Topic perimeter with missing sides worksheets: Explore comprehensive perimeter with missing sides worksheets designed to enhance your geometry skills. Learn to calculate the perimeter of various shapes even when some sides are unknown. These worksheets provide clear instructions and practical examples, making it easy to master the concept of perimeter and apply it to real-world problems.
Table of Content
- Perimeter with Missing Sides Worksheets
- Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- How to Find Missing Sides
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Worksheets for Different Shapes
- Rectangles with Missing Sides
- Triangles with Missing Sides
- Squares and Other Polygons
- Using Properties to Determine Unknown Sides
- Sample Problems and Solutions
- Practice Worksheets
- Word Problems Involving Perimeter
- Advanced Techniques for Complex Shapes
- Interactive Exercises and Tools
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Benefits of Practicing with Worksheets
- Conclusion and Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình dạng kết hợp, sử dụng ví dụ về hình L. Hãy đảm bảo bạn hiểu rõ cách tính chu vi và diện tích của những hình dạng phức tạp như vậy!
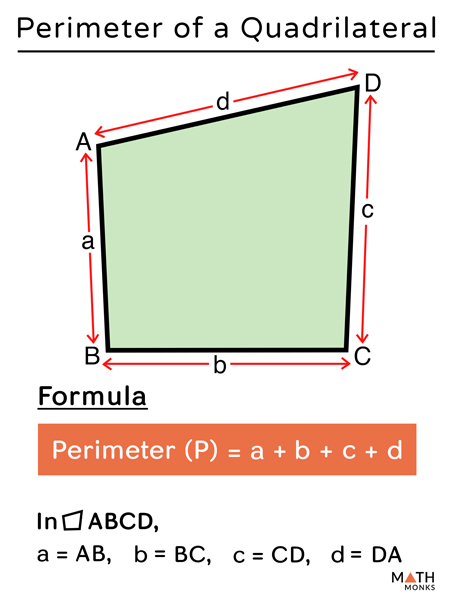
Perimeter with Missing Sides Worksheets
Calculating the perimeter of shapes when some side lengths are missing can be a practical application of basic geometry concepts. These worksheets are designed to help students develop problem-solving skills and understand the relationship between different sides of geometric figures.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length around it. For a polygon, it is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. When some sides are missing, students must use the given information and properties of shapes to find the unknown lengths.
How to Calculate Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Identify the known sides of the shape.
- Determine if the shape has any special properties (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle).
- Use properties of the shape to find the lengths of missing sides. For example, in rectangles, opposite sides are equal.
- Add the lengths of all sides to find the perimeter.
Sample Problems
-
Rectangle: One side is 7 cm, and the adjacent side is 3 cm. The other two sides are missing. Find the perimeter.
Solution: Opposite sides of a rectangle are equal. Therefore, the missing sides are also 7 cm and 3 cm. The perimeter is \( P = 7 + 3 + 7 + 3 = 20 \) cm.
-
Triangle: Two sides of a triangle are 5 cm and 12 cm. The perimeter is 30 cm. Find the missing side.
Solution: Let the missing side be \( x \). Then \( 5 + 12 + x = 30 \). Solving for \( x \), we get \( x = 30 - 17 = 13 \) cm.
Worksheets
Here are some types of worksheets you might find:
- Worksheets with rectangular shapes and missing sides
- Worksheets with triangular shapes and missing sides
- Mixed shapes including squares, rectangles, and polygons
- Word problems involving missing side lengths
Sample Worksheet Table
| Shape | Given Sides | Missing Side | Perimeter |
| Rectangle | 5 cm, 8 cm | 5 cm, 8 cm | \( P = 26 \) cm |
| Triangle | 6 cm, 10 cm | 8 cm | \( P = 24 \) cm |
These worksheets are great for reinforcing perimeter concepts and for challenging students to apply their knowledge in finding missing sides.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter with Missing Sides
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. When calculating the perimeter with some missing sides, students need to use their understanding of geometry to find the unknown lengths. This skill is essential for solving real-world problems and deepening one's comprehension of geometric properties.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to understanding and calculating the perimeter with missing sides:
- Identify Known Sides: Start by identifying all the given side lengths in the shape.
- Determine Shape Properties: Use the properties of the shape (e.g., opposite sides in rectangles are equal, sides of a square are all equal).
- Calculate Missing Sides: Apply known properties or relationships to calculate the lengths of missing sides. For example, in a rectangle, if two sides are given, the other two can be determined as they are equal to the opposite sides.
- Sum All Sides: Once all sides are known, add them together to find the total perimeter.
Let’s illustrate this with examples:
- Example 1: Consider a rectangle where the length is 10 cm, and the width is unknown. If the perimeter is 30 cm, find the width.
Solution: Let the width be \( w \). The perimeter \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \). Thus, \( 30 = 2 \times (10 + w) \). Solving for \( w \), we get \( w = 5 \) cm. - Example 2: A triangle has two sides of 6 cm and 8 cm, and the perimeter is 20 cm. Find the missing side.
Solution: Let the missing side be \( x \). Then, \( 6 + 8 + x = 20 \). Solving for \( x \), we get \( x = 6 \) cm.
These worksheets provide a variety of problems to practice finding perimeters with missing sides, enhancing both problem-solving skills and geometric understanding. Through practice, students can confidently tackle different shapes and learn to apply these concepts effectively.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundaries. It is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Understanding the basic concepts of perimeter is crucial for solving problems that involve missing sides.
Here are some key points to remember:
- Definition: The perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape.
- Formula: The formula to calculate the perimeter varies depending on the shape.
- Units: The perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, etc.
Formulas for Common Shapes
| Shape | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \) | The perimeter is twice the sum of the length and width. |
| Square | \( P = 4 \times s \) | The perimeter is four times the length of one side. |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) | The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all three sides. |
| Circle | \( P = 2 \pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \) | The perimeter (circumference) is calculated using the radius or diameter. |
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are working with.
- Measure the Sides: Measure the lengths of all sides of the shape. If some sides are missing, use properties or formulas to find them.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate perimeter formula for the shape.
- Add the Lengths: Sum the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter.
Understanding these basic concepts and steps will help you solve problems involving the perimeter, even when some sides are missing. Practice with different shapes to become proficient in calculating perimeter.
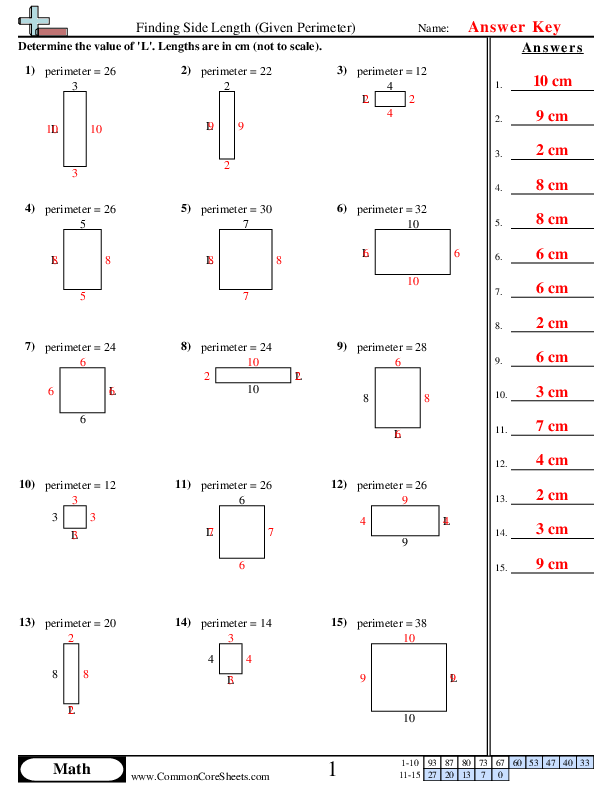
How to Find Missing Sides
Finding the missing sides of a shape when given its perimeter involves understanding the relationship between the perimeter and the side lengths. Here are the steps to determine the missing side length:
- Understand the Perimeter:
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. For regular polygons, it is the sum of the lengths of all sides.
- Identify Given Sides:
Note the lengths of the sides that are already provided. This information is crucial for calculating the missing side length.
- Sum of Known Sides:
Add together the lengths of the known sides.
For example, if you have a rectangle with one side missing, and the known sides are 5 units and 7 units:
- Rectangle has opposite sides equal: known sides = 5, 7, 5
- Sum of known sides = \(5 + 7 + 5 = 17\) units
- Subtract from Perimeter:
Subtract the sum of the known sides from the total perimeter to find the length of the missing side.
Using the previous example, if the total perimeter is 24 units:
\(\text{Missing side} = 24 - 17 = 7\) units
- Double-Check Your Work:
Add the missing side length back into the total to ensure that the sum equals the given perimeter.
Here are some examples of how to find missing sides for different shapes:
Example 1: Rectangle
Given: Perimeter = 30 units, Known sides = 8 units, 6 units
Sum of known sides = \(8 + 6 + 8 = 22\) units
Missing side = \(30 - 22 = 8\) units
Example 2: Triangle
Given: Perimeter = 18 units, Known sides = 5 units, 7 units
Sum of known sides = \(5 + 7 = 12\) units
Missing side = \(18 - 12 = 6\) units
Example 3: Irregular Polygon
Given: Perimeter = 50 units, Known sides = 10 units, 12 units, 8 units, 6 units
Sum of known sides = \(10 + 12 + 8 + 6 = 36\) units
Missing side = \(50 - 36 = 14\) units
Practicing with different shapes and worksheets will help solidify these concepts. Utilize resources such as printable worksheets and interactive exercises to enhance understanding and accuracy in finding missing sides.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing the lengths of all its sides. When sides are missing, follow these steps to find the perimeter:
- Identify Known Sides:
First, identify all the sides whose lengths are given. For example, in a rectangle, you might know the lengths of two opposite sides.
- Use Geometric Properties:
Use the properties of the shape to determine the lengths of the missing sides. For instance:
- In a rectangle, opposite sides are equal. If you know one side, you know its opposite.
- In a triangle, use the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles or the triangle inequality theorem for other types of triangles.
- For polygons, divide the shape into known geometric figures (like triangles or rectangles) to find the missing lengths.
- Calculate Missing Lengths:
Use algebra to solve for missing side lengths if the perimeter is provided. For example, in a rectangle where the perimeter is given, and you know one side:
- Let the known side be \(a\) and the unknown side be \(b\).
- Perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is \(P = 2a + 2b\).
- Solve for \(b\): \(b = \frac{P - 2a}{2}\).
- Add All Sides:
Once you have all the side lengths, add them together to get the perimeter.
For example, in a rectangle with sides \(a\) and \(b\), the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
\[
P = 2a + 2b
\]
Here are some examples for practice:
| Shape | Known Sides | Missing Sides | Steps to Find Perimeter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \(a = 5\), \(b = ?\) | \(b\) | \(P = 2a + 2b\), Solve for \(b\) |
| Triangle | \(a = 3\), \(b = 4\), \(c = ?\) | \(c\) | Use Pythagorean theorem: \(c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\) |
| Square | \(a = 4\) | None | \(P = 4a\) |
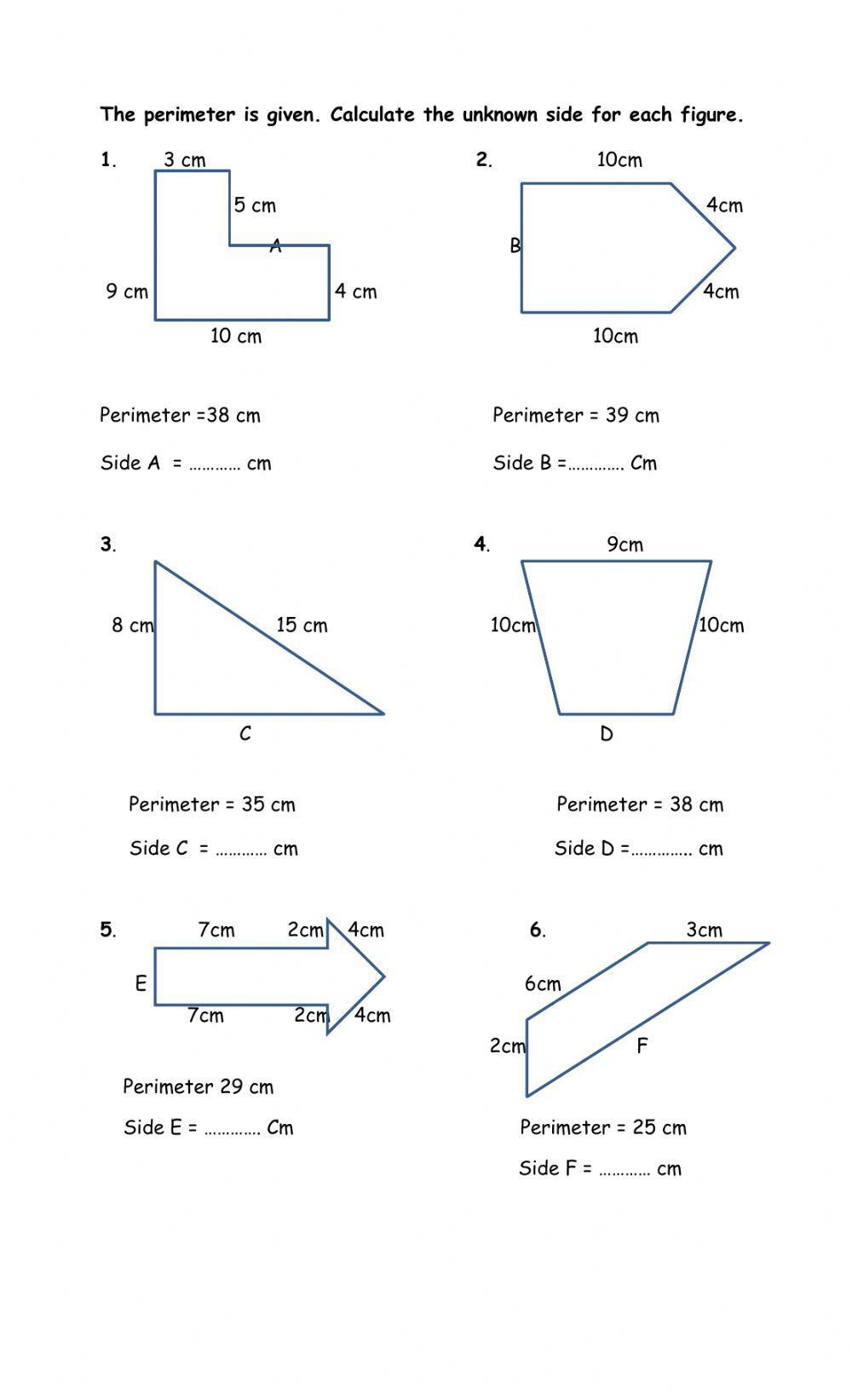
Worksheets for Different Shapes
Practicing perimeter calculation with different shapes helps students understand the concepts thoroughly. Here are some types of worksheets available for different shapes:
Basic Shapes
- Rectangles: Calculate the perimeter by adding the lengths of all four sides. These worksheets often provide some sides and ask students to find the missing ones.
- Squares: Since all sides are equal, students can multiply one side length by four to find the perimeter.
- Triangles: Worksheets might include various types of triangles (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and require students to add the lengths of the three sides.
Intermediate Shapes
- Polygons: These worksheets help students practice finding the perimeter of polygons with more than four sides. Students add the lengths of all the sides.
- Irregular Shapes: Students might be given complex shapes, and they have to determine the lengths of all sides to find the total perimeter.
Special Worksheets
- Missing Side Lengths: These worksheets provide the total perimeter and some side lengths, requiring students to find the missing side lengths using subtraction.
- Word Problems: Engaging scenarios where students have to apply perimeter concepts to solve real-world problems.
Interactive Exercises
- Games: Interactive games where students can calculate perimeters of shapes in a fun, engaging way.
- Activities: Group activities where students work together to measure and calculate perimeters of objects around them.
By working through these different types of worksheets, students can enhance their understanding of perimeter and its application to various shapes.
Rectangles with Missing Sides
Rectangles are four-sided shapes with opposite sides being equal in length. To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you add up the lengths of all its sides. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times (l + w) \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
When one of the sides is missing, you can use the given perimeter and the known side lengths to find the missing side. Here’s how:
- Write down the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle.
- Substitute the known values into the formula.
- Solve for the missing side.
For example, if you know the perimeter and the length of one side, you can find the missing width as follows:
Suppose a rectangle has a perimeter of 24 units and one of its lengths is 7 units. To find the missing width:
- Write the perimeter formula:
\[ 24 = 2 \times (7 + w) \]
- Divide both sides by 2:
\[ 12 = 7 + w \]
- Subtract 7 from both sides to solve for \( w \):
\[ w = 5 \]
Therefore, the width of the rectangle is 5 units.
Here are some steps to practice finding missing sides with worksheets:
- Identify the given perimeter and the known side length.
- Set up the perimeter equation with the known values.
- Solve for the missing side length.
- Double-check your calculations by adding all sides to ensure the perimeter matches the given value.
Using these methods, students can effectively find the missing side lengths of rectangles in various problems, enhancing their understanding of geometry and the properties of rectangles.
Triangles with Missing Sides
Calculating the perimeter of triangles with missing sides can be an engaging and educational exercise for students. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help students master this concept:
-
Understand the Formula: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
-
Identify Known and Unknown Sides: In problems involving missing sides, students will typically be given the perimeter and the lengths of some sides. The task is to find the missing side length.
- For example, if the perimeter \( P \) and sides \( a \) and \( b \) are known, find side \( c \).
-
Set Up the Equation: Substitute the known values into the perimeter formula and solve for the unknown side. For instance:
Given \( P = 20 \) units, \( a = 7 \) units, and \( b = 6 \) units, find \( c \).
Set up the equation:
\[ 20 = 7 + 6 + c \]
-
Solve for the Missing Side: Rearrange the equation to solve for \( c \):
\[ c = 20 - 7 - 6 \]
\[ c = 7 \] units
-
Verify the Solution: Double-check the work by adding all side lengths to ensure they match the given perimeter:
\[ 7 + 6 + 7 = 20 \]
This method can be applied to any triangle, whether it is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. Practicing with different types of triangles helps reinforce the concept and ensures students are well-prepared for various problems.
To aid in learning, here are some practice worksheets:
- Worksheet 1: Find the missing side of an equilateral triangle with a given perimeter.
- Worksheet 2: Calculate the missing side length of an isosceles triangle.
- Worksheet 3: Solve for the missing side in a scalene triangle with mixed measurements.
These worksheets provide a range of problems that will help students become proficient in calculating the perimeter of triangles with missing sides. Encouraging the use of visual aids, such as drawing the triangles, can also help students better understand the geometric relationships.
Squares and Other Polygons
Understanding the perimeter of squares and other polygons, especially when some sides are missing, requires a clear approach. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you master this concept:
1. Perimeter of Squares
A square has four equal sides. If one side is missing, you can easily find it if the other sides are known.
- Formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a square with side length \( s \) is given by \( P = 4s \).
- Finding Missing Side: If the perimeter is given and one side is missing, rearrange the formula to find the side: \( s = \frac{P}{4} \).
Example: If the perimeter of a square is 20 units, each side is \( \frac{20}{4} = 5 \) units.
2. Perimeter of Rectangles
Rectangles have opposite sides that are equal. You need to know either the length ( \( l \) ) or the width ( \( w \) ) along with the perimeter to find the missing side.
- Formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is given by \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Finding Missing Side: Rearrange the formula to find the missing side:
- If the length is missing: \( l = \frac{P - 2w}{2} \).
- If the width is missing: \( w = \frac{P - 2l}{2} \).
3. Perimeter of Triangles
For triangles, knowing the perimeter and two side lengths allows you to find the missing side.
- Formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is given by \( P = a + b + c \).
- Finding Missing Side: Rearrange the formula:
- If side \( c \) is missing: \( c = P - a - b \).
- If side \( b \) is missing: \( b = P - a - c \).
- If side \( a \) is missing: \( a = P - b - c \).
4. Perimeter of Other Polygons
For polygons with more than four sides, sum up all the known side lengths and subtract from the total perimeter to find the missing side(s).
- General Formula: For a polygon with \( n \) sides, \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + ... + s_n \).
- Finding Missing Side: If one side \( s_k \) is missing, rearrange the formula: \( s_k = P - (s_1 + s_2 + ... + s_{k-1} + s_{k+1} + ... + s_n) \).
Example Problem
Let's find the missing side of a pentagon (5-sided polygon) with a perimeter of 30 units and sides measuring 5, 6, 4, and 7 units:
- Total of known sides: \( 5 + 6 + 4 + 7 = 22 \) units.
- Missing side: \( s_5 = 30 - 22 = 8 \) units.
By practicing with various worksheets, you can reinforce your understanding of these concepts and improve your ability to solve problems involving missing sides in different shapes.

Using Properties to Determine Unknown Sides
When calculating the perimeter of shapes with missing sides, you can use various properties and known side lengths to find the missing measurements. Below are detailed steps and examples to help you determine the unknown sides and calculate the perimeter effectively.
Steps to Determine Unknown Sides:
-
Identify Known Side Lengths:
Start by noting down the lengths of the sides that are provided. This information will be crucial for calculating the missing sides.
-
Use Opposite Sides for Rectangles and Squares:
For rectangles and squares, opposite sides are equal. If you know one side of a rectangle or square, you can easily determine the length of its opposite side.
Example: If a rectangle has a length of 8 cm and the other length is unknown, you know the opposite side must also be 8 cm.
-
Apply the Perimeter Formula:
Use the formula for the perimeter to set up an equation. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
Rearrange this formula to solve for the missing side.
Example: If the perimeter of a rectangle is 30 cm and the length is 8 cm, you can find the width (w) by:
\[ 30 = 2 \times (8 + w) \]
\[ 15 = 8 + w \]
\[ w = 7 \text{ cm} \]
-
Use Sum of Angles for Triangles:
For triangles, if you know two sides and the perimeter, you can find the third side. Use the perimeter formula for triangles:
\[ P = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 \]
Example: If the perimeter of a triangle is 24 cm, and two sides are 9 cm and 7 cm, the third side (s) is:
\[ 24 = 9 + 7 + s \]
\[ s = 8 \text{ cm} \]
-
Use Properties of Regular Polygons:
For regular polygons (all sides and angles are equal), if you know the length of one side, you can determine the perimeter and vice versa. The perimeter (P) of a regular polygon with n sides, each of length s, is:
\[ P = n \times s \]
If the perimeter and number of sides are known, solve for the side length.
Example: A regular pentagon (5 sides) with a perimeter of 35 cm:
\[ 35 = 5 \times s \]
\[ s = 7 \text{ cm} \]
Examples and Practice:
Here are some practice problems to help you understand and apply these concepts:
-
Problem 1: A rectangle has a length of 12 cm and a perimeter of 40 cm. Find the width.
Solution: \[ 40 = 2 \times (12 + w) \]
\[ 20 = 12 + w \]
\[ w = 8 \text{ cm} \]
-
Problem 2: The perimeter of a triangle is 30 cm. Two of its sides are 10 cm and 8 cm. Find the third side.
Solution: \[ 30 = 10 + 8 + s \]
\[ s = 12 \text{ cm} \]
-
Problem 3: A regular hexagon (6 sides) has a perimeter of 48 cm. Find the length of each side.
Solution: \[ 48 = 6 \times s \]
\[ s = 8 \text{ cm} \]
Using these methods, you can confidently determine the unknown sides of various shapes and accurately calculate their perimeters.
Sample Problems and Solutions
Understanding how to find the perimeter when some side lengths are missing involves using known properties and relationships within geometric shapes. Here are several sample problems with step-by-step solutions to help you grasp these concepts:
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Problem: A rectangular garden has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. Find the perimeter of the garden.
- Identify the lengths of all sides. For a rectangle, opposite sides are equal.
- Length (l) = 8 meters
- Width (w) = 5 meters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Substitute the given values into the formula: \( P = 2(8) + 2(5) \)
- Simplify: \( P = 16 + 10 = 26 \) meters
Solution: The perimeter of the garden is 26 meters.
Example 2: Perimeter of a Triangle with Missing Side
Problem: A triangle has two known sides measuring 7 cm and 10 cm. The perimeter of the triangle is 28 cm. Find the length of the third side.
- Let the length of the third side be \( x \) cm.
- Use the perimeter formula for a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Substitute the known values: \( 28 = 7 + 10 + x \)
- Solve for \( x \): \( 28 = 17 + x \)
- Subtract 17 from both sides: \( x = 28 - 17 \)
- Simplify: \( x = 11 \) cm
Solution: The length of the third side is 11 cm.
Example 3: Word Problem Involving Perimeter
Problem: A rectangular playground is three times as long as it is wide. If the perimeter is 64 meters, find the dimensions of the playground.
- Let the width be \( w \) meters. Then the length \( l \) is \( 3w \) meters.
- Use the perimeter formula for a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Substitute the given perimeter and expressions for \( l \) and \( w \): \( 64 = 2(3w) + 2w \)
- Simplify: \( 64 = 6w + 2w \)
- Combine like terms: \( 64 = 8w \)
- Solve for \( w \): \( w = \frac{64}{8} \)
- Simplify: \( w = 8 \) meters
- Find the length: \( l = 3w = 3 \times 8 = 24 \) meters
Solution: The width of the playground is 8 meters and the length is 24 meters.
Example 4: Perimeter of a Parallelogram
Problem: A parallelogram has two sides measuring 15 cm each and the other two sides measuring 25 cm each. Find the perimeter of the parallelogram.
- Identify the lengths of all sides. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal.
- Side lengths: \( a = 15 \) cm and \( b = 25 \) cm
- Use the perimeter formula for a parallelogram: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute the given values: \( P = 2(15) + 2(25) \)
- Simplify: \( P = 30 + 50 = 80 \) cm
Solution: The perimeter of the parallelogram is 80 cm.
Example 5: Finding Perimeter from Word Problem
Problem: A farmer wants to fence a rectangular field. The field's width is 20 meters and its length is 35 meters. How much fencing is needed?
- Identify the lengths of all sides. Opposite sides are equal.
- Width (w) = 20 meters
- Length (l) = 35 meters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Substitute the given values into the formula: \( P = 2(35) + 2(20) \)
- Simplify: \( P = 70 + 40 = 110 \) meters
Solution: The farmer needs 110 meters of fencing.
Example 6: Perimeter of a Pentagon
Problem: A regular pentagon has each side measuring 12 cm. Find the perimeter of the pentagon.
- For a regular pentagon, all sides are equal.
- Side length \( s = 12 \) cm
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a pentagon: \( P = 5s \)
- Substitute the given value: \( P = 5(12) \)
- Simplify: \( P = 60 \) cm
Solution: The perimeter of the pentagon is 60 cm.
Practice Worksheets
To master the concept of calculating the perimeter with missing sides, here are some practice worksheets designed to enhance your understanding and skills. Each worksheet includes a variety of problems that require different approaches and techniques. Follow the steps below for detailed instructions on how to use these worksheets effectively.
- Basic Perimeter Worksheets
- Calculate the perimeter of regular shapes with given side lengths.
- Identify and fill in missing side lengths using known perimeters.
- Worksheets are available in both PDF and Google Slides formats for easy printing and editing.
- Irregular Shapes Perimeter Worksheets
- Find the perimeter of irregular shapes with some sides missing.
- Use provided side lengths and properties of shapes to determine missing sides.
- Focus on problem-solving and applying geometry principles to real-world shapes.
- Word Problems on Perimeter
- Solve real-life perimeter word problems that include missing side lengths.
- Draw shapes and label dimensions to visualize and solve the problems effectively.
- Worksheets include step-by-step solutions to guide through complex problems.
- Advanced Perimeter Worksheets
- Tackle more complex shapes and scenarios involving multiple missing sides.
- Utilize advanced geometry techniques and properties to solve for unknown sides.
- Worksheets are designed to challenge and improve higher-level thinking skills.
Example Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the perimeter of a rectangle with one side missing. The given sides are 8 cm and 5 cm, and the perimeter is 26 cm. |
|
| Determine the missing side of a triangle where two sides are 7 m and 9 m, and the perimeter is 24 m. |
|
Additional Resources
For more practice and detailed explanations, explore additional worksheets and tools available online. These resources provide various problems and interactive exercises to reinforce your learning.
Word Problems Involving Perimeter
Solving word problems involving the perimeter of various shapes helps students understand the application of perimeter in real-world contexts. Here are some detailed examples and steps to tackle these problems:
Example 1: Finding the Missing Side of a Rectangle
Problem: A rectangular garden has a length of 12 meters and a total perimeter of 40 meters. What is the width of the garden?
- Recall the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \).
- Substitute the known values into the formula: \( 40 = 2 \times (12 + w) \).
- Solve for the width:
- Divide both sides by 2: \( 20 = 12 + w \).
- Subtract 12 from both sides: \( w = 8 \).
- The width of the garden is 8 meters.
Example 2: Perimeter of a Triangle
Problem: A triangle has two sides measuring 7 cm and 10 cm. If the perimeter is 28 cm, what is the length of the third side?
- Recall the formula for the perimeter of a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \).
- Substitute the known values into the formula: \( 28 = 7 + 10 + c \).
- Solve for the third side:
- Combine like terms: \( 28 = 17 + c \).
- Subtract 17 from both sides: \( c = 11 \).
- The length of the third side is 11 cm.
Example 3: Word Problem Involving a Square
Problem: A square park has a perimeter of 48 meters. What is the length of one side of the park?
- Recall the formula for the perimeter of a square: \( P = 4s \).
- Substitute the known values into the formula: \( 48 = 4s \).
- Solve for the side length:
- Divide both sides by 4: \( s = 12 \).
- The length of one side of the park is 12 meters.
Practice Problems
- 1. A rectangular swimming pool is twice as long as it is wide. If the perimeter of the pool is 60 meters, what are its dimensions?
- 2. A triangle has sides of 9 cm, 14 cm, and an unknown length. If the perimeter is 30 cm, find the unknown side.
- 3. The perimeter of a square garden is 36 meters. Find the length of one side of the garden.
By working through these examples and practice problems, students can develop a solid understanding of how to approach and solve perimeter word problems.
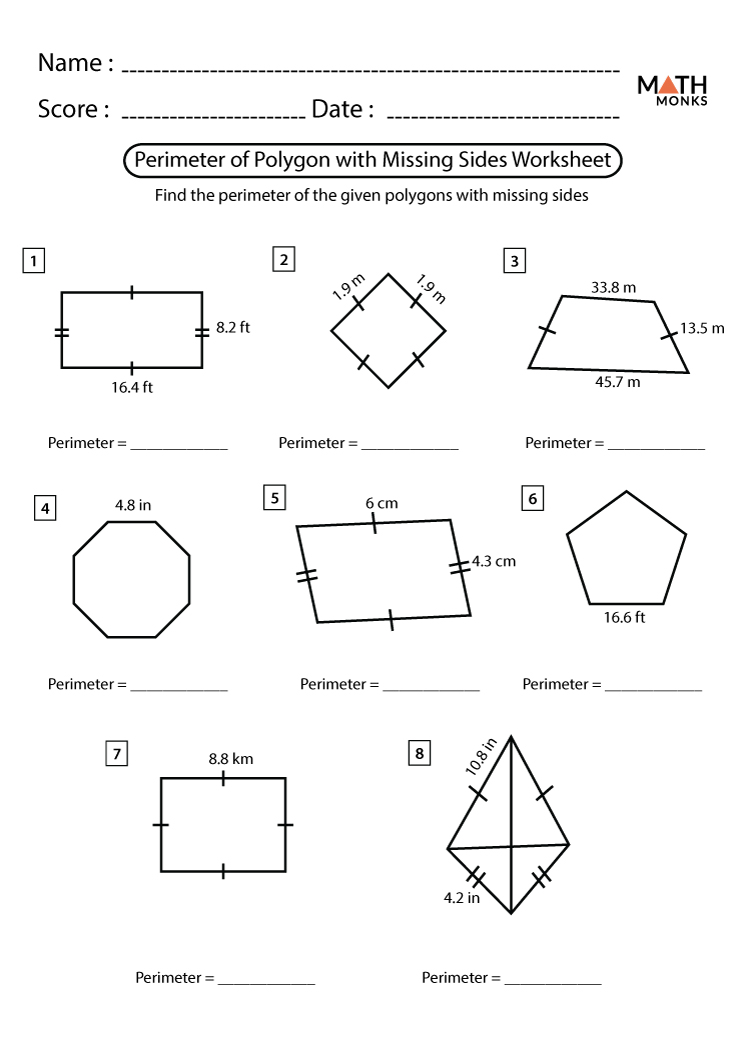
Advanced Techniques for Complex Shapes
Finding the perimeter of complex shapes can be challenging, but with some advanced techniques, it becomes manageable. Here are some strategies to help you calculate the perimeter of various complex shapes.
1. Decompose the Shape
Break down the complex shape into simpler shapes such as rectangles, triangles, and circles. Calculate the perimeter of each simpler shape and then sum them up.
- Identify the individual shapes within the complex shape.
- Calculate the perimeter of each individual shape.
- Add the perimeters of all the shapes to find the total perimeter.
2. Use Coordinates and Distance Formula
For shapes with vertices on a coordinate plane, use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of sides.
The distance formula between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is:
$$ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} $$
Sum up all the side lengths to get the perimeter.
3. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem
For shapes with right angles, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find missing side lengths.
The Pythagorean theorem states:
$$ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 $$
where \(c\) is the hypotenuse and \(a\) and \(b\) are the other two sides of the right triangle.
4. Use the Properties of Polygons
Different polygons have specific properties that can simplify perimeter calculations. For example:
- Regular polygons: All sides are equal, so multiply the length of one side by the number of sides.
- Irregular polygons: Sum the lengths of all sides directly.
5. Trigonometric Methods
For non-right-angled triangles, use the law of cosines to find missing sides:
$$ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cdot \cos(C) $$
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the sides, \(C\) is the included angle, and \(c\) is the side opposite the angle.
6. Combine Different Methods
Often, a combination of the above methods will be required to solve for the perimeter of a complex shape. Use the method that best fits each part of the shape and sum the results.
Examples
Here are a couple of examples to illustrate these techniques:
Example 1: Irregular Polygon
An irregular polygon with vertices at \((0,0)\), \((4,0)\), \((4,3)\), and \((0,3)\). To find the perimeter:
- Calculate the distance between each pair of vertices.
- Sum the distances: \(4 + 3 + 4 + 3 = 14\) units.
Example 2: Composite Shape
A shape composed of a rectangle and a semicircle:
- Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
- Calculate the circumference of the semicircle: \( \pi \times r \).
- Add the perimeter of the rectangle and the semicircle to get the total perimeter.
By using these advanced techniques, you can tackle even the most complex perimeter problems with confidence and precision.
Interactive Exercises and Tools
Engaging students in learning about the perimeter with missing sides can be effectively achieved through interactive exercises and tools. These resources not only help in understanding the concepts but also make learning fun and engaging.
Interactive Digital Puzzles
One effective tool is the Find the Missing Side Interactive Puzzle. This puzzle involves using the given perimeter to find the length of the missing side. Students can drag and drop puzzle pieces with the correct measurements to complete the shapes, revealing a hidden picture as they solve each puzzle.
- Accessible via Google Slides, ensuring easy access and editing.
- Combines metric and customary units to enhance familiarity with both measurement systems.
- Can be used for various activities:
- Lesson Introduction or Wrap-Up: Project the puzzle on an interactive whiteboard and invite students to participate.
- Pair Challenge: Students can work in pairs to complete the puzzle as a competitive activity.
- Individual Practice: Ideal for students who prefer self-paced learning.
Online Interactive Worksheets
Several online platforms provide interactive worksheets focused on finding the perimeter with missing sides. These worksheets often include step-by-step instructions and immediate feedback, allowing students to learn and correct mistakes in real-time.
- Teach Starter: Offers a variety of resources including interactive puzzles and worksheets that can be used for classroom activities or individual practice.
- SplashLearn: Features worksheets and games designed to master finding the perimeter of shapes with missing side lengths, catering to different grade levels.
- Saylor Academy: Provides comprehensive courses and practice exercises focusing on geometry and measurement, including finding missing side lengths given the perimeter.
Virtual Manipulatives
Virtual manipulatives are another excellent tool for teaching perimeter concepts. These digital tools allow students to manipulate shapes and measurements interactively, providing a hands-on learning experience.
- Use virtual manipulatives to explore different shapes and their properties.
- Interactive features help in understanding the relationship between side lengths and perimeter.
Interactive Geometry Software
Software like GeoGebra offers dynamic geometry environments where students can create shapes, adjust side lengths, and observe changes in perimeter. This hands-on approach reinforces theoretical concepts through practical application.
- Allows for the creation and manipulation of geometric figures.
- Real-time updates help in visualizing the impact of changing side lengths on the perimeter.
Incorporating these interactive exercises and tools into the curriculum can significantly enhance students' understanding and retention of perimeter concepts, particularly when dealing with missing side lengths.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When solving perimeter problems, especially those involving missing sides, students often encounter several common mistakes. Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls can greatly improve accuracy and confidence.
-
Not Double-Checking Figures:
Always recheck the numbers used in calculations. A simple misreading can lead to incorrect answers.
-
Incorrectly Applying Formulas:
Ensure you're using the correct formula for the shape you are working with. Memorize the perimeter formulas for different shapes to avoid confusion.
-
Forgetting Units:
Always include units in your final answer. Mixing up or omitting units can cause misunderstandings, especially in real-world applications.
-
Misinterpreting the Question:
Take time to understand what the problem is asking. Look out for key details that affect how you should approach the calculation.
-
Overlooking Shape Properties:
Remember the properties of shapes, such as the fact that opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, which can simplify your calculations.
Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes
-
Double-Check Your Work:
After solving a problem, revisit it to ensure your solution makes sense within the context provided.
-
Understand Shape Properties:
Utilize properties of geometric shapes (e.g., all sides of a square are equal) to simplify your perimeter calculations.
-
Use Visual Aids:
Draw diagrams and label all known and unknown sides to visualize the problem better.
-
Practice Regularly:
Regular practice helps reinforce the correct methods and reduce errors.
-
Ask for Feedback:
Seek feedback from teachers or peers to understand where you might be going wrong and how to correct it.
Example Problem
Let's look at an example to illustrate these points:
Suppose we have a rectangle with a perimeter of 24 units and one side measuring 7 units. To find the missing side:
- Step 1: Use the perimeter formula for a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Step 2: Substitute the known values into the formula: \( 24 = 2(7) + 2w \).
- Step 3: Solve for \( w \): \( 24 = 14 + 2w \) ⟹ \( 10 = 2w \) ⟹ \( w = 5 \).
- Step 4: Double-check the calculation by plugging the values back into the perimeter formula: \( 2(7) + 2(5) = 24 \).
By following these steps, we avoid common mistakes and ensure our solution is accurate.
Benefits of Practicing with Worksheets
Practicing with worksheets offers numerous benefits for students learning about perimeter, especially when dealing with missing sides. Here are some key advantages:
- Reinforcement of Concepts: Regular practice helps solidify understanding of perimeter calculations, ensuring that students grasp both basic and advanced concepts.
- Step-by-Step Learning: Worksheets often provide problems that increase in difficulty, allowing students to build their skills gradually. This step-by-step approach is essential for mastering complex topics.
- Immediate Feedback: Many interactive worksheets and online tools provide instant feedback, helping students quickly identify and correct mistakes. This immediate reinforcement is crucial for effective learning.
- Variety of Problems: Worksheets offer a wide range of problem types, from simple calculations to complex, real-world applications. This variety ensures that students can apply their knowledge in different contexts.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: By tackling diverse problems, students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. They learn to apply mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios, enhancing their overall analytical abilities.
- Enhanced Retention: Consistent practice with worksheets aids in better retention of mathematical concepts. The repetitive nature of practice helps embed these concepts in long-term memory.
- Accessibility: Online worksheets are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easy for students to practice at their own pace and convenience, whether at home or in the classroom.
- Engagement: Interactive worksheets and tools often incorporate games and challenges, making learning more enjoyable. This increased engagement can lead to a more positive attitude towards math.
Overall, worksheets are an invaluable resource for students learning about perimeter. They provide a structured and effective way to practice and master this essential mathematical concept.

Conclusion and Additional Resources
Understanding how to find the perimeter of shapes with missing sides is a fundamental skill in geometry. Practicing with worksheets can significantly enhance students' problem-solving abilities and mathematical reasoning. These worksheets not only help in mastering basic perimeter calculations but also in applying these concepts to more complex shapes and real-world problems.
By consistently working on these exercises, students can:
- Develop a deeper understanding of geometric properties.
- Improve their ability to visualize and solve spatial problems.
- Gain confidence in handling both regular and irregular shapes.
To further your learning, here are some additional resources:
- SplashLearn: Offers a variety of worksheets and interactive exercises focused on finding the perimeter with missing side lengths. Great for reinforcing concepts through engaging activities.
- You've Got This Math: Provides printable worksheets for different grades, including exercises for triangles, quadrilaterals, and irregular shapes. These worksheets are perfect for hands-on practice.
- Teach Starter: Features downloadable worksheets and teaching resources, including Google Slides and PDF formats. This site is ideal for teachers looking to integrate perimeter lessons into their curriculum.
In conclusion, practicing perimeter with missing sides worksheets can be highly beneficial for students. It not only solidifies their understanding of geometry but also enhances their analytical and problem-solving skills. Utilize the resources provided to ensure a comprehensive learning experience.
Happy learning!
Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình dạng kết hợp, sử dụng ví dụ về hình L. Hãy đảm bảo bạn hiểu rõ cách tính chu vi và diện tích của những hình dạng phức tạp như vậy!
Tìm Chu vi và Diện tích của Hình dạng Kết hợp | Ví dụ Hình L | Học Toán cùng Thầy J
READ MORE:
Xem video này để học cách giải chu vi và tìm bên thiếu trong bài toán toán học lớp 5. Hãy cùng tham gia để nắm vững kiến thức và kỹ năng cần thiết!
Toán học - Lớp 5: Chu vi - Giải cho bên thiếu