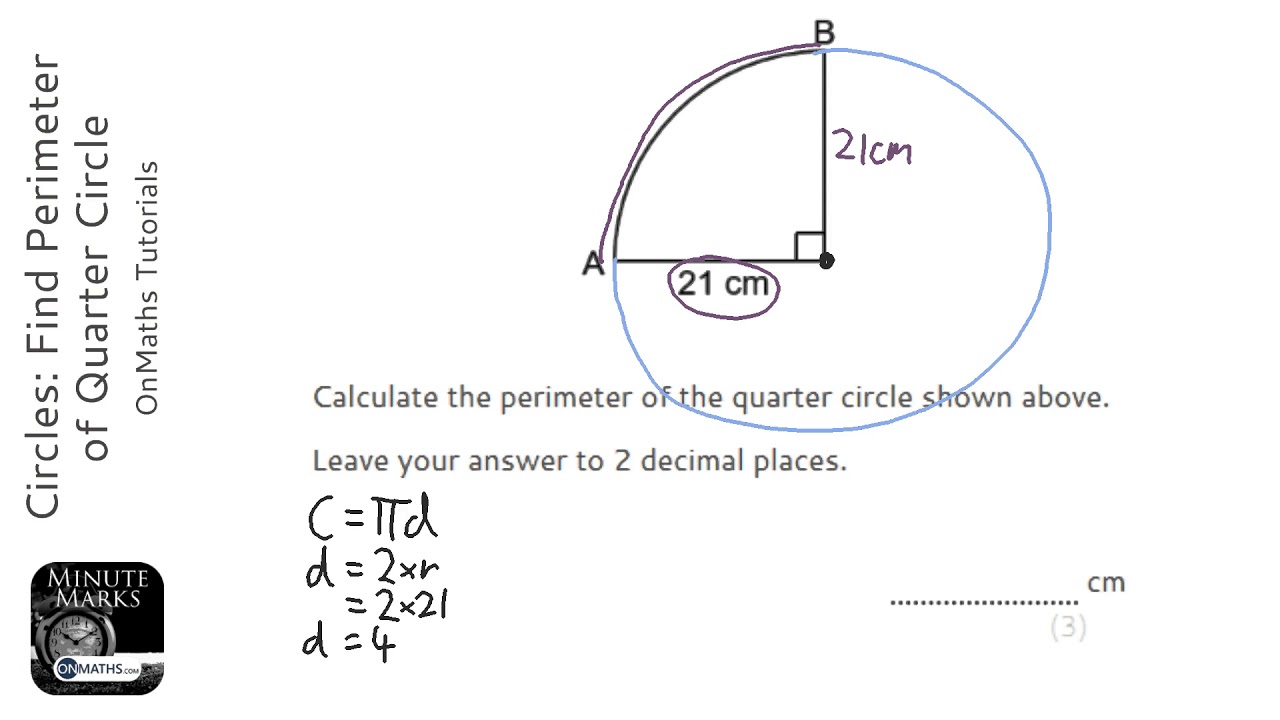
- For quadrilaterals on a graph, the coordinates of the vertices can be used with the distance formula to calculate side lengths before summing them to find the perimeter.
It\"s important to note that these methods may require additional geometric knowledge or measurements depending on the specific attributes of the irregular quadrilateral.
_HOOK_
... [Other Sections] ...
![... [Other Sections] ...](https://mathtechconnections.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/3rd-Guided-Math-Measurement-Lessons-1.png)
Practical Applications and Examples
The concept of finding the perimeter of a quadrilateral has several practical applications in real life. Understanding this concept is crucial in fields such as architecture, engineering, and various everyday scenarios.
- Architecture and Engineering: Architects and engineers often need to calculate the perimeter of quadrilateral-shaped plots or land areas to determine fencing requirements, layout plans, or for constructing foundations.
- Interior Design: In interior design, calculating the perimeter of a room is essential for tasks like installing baseboards, flooring, or decorating the edges of a room.
- Agriculture and Landscaping: In agriculture, knowing the perimeter of quadrilateral fields helps in planning irrigation systems and boundary marking. Similarly, in landscaping, this knowledge assists in designing garden layouts and paths.
- Education: In educational contexts, perimeter calculations are a fundamental part of geometry teaching, helping students understand spatial awareness and measurement concepts.
- Mathematical Problems: Perimeter calculation of quadrilaterals often appears in mathematical problems and puzzles, enhancing problem-solving and analytical skills.
- Practical Examples: Examples include finding the perimeter of a kite with sides of 7 and 13 units, leading to a perimeter of 40 units, or calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides of 4, 6, 7, and 9 units, resulting in a perimeter of 26 units.
These applications show how the theoretical concept of perimeter calculation is integrated into various practical scenarios, making it an essential mathematical skill.
... [Other Sections] ...
Calculating Perimeter with an Inscribed Circle
Calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral with an inscribed circle involves a unique approach using the properties of tangents. A quadrilateral with an inscribed circle, also known as a circumscribed quadrilateral, means that each side of the quadrilateral is tangent to the circle.
The key property of tangents used here is that any two tangents drawn to a circle from a single external point are of equal lengths. This helps in determining the lengths of sides of the quadrilateral.
- Identify Tangent Points: Find the points where each side of the quadrilateral touches the circle.
- Calculate Tangent Lengths: Measure the lengths of the tangents from a single point to the circle. These lengths will be equal.
- Sum Up the Lengths: Add the lengths of the tangents to find the perimeter of the quadrilateral.
Example: Consider a quadrilateral with an inscribed circle where the tangents from a point to the circle measure 5 inches, 2 inches, 3 inches, and 4 inches respectively.
- Calculate the lengths of each side: For instance, one side could be the sum of a 5-inch and a 2-inch tangent.
- Add these lengths: (5 + 2) + (2 + 3) + (3 + 4) + (4 + 5) = 28 inches.
- The perimeter of the quadrilateral is 28 inches.
Note: This method also applies to cyclic quadrilaterals (quadrilaterals inscribed in a circle) by utilizing the same tangent properties.
Understanding the properties of tangents and applying them to the sides of a quadrilateral can simplify the process of finding its perimeter, especially in complex geometrical scenarios.
Interactive Tools and Calculators for Quadrilaterals
Interactive tools and calculators are invaluable for students, educators, and professionals in understanding and working with quadrilaterals. These digital resources simplify calculations related to the perimeter of various quadrilateral shapes, catering to both regular and irregular forms.
Features of Quadrilateral Perimeter Calculators
- Simple User Interface: Enter the lengths of the four sides of a quadrilateral to receive instant results.
- Flexibility: Accommodates different quadrilateral types, including rectangles, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, and irregular shapes.
- Formula Transparency: Most calculators display the formula used, enhancing learning and understanding.
- Examples and Guides: Many websites provide examples and step-by-step guides for various quadrilateral calculations.
Using Quadrilateral Perimeter Calculators
- Input the length of each side of the quadrilateral.
- The calculator processes the input based on the geometric properties of the specified quadrilateral.
- Instantly receive the calculated perimeter, often accompanied by the formula used.
These calculators prove especially useful in educational settings for demonstrating geometric concepts, in architectural and engineering fields for quick calculations, and for anyone looking to understand or verify the properties of quadrilaterals.
Examples of Quadrilateral Calculations
| Quadrilateral Type | Example Measurement (sides) | Perimeter Calculation |
| Square | 4 units each | 4 * 4 = 16 units |
| Rectangle | Length: 6 units, Width: 4 units | 2 * (6 + 4) = 20 units |
| Irregular Quadrilateral | 4, 3, 5, 6 units | 4 + 3 + 5 + 6 = 18 units |
By integrating these digital tools into the learning process, the understanding of geometric concepts becomes more accessible and engaging.