Topic perimeter word problems worksheet: Perimeter word problems worksheets are a great way to help students learn and apply their understanding of geometry in real-world scenarios. These worksheets provide a variety of problems involving different shapes and contexts, making learning engaging and effective for students of all levels.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Word Problems Worksheet
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Basic Perimeter Calculations
- Perimeter of Rectangles
- Perimeter of Triangles
- Perimeter of Squares
- Perimeter of Polygons
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Real-Life Perimeter Word Problems
- Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Mixed Perimeter Word Problems
- Same Perimeter, Different Area
- Perimeter Challenge Problems
- Interactive Perimeter Activities
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn bài toán chu vi cho học sinh lớp 3 bằng tiếng Việt, giúp thu hút người xem và cung cấp bài tập chu vi cho trẻ em.
Perimeter Word Problems Worksheet
Enhance your students' understanding of perimeter with a variety of worksheets and activities designed for different grade levels. These resources are ideal for practicing how to solve perimeter word problems in real-life and geometric contexts.
Example Problems
- A rectangular path is 2 feet wide and 28 feet longer than it is wide. What is the perimeter of the path?
- Calculate the perimeter of a picture frame that measures 16 inches by 20 inches.
- Camden is roping off a soccer field in his backyard measuring 50 feet by 35 feet. How much rope does he need?
Real-Life Applications
Understanding perimeter is essential in everyday situations, such as installing fencing, lining a pool with chairs, or putting up Christmas lights. These worksheets provide practical examples that help students relate mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios.
Grade-Level Worksheets
- Grades 3-4: Basic perimeter problems, including finding the perimeter of squares, rectangles, and other polygons.
- Grades 5-6: More challenging problems, including those involving missing sides and complex shapes.
Interactive and Printable Worksheets
These resources include interactive worksheets that can be used in digital formats, such as Google Slides, as well as printable PDFs. This flexibility ensures that you can use these tools in various teaching environments.
| Resource | Description | Grade Level |
|---|---|---|
| Perimeter word problems with space for students to show their work. | 3-5 | |
| Step-by-step solutions for perimeter word problems. | 3-6 | |
| Printable worksheets with differentiated problems to meet various learning needs. | 3-4 |
Additional Resources
For more perimeter activities and resources, visit and . These sites offer a variety of printable and interactive worksheets to support your math curriculum.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
Perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is essentially the distance around the edge of a figure. Understanding how to calculate perimeter is crucial for solving many real-life problems, such as determining the length of fencing needed to enclose a garden or the amount of material required to frame a picture.
To calculate the perimeter of common shapes, you can use the following formulas:
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
Let's explore a step-by-step example:
- Identify the shape you are dealing with. For example, if it's a rectangle, note its length and width.
- Apply the formula for the perimeter of the shape. For a rectangle with length \( l = 8 \) units and width \( w = 3 \) units, use \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Calculate: \( P = 2(8) + 2(3) = 16 + 6 = 22 \) units.
Understanding perimeter not only helps in academic problems but also in practical scenarios. For instance, when installing a fence around a yard, knowing the perimeter will tell you how much fencing material you need to purchase.
As you practice solving perimeter word problems, remember to break down complex shapes into simpler ones, calculate the perimeter of each part, and then sum them up for the total perimeter.
Basic Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the perimeter of a shape is essential in solving various geometric problems. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a polygon. Here, we will explore how to calculate the perimeter of different shapes, step-by-step.
1. Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares
To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle or a square, you add up the lengths of all the sides.
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is given by the formula \( P = 2l + 2w \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Example: For a rectangle with length 5 units and width 3 units, the perimeter is \( P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \) units.
2. Perimeter of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- General Formula: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
Example: For a triangle with sides 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units, the perimeter is \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) units.
3. Perimeter of Circles (Circumference)
For circles, the perimeter is referred to as the circumference.
- Formula: The circumference \( C \) of a circle is \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \), where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
Example: For a circle with a radius of 4 units, the circumference is \( C = 2\pi(4) = 8\pi \) units.
4. Perimeter of Polygons
To find the perimeter of any polygon, sum the lengths of all its sides.
- Regular Polygon: For a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = n \times s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side.
Example: For a regular hexagon with each side measuring 6 units, the perimeter is \( P = 6 \times 6 = 36 \) units.
These basic perimeter calculations provide a foundation for solving more complex word problems involving the perimeter of various shapes.
Perimeter of Rectangles
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the rectangle. It can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 2L + 2W \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter, \( L \) is the length, and \( W \) is the width.
To solve perimeter word problems involving rectangles, follow these steps:
- Identify the length and width: Read the problem carefully to determine the dimensions of the rectangle. For example, if a problem states that the length is 10 meters and the width is 5 meters, these are your dimensions.
- Substitute the values into the formula: Replace \( L \) and \( W \) in the formula with the given values. For example:
- Length (\( L \)) = 10 meters
- Width (\( W \)) = 5 meters
- Calculate the perimeter: Perform the arithmetic to find the perimeter.
- \( P = 2L + 2W \)
- \( P = 2(10) + 2(5) \)
- \( P = 20 + 10 \)
- \( P = 30 \) meters
For example, if you have a rectangle where the length is 15 feet and the width is 8 feet, you would calculate the perimeter as follows:
\[ P = 2L + 2W = 2(15) + 2(8) = 30 + 16 = 46 \text{ feet} \]
Another example could be a rectangle where the length is described as being 5 units more than twice the width, and the perimeter is 40 units. Set up an equation to solve for the width (\( W \)) and then find the length (\( L \)).
Let's denote the width by \( W \). The length is then \( 2W + 5 \). The perimeter equation is:
\[ 2L + 2W = 40 \]
\[ 2(2W + 5) + 2W = 40 \]
\[ 4W + 10 + 2W = 40 \]
\[ 6W + 10 = 40 \]
\[ 6W = 30 \]
\[ W = 5 \]
Now, substitute \( W \) back to find \( L \):
\[ L = 2W + 5 = 2(5) + 5 = 10 + 5 = 15 \]
Thus, the dimensions of the rectangle are 5 units for the width and 15 units for the length. Verifying the perimeter:
\[ P = 2L + 2W = 2(15) + 2(5) = 30 + 10 = 40 \text{ units} \]
This approach helps in solving various word problems related to the perimeter of rectangles effectively.
Perimeter of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Calculating the perimeter is straightforward and involves adding the lengths of all sides. This can be represented by the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
Where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- Step 1: Identify the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Step 2: Add the lengths of the sides together.
- Step 3: The sum is the perimeter of the triangle.
For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm} = 21 \, \text{cm} \]
This concept applies to all types of triangles, whether they are equilateral, isosceles, or scalene:
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal, so the perimeter is three times the length of one side.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal, and the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of the two equal sides plus the length of the base.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides are of different lengths, and the perimeter is the sum of all three side lengths.
Let's take another example with different types of triangles:
| Type of Triangle | Sides (a, b, c) | Perimeter Calculation | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilateral | 6 cm, 6 cm, 6 cm | \(6 + 6 + 6\) | 18 cm |
| Isosceles | 8 cm, 8 cm, 5 cm | \(8 + 8 + 5\) | 21 cm |
| Scalene | 7 cm, 10 cm, 12 cm | \(7 + 10 + 12\) | 29 cm |
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry that helps in solving various real-life problems and more complex mathematical tasks.
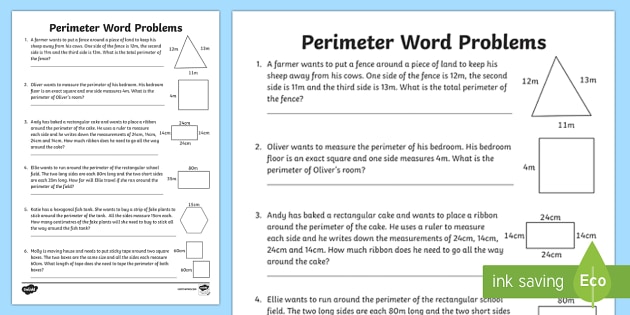
Perimeter of Squares
Calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward since all four sides are equal in length. The formula for finding the perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by:
\[
P = 4 \times \text{side length}
\]
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of a square:
- Identify the length of one side: Measure or find the given length of one side of the square.
- Apply the formula: Multiply the length of one side by 4.
- Calculate the perimeter: This multiplication gives you the total perimeter of the square.
For example, if the side length of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is essential for solving various real-life problems, such as determining the amount of material needed for framing or fencing around a square area.
Perimeter of Polygons
Understanding the perimeter of polygons is crucial for solving various geometric problems. A polygon is a closed figure with multiple sides. The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundaries.
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon:
- Identify the number of sides in the polygon.
- Measure the length of each side.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides.
For example, consider a pentagon with sides of lengths \(a, b, c, d, e\). The perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e
\]
For regular polygons, where all sides are equal, the formula simplifies. For an \(n\)-sided regular polygon with side length \(s\), the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = n \times s
\]
Let's apply this to a few common polygons:
- Triangle: A three-sided polygon. If the sides are \(a, b, c\), then \(P = a + b + c\).
- Square: A four-sided polygon with equal sides. If the side length is \(s\), then \(P = 4 \times s\).
- Hexagon: A six-sided regular polygon. If each side is \(s\), then \(P = 6 \times s\).
By practicing these calculations with different polygons, students can become proficient in finding perimeters, an essential skill in geometry.
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes can be a bit trickier to find the perimeter of compared to regular shapes like squares or rectangles. However, with a systematic approach, you can still calculate their perimeters accurately.
Here's a step-by-step guide to finding the perimeter of irregular shapes:
- Identify all the sides of the shape.
- Measure each side using a ruler or another measuring tool.
- Add up all the measurements of the sides to find the total perimeter.
If the irregular shape has curves or rounded edges, you may need to approximate the lengths of these sections by breaking them down into smaller straight segments.
Alternatively, you can use the "string method." Here's how it works:
- Place a piece of string or a flexible measuring tape along the perimeter of the irregular shape, following its contours closely.
- Once you've covered the entire perimeter with the string, lay it out straight and measure its length using a ruler or measuring tape.
This measurement will give you an approximation of the perimeter of the irregular shape.
Remember, precision is key when measuring irregular shapes, so take your time and double-check your measurements if needed.
Real-Life Perimeter Word Problems
Real-life perimeter word problems often involve scenarios where understanding perimeter is crucial for practical applications. Let's explore some examples:
Fencing a Garden: Imagine you have a rectangular garden that needs to be fenced. You need to calculate the perimeter of the garden to determine how much fencing material you'll need.
Building a Pathway: You're designing a pathway around a playground. To ensure safety, you must find the perimeter of the playground area to know how much paving material is required.
Wrapping Gifts: When wrapping gifts, you may want to add decorative ribbon around the package. Calculating the perimeter of the box helps determine the length of ribbon needed.
Constructing a Swimming Pool: A swimming pool contractor needs to know the perimeter of the pool area to estimate the amount of paving stones or tiles required for the pool deck.
Bordering Flower Beds: In landscaping, bordering flower beds or garden plots often requires measuring the perimeter to determine the length of fencing or decorative borders needed.
These real-life scenarios demonstrate how understanding perimeter is essential in various everyday situations, from construction projects to creative endeavors.

Perimeter with Missing Sides
Calculating the perimeter of a shape when some sides are missing requires a bit of problem-solving and critical thinking. Here's how you can approach such problems:
Identify the Given Information: Determine which sides of the shape are provided and which ones are missing.
Use Known Information: If you have enough information about the shape's dimensions, use it to find the missing sides.
Apply Perimeter Formula: Once you have all the sides (including the missing ones), use the appropriate formula to calculate the perimeter. For example, for a rectangle, the perimeter formula is \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) and \( w \) are the length and width, respectively.
Use Perimeter Constraints: In some cases, the perimeter of the shape may be provided even if some sides are missing. Use this information to find the missing sides or to check if the provided sides are consistent with the given perimeter.
Consider Similar Shapes: If the shape resembles a known geometric figure (e.g., a rectangle, square, or triangle), you can use properties of similar shapes to find missing sides.
By following these steps and applying problem-solving strategies, you can effectively calculate the perimeter of shapes with missing sides.
Mixed Perimeter Word Problems
Mixed perimeter word problems involve a combination of different geometric shapes and scenarios, requiring comprehensive problem-solving skills. Here are some strategies to tackle these types of problems:
Identify the Shapes: Determine which geometric shapes are involved in the problem and understand their properties.
Break Down the Problem: Analyze the problem carefully, breaking it down into smaller, more manageable parts.
Use Formulas: Apply the appropriate perimeter formulas for each shape involved. For example, for rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
Consider Constraints: Take into account any constraints provided in the problem, such as given measurements or relationships between shapes.
Draw Diagrams: Visualize the problem by drawing diagrams or sketches to better understand the relationships between the shapes and the given information.
Apply Problem-Solving Strategies: Use problem-solving techniques such as trial and error, working backwards, or organizing information systematically to find solutions.
Check Your Answer: Once you've found a solution, double-check your work to ensure accuracy and consistency with the problem statement.
By following these steps and employing critical thinking skills, you can effectively solve mixed perimeter word problems and strengthen your understanding of geometric concepts.
Same Perimeter, Different Area
In some mathematical problems, you may encounter situations where two different shapes have the same perimeter but different areas. This concept can be intriguing and offers insights into the relationship between perimeter and area. Here's how you can understand and explore this phenomenon:
Definition: Perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary of a shape, while area represents the space enclosed by the shape.
Example: Consider two rectangles with different dimensions. Although they have different areas, it's possible for them to have the same perimeter.
Exploration: Investigate various combinations of length and width for rectangles to find pairs that yield the same perimeter but different areas.
Visualization: Use diagrams or geometric representations to visualize how different shapes with the same perimeter can have different areas.
Mathematical Analysis: Explore the mathematical relationships between perimeter and area for different shapes, such as rectangles, triangles, and circles.
Application: Understand the practical implications of shapes with the same perimeter but different areas in real-world scenarios, such as urban planning, landscaping, or packaging design.
Further Study: Delve deeper into the concepts of perimeter and area, including their formulas, properties, and applications in geometry and beyond.
By exploring the concept of shapes with the same perimeter but different areas, you can enhance your understanding of geometric principles and their relevance in various contexts.
Perimeter Challenge Problems
Welcome to the Perimeter Challenge Problems section! Here, you will find a variety of challenging problems designed to test and enhance your understanding of perimeter calculations. Follow the steps and use your problem-solving skills to find the solutions.
-
Mrs. Kozlow put a border around a 5-foot by 6-foot rectangular bulletin board. How many feet of border did Mrs. Kozlow use?
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle using the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- \( P = 2(5 + 6) \)
- \( P = 2(11) = 22 \) feet
-
Jason built a model of the Pentagon for a social studies project. Each outside wall is 33 centimeters long. What is the perimeter of Jason's model?
Solution:
- The Pentagon has 5 sides.
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: \( P = 5 \times \text{side length} \)
- \( P = 5 \times 33 = 165 \) centimeters
-
Manny fenced in a rectangular area for his dog to play in the backyard. The area measures 35 yards by 45 yards. What is the total length of fence that Manny uses?
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle using the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- \( P = 2(35 + 45) \)
- \( P = 2(80) = 160 \) yards
-
Francis made a rectangular path from her driveway to the porch. The width of the path is 2 feet. The length is 28 feet longer than the width. What is the perimeter of the path?
Solution:
- Width = 2 feet
- Length = 2 + 28 = 30 feet
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- \( P = 2(30 + 2) \)
- \( P = 2(32) = 64 \) feet
-
Tyler uses 6 craft sticks to make a hexagon. Each craft stick is 6 inches long. What is the perimeter of Tyler's hexagon?
Solution:
- A hexagon has 6 sides.
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: \( P = 6 \times \text{side length} \)
- \( P = 6 \times 6 = 36 \) inches
-
The gym teacher uses tape to mark a 4-square court on the gym floor. The outer square has side lengths of 16 feet. What is the total length of tape the teacher uses?
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the square using the formula: \( P = 4 \times \text{side length} \)
- \( P = 4 \times 16 = 64 \) feet
-
A building at Elmira College has a room shaped like an octagon. The length of each side of the room is 35 feet. What is the perimeter of this room?
Solution:
- An octagon has 8 sides.
- Calculate the perimeter using the formula: \( P = 8 \times \text{side length} \)
- \( P = 8 \times 35 = 280 \) feet
Challenge yourself with these problems, and verify your answers step-by-step. Good luck!
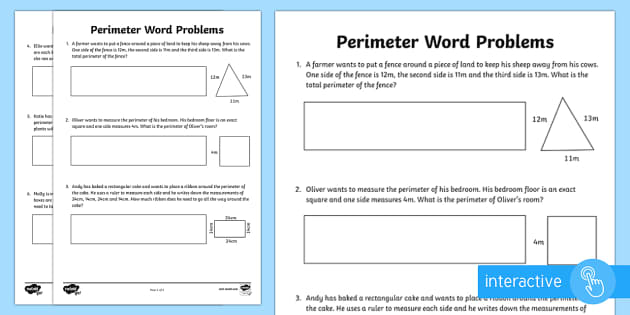
Interactive Perimeter Activities
Engaging students with interactive perimeter activities can enhance their understanding and make learning more fun. Below are several activities designed to make perimeter calculations interactive and enjoyable.
-
Virtual Manipulatives
Use online tools to create shapes and measure their perimeters. Websites like GeoGebra offer interactive platforms where students can draw shapes and instantly calculate the perimeter by adjusting the lengths of sides.
-
Perimeter Scavenger Hunt
Organize a scavenger hunt where students find objects around the classroom or home and measure their perimeters. Provide a list of items and a measuring tape, and have students record their findings in a table.
Item Measured Perimeter Book 30 cm Desk 120 cm -
Interactive Worksheets
Use interactive online worksheets where students can drag and drop answers or use digital tools to draw shapes and calculate their perimeters. Websites like LiveWorksheets provide these interactive worksheets.
-
Math Games
Incorporate games that focus on perimeter calculations. For example, create a game where students have to build a fence around a virtual garden, ensuring the perimeter matches a given length. This can be done using platforms like Kahoot! or Quizizz for a competitive edge.
-
Group Projects
Assign group projects where students create models of different shapes using string or sticks and measure their perimeters. They can then present their findings to the class, explaining their process and results.
-
Real-World Applications
Ask students to find the perimeter of real-world objects, such as the school playground or a section of their yard. They can use tools like Google Maps to measure large areas and convert these measurements into practical problems to solve.
-
Perimeter Puzzles
Create puzzles where students need to figure out missing side lengths based on given perimeters. For example, if a rectangle has a perimeter of 24 cm and one side is 5 cm, what are the lengths of the other sides?
These activities not only make learning about perimeters interactive but also help students see the practical applications of their math skills.
Video hướng dẫn bài toán chu vi cho học sinh lớp 3 bằng tiếng Việt, giúp thu hút người xem và cung cấp bài tập chu vi cho trẻ em.
Bài Toán Chu Vi | Toán Học | Lớp 3 - Học Viện Trẻ Em
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn tìm chu vi bằng tiếng Việt, giúp thu hút người xem và cung cấp bài tập chu vi cho trẻ em.
Tìm Chu Vi














