Topic what is the square root of 54: The square root of 54 is an interesting mathematical concept that results in approximately 7.348. Understanding this value involves breaking down the number into its simplest form, \(3\sqrt{6}\). In this article, we will explore the methods to calculate the square root of 54, its properties, and its applications in various fields. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of square roots!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 54
- Introduction to Square Root of 54
- Definition and Symbol
- Is 54 a Perfect Square?
- Rational or Irrational?
- Simplifying the Square Root of 54
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 54
- Using a Calculator
- Using a Computer
- Square Root of 54 Rounded
- Square Root of 54 as a Fraction
- Applications and Examples
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 54 bằng các bước dễ hiểu. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính toán và ứng dụng của căn bậc hai.
Square Root of 54
The square root of 54 is an interesting number that can be expressed in both exact and decimal forms. Here's a detailed explanation:
Mathematical Representation
The square root of 54 can be simplified and expressed as follows:
- Exact Form: \( 3\sqrt{6} \)
- Decimal Form: \( \approx 7.348 \)
Prime Factorization Method
- Express 54 as a product of its prime factors: \( 54 = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \).
- Simplify under the radical: \( \sqrt{54} = \sqrt{2 \times 3^3} = 3\sqrt{6} \).
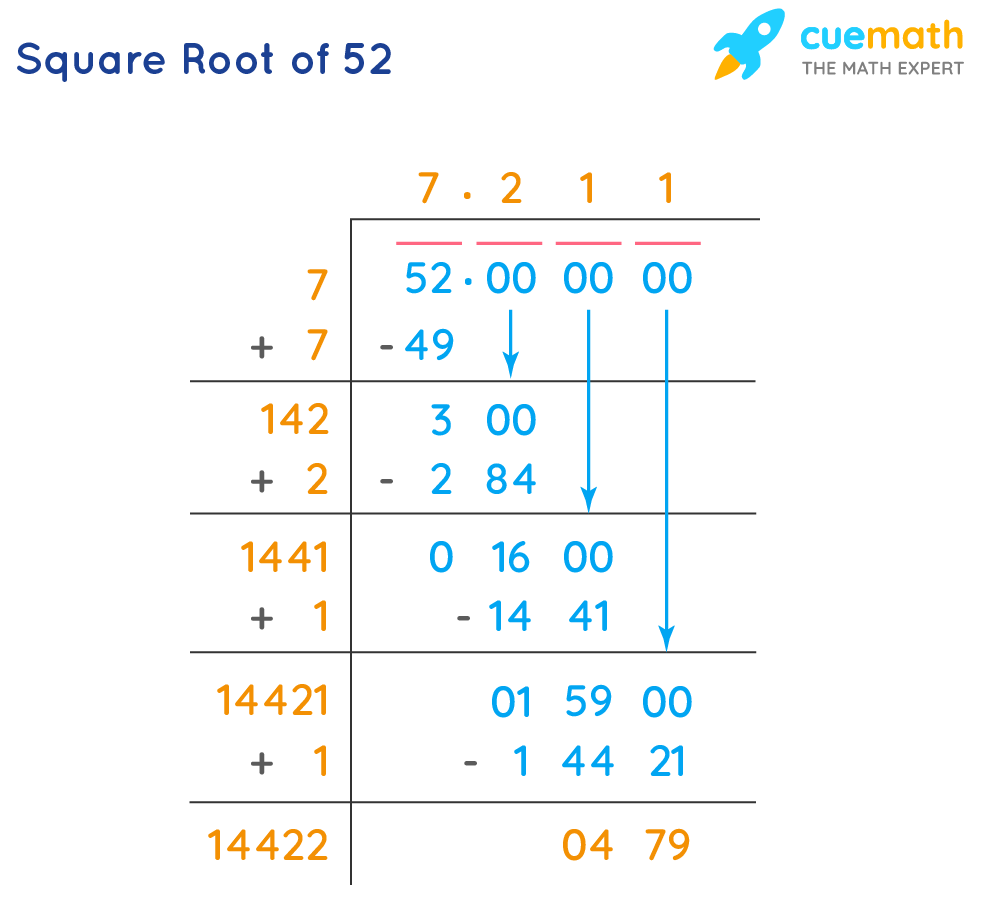
Long Division Method
- Pair the digits of 54 from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 54 (7 in this case, as \( 7^2 = 49 \)).
- Divide and get the quotient and remainder, then continue with pairs of zeros to get a more precise value.
Properties
- The square root of 54 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- The positive and negative roots are \( +7.348 \) and \( -7.348 \), respectively.
Table of Roots
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 54 | ²√54 | ±7.348 |
| 3 | 54 | ³√54 | 3.780 |
| 4 | 54 | ⁴√54 | ±2.711 |
| 5 | 54 | ⁵√54 | 2.221 |
Additional Information
The square root of 54 is often needed in various mathematical problems and applications, from algebra to geometry. Knowing its exact and approximate forms can be useful in solving equations and understanding mathematical concepts.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 54
The square root of 54 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the product 54. This mathematical operation is fundamental in various fields, including algebra and geometry. The square root of 54 can be expressed in both its decimal and simplest radical forms. Understanding how to determine and simplify this square root is crucial for solving related mathematical problems.
Mathematically, the square root of 54 is represented as:
$$\sqrt{54}$$
This value can be simplified by factorizing the number under the radical. The steps to simplify the square root of 54 are:
- Identify the prime factors of 54: \(54 = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3\).
- Group the prime factors: \(54 = (3 \times 3) \times 6\).
- Simplify the square root: \(\sqrt{54} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 6} = 3\sqrt{6}\).
Therefore, the simplest radical form of the square root of 54 is:
$$3\sqrt{6}$$
In its decimal form, the square root of 54 is approximately:
$$\sqrt{54} \approx 7.348469228$$
This value is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Definition and Symbol
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 54, the square root is denoted as \( \sqrt{54} \). The square root symbol, \( \sqrt{} \), is called a radical sign, and the number under the radical sign is called the radicand.
Since 54 is not a perfect square, its square root cannot be simplified to an integer. Instead, it can be expressed in its simplest radical form or as a decimal. The simplest radical form of \( \sqrt{54} \) is \( 3\sqrt{6} \), because 54 can be factored into 9 and 6, with 9 being a perfect square. Thus:
- 54 = 9 × 6
- \( \sqrt{54} = \sqrt{9 \times 6} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{6} = 3\sqrt{6} \)
When approximated as a decimal, the square root of 54 is approximately 7.348. This value is irrational, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion.
| Radical Form | \( 3\sqrt{6} \) |
| Decimal Form | 7.348 |
Is 54 a Perfect Square?
No, 54 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer. In other words, there must be an integer \( n \) such that \( n^2 = 54 \). However, there is no such integer because:
- The integers closest to the square root of 54 are 7 and 8 (since \( 7^2 = 49 \) and \( 8^2 = 64 \)).
- 54 falls between these two squares, indicating that its square root is not an integer.
Since 54 cannot be expressed as the product of an integer with itself, it is not a perfect square.
The exact value of the square root of 54 is approximately 7.34846922835, which is an irrational number. This means it cannot be represented as a simple fraction of two integers and has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion.
To further understand why 54 is not a perfect square, consider its prime factorization:
- 54 can be factored into prime numbers as \( 54 = 2 \times 3^3 \).
- A perfect square would require all prime factors to be in even powers. Here, the power of 3 is odd, which prevents 54 from being a perfect square.
Therefore, the square root of 54, when simplified, is expressed as \( 3\sqrt{6} \), further confirming that it is not a perfect square.
Rational or Irrational?
To determine whether the square root of 54 is rational or irrational, we first need to understand the definitions of these terms:
- A rational number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero.
- An irrational number cannot be written as a simple fraction. Instead, it is a decimal that goes on forever without repeating.
Let's analyze the square root of 54:
The square root of 54 is approximately 7.3484692283495. Since this number is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal, it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Thus, the square root of 54 is an irrational number.
Another way to confirm this is to consider whether 54 is a perfect square. A number is a perfect square if its square root is a whole number. However, since 54 is not a perfect square (because √54 ≈ 7.3484692283495 is not an integer), the square root of 54 is irrational.
Therefore, we conclude that the square root of 54 is irrational because it cannot be precisely written as a fraction, and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
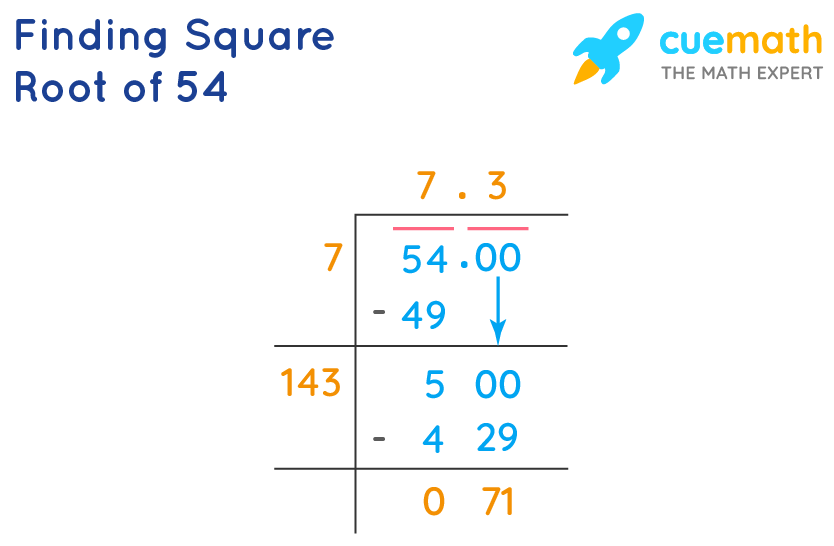
Simplifying the Square Root of 54
Simplifying the square root of 54 involves breaking it down into its simplest radical form. Here are the steps:
-
Prime Factorization: Start by expressing 54 as a product of its prime factors.
\[ 54 = 2 \times 3^3 \]
-
Group the Factors: Identify and group the perfect square factors.
\[ 54 = 3^2 \times 6 \]
-
Separate the Radicals: Rewrite the square root of the product as the product of the square roots.
\[ \sqrt{54} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 6} = \sqrt{3^2} \times \sqrt{6} \]
-
Simplify: Take the square root of the perfect square.
\[ \sqrt{3^2} = 3 \]
-
Combine: Multiply the simplified term by the remaining radical.
\[ \sqrt{54} = 3 \sqrt{6} \]
Therefore, the square root of 54 simplified is \( 3 \sqrt{6} \).
In decimal form, \( \sqrt{54} \approx 7.3485 \).
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 54
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 54. The two most common methods are the Prime Factorization method and the Long Division method. Here, we will also introduce the Newton-Raphson method as an alternative approach.
Prime Factorization
The Prime Factorization method involves breaking down 54 into its prime factors and simplifying the square root.
- Find the prime factors of 54:
\(54 = 2 \times 3^3\)
- Express 54 under the square root:
\(\sqrt{54} = \sqrt{2 \times 3^3}\)
- Simplify by taking out pairs of prime factors:
\(\sqrt{54} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 6} = 3\sqrt{6}\)
Long Division Method
The Long Division method is useful for finding the decimal value of the square root. Here’s how you can use it:
- Pair the digits of 54 starting from the decimal point. If there is an odd number of digits, add a zero to the left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 54. In this case, it is 7, because \(7^2 = 49\).
- Subtract 49 from 54, giving a remainder of 5. Bring down pairs of zeros and repeat the process.
- The result will converge to 7.348 after several iterations.
Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson method is an iterative numerical method to find the square root. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Choose an initial estimate, \(x_0\). For 54, we start with \(x_0 = 7\).
- Use the formula \(x_{n+1} = \frac{x_n + \frac{54}{x_n}}{2}\) to get a new estimate.
- Repeat the process until the value stabilizes. For example:
- Initial estimate: \(x_0 = 7\)
- First iteration: \(x_1 = \frac{7 + \frac{54}{7}}{2} = 7.0714\)
- Second iteration: \(x_2 = \frac{7.0714 + \frac{54}{7.0714}}{2} \approx 7.3484\)
- The value will converge to approximately 7.348 after a few iterations.
Using these methods, the square root of 54 can be found accurately. Each method has its advantages and applications depending on the context.
Using a Calculator
Calculating the square root of 54 using a calculator is straightforward and can be done in a few simple steps. Here's how you can do it:
-
Basic Calculator:
- Turn on your calculator.
- Enter the number 54.
- Press the square root (√) button. This is often labeled as "√", "√x", or "sqrt".
- The display will show the result, which is approximately 7.3485.
-
Scientific Calculator:
- Turn on your scientific calculator.
- Enter the number 54.
- Press the square root button (usually labeled as "√" or "√x").
- Alternatively, you can use the exponent key to raise 54 to the power of 0.5 (which is the same as taking the square root): Enter 54, press the exponent key (usually "^" or "y^x"), enter 0.5, and then press equals (=).
- The display will show the square root of 54, which is approximately 7.3485.
-
Online Calculator:
- Open your web browser and go to an online calculator website.
- Enter "54" in the input field.
- Select the square root function, often found in the calculator's scientific mode or by selecting the "√" button.
- The website will display the square root of 54, which is approximately 7.3485.
Using these steps, you can quickly and accurately find the square root of 54 using any calculator.
Using a Computer
To find the square root of 54 using a computer, you can utilize various software programs or online tools that perform mathematical calculations. Below are step-by-step instructions for different methods:
Using a Calculator Application
- Open the calculator application on your computer. This can usually be found in the accessories or tools section of your operating system.
- Ensure the calculator is in scientific mode. This mode provides functions beyond basic arithmetic, such as square roots.
- Enter the number 54.
- Press the square root (√) button. The result, approximately 7.348469, will be displayed.
Using an Online Calculator
- Open a web browser and navigate to an online calculator tool, such as the one provided by BYJU’S or any other reliable source.
- In the input field, type 54.
- Click on the button labeled "Find Square Root" or a similar command.
- The tool will display the square root of 54, which is approximately 7.348469.
Using a Programming Language
If you are familiar with programming, you can use a programming language to calculate the square root of 54. Below are examples using Python and JavaScript:
Python
import math
result = math.sqrt(54)
print(result) # Output: 7.3484692283495345
JavaScript
let result = Math.sqrt(54);
console.log(result); // Output: 7.3484692283495345
By following these methods, you can easily calculate the square root of 54 using a computer, whether through a calculator application, an online tool, or a programming language.

Square Root of 54 Rounded
The square root of 54 is an irrational number, which means it has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion. When rounded to different decimal places, the value of the square root of 54 can be expressed as follows:
- Rounded to the nearest tenth: \( \sqrt{54} \approx 7.3 \)
- Rounded to the nearest hundredth: \( \sqrt{54} \approx 7.35 \)
- Rounded to the nearest thousandth: \( \sqrt{54} \approx 7.348 \)
For most practical purposes, rounding to the nearest hundredth or thousandth is often sufficient. However, if higher precision is required, one can use more decimal places as needed.
In summary, the rounded values of the square root of 54 are:
| Decimal Places | Value |
|---|---|
| 1 (tenth) | 7.3 |
| 2 (hundredth) | 7.35 |
| 3 (thousandth) | 7.348 |
These approximations can be useful in various mathematical and scientific applications where exact precision is not critical.
Square Root of 54 as a Fraction
The square root of 54 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as an exact fraction. However, we can approximate it as a fraction for practical purposes. Here's how we can represent the square root of 54 in fractional form:
Approximation: The decimal value of the square root of 54 is approximately 7.34846922835. To express this as a fraction, we can start with a simple form.
Express as a Fraction: We approximate 7.34846922835 to 7.35 (to the nearest hundredth).
Convert Decimal to Fraction: Convert 7.35 into a fraction:
Simplify the Fraction: Simplify to its simplest form:
Mixed Number Form: Convert the improper fraction to a mixed number:
Therefore, an approximate fractional representation of the square root of 54 is .
Applications and Examples
The square root of 54, approximately 7.348, has numerous applications in various fields. Understanding these applications can provide practical insights into how this mathematical concept is utilized in real-world scenarios. Here are some detailed examples:
- Architecture and Construction: In architecture, square roots are used to calculate dimensions and structural integrity. For example, when designing a building, architects might use the square root to determine the length of diagonal supports needed for stability. This ensures that the structure can withstand various loads and stresses.
- Engineering: Engineers frequently use square roots in their calculations. For instance, in electrical engineering, the square root is used to calculate the power dissipation in resistive circuits, where the power \( P \) is given by \( P = I^2 \times R \), and \( I \) can be found using the square root of \( P \) divided by \( R \).
- Finance: In finance, the square root is used to calculate the standard deviation, a measure of market volatility. For example, if the variance of a stock's returns is known, the standard deviation (which is the square root of the variance) helps investors understand the risk associated with the stock.
- Navigation: Pilots and navigators use the square root to determine distances between points on a map. The distance formula, which includes square roots, helps in plotting the shortest path between two locations on Earth.
- Statistics: The square root is essential in statistics for calculating standard deviations and variances. These measures are crucial for data analysis, helping statisticians understand data dispersion and make predictions based on statistical models.
- Science: In physics, square roots are used in formulas involving motion and energy. For example, the velocity of an object in free fall can be determined using the square root of the product of the gravitational constant and the height from which it falls.
- Computer Science: Square roots are used in algorithms for encryption and decryption, ensuring data security. Additionally, in graphics programming, the square root is used to calculate distances and render realistic images.
These examples highlight the diverse applications of the square root of 54 in various fields, demonstrating its importance beyond simple mathematical calculations.
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 54 bằng các bước dễ hiểu. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính toán và ứng dụng của căn bậc hai.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 54: Sqrt(54)
READ MORE:
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 54 được giải thích trong #shorts.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 54 | #shorts