Topic perimeter volume area: The concepts of perimeter, volume, and area are fundamental in mathematics and essential in various practical applications. Understanding how to calculate these measurements is crucial for tasks ranging from construction to crafting. This article provides an in-depth look at these concepts, their formulas, and practical examples to enhance your comprehension and application skills.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter, Area, and Volume
- Introduction
- Definitions and Formulas
- Calculating Perimeter
- Calculating Area
- Calculating Volume
- Interactive Learning Activities
- Practice Problems and Quizzes
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video giải thích chi tiết về chu vi, diện tích và thể tích, phù hợp cho học sinh và người mới bắt đầu học toán.
Understanding Perimeter, Area, and Volume
The concepts of perimeter, area, and volume are fundamental in geometry and are used to measure different aspects of shapes and solids. Below is a detailed explanation and formulas related to these concepts.
Perimeter
The perimeter is the distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape.
- Rectangle: Perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: Perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
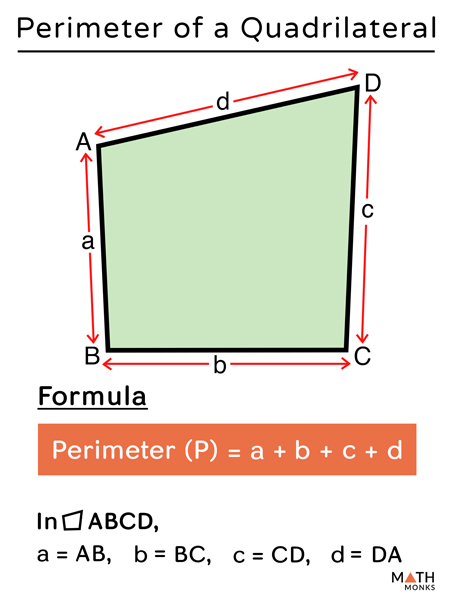
- Triangle: Perimeter \( P \) is the sum of all sides, \( P = a + b + c \).
- Circle: Perimeter (Circumference) \( C \) is given by \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
Area
Area is the amount of space inside the boundary of a two-dimensional shape.
- Rectangle: Area \( A \) is given by \( A = l \times w \).
- Square: Area \( A \) is given by \( A = s^2 \).
- Triangle: Area \( A \) is given by \( A = \frac{1}{2} b h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Circle: Area \( A \) is given by \( A = \pi r^2 \).
Volume
Volume is the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object.
- Cube: Volume \( V \) is given by \( V = s^3 \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangular Prism: Volume \( V \) is given by \( V = l \times w \times h \).
- Cylinder: Volume \( V \) is given by \( V = \pi r^2 h \), where \( r \) is the radius and \( h \) is the height.
- Pyramid: Volume \( V \) is given by \( V = \frac{1}{3} A_b h \), where \( A_b \) is the area of the base and \( h \) is the height.
Applications and Activities
These geometric principles are not just theoretical but have practical applications in various fields such as construction, design, and education. Engaging activities like using graph paper for area calculations, scavenger hunts for perimeter, and hands-on projects for volume can greatly enhance understanding.
Additional Resources

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the concepts of perimeter, area, and volume is essential for solving many real-world problems. These fundamental geometric properties allow us to measure and describe the size and space of various shapes and objects. Whether you are calculating the perimeter of a garden, the area of a room, or the volume of a container, mastering these concepts can help in diverse applications from construction to crafts.
To start with, the perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by summing up the lengths of all sides of the shape. For instance, the perimeter of a rectangle is given by the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
The area represents the space enclosed within a two-dimensional shape. Different shapes have different formulas for area calculation. For example, the area of a rectangle is \( A = l \times w \), while the area of a triangle is \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
Volume measures the three-dimensional space occupied by an object. The volume of a rectangular prism is calculated using the formula \( V = l \times w \times h \). Understanding these measurements can greatly aid in practical tasks such as packing, construction, and even crafting.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the formulas and applications of perimeter, area, and volume, providing examples and practical tips for better comprehension and utilization.
Definitions and Formulas
Understanding perimeter, volume, and area is fundamental in geometry. Each concept has specific definitions and associated formulas used to calculate measurements of different shapes and objects.
- Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all sides.
- Area: The area is the amount of space inside the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is typically measured in square units.
- Volume: The volume is the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It is measured in cubic units.
Formulas
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula | Volume Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square | P = 4a | A = a^2 | N/A |
| Rectangle | P = 2(l + w) | A = lw | N/A |
| Triangle | P = a + b + c | A = \(\frac{1}{2}bh\) | N/A |
| Circle | P = 2\(\pi r\) | A = \(\pi r^2\) | N/A |
| Rectangular Prism | N/A | N/A | V = lwh |
| Cylinder | N/A | N/A | V = \(\pi r^2h\) |
These formulas are essential tools in various practical applications, from constructing buildings to solving mathematical problems. Understanding how to apply these formulas accurately can help in estimating material quantities, planning projects, and solving geometric problems.
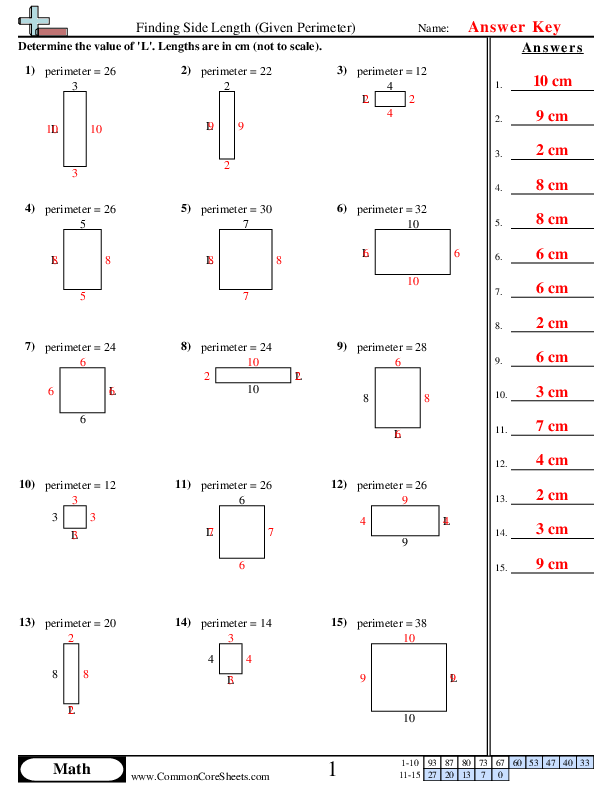
Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. Calculating the perimeter depends on the type of geometric figure.
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) is calculated using the formula: \[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Square: For a square, all sides are equal, so the perimeter is: \[ P = 4 \times side \]
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides: \[ P = a + b + c \]
- Circle: The perimeter (circumference) of a circle is calculated as: \[ P = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
These formulas can be applied to various practical problems to find the total distance around different geometric shapes. For instance, if you have a rectangular garden that is 10 meters long and 5 meters wide, the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 2 \times (10 + 5) = 2 \times 15 = 30 \text{ meters} \]
Understanding and applying these formulas can simplify many real-world calculations, ensuring accurate measurements in fields ranging from construction to landscaping.
Calculating Area
Calculating the area of various geometric shapes involves using specific formulas based on the dimensions and properties of the shape. Below are the steps and formulas for calculating the area of common shapes:
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length (\( l \)) by its width (\( w \)).
Formula: \( A = l \times w \)
- Square: The area of a square is found by squaring the length of one of its sides (\( a \)).
Formula: \( A = a^2 \)
- Triangle: To find the area of a triangle, multiply the base (\( b \)) by the height (\( h \)), then divide by 2.
Formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Circle: The area of a circle is calculated by squaring the radius (\( r \)) and multiplying by π (pi).
Formula: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Parallelogram: The area is found by multiplying the base (\( b \)) by the height (\( h \)).
Formula: \( A = b \times h \)
For composite shapes, divide the shape into simpler shapes, calculate the area for each part, and then sum them up to find the total area.

Calculating Volume
Volume is a measure of the three-dimensional space occupied by an object. Calculating the volume of different geometric shapes involves specific formulas. Here are detailed steps for various shapes:
- Cube:
For a cube with side length \(a\):
Volume, \(V = a^3\)
- Rectangular Prism:
For a rectangular prism with length \(l\), width \(w\), and height \(h\):
Volume, \(V = l \times w \times h\)
- Cylinder:
For a cylinder with radius \(r\) and height \(h\):
Volume, \(V = \pi r^2 h\)
- Sphere:
For a sphere with radius \(r\):
Volume, \(V = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\)
- Cone:
For a cone with radius \(r\) and height \(h\):
Volume, \(V = \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h\)
- Pyramid:
For a pyramid with base area \(A\) and height \(h\):
Volume, \(V = \frac{1}{3} A h\)
These formulas provide a straightforward way to calculate the volume for common geometric shapes. For more complex shapes, decomposing them into these basic shapes and summing their volumes can be an effective strategy.
Interactive Learning Activities
Engaging students in learning about perimeter, volume, and area can be made fun and interactive through various activities. Here are some creative and educational activities to consider:
-
Graph Paper Art:
Students can use graph paper to draw pictures using complete squares only. They then calculate the area and perimeter of different elements in their drawings, combining creativity with math practice.
-
Scavenger Hunts:
Task cards hidden around the classroom or playground can have questions related to perimeter, area, and volume. Students search for the cards and solve the problems they find.
-
Area Builder Simulation:
Interactive simulations like the PhET Area Builder allow students to visually understand and calculate area and perimeter through virtual manipulation of shapes.
-
Game-Based Learning:
Games like "Connect Four" adapted for area calculations or "Stinky Feet" for reviewing perimeter and volume concepts can make learning competitive and enjoyable.
-
Name Measurement Activity:
Students use graph paper to draw and measure the perimeter and area of letters in their names, which can then be displayed in the classroom for a personalized touch.
These activities not only help in understanding mathematical concepts but also in retaining them through interactive and hands-on experiences.
Practice Problems and Quizzes
To solidify your understanding of perimeter, area, and volume, the following practice problems and quizzes will help you apply the concepts in various scenarios. Each set of problems is designed to progressively build your skills and confidence.
-
Practice Problems for Perimeter
Calculate the perimeter of the following shapes:
- Rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm.
- Square with side length 7 m.
- Triangle with sides 6 cm, 8 cm, and 10 cm.
- Circle with radius 4 cm. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
-
Practice Problems for Area
Find the area of the following shapes:
- Rectangle with length 10 m and width 4 m.
- Square with side length 9 cm.
- Right triangle with base 6 cm and height 8 cm.
- Circle with radius 5 m. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
-
Practice Problems for Volume
Determine the volume of the following solids:
- Cube with side length 3 m.
- Rectangular prism with length 6 cm, width 4 cm, and height 5 cm.
- Cylinder with radius 3 cm and height 7 cm. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
- Sphere with radius 2 m. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
-
Quizzes and Assessments
Test your knowledge with these quizzes:
-
Quiz 1: Perimeter
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with sides 15 cm and 10 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side 12 cm.
- What is the perimeter of a circle with diameter 14 cm? (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
-
Quiz 2: Area
- Calculate the area of a parallelogram with base 5 m and height 12 m.
- What is the area of a trapezoid with bases 8 cm and 5 cm, and height 4 cm?
- Find the area of a circle with radius 7 cm. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
-
Quiz 3: Volume
- What is the volume of a cube with edge length 5 cm?
- Find the volume of a cone with radius 3 cm and height 9 cm. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
- Calculate the volume of a rectangular tank with length 10 m, width 5 m, and height 2 m.
-
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of perimeter, area, and volume is fundamental to grasping the basics of geometry. These measurements are not just theoretical; they have practical applications in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and daily life scenarios.
By mastering these concepts, individuals can solve real-world problems more effectively. For instance, calculating the perimeter can help in determining the length of fencing required for a property. Knowing how to compute the area is essential for tasks such as painting walls or installing flooring, while understanding volume is crucial for activities like filling a swimming pool or packing boxes.
The ability to calculate perimeter, area, and volume also enhances spatial reasoning skills. This is particularly important in fields that require precise measurements and spatial planning, such as construction, interior design, and landscape architecture.
Moreover, these geometric concepts are foundational for more advanced mathematical studies. They form the basis for topics in calculus, physics, and engineering, where precise measurements and calculations are essential.
In conclusion, a solid grasp of perimeter, area, and volume calculations not only equips individuals with practical skills for everyday tasks but also lays the groundwork for academic and professional success in various STEM fields. Encouraging the practice and application of these concepts through interactive learning and problem-solving activities can greatly enhance understanding and proficiency.

Video giải thích chi tiết về chu vi, diện tích và thể tích, phù hợp cho học sinh và người mới bắt đầu học toán.
Giải Thích Chu Vi, Diện Tích và Thể Tích | Toán với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Video cung cấp những kiến thức cơ bản về chu vi và diện tích, giúp người xem nắm vững các khái niệm hình học cơ bản.
Chu Vi và Diện Tích: Những Điều Cơ Bản | Chu Vi, Diện Tích và Thể Tích | Hình Học | Khan Academy