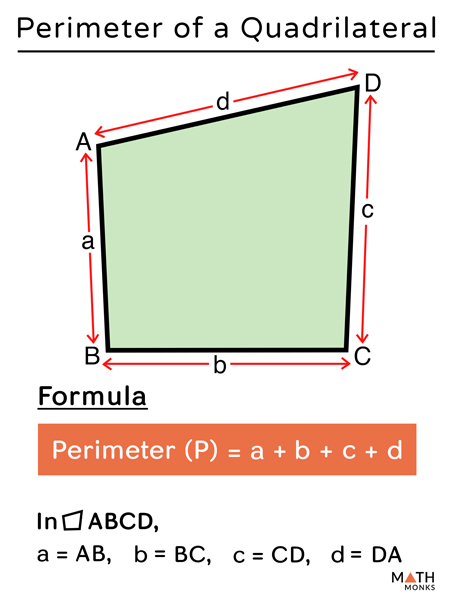
Topic perimeter with missing sides worksheet: Discover the essential techniques for calculating the perimeter when some side lengths are missing. This guide provides detailed worksheets, engaging activities, and practical examples to help students master the concept of perimeter with missing sides. Perfect for enhancing math skills and ensuring a thorough understanding of geometric properties.
Table of Content
- Perimeter with Missing Sides Worksheet
- Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Understanding Perimeter
- Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Example: Finding the Missing Side of a Rectangle
- Worksheets for Different Grades
- Finding Missing Side Lengths
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Common Core Standards
- Interactive and Printable Worksheets
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Classroom Activities and Games
- Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Resources for Teachers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn toán học lớp 5 về cách tìm chiều dài còn thiếu trong bài toán chu vi, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức cơ bản và thực hành giải quyết bài toán thực tế.
Perimeter with Missing Sides Worksheet
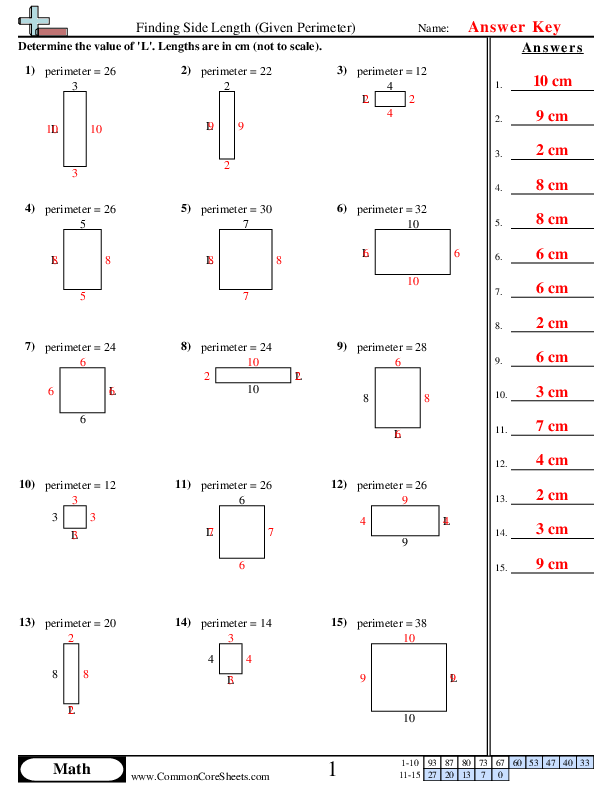
Worksheets focused on calculating the perimeter with missing sides are valuable tools for teaching students the concept of perimeter in geometry. These worksheets typically involve providing some side lengths of various shapes and requiring students to determine the missing side length based on the given perimeter.
Worksheet Details
- Grades: 3 - 5
- Available Formats: PDF, Google Slides
- Topics Covered:
- Finding one missing length when given the perimeter
- Finding one side length of a regular polygon when given perimeter
- Finding the missing lengths and then the perimeter on compound shapes
- Teaching Strategies:
- Highlight key information to help students focus on important details
- Support with concrete materials like rulers or string
- Extend learning with real-world word problems
Example Problem
Given a rectangle with a perimeter of 20 meters and one side length of 6 meters, find the missing side length.
Solution:
- Formula for perimeter: \(P = 2(l + w)\)
- Given \(P = 20\) meters and \(l = 6\) meters, we can set up the equation:
- \(20 = 2(6 + w)\)
- Solve for \(w\): \(10 = 6 + w\), so \(w = 4\) meters
Download Options
Additional Resources
- Interactive games and activities for classroom use
- Printable word problems for further practice
- Visual aids and manipulatives to enhance understanding
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
Understanding the perimeter of shapes, especially when sides are missing, is a fundamental math skill. This concept involves calculating the total distance around a shape by determining the lengths of all sides, including the missing ones. By practicing with various worksheets and problems, students can enhance their ability to solve for missing dimensions and gain a deeper understanding of geometric principles.
Here is a step-by-step guide to solving perimeter problems with missing sides:
- Identify the given side lengths and the total perimeter of the shape.
- Sum the lengths of the known sides.
- Subtract the sum of the known sides from the total perimeter to find the length of the missing side.
For example, if the perimeter of a rectangle is 20 units and the known lengths are 6 units and 4 units, the calculation would be:
\[
\text{Total Perimeter} = 20 \\
\text{Sum of Known Sides} = 6 + 4 + 6 \\
\text{Missing Side} = 20 - 16 = 4
\]
This method can be applied to various shapes, including rectangles, squares, and other polygons, enhancing students' problem-solving skills and their understanding of geometry.
By using interactive and printable worksheets, students can practice these calculations in a structured way. These worksheets often include visual aids and step-by-step instructions to guide students through the process.
Incorporating practical tools, such as rulers or string, can help students visualize and measure the sides of shapes, making the learning process more engaging and effective.
For more complex problems, such as those involving irregular shapes or word problems, additional practice and guidance can further support students' learning. These exercises encourage students to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts, enhancing their analytical skills and confidence in mathematics.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Understanding how to find the perimeter is fundamental in geometry and has practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday tasks.
Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
In some problems, you might be given the total perimeter of a shape but one or more side lengths are missing. To find the missing side, you need to use the given perimeter and the lengths of the known sides. The process involves subtracting the sum of the known sides from the total perimeter to find the length of the missing side.
- Identify the total perimeter provided.
- Add up the lengths of the known sides.
- Subtract the sum of the known sides from the total perimeter to find the missing length.
Example: Finding the Missing Side of a Rectangle
Consider a rectangle where the total perimeter is given as 20 units, and the lengths of two sides are 5 units each. To find the missing lengths:
- Calculate the sum of the known sides: \(5 + 5 = 10\) units.
- Subtract this sum from the total perimeter: \(20 - 10 = 10\) units.
- Divide by the number of missing sides. Since a rectangle has two pairs of equal sides: \(10 \div 2 = 5\) units.
Thus, each of the missing sides is 5 units long.
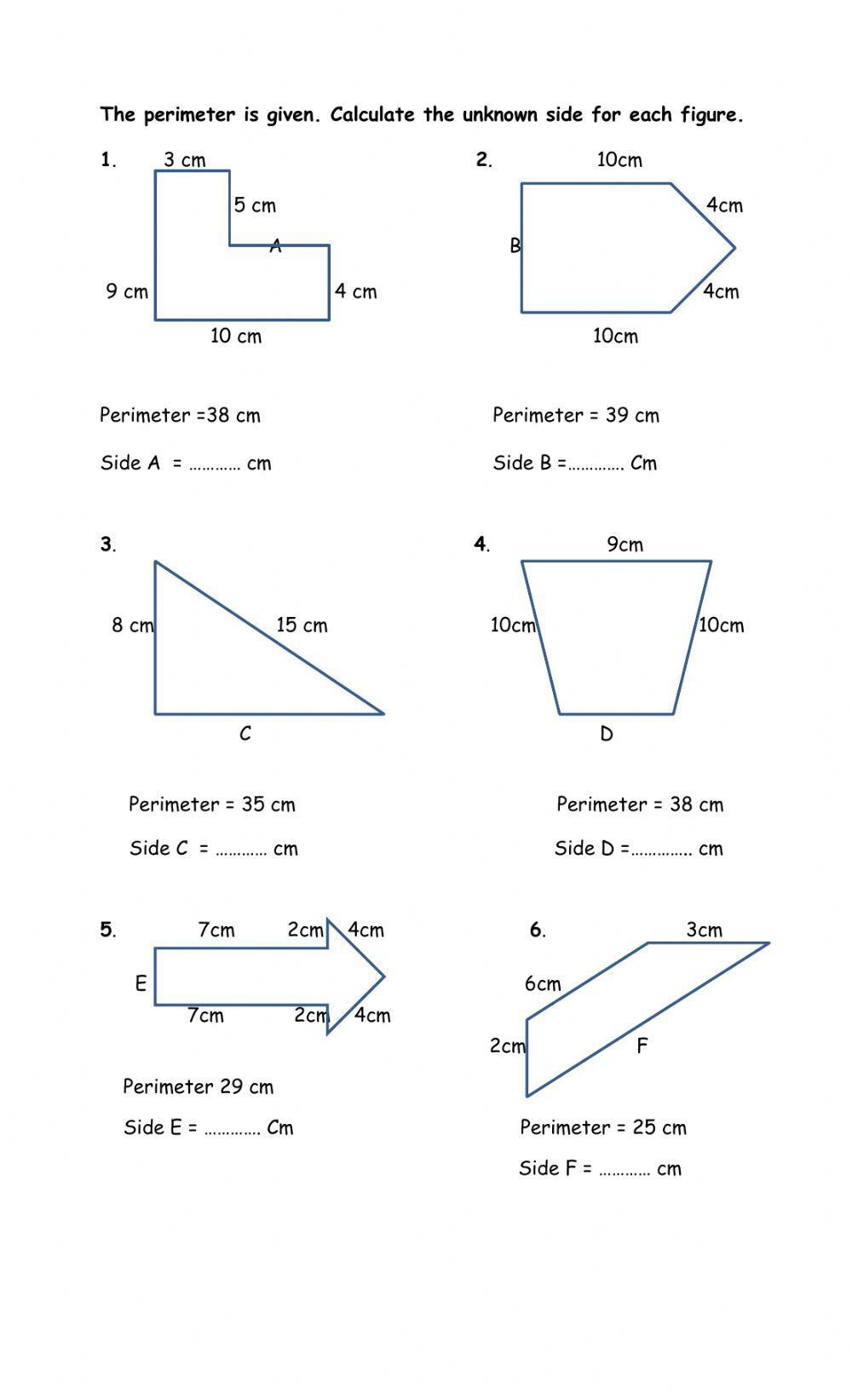
Worksheets for Different Grades
Perimeter worksheets with missing sides are available for different grade levels, providing tailored exercises to help students understand and master the concept of perimeter calculation. These worksheets are designed to cater to various learning stages, from simple shapes for younger students to complex problems for older students.
Kindergarten to Grade 2
- Simple shapes like squares and rectangles.
- Focus on understanding the basic concept of perimeter.
- Visual aids and step-by-step guidance.
Grade 3 to Grade 5
- Introduction to more complex shapes including triangles and irregular polygons.
- Problems requiring basic addition and subtraction skills.
- Interactive activities and practice worksheets to reinforce learning.
Grade 6 and Above
- Advanced problems involving compound shapes and algebraic expressions.
- Focus on higher-level thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Worksheets that integrate real-world applications and word problems.
These worksheets are designed to progressively build students' confidence and competence in calculating the perimeter with missing sides, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the concept at each educational level.
Finding Missing Side Lengths
When calculating the perimeter of a shape, you add the lengths of all its sides. Sometimes, you may be given the total perimeter and a few side lengths, but one side length is missing. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to find that missing length.
- Understand the Problem: Start by identifying the total perimeter of the shape and the known side lengths.
- Set Up the Equation: Write down the formula for the perimeter of the shape. For a rectangle, the perimeter \(P\) is given by: \[ P = 2 \cdot (l + w) \] where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width. For other polygons, sum up all side lengths.
- Subtract Known Sides: Subtract the sum of the known side lengths from the total perimeter to find the combined length of the missing sides. For instance, if you know three sides of a rectangle, subtract their sum from the perimeter and divide by 2 to find the missing side: \[ \text{Missing Side} = \frac{P - (\text{Sum of Known Sides})}{2} \]
- Check Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same units before performing calculations. If necessary, convert them.
- Verification: Add the missing side length back into the total and verify it matches the given perimeter.
With practice, these steps will help you solve for missing side lengths quickly and accurately. Worksheets tailored for different grade levels often include these types of problems, allowing students to practice and master the concept.
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes involves determining the length of each side and summing them up. This process can be broken down into several steps:
- Identify all the sides of the shape. This includes both given sides and those that need to be calculated.
- For sides with missing lengths, use known geometric properties to find their measurements. For example, in rectangles, opposite sides are equal.
- Add up the lengths of all sides to find the total perimeter.
Here is an example of calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape:
| Side | Length |
|---|---|
| Side 1 | 5 units |
| Side 2 | 7 units |
| Side 3 | 4 units |
| Side 4 | 3 units |
| Side 5 (missing) | Use other sides to find the length |
In this example, if Side 5 can be determined as 6 units by calculating, the total perimeter is:
\[
P = 5 + 7 + 4 + 3 + 6 = 25 \text{ units}
\]
Using worksheets designed for different grades, students can practice these steps, enhance their problem-solving skills, and better understand the concept of perimeter for various shapes.
- Grade 3: Simple irregular shapes with fewer missing sides.
- Grade 4: More complex shapes with multiple missing sides.
- Grade 5: Advanced problems involving compound shapes.
Such exercises help build a strong foundation in geometry and improve mathematical reasoning.
Common Core Standards
The Common Core Standards for Mathematics establish clear and consistent guidelines for what students should understand and be able to do at each grade level. Specifically, regarding the perimeter and finding missing sides, the standards focus on several key areas:
-
Grade 3 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.MD.D.8)
- Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths, finding an unknown side length, and exhibiting rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or with the same area and different perimeters.
-
Grade 4 (CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.A.3)
- Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real-world and mathematical problems. For example, finding the width of a rectangular room given the area and the length.
-
Grade 5 and Beyond
- Continue to apply these concepts in more complex and abstract ways, integrating decimals and fractions, and solving problems that involve irregular shapes and composite figures.
These standards are designed to ensure that students build a strong foundation in measurement and geometric reasoning, which will be essential for their success in higher-level math courses and real-world problem solving.
| Grade | Standard | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.MD.D.8 | Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths and finding an unknown side length. |
| 4 | CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.A.3 | Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real-world and mathematical problems. |
| 5+ | Advanced Applications | Include integration of decimals and fractions, and solving problems with irregular shapes. |
Teachers are encouraged to use a variety of worksheets, activities, and games to help students master these concepts. Resources such as and provide excellent practice problems and activities aligned with these standards.

Interactive and Printable Worksheets
Engaging students in learning about perimeter, especially with missing sides, can be made easier with interactive and printable worksheets. Here are some useful resources and activities:
- Interactive Worksheets: These worksheets often come in digital formats, such as Google Slides, allowing students to interact with the content directly on their devices. They include activities where students can drag and drop measurements or use interactive tools to find missing side lengths.
- Printable Worksheets: For hands-on practice, printable worksheets are invaluable. They can be downloaded in various formats such as PDF, and printed for classroom or home use. These worksheets typically provide problems that require students to calculate the missing side length when given the perimeter of shapes like squares, rectangles, and other polygons.
Here are some types of worksheets you can find:
- Finding Missing Sides of Regular Shapes: These worksheets provide exercises on calculating the length of the missing side for shapes like rectangles and squares when the perimeter is known.
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes: Students can enhance their skills by working on problems that involve finding the perimeter of various irregular shapes.
- Word Problems: These worksheets offer real-world scenarios where students must apply their knowledge of perimeter to find missing side lengths, enhancing their problem-solving skills.
- Interactive Games: Games and puzzles related to perimeter can make learning more engaging. For example, perimeter puzzles require students to solve for missing sides to complete a shape.
These resources are aligned with Common Core standards, ensuring that students meet the required learning goals while making the process enjoyable. They cater to different grades and levels, providing appropriate challenges for each stage of learning.
Download these resources from websites like SplashLearn, Math Worksheets 4 Kids, and Teach Starter to provide comprehensive practice and reinforce students' understanding of perimeter with missing sides.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practice problems are an essential part of mastering perimeter calculations, especially when some sides are missing. Below, we provide a variety of problems along with detailed solutions to help students understand the concepts thoroughly.
Example Problems
-
Problem 1: A rectangle has a perimeter of 24 units. One side is 7 units long. Find the length of the missing side.
Solution:
Let the missing side be \( x \).
The perimeter of a rectangle is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \).
Given \( P = 24 \) and one side \( l = 7 \):
\[
24 = 2(7 + x) \implies 24 = 14 + 2x \implies 2x = 10 \implies x = 5
\]So, the length of the missing side is 5 units.
-
Problem 2: The perimeter of a triangle is 30 cm. Two sides are 8 cm and 12 cm. Find the length of the third side.
Solution:
Let the missing side be \( x \).
The perimeter of a triangle is given by \( P = a + b + c \).
Given \( P = 30 \), \( a = 8 \), and \( b = 12 \):
\[
30 = 8 + 12 + x \implies 30 = 20 + x \implies x = 10
\]So, the length of the missing side is 10 cm.
Word Problems
-
Problem 3: A garden is shaped like a pentagon with one side missing. The perimeter of the garden is 50 meters, and the known sides are 8 m, 10 m, 9 m, and 7 m. Find the missing side.
Solution:
Let the missing side be \( x \).
The perimeter of the pentagon is given by the sum of all its sides.
Given \( P = 50 \) and known sides are 8, 10, 9, and 7 meters:
\[
50 = 8 + 10 + 9 + 7 + x \implies 50 = 34 + x \implies x = 16
\]So, the length of the missing side is 16 meters.
-
Problem 4: A rectangular park has a perimeter of 60 meters. The length of the park is twice its width. Find the dimensions of the park.
Solution:
Let the width be \( w \) meters. Then the length is \( 2w \) meters.
The perimeter of a rectangle is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \).
Given \( P = 60 \):
\[
60 = 2(2w + w) \implies 60 = 6w \implies w = 10
\]Therefore, the width is 10 meters and the length is \( 2 \times 10 = 20 \) meters.
Advanced Problems
-
Problem 5: A hexagon has a perimeter of 72 units. Five of its sides are 10 units each. Find the length of the missing side.
Solution:
Let the missing side be \( x \).
Given that the perimeter \( P = 72 \) and five sides are 10 units each:
\[
72 = 5 \times 10 + x \implies 72 = 50 + x \implies x = 22
\]So, the length of the missing side is 22 units.
By practicing these problems, students will enhance their skills in determining missing side lengths when the perimeter is known. Consistent practice with a variety of shapes and complexity levels is key to mastering these concepts.
Classroom Activities and Games
Engaging students in learning about the perimeter with missing sides can be both educational and fun. Below are several classroom activities and games designed to reinforce these concepts:
1. Perimeter Puzzle Hunt
Organize a puzzle hunt where students solve perimeter problems to find missing sides and uncover clues leading them to the next challenge. This activity encourages teamwork and problem-solving.
- Prepare several puzzles with different shapes and missing side lengths.
- Hide clues around the classroom, each leading to the next puzzle.
- Students must solve the perimeter problem at each station to find the next clue.
2. Interactive Perimeter Bingo
Create a bingo game where each square contains a shape with a missing side. Students solve the problems and mark their bingo cards accordingly.
- Generate bingo cards with various shapes and given perimeters.
- Call out problems or perimeter measurements, and students solve to mark their cards.
- The first student to complete a line wins a small prize.
3. Perimeter Relay Race
Divide students into teams and set up a relay race where each team member must solve a perimeter problem before passing the baton to the next runner.
- Set up stations with different perimeter problems for each team.
- Each student solves a problem, writes down the missing side length, and hands off to the next team member.
- The first team to complete all problems correctly wins.
4. Digital Perimeter Games
Use online games and interactive resources to practice perimeter calculations in a fun and engaging way.
- Utilize websites that offer perimeter games, such as solving for missing sides in virtual environments.
- Encourage students to play these games during computer lab sessions or as homework.
- Track progress and provide feedback to ensure understanding.
5. Perimeter Construction Challenge
Provide students with materials like string, rulers, and grid paper to create shapes with specified perimeters and find the missing side lengths.
- Give each student or group a specific perimeter to achieve with their shapes.
- Students use the materials to construct shapes and calculate any missing side lengths.
- Display the completed shapes around the classroom for everyone to see and discuss.
These activities not only help reinforce the mathematical concept of perimeter but also promote collaboration, critical thinking, and hands-on learning.
Advanced Perimeter Problems
Advanced perimeter problems challenge students to apply their understanding of geometry, algebra, and problem-solving skills. These problems often involve complex shapes, missing side lengths, and require a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Below are several types of advanced perimeter problems and solutions:
- Problem Type 1: Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Problem Type 2: Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Problem Type 3: Perimeter with Algebraic Expressions
Given the perimeter of a polygon and some of its side lengths, find the missing side length(s).
Example: A rectangle has a perimeter of 30 cm. If one of its sides is 8 cm, what is the length of the missing side?
Solution: Let the length of the missing side be \( x \). Since the perimeter of a rectangle is given by \( 2(l + w) \), we can write:
\[ 2(8 + x) = 30 \]
Simplifying the equation, we get:
\[ 16 + 2x = 30 \]
\[ 2x = 14 \]
\[ x = 7 \]
Thus, the missing side length is 7 cm.
Calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes where not all side lengths are given.
Example: An irregular pentagon has sides of lengths 5 cm, 7 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm. If the perimeter is 28 cm, find the length of the missing side.
Solution: Let the length of the missing side be \( x \). The perimeter of the pentagon is the sum of all its side lengths, so:
\[ 5 + 7 + 6 + 4 + x = 28 \]
Simplifying the equation, we get:
\[ 22 + x = 28 \]
\[ x = 6 \]
Thus, the length of the missing side is 6 cm.
Incorporate algebraic expressions to find unknown side lengths or the perimeter of a given shape.
Example: A rectangle has a length of \( (3x + 2) \) cm and a width of \( x \) cm. If the perimeter is 24 cm, find the value of \( x \).
Solution: Using the perimeter formula \( 2(l + w) = 24 \), we substitute the given expressions:
\[ 2((3x + 2) + x) = 24 \]
\[ 2(4x + 2) = 24 \]
\[ 8x + 4 = 24 \]
\[ 8x = 20 \]
\[ x = 2.5 \]
Thus, the value of \( x \) is 2.5 cm.
These advanced perimeter problems enhance students' critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, preparing them for more complex mathematical concepts.
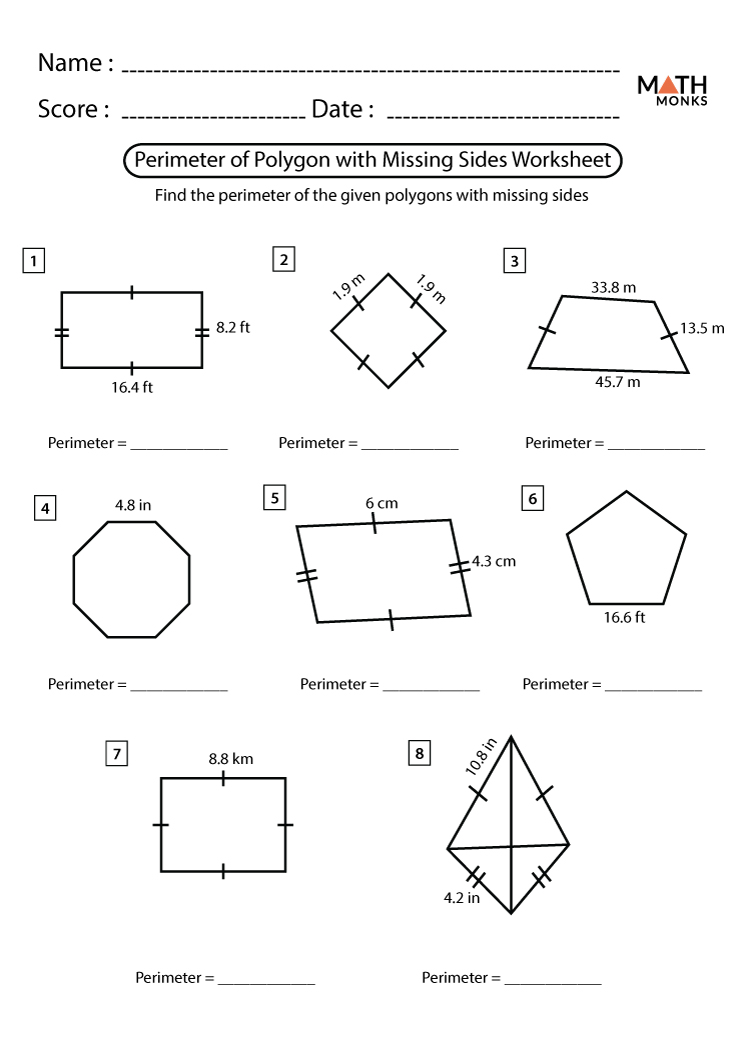
Resources for Teachers
Providing comprehensive resources for teaching perimeter with missing sides is essential for effective learning. Here are some valuable resources and tools that teachers can use to enhance their instruction:
- Lesson Plans and Worksheets
- Pre-made worksheets with a variety of problems involving missing sides and perimeters.
- Customizable worksheets where teachers can select specific problems and difficulty levels.
- Interactive Activities
- Online platforms offering interactive perimeter exercises.
- Virtual manipulatives to help students visualize and solve perimeter problems.
- Assessment Tools
- Printable quizzes and tests with varying levels of difficulty.
- Online assessment tools that provide instant feedback and detailed reports.
- Professional Development
- Workshops and seminars focused on geometry and measurement.
- Online courses that offer in-depth training and certification.
- Additional Teaching Resources
- Textbooks and e-books covering geometry topics.
- Educational websites with lesson plans, teaching strategies, and printable resources.
Various lesson plans and worksheets are available that focus on finding missing side lengths and calculating perimeters. These resources are designed to align with Common Core Standards and can be used to supplement classroom activities.
Engage students with interactive activities such as digital games, online quizzes, and virtual manipulatives. These tools help reinforce concepts in a fun and interactive way.
Use assessment tools to evaluate student understanding and progress. These can include formative assessments, quizzes, and standardized tests tailored to measuring skills related to perimeter and missing sides.
Teachers can benefit from professional development resources that provide strategies and best practices for teaching perimeter with missing sides. These can include workshops, webinars, and online courses.
Explore additional resources such as textbooks, reference guides, and educational websites that offer comprehensive materials on teaching perimeter and geometry.
By utilizing these resources, teachers can create a dynamic and effective learning environment that helps students master the concept of perimeter with missing sides.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about finding the perimeter with missing sides.
- Q: How do you find the perimeter when a side length is missing?
- Q: What formulas are useful for these problems?
- Q: What types of shapes can these worksheets cover?
- Q: How can I help my students understand these problems better?
- Q: Are there any online resources or tools that can assist with these worksheets?
- Q: Can these worksheets be used to align with Common Core standards?
- Q: What are some tips for solving perimeter problems with missing sides?
A: To find the missing side length when the perimeter is given, add the lengths of all the known sides and subtract this sum from the total perimeter.
A: The basic formula for the perimeter of a polygon is the sum of all its side lengths. For a missing side length, use \( P = \sum \text{known sides} + \text{missing side} \).
A: These worksheets can cover a variety of shapes, including triangles, rectangles, polygons, and irregular shapes. Each type has its unique method of finding the missing side, but the principle remains the same: use the given perimeter to solve for the missing side.
A: Use visual aids and interactive tools to demonstrate how to add the sides and solve for the missing length. Practical exercises and real-life examples also help in understanding.
A: Yes, there are several online resources like Khan Academy and various educational websites that provide interactive problems and step-by-step solutions for these types of questions.
A: Absolutely. These worksheets are designed to help students meet and exceed Common Core standards for geometry and measurement by providing practical problems involving perimeter and missing side lengths.
A: Ensure you clearly understand the shape's total perimeter and the lengths of all known sides. Set up the equation correctly and solve for the missing side by isolating it on one side of the equation.
Conclusion
Understanding how to find the perimeter with missing sides is an essential skill in geometry that enhances students' problem-solving abilities and spatial awareness. This guide has provided comprehensive information, from basic concepts to advanced problems, aligned with Common Core standards.
Interactive and printable worksheets offer practical, hands-on experience, while practice problems and solutions reinforce learning. Engaging classroom activities and games make learning fun and dynamic, helping to cement students' understanding of perimeter calculations in various contexts.
Advanced perimeter problems challenge students to apply their knowledge creatively, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills. Teachers can utilize a wealth of resources to support diverse learning needs and styles, ensuring that every student can master the topic effectively.
By integrating these tools and strategies, educators can create a robust learning environment that not only meets curriculum standards but also inspires a lifelong interest in mathematics.
We hope this guide serves as a valuable resource in your teaching journey, helping students to achieve success in understanding and applying the concepts of perimeter with missing sides.
Video hướng dẫn toán học lớp 5 về cách tìm chiều dài còn thiếu trong bài toán chu vi, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức cơ bản và thực hành giải quyết bài toán thực tế.
Toán Học - Lớp 5: Chu Vi - Tìm Chiều Dài Còn Thiếu
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi khi các cạnh bị thiếu, rất hữu ích cho việc học toán.
Chu Vi của Các Cạnh Thiếu