Topic which figure has a perimeter of 34 feet: Discover how different geometric figures can have a perimeter of 34 feet. This article explores various shapes, including rectangles, squares, and triangles, providing clear examples and calculations. Whether you're a student or simply curious, learn how to identify and calculate the perimeter of shapes to match a specific measurement.
Table of Content
Which Figure Has a Perimeter of 34 Feet?
Determining which figure has a perimeter of 34 feet involves understanding the perimeter formulas for various geometric shapes. Here, we will explore the perimeter calculations for a rectangle, square, and triangle.
Rectangle
For a rectangle, the perimeter P is calculated as:
L = LengthW = Width
Example: If
Square
For a square, the perimeter P is calculated as:
s = Side length
Example: If
Triangle
For a triangle, the perimeter P is calculated as:
a, b, c = Lengths of the sides
Example: If
Conclusion
Any figure with sides that sum up to 34 feet in total will have a perimeter of 34 feet. This could be various combinations of length and width for rectangles, equal side lengths for squares, or differing side lengths for triangles.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Determining which figure has a perimeter of 34 feet involves understanding the basic formulas for calculating the perimeters of various geometric shapes. Different shapes, such as rectangles, triangles, circles, and polygons, have unique perimeter formulas. Knowing the dimensions of these shapes allows us to apply these formulas and find the figure with the desired perimeter. This article will guide you through the process of identifying figures with a perimeter of 34 feet by explaining the perimeter calculations for common shapes and providing examples.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundaries. It is a measure of the distance around the shape and is calculated by summing the lengths of all the sides. Perimeter is typically measured in linear units such as feet, meters, or inches.
Mathematically, the perimeter \( P \) of a polygon can be represented as:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i
\]
where \( a_i \) represents the length of the \( i \)-th side and \( n \) is the total number of sides.
For specific shapes, the formulas are:
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \) where \( l \) and \( w \) are the lengths of the rectangle's length and width, respectively.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the triangle's sides.
- Circle: The perimeter, also known as the circumference, is given by \( P = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
Understanding the perimeter is essential in various real-world applications, such as fencing a yard, framing a picture, or any scenario where enclosing an area is necessary.
How to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing up the lengths of all its sides. The specific formula and steps depend on the type of shape. Below is a detailed guide for different shapes:
-
Square:
The perimeter (P) of a square with side length \( s \) is given by:
\[
P = 4s
\]Example: If \( s = 8.5 \) feet, then:
\[
P = 4 \times 8.5 = 34 \text{ feet}
\] -
Rectangle:
The perimeter (P) of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is calculated as:
\[
P = 2l + 2w
\]Example: If \( l = 10 \) feet and \( w = 7 \) feet, then:
\[
P = 2 \times 10 + 2 \times 7 = 20 + 14 = 34 \text{ feet}
\] -
Equilateral Triangle:
The perimeter (P) of an equilateral triangle with side length \( s \) is:
\[
P = 3s
\]Example: If \( s = 11.33 \) feet, then:
\[
P = 3 \times 11.33 = 33.99 \text{ feet} \approx 34 \text{ feet}
\] -
Regular Pentagon:
The perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon with side length \( s \) is:
\[
P = 5s
\]Example: If \( s = 6.8 \) feet, then:
\[
P = 5 \times 6.8 = 34 \text{ feet}
\]
For irregular shapes, simply add the length of each side. Perimeter calculations are essential for practical tasks like fencing a garden or framing a picture, providing a clear measurement of the boundary of a shape.
Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
The perimeter of a geometric figure is the total length of its boundaries. Here are the formulas for calculating the perimeter of various shapes:
- Square:
- Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Description: The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side.
- Rectangle:
- Formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Description: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
- Triangle:
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Description: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Circle:
- Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Description: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is twice the product of pi and the radius.
- Trapezoid:
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Description: The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all four sides.
- Parallelogram:
- Formula: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Description: The perimeter of a parallelogram is twice the sum of the lengths of adjacent sides.
- Rhombus:
- Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Description: The perimeter of a rhombus is four times the length of one side.
- Ellipse:
- Approximation Formula: \( P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \)
- Description: The perimeter of an ellipse is complex, often approximated by Ramanujan’s formula, involving the semi-major and semi-minor axes.
Understanding these formulas allows for accurate calculation of the perimeter for different shapes, which is essential for various practical applications like fencing a yard or framing a picture.

Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of different geometric shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Here are a few examples to illustrate the process:
-
Square:
For a square with each side measuring 8.5 feet, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = 4 \times \text{side} = 4 \times 8.5 = 34 \text{ feet}
\] -
Rectangle:
If a rectangle has a length of 11 feet and a width of 6 feet, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (11 + 6) = 2 \times 17 = 34 \text{ feet}
\] -
Triangle:
For a triangle with sides measuring 10 feet, 12 feet, and 12 feet, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 = 10 + 12 + 12 = 34 \text{ feet}
\]
These examples show how different shapes can have the same perimeter of 34 feet by applying the respective formulas.
Special Cases and Word Problems
Understanding the perimeter of various shapes can help solve real-world problems. Here are some special cases and word problems that illustrate how to work with perimeters:
-
Rectangle Perimeter Problem:
Given a rectangle with a perimeter of 34 feet, where the length is 5 feet more than twice the width, find the dimensions.
- Let \( w \) be the width and \( l \) be the length.
- We know \( l = 2w + 5 \).
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = 2l + 2w \), substitute the given values:
- \( 34 = 2(2w + 5) + 2w \)
- Simplify and solve for \( w \):
- \( 34 = 4w + 10 + 2w \)
- \( 34 = 6w + 10 \)
- \( 24 = 6w \)
- \( w = 4 \)
- Thus, the width is 4 feet and the length is:
- \( l = 2(4) + 5 = 13 \) feet
-
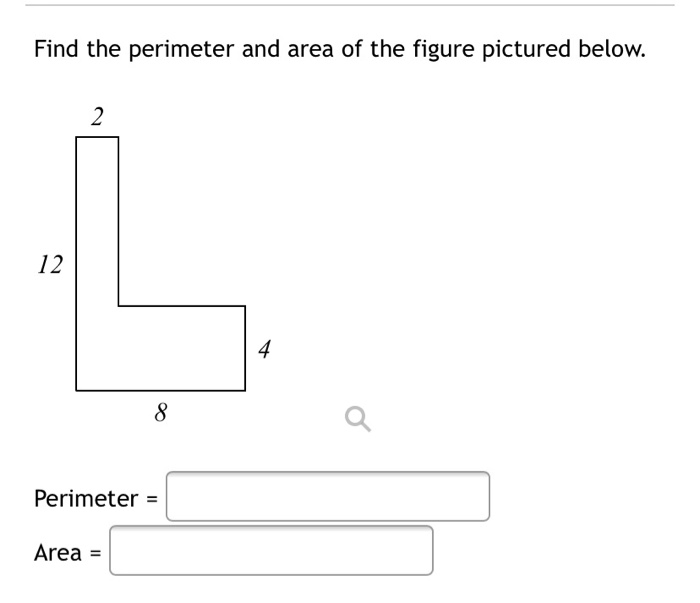
Irregular Polygon Problem:
Consider a polygon with sides of various lengths. If the sides are 10 ft, 12 ft, 8 ft, 4 ft, then the perimeter is the sum of all sides.
- Sum the side lengths:
- \( 10 + 12 + 8 + 4 = 34 \) feet
- Thus, the polygon's perimeter is 34 feet.
-
Complex Shape Problem:
If a complex shape is composed of multiple simple shapes, calculate each shape's perimeter separately and then sum them.
These examples illustrate how to handle various perimeter-related problems using basic algebra and geometry principles.
Cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật
READ MORE:
Tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình phức hợp sau: 34 ft 34 ft 32 ft 32 ft 10 ft 1 ft 1…