Topic what is the square root of 55: The square root of 55 is approximately 7.416. This article will explore the mathematical concept of square roots, methods to calculate the square root of 55, and its applications. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for various fields in mathematics and science. Dive in to learn more about the square root of 55 and its significance.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 55
- Introduction
- Definition and Value
- Properties
- Calculation Methods
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples
- Applications
- FAQs
- Related Topics
- YOUTUBE: Video 'Square Root 55' cung cấp kiến thức về căn bậc hai của 55, giúp người xem hiểu rõ hơn về giá trị và cách tính toán căn bậc hai của số này.
Understanding the Square Root of 55
The square root of 55 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the result of 55. This can be represented using the radical sign as follows:
\[ \sqrt{55} \approx 7.416 \]
Since the square root of 55 is not a whole number, it indicates that 55 is not a perfect square. Additionally, the square root of 55 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 55
- Using a Calculator: On most calculators, you can find the square root of 55 by entering 55 and pressing the square root button (√). The result will be approximately 7.416.
- Using a Computer: In programs like Excel or Google Sheets, you can use the function
=SQRT(55)to get the result. - Long Division Method: This traditional method involves a series of steps to manually find the square root and is useful for educational purposes.
Properties of the Square Root of 55
The square root of 55 can be expressed in several forms:
- Decimal Form: \(\sqrt{55} \approx 7.4161984871\)
- Fraction Form (Approximated): \(\frac{742}{100} \approx 7.42\)
- Exponent Form: \(55^{1/2}\)
Table of n-th Roots of 55
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 55 | ²√55 | ±7.4161984871 |
| 3 | 55 | ³√55 | 3.8029524608 |
| 4 | 55 | ⁴√55 | ±2.7232698153 |
| 5 | 55 | ⁵√55 | 2.228807384 |
Conclusion
The square root of 55, approximately 7.416, is an irrational number and not a perfect square. Various methods, such as using a calculator, a computer, or long division, can be employed to find this value.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 55 is a mathematical concept that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 55. This value is represented by the radical sign √55 and is approximately equal to 7.416198487. Since 55 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as an exact fraction. In this introduction, we will explore how to calculate the square root of 55, its properties, and various methods used to approximate its value.
Definition and Value
The square root of a number is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 55, this value is approximately 7.416198487. Mathematically, this is represented as:
\\[ \sqrt{55} \approx 7.416198487 \\]
This means that:
\\[ 7.416198487 \times 7.416198487 \approx 55 \\]
Understanding the Calculation
Calculating the square root of 55 can be approached through several methods:
- Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors, but since 55 is not a perfect square, prime factorization is less efficient.
- Long Division Method: This is a more suitable approach for finding the square roots of numbers that are not perfect squares. It involves a step-by-step process similar to traditional long division.
- Calculator: For quick calculations, using a calculator or spreadsheet software (e.g., using the SQRT function in Excel) is efficient.
Rationality of the Square Root of 55
The square root of 55 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. Irrational numbers have unique properties and are important in various fields of mathematics.
Applications and Examples
Understanding the square root of a number is crucial in various mathematical concepts, including geometry, algebra, and calculus. For instance, in the Pythagorean theorem, square roots are used to find the lengths of sides in right-angled triangles.
Example:
| Number | Square Root |
| 55 | 7.416198487 |
Properties
The square root of 55 has several important properties that are useful in various mathematical contexts. Understanding these properties helps in grasping more complex mathematical concepts and operations. Here are some key properties of the square root of 55:
- Non-Perfect Square: The number 55 is not a perfect square, which means its square root is not an integer. Specifically, the square root of 55 is approximately 7.416.
- Principal Square Root: The principal (positive) square root of 55 is denoted as \( \sqrt{55} \) and is approximately 7.416. The negative square root is -7.416.
- Irrational Number: Since 55 is not a perfect square, \( \sqrt{55} \) is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Calculation Methods: The square root of 55 can be calculated using various methods such as the long division method or using a calculator. For example, using a calculator, you can simply enter 55 and press the square root button to get the result of approximately 7.416.
- Expression in Radical Form: The square root of 55 is expressed in its simplest radical form as \( \sqrt{55} \).
- Approximation: For practical purposes, the square root of 55 is often approximated to two decimal places as 7.42.
These properties highlight the uniqueness of the square root of 55 and its significance in mathematics.
Calculation Methods
The square root of 55 can be calculated using various methods. Here are some of the most common techniques:
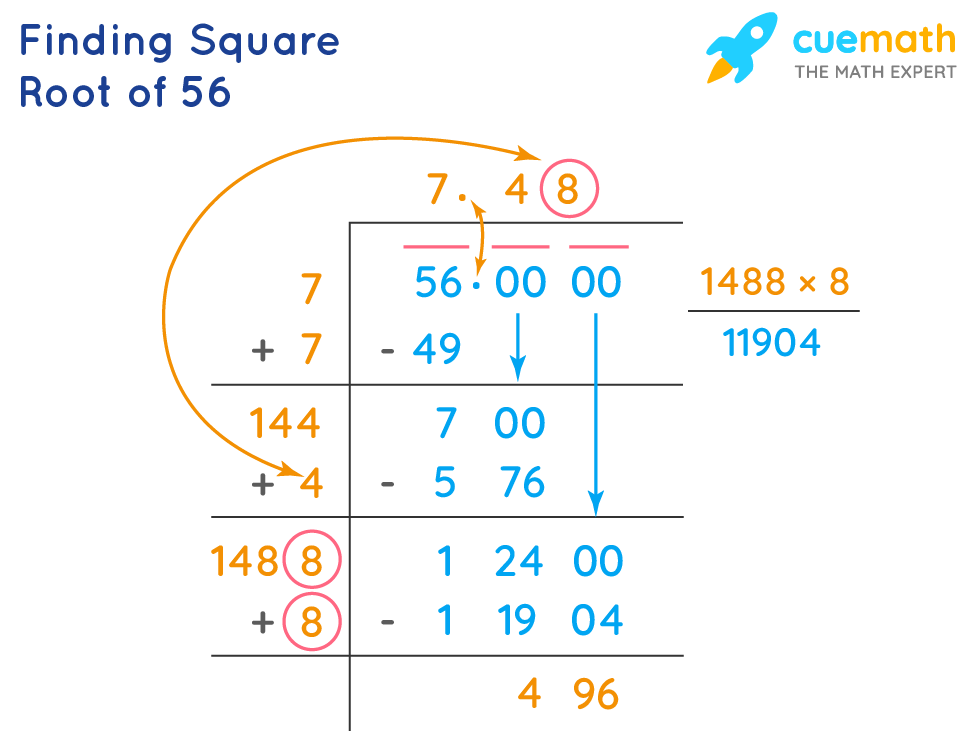
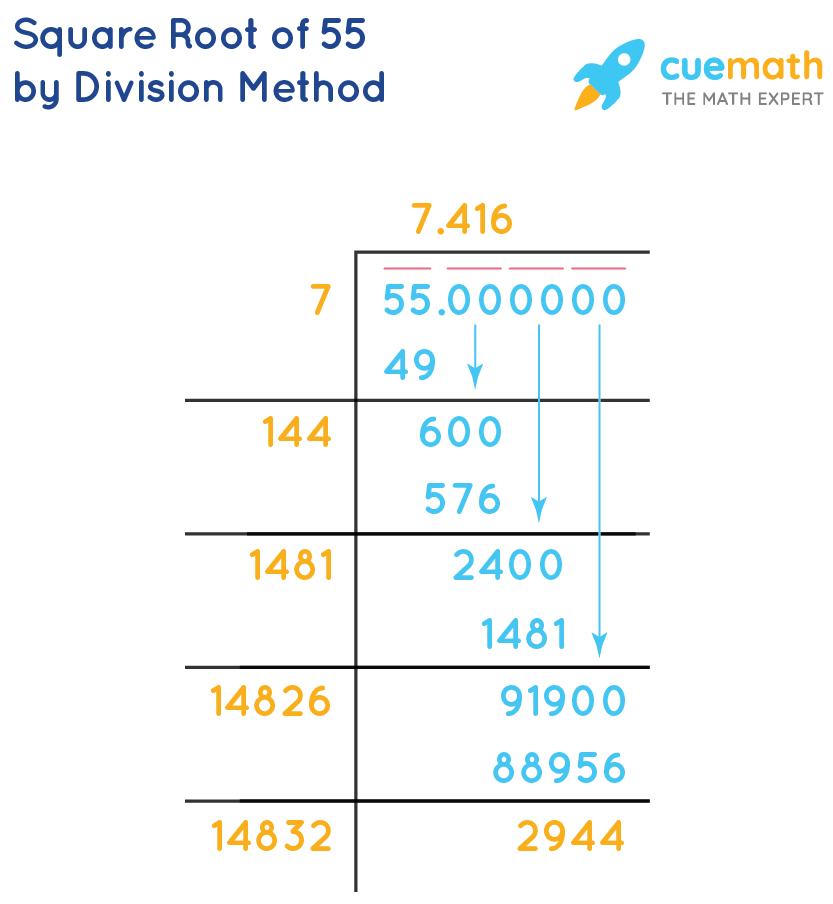
1. Long Division Method
- Start by expressing 55 as 55.000000.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 55. Here, it is 7, because \(7^2 = 49\).
- Subtract 49 from 55 to get 6, then bring down a pair of zeros, making it 600.
- Double the quotient (7), making it 14, and find a number that, when added to 14 and multiplied by itself, is less than or equal to 600. Here, it is 4, making the new number 144. \(144 \times 4 = 576\).
- Continue this process to get more decimal places. The square root of 55 up to three decimal places is 7.416.
2. Approximation Method
- Identify the two closest perfect squares around 55, which are 49 and 64.
- Since 49 is \(7^2\) and 64 is \(8^2\), the square root of 55 is between 7 and 8.
- Using the average method, you can refine this to get a closer approximation.
3. Babylonian (or Heron’s) Method
- Start with an initial guess, say 7.5.
- Divide 55 by this guess (55 / 7.5 = 7.333).
- Calculate the average of this result and the initial guess \((7.5 + 7.333) / 2 = 7.4165\).
- Repeat the steps until the difference between two consecutive results is negligible. The result will converge to approximately 7.4162.
By using these methods, you can calculate or approximate the square root of 55 efficiently.

Step-by-Step Calculation
The square root of 55 can be calculated through several methods. One of the most detailed methods is the Babylonian (or Heron's) method, which involves iterative steps to approximate the square root. Here is a step-by-step calculation:
-
Start with an initial guess. For simplicity, divide 55 by 2:
\(\frac{55}{2} = 27.5\)
-
Divide 55 by the previous result:
\(\frac{55}{27.5} = 2\)
Calculate the average of 27.5 and 2:
\(\frac{27.5 + 2}{2} = 14.75\)
This is our new guess.
-
Repeat the division with the new guess:
\(\frac{55}{14.75} = 3.7288\)
Average the result with 14.75:
\(\frac{14.75 + 3.7288}{2} = 9.2394\)
-
Continue this process:
\(\frac{55}{9.2394} = 5.9528\)
Average with 9.2394:
\(\frac{9.2394 + 5.9528}{2} = 7.5961\)
-
Next iteration:
\(\frac{55}{7.5961} = 7.2406\)
Average with 7.5961:
\(\frac{7.5961 + 7.2406}{2} = 7.4184\)
-
One more iteration:
\(\frac{55}{7.4184} = 7.414\)
Average with 7.4184:
\(\frac{7.4184 + 7.414}{2} = 7.4162\)
-
Final iteration to confirm the result:
\(\frac{55}{7.4162} = 7.4162\)
The average remains 7.4162, and the error is minimal.
Thus, the square root of 55 is approximately 7.4162.
Examples
Here are some detailed examples to help understand the application of the square root of 55:
Example 1: Simplifying Expressions Involving √55
Consider the expression \( \sqrt{55} + 5\sqrt{55} \):
- First, notice that both terms contain \( \sqrt{55} \).
- Factor out \( \sqrt{55} \):
- Thus, \( \sqrt{55} + 5\sqrt{55} = 6\sqrt{55} \).
Example 2: Multiplying Expressions Involving √55
Consider the expression \( 2\sqrt{55} \times 5\sqrt{55} \):
- First, multiply the coefficients (2 and 5): \( 2 \times 5 = 10 \).
- Next, multiply the square roots: \( \sqrt{55} \times \sqrt{55} = 55 \).
- Thus, \( 2\sqrt{55} \times 5\sqrt{55} = 10 \times 55 = 550 \).
Example 3: Using the Square Root in a Right Triangle
Consider a right triangle where one leg is 5 units and the hypotenuse is \( \sqrt{55} \) units:
- Use the Pythagorean theorem: \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \), where \( c \) is the hypotenuse.
- Substitute the known values: \( 5^2 + b^2 = (\sqrt{55})^2 \).
- Simplify: \( 25 + b^2 = 55 \).
- Solve for \( b^2 \): \( b^2 = 55 - 25 = 30 \).
- Take the square root of both sides: \( b = \sqrt{30} \).
- Thus, the other leg of the triangle is \( \sqrt{30} \) units.
Example 4: Solving Quadratic Equations
Consider the quadratic equation \( x^2 - 55 = 0 \):
- Isolate the \( x^2 \) term: \( x^2 = 55 \).
- Take the square root of both sides: \( x = \pm\sqrt{55} \).
- Thus, the solutions to the equation are \( x = \sqrt{55} \) and \( x = -\sqrt{55} \).
Applications
The square root of 55 has various applications in mathematics and science, particularly in solving equations, geometry, and real-world problem-solving scenarios. Here are some detailed applications:
1. Solving Quadratic Equations
The square root of 55 can be used to solve quadratic equations where the discriminant (b2 - 4ac) is 55. For example:
Consider the quadratic equation: \(x^2 - 2x - 55 = 0\)
- Calculate the discriminant: \(2^2 + 4 \cdot 1 \cdot 55 = 224\)
- Find the square root of the discriminant: \(\sqrt{224} \approx 14.9666\)
- Use the quadratic formula: \(x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\)
- Solve for x: \(x = \frac{2 \pm 14.9666}{2}\)
- Solutions: \(x \approx 8.483\) and \(x \approx -6.483\)
2. Geometry Problems
In geometry, the square root of 55 is used in various contexts, such as finding the length of the diagonal of a rectangle or the hypotenuse of a right triangle. For instance:
For a right triangle with legs of length 5 and \(\sqrt{30}\), the hypotenuse (c) can be calculated as:
\(c = \sqrt{5^2 + (\sqrt{30})^2} = \sqrt{25 + 30} = \sqrt{55} \approx 7.416\)
3. Scientific Calculations
In physics and engineering, the square root of 55 might be used in formulas involving wave equations, signal processing, and other calculations where precise square root values are necessary.
For example, calculating the resonant frequency (f) in a system where \(f = \frac{1}{2\pi} \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}\) and the resulting term inside the square root is 55.
4. Real-World Applications
The square root of 55 is also used in various practical applications such as calculating distances, areas, and other measurements in fields like construction, navigation, and computer graphics.
For instance, if a plot of land has an area of 55 square units, the length of each side (assuming a square plot) would be \(\sqrt{55} \approx 7.416\) units.
5. Statistical Analysis
In statistics, the square root of 55 can be used in calculations involving standard deviation and variance, especially in large datasets where the sum of squared deviations is 55.
For example, if the sum of squared deviations from the mean is 55, the standard deviation (σ) would be \(\sqrt{\frac{55}{N-1}}\) for a sample size of N.
Summary Table
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Quadratic Equations | Used to find roots where the discriminant is 55 |
| Geometry | Calculates lengths in right triangles and other shapes |
| Scientific Calculations | Utilized in physics and engineering formulas |
| Real-World Measurements | Helps in construction, navigation, and other fields |
| Statistics | Applied in standard deviation and variance calculations |
FAQs
-
What is the square root of 55?
The square root of 55 is approximately 7.416198487096.
-
Is the square root of 55 rational?
No, the square root of 55 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
-
How to find the square root of 55?
There are several methods to find the square root of 55, including using a calculator, the long division method, and the Babylonian (or Heron’s) method.
-
How to calculate the square root of 55 using a calculator?
On most calculators, you can find the square root of 55 by typing in 55 and pressing the square root (√) button.
-
What is the Babylonian method for finding the square root of 55?
The Babylonian method involves making an initial guess and then iteratively improving that guess by averaging it with the quotient of 55 and the previous guess. This process is repeated until the value converges to an accurate result.
-
Can the square root of 55 be simplified?
No, the square root of 55 cannot be simplified further as 55 does not have any square factors other than 1.
-
What is the square root of 55 rounded to the nearest tenth?
The square root of 55 rounded to the nearest tenth is approximately 7.4.
-
What is the square root of 55 as a fraction?
Since the square root of 55 is an irrational number, it cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction. However, it can be approximated as a fraction, such as 742/100 or 7 21/50.
-
How to express the square root of 55 in exponential form?
The square root of 55 can be written in exponential form as 551/2.
Related Topics
-
Square Root of 36
The square root of 36 is 6. This is because 6 × 6 = 36. The number 36 is a perfect square, making its square root a rational number. Calculating the square root of 36 can be easily done using a calculator or through the long division method. In geometry, it is often used in calculations involving the area of squares.
-
Square Root of 64
The square root of 64 is 8, as 8 × 8 = 64. Like 36, 64 is also a perfect square, and thus its square root is rational. This calculation is straightforward and can be performed using various methods such as prime factorization or estimation techniques. It frequently appears in problems related to area and volume in geometry.
-
Finding Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
Calculating the square roots of non-perfect squares, like 55, often results in irrational numbers. Techniques such as the long division method or the Babylonian method (also known as Heron’s method) are used for finding these roots. The values obtained are typically approximations, as the decimal expansions of these roots are non-terminating and non-repeating. Understanding these methods is crucial for higher-level mathematics and various applications in engineering and physics.
Video 'Square Root 55' cung cấp kiến thức về căn bậc hai của 55, giúp người xem hiểu rõ hơn về giá trị và cách tính toán căn bậc hai của số này.
Square Root 55
READ MORE:
Video 'Căn Bậc Hai Của 55' cung cấp kiến thức về căn bậc hai của 55, giúp người xem hiểu rõ hơn về giá trị và cách tính toán của số này.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 55