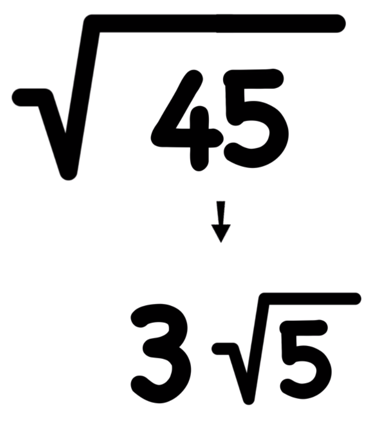Topic 5 times square root of 5: Discover the fascinating world of mathematics through the exploration of the expression "5 times square root of 5." This article delves into its calculation, properties, and real-life applications, making complex concepts accessible and engaging for all readers.
Table of Content
Calculation of 5 Times Square Root of 5
The expression \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \) can be calculated as follows:
- Step 1: Identify the expression to be calculated: \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \)
- Step 2: Simplify the square root expression: \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \)
- Step 3: Multiply the simplified square root by 5: \( 5 \times 2.236 = 11.18 \)
Thus, \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \approx 11.18 \).
Square Root Calculation Methods
There are various methods to calculate the square root of a number, which include:
- Using a calculator for quick results
- Manual methods involving estimation and iteration
- Using online square root calculators for precise results
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are widely used in various fields such as:
- Algebra and solving quadratic equations
- Geometry for calculating distances and areas
- Physics and engineering for solving problems involving wave functions and signal processing
Resources
For further reading and practice, you can use the following online tools:
READ MORE:
Introduction
The expression "5 times the square root of 5" involves calculating the product of the number 5 and the square root of 5, represented mathematically as \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\). This calculation is significant in various mathematical contexts, including algebra, geometry, and practical applications. The square root of 5 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.236. Therefore, multiplying this by 5 gives a value of approximately 11.18. Understanding how to compute and apply this value can be beneficial in solving a range of mathematical problems.
Mathematical Definition
The expression \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) combines a whole number and an irrational number. To understand it comprehensively, let's break down the components:
- Square Root of 5: The square root of 5, denoted as \(\sqrt{5}\), is an irrational number. It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating, approximately equal to 2.236.
- Multiplication: Multiplying 5 by \(\sqrt{5}\) means scaling the value of \(\sqrt{5}\) by 5. In mathematical terms, \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) can be written as: \[ 5 \times \sqrt{5} = 5\sqrt{5} \]
To further understand, let's simplify the expression step-by-step:
-
Identify the square root: \(\sqrt{5}\) is approximately 2.236. -
Multiply the whole number by the square root: \(5 \times 2.236 \approx 11.18\).
Therefore, \(5 \times \sqrt{5} \approx 11.18\). This multiplication showcases the combination of whole numbers and irrational numbers in algebraic expressions.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the value of \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) can be approached using several methods. Here, we will discuss three common methods: estimation, the long division method, and Newton’s method.
- Estimation:
- Find the nearest perfect squares around the number 5, which are 4 and 9.
- Since \(\sqrt{4} = 2\) and \(\sqrt{9} = 3\), we know \(\sqrt{5}\) is between 2 and 3.
- Approximate \(\sqrt{5}\) as 2.236. Then, \(5 \times 2.236 \approx 11.18\).
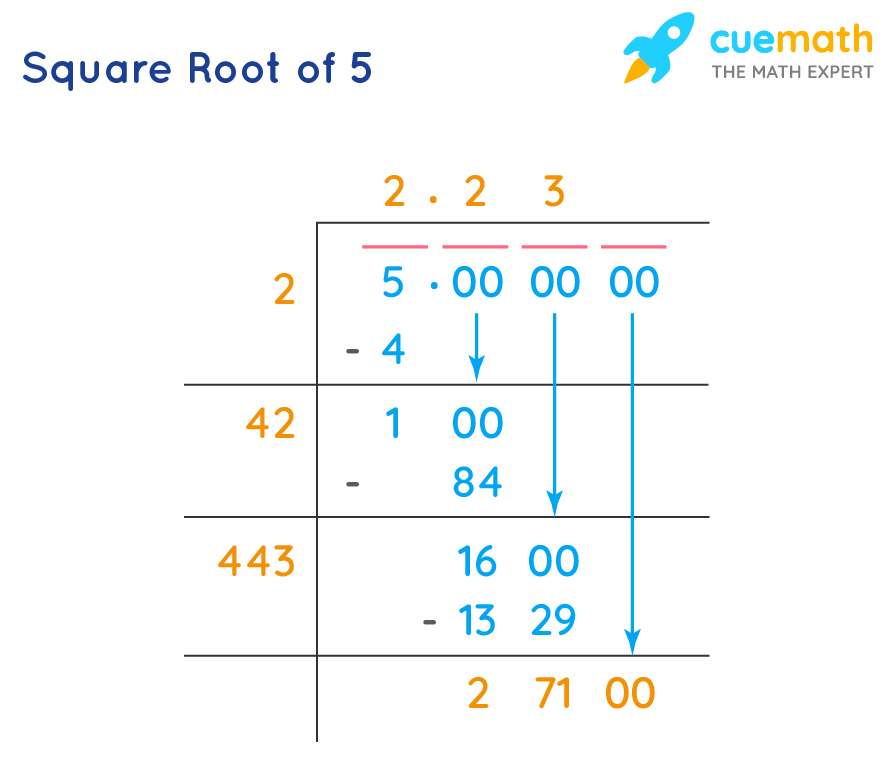
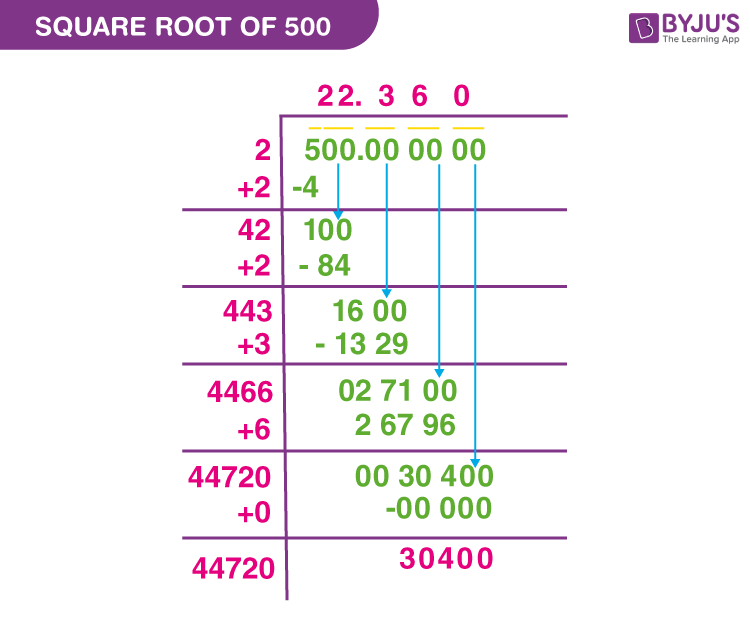
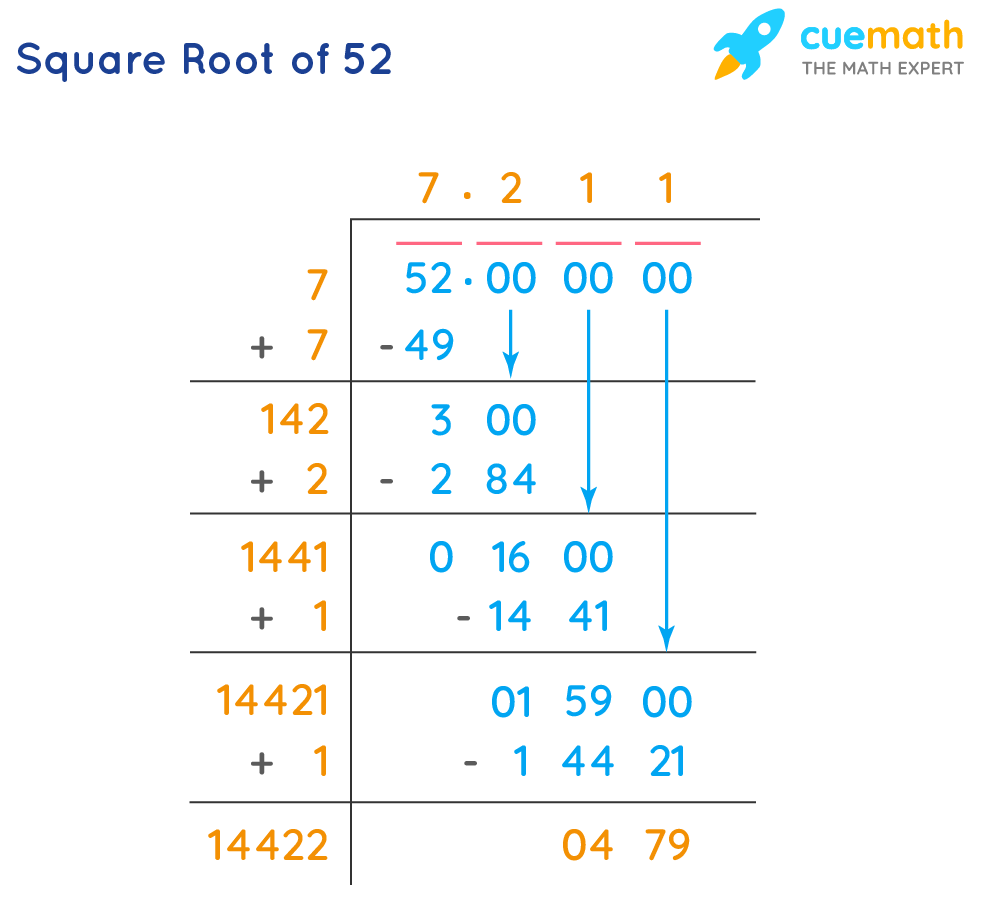
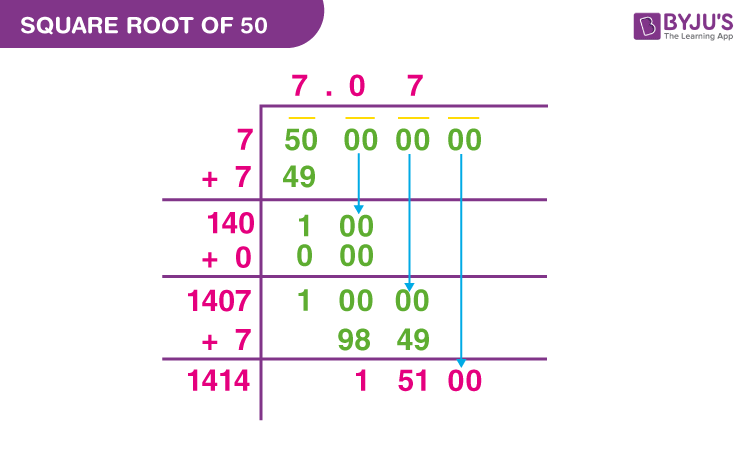
- Long Division Method:
- Pair the digits of the number starting from the decimal point. For 5, we write it as 5.00.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 5. The largest number is 2 because \(2^2 = 4\).
- Double the divisor and bring down the next pair of zeros, making it 20.
- Estimate the next digit by finding a number which, when multiplied by the new divisor, is less than or equal to the dividend.
- Repeat until the desired precision is achieved. For \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\), continue to refine the approximation of \(\sqrt{5}\).
- Newton’s Method:
- Start with an initial guess. For \(\sqrt{5}\), let’s guess 2.2.
- Use the formula \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{5}{x_n} \right) \).
- Calculate: \( x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 2.2 + \frac{5}{2.2} \right) = 2.238 \).
- Repeat until the value stabilizes. Once \(\sqrt{5}\) is approximated, multiply by 5 to get the final result.
These methods provide a structured approach to finding the value of \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\), allowing for accurate results in various practical applications.
Properties and Applications
The expression \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) demonstrates interesting mathematical properties and applications. Below, we explore these properties and how this expression can be used in various fields.
- The square root of 5, denoted as \(\sqrt{5}\), is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.236. When multiplied by 5, the product is approximately 11.18.
- Expressing the square root as a power: \(\sqrt{5} = 5^{0.5}\). Therefore, \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) can be written as \(5 \times 5^{0.5}\) or \(5^{1.5}\).
- The square root of a product rule: For any positive numbers \(a\) and \(b\), \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\). Applying this, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\), simplifies \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) further.
Applications of the expression \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) include:
- Geometry: This expression can represent the length of a diagonal in a rectangular prism with specific dimensions, leveraging the Pythagorean theorem.
- Physics: In physics, such expressions can be used in wave mechanics and quantum physics where root values are frequently encountered.
- Engineering: Calculations involving the square roots of various constants are common in engineering, especially in signal processing and control systems.
Understanding the properties of \(5 \times \sqrt{5}\) enriches our comprehension of mathematical principles and enhances their practical application across different scientific and engineering disciplines.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding how to work with the expression \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \) involves practicing with various examples and problems. Below are some examples and practice problems that will help you master the concept:
- Example 1: Simplify \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \)
- Example 2: Evaluate \( 5 \times \sqrt{25} \)
- Practice Problem 1: Simplify \( 5 \times \sqrt{45} \)
- Practice Problem 2: Evaluate \( 5 \times \sqrt{80} \)
- Practice Problem 3: Solve \( 5 \times \sqrt{8} \)
To simplify \( 5 \times \sqrt{5} \), you can write it as:
\[ 5 \times \sqrt{5} = 5 \times 2.236 = 11.18 \]
Here, you can simplify inside the square root first:
\[ \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
Then multiply by 5:
\[ 5 \times 5 = 25 \]
First, factorize 45 inside the square root:
\[ 45 = 9 \times 5 \]
So, \( \sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} = 3 \times \sqrt{5} \)
Then, multiply by 5:
\[ 5 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} = 15 \sqrt{5} \]
First, simplify the square root of 80:
\[ \sqrt{80} = \sqrt{16 \times 5} = 4 \times \sqrt{5} \]
Then, multiply by 5:
\[ 5 \times 4 \times \sqrt{5} = 20 \sqrt{5} \]
Simplify the square root of 8:
\[ \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} = 2 \times \sqrt{2} \]
Then, multiply by 5:
\[ 5 \times 2 \times \sqrt{2} = 10 \sqrt{2} \]
These examples and practice problems illustrate how to work with expressions involving square roots and multiplication. Practice these steps to become more proficient in simplifying and solving such mathematical expressions.
Tools and Resources
When dealing with calculations involving the square root of 5, including 5 times the square root of 5, several tools and resources can be extremely helpful. These tools not only facilitate the computation but also enhance understanding through step-by-step solutions and visual aids.
-
Mathway Square Root Calculator:
Mathway offers a comprehensive square root calculator that allows users to enter radical expressions and obtain step-by-step solutions. It is a valuable resource for understanding how to simplify square roots and solve related problems.
-
Calculator.net Root Calculator:
This tool provides the ability to calculate square roots as well as cube roots and higher-order roots. It includes a detailed explanation of the methods used, making it an excellent resource for learning the calculation process.
-
Math.net Square Root Calculator:
Math.net offers an intuitive calculator that helps find the principal square root of any nonnegative real number. This tool is useful for both quick calculations and educational purposes.
-
Math is Fun - Squares and Square Roots:
This website provides a thorough explanation of square roots, including properties, methods of calculation, and practical examples. It also offers interactive tools to practice calculating square roots.
READ MORE:
Video giải thích về biểu thức căn bậc hai của 5 lặp lại đến vô hạn. Hãy xem để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Căn bậc hai của 5 lặp lại vô hạn