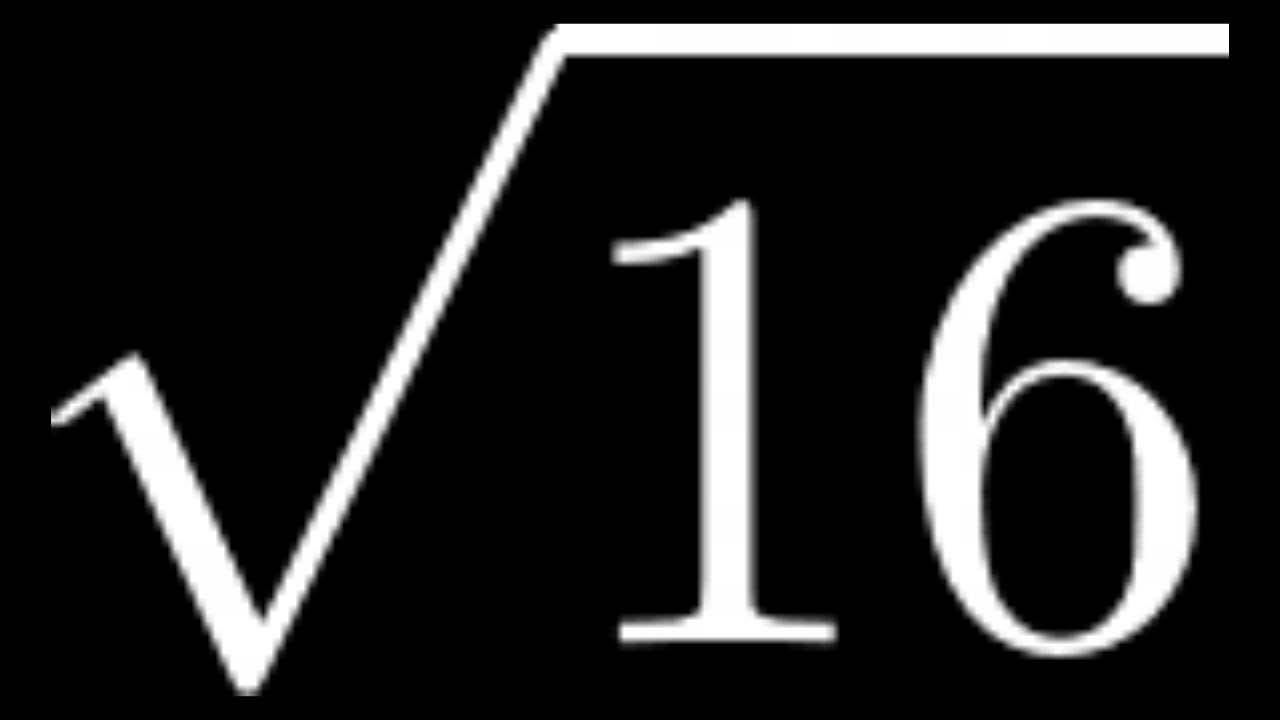Topic what is the square root of 16x36: Discover the intriguing process of finding the square root of 16x36. This guide will take you through a step-by-step approach to understand how to calculate the square root, its applications in various fields, and common mistakes to avoid. Master this fundamental mathematical concept with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
Understanding the Square Root of 16x36
The square root of a product like 16x36 can be calculated by finding the square roots of each factor separately and then multiplying the results.
Steps to Simplify
- Simplify the square root of 16: \(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
- Simplify the square root of 36: \(\sqrt{36} = 6\)
- Multiply the results: \(4 \times 6 = 24\)
Therefore, the square root of 16x36 is \(24\).
Applications
- Finance: Used in calculating standard deviations to measure investment risks.
- Physics: Integral in formulas for gravitational force, motion, and energy.
- Computer Graphics: Important for rendering images and animations.
- Healthcare: Used in medical dosage calculations and interpreting medical images.
Common Mistakes
- Confusing the square of a number with its square root.
- Neglecting negative roots.
- Incorrectly simplifying square roots without breaking down into prime factors.
Advanced Concepts
- Imaginary and Complex Numbers
- Quadratic Equations
- Radical Equations
- Conic Sections
- Calculus
Conclusion
Mastering square roots, such as calculating \(\sqrt{16x36}\), is fundamental in various fields, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking skills.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the square root of a mathematical expression is fundamental in various fields such as finance, physics, and computer graphics. The square root of 16x36 might seem complex, but it can be simplified by breaking it down into more manageable parts.
First, recognize that the expression 16x36 can be decomposed into its factors. The number 16 is a perfect square (42), as is 36 (62). Therefore, the square root of 16x36 involves taking the square root of each factor separately.
- The square root of 16 is 4.
- The square root of 36 is 6.
When multiplied together, the square roots of these factors give:
\[\sqrt{16 \cdot 36} = \sqrt{16} \cdot \sqrt{36} = 4 \cdot 6 = 24\]
This step-by-step approach helps in simplifying and understanding the calculation. By breaking down the problem into smaller parts, you can easily find that the square root of 16x36 is 24.
This concept is not only crucial for solving mathematical problems but also has practical applications in different domains, making it an essential skill to master.
Basics of Square Roots
Understanding square roots is fundamental in mathematics. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. This is denoted by the radical symbol √. For example, the square root of 16 is 4, because 4 x 4 = 16. Similarly, the square root of 36 is 6, because 6 x 6 = 36.
To calculate the square root of a product, such as 16x36, you can simplify it step by step:
- First, find the square root of each factor individually:
- The square root of 16 is 4.
- The square root of 36 is 6.
- Then, multiply the results of these square roots:
- \(4 \times 6 = 24\).
Therefore, the square root of 16x36 is 24.
Square roots have various applications in different fields:
- In finance, to calculate standard deviation and assess investment risks.
- In physics, for formulas involving gravitational force and motion.
- In computer graphics, for rendering images and animations.
- In healthcare, for determining medication dosages based on body surface area.
Mastering square roots can significantly enhance problem-solving skills and open up numerous practical applications in various disciplines.
Calculating the Square Root of 16x36
Calculating the square root of a product of numbers can be simplified by breaking down the calculation into manageable steps. Here, we will find the square root of \(16 \times 36\).
- Understanding the Problem: We need to find the square root of the product of 16 and 36.
- Prime Factorization:
- Prime factorization of 16 is \(2^4\).
- Prime factorization of 36 is \(2^2 \times 3^2\).
- Multiplying the Factors:
Combine the prime factors:
\(16 \times 36 = 2^4 \times 2^2 \times 3^2\)
This simplifies to \(2^{4+2} \times 3^2 = 2^6 \times 3^2\).
- Applying the Square Root:
Use the property of square roots: \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\).
\(\sqrt{2^6 \times 3^2} = \sqrt{2^6} \times \sqrt{3^2}\)
Since \(\sqrt{2^6} = 2^3\) and \(\sqrt{3^2} = 3\), we get:
\(2^3 \times 3 = 8 \times 3 = 24\).
Therefore, the square root of \(16 \times 36\) is 24.
Step-by-Step Summary
- Prime factorize each number: 16 is \(2^4\) and 36 is \(2^2 \times 3^2\).
- Combine the factors: \(16 \times 36 = 2^6 \times 3^2\).
- Take the square root of each part: \(\sqrt{2^6} = 2^3\) and \(\sqrt{3^2} = 3\).
- Multiply the results: \(8 \times 3 = 24\).
In conclusion, the square root of \(16 \times 36\) is 24.
Applications of Square Roots
The square root function is a fundamental mathematical tool with numerous applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where square roots are particularly useful:
-
Geometry:
Square roots are used to calculate the length of the sides of a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem. For example, if the sides of a right triangle are 3 and 4 units, the hypotenuse is calculated as:
\[\sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\]
-
Physics:
In physics, square roots are used in various formulas. For instance, the period \(T\) of a pendulum is given by:
\[T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{L}{g}}\]
where \(L\) is the length of the pendulum and \(g\) is the acceleration due to gravity.
-
Statistics:
In statistics, the standard deviation, which measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values, is calculated using square roots. The standard deviation \( \sigma \) of a dataset is given by:
\[\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} (x_i - \mu)^2}\]
where \(N\) is the number of observations, \(x_i\) is each individual observation, and \( \mu \) is the mean of the observations.
-
Engineering:
Square roots are essential in engineering for calculations involving areas and volumes. For example, the power dissipated in an electrical circuit with resistance \(R\) and current \(I\) is:
\[P = I^2 R\]
If we need to find the current given the power and resistance, we use the square root:
\[I = \sqrt{\frac{P}{R}}\]
-
Finance:
Square roots are used in finance to calculate the volatility of stocks and to find compound interest rates. For example, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is calculated as:
\[CAGR = \left( \frac{V_f}{V_i} \right)^{\frac{1}{n}} - 1\]
where \(V_f\) is the final value, \(V_i\) is the initial value, and \(n\) is the number of years.
In conclusion, the square root function is a versatile mathematical tool that finds applications in a wide range of disciplines, helping solve problems and understand relationships in both theoretical and practical contexts.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating square roots is a fundamental skill in mathematics, yet it is common for students and even experienced individuals to make certain errors. Recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes can improve accuracy and understanding in dealing with square roots. Here are some key pitfalls to watch out for:
-
Misunderstanding the Concept of Squares and Square Roots: A frequent mistake is confusing the square of a number with its square root. Remember, the square of a number is the number multiplied by itself (e.g., \( 4^2 = 16 \)), while the square root is the number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number (e.g., \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \)).
-
Ignoring Negative Roots: For positive numbers, there are always two square roots—one positive and one negative. Neglecting the negative root, especially when solving equations, can lead to incomplete solutions. For instance, the square roots of 36 are \( \pm 6 \).
-
Incorrectly Simplifying Square Roots: Simplifying square roots without fully breaking down the number into its prime factors can lead to incorrect simplifications. Ensure all prime factors are considered to accurately simplify the root. For example, \( \sqrt{72} \) should be simplified to \( 6\sqrt{2} \) by recognizing it as \( \sqrt{36 \times 2} \).
-
Decimal Approximations: Relying too heavily on decimal approximations instead of exact values can lead to inaccuracies in further calculations. Where possible, keep the square root in its radical form until the final step. For example, use \( \sqrt{2} \) instead of approximating it as 1.41.
-
Overcomplicating the Problem: Sometimes, the simplest path to the solution is overlooked. For example, when calculating the square root of a product like \( 16 \times 36 \), recognize that these can be simplified individually before multiplication to make the calculation easier: \( \sqrt{16 \times 36} = \sqrt{16} \times \sqrt{36} = 4 \times 6 = 24 \).
By being mindful of these common errors and applying a thoughtful approach to solving problems involving square roots, one can enhance their mathematical skills and avoid potential pitfalls. Practice and patience are key to mastering the calculation of square roots.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính căn bậc hai của 16x36 hoặc 36x16. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp và mẹo tính nhanh.
Raiz Cuadrada de 16x36 o 36x16, Raices de una Multiplicacion (Producto)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức về căn bậc hai và áp dụng vào các bài toán thực tế.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai