Topic perimeter worksheets with missing sides: Discover our comprehensive collection of perimeter worksheets with missing sides, designed to boost your math skills. Perfect for students and teachers alike, these worksheets offer engaging problems and detailed solutions, making learning fun and effective. Start exploring now to master the concept of perimeter with ease and confidence!
Table of Content
- Perimeter Worksheets with Missing Sides
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Worksheets for Different Grade Levels
- Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 3
- Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 4
- Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 5
- Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Rectangles and Squares
- Triangles and Polygons
- Real-world Applications
- Step-by-step Solutions
- Printable Worksheets
- Interactive Online Worksheets
- Teacher Resources and Guides
- Homework Assignments
- Classroom Activities
- Fun Perimeter Challenges
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn học sinh lớp 5 cách tính chu vi và tìm cạnh thiếu.
Perimeter Worksheets with Missing Sides
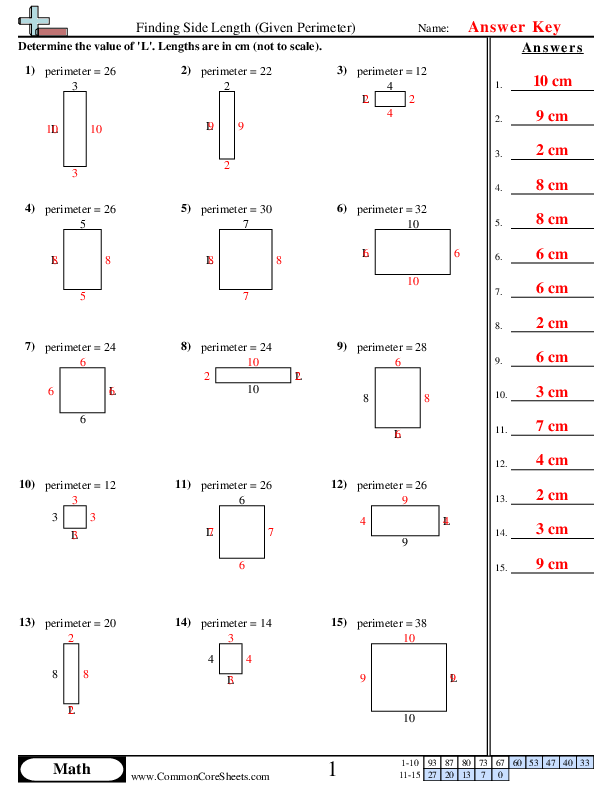
Enhance your math skills with our comprehensive perimeter worksheets focusing on finding missing sides. These worksheets are designed to provide practice in calculating the perimeter of various geometric shapes when some side lengths are unknown. Ideal for students and educators, these worksheets come with detailed solutions to help understand the concepts better.
Key Features:
- Various geometric shapes including rectangles, squares, triangles, and polygons
- Step-by-step solutions included
- Worksheets suitable for different grade levels
- Printable and easy to use
Example Problems:
Below are a few example problems to give you an idea of what the worksheets include:
-
Rectangle: Find the missing side length of a rectangle if the perimeter is given as 30 cm, and one of the known sides is 7 cm.
-
Triangle: Find the missing side of a triangle with a perimeter of 24 m, and two known sides are 8 m and 6 m.
Download Worksheets:
Click the links below to download the worksheets suitable for different grades:
Teacher Resources:
These worksheets are excellent resources for teachers to use in the classroom to reinforce students' understanding of perimeters and missing side calculations. Teachers can also use these worksheets as homework assignments or for in-class practice.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the edge of the shape. It is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for understanding more complex mathematical topics. Calculating the perimeter involves summing the lengths of all sides of the shape. Below are the steps and examples to understand the concept of perimeter:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of geometric shape (rectangle, square, triangle, polygon, etc.).
- Measure the Sides: Measure the length of each side of the shape. For missing sides, use the given information to calculate the unknown lengths.
- Sum the Lengths: Add all the side lengths together to find the perimeter.
Let's look at specific examples:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is given by:
where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width. For example, if \(l = 8 \, \text{cm}\) and \(w = 5 \, \text{cm}\), then:
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) of a square is given by:
where \(s\) is the length of a side. For example, if \(s = 6 \, \text{cm}\), then:
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle is given by:
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides. For example, if \(a = 5 \, \text{cm}\), \(b = 7 \, \text{cm}\), and \(c = 9 \, \text{cm}\), then:
Understanding the concept of perimeter is crucial for solving real-world problems, such as finding the length of fencing required to enclose a garden or the trim needed for the edge of a carpet. Practice with our worksheets to become proficient in calculating perimeters, even when some side lengths are missing.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter
Understanding the basic concepts of perimeter is essential for solving various geometric problems. The perimeter is the total distance around the edges of a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by adding up the lengths of all the sides. Below are the steps and examples to grasp the fundamental concepts of perimeter:
- Definition of Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary. It is measured in linear units such as centimeters (cm), meters (m), or inches (in).
- Formula for Common Shapes: Different shapes have specific formulas to calculate the perimeter.
- Rectangle:
The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is given by:
where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square:
The perimeter \(P\) of a square is given by:
where \(s\) is the length of one side.
- Triangle:
The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle is given by:
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Polygon:
The perimeter \(P\) of a polygon is given by:
where \(s_i\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Rectangle:
- Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides:
When some side lengths are missing, you can use the known lengths and properties of the shape to find the missing values. Here are steps to solve such problems:
- Use the known perimeter formula of the shape.
- Substitute the known side lengths into the formula.
- Solve for the missing side length(s).
- Example Problem:
Consider a rectangle with a perimeter of 28 cm, where one side length is 8 cm. To find the missing side length:
By mastering these basic concepts, students will be able to tackle a wide range of problems involving perimeter, including those with missing sides. Practice regularly with our worksheets to gain confidence and improve your skills.
Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
Calculating the perimeter when some sides are missing involves using the known values and properties of the shape to determine the unknown side lengths. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to help you solve these problems effectively:
- Understand the Shape:
Identify the type of shape you are working with (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle, polygon). Knowing the properties of the shape is crucial for setting up the correct perimeter formula.
- Write Down the Perimeter Formula:
For the given shape, write down the standard formula for calculating the perimeter.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Polygon: \( P = \sum s_i \)
- Substitute Known Values:
Insert the known side lengths into the formula. If the perimeter is given, include that value as well.
- Formulate the Equation:
Create an equation based on the formula and known values. This will typically involve one or more unknown variables representing the missing side lengths.
- Solve for Missing Sides:
Rearrange the equation to solve for the unknown side lengths. Use algebraic methods to isolate the variable(s).
- Verify Your Answer:
After finding the missing side lengths, add all sides to ensure they match the given perimeter. This step confirms the accuracy of your solution.
Let's look at some examples to illustrate these steps:
- Example 1: Rectangle
A rectangle has a perimeter of 40 cm. One side is 12 cm. Find the missing side.
Using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
- Example 2: Triangle
A triangle has a perimeter of 30 m. Two sides are 11 m and 7 m. Find the missing side.
Using the formula \( P = a + b + c \):
By following these steps and practicing with different shapes and problems, you will become proficient in calculating the perimeter even when some sides are missing. Our worksheets provide a variety of problems to help you master this skill.
Worksheets for Different Grade Levels
Perimeter worksheets with missing sides are designed to cater to various grade levels, ensuring that students of all ages can practice and master the concept. These worksheets are structured to gradually increase in complexity, providing appropriate challenges for each grade. Below is a detailed guide on the types of perimeter worksheets available for different grade levels:
Grade 3
At this level, students are introduced to the basic concept of perimeter. Worksheets focus on simple shapes like rectangles and squares with given side lengths. Problems involve finding the total perimeter and solving for one missing side.
- Identify and measure sides of rectangles and squares.
- Use addition to calculate the total perimeter.
- Solve for one missing side using known perimeter values.
Grade 4
In Grade 4, students encounter more diverse shapes, including triangles and polygons. Worksheets include problems with missing sides and require the application of basic algebra to solve for unknown lengths.
- Calculate perimeter for triangles and polygons.
- Use subtraction to find missing sides.
- Work with word problems involving real-world scenarios.
Grade 5
Grade 5 worksheets introduce more complex shapes and compound figures. Students learn to break down complex shapes into simpler components to calculate the perimeter. Problems also involve multiple missing sides.
- Find perimeter of compound shapes by decomposing them.
- Use algebraic equations to solve for multiple missing sides.
- Apply perimeter concepts to more advanced word problems.
Grade 6 and Above
For Grade 6 and beyond, worksheets become increasingly sophisticated, involving irregular shapes and advanced geometric figures. These problems require a strong understanding of both basic and complex perimeter calculations.
- Calculate perimeter for irregular and complex shapes.
- Apply knowledge to advanced real-world problems.
- Use higher-order thinking skills to solve challenging problems.
Our perimeter worksheets are tailored to meet the learning needs at each grade level, ensuring that students build a solid foundation and progress confidently through their mathematical journey. Regular practice with these worksheets will help students enhance their problem-solving skills and master the concept of perimeter, even with missing sides.
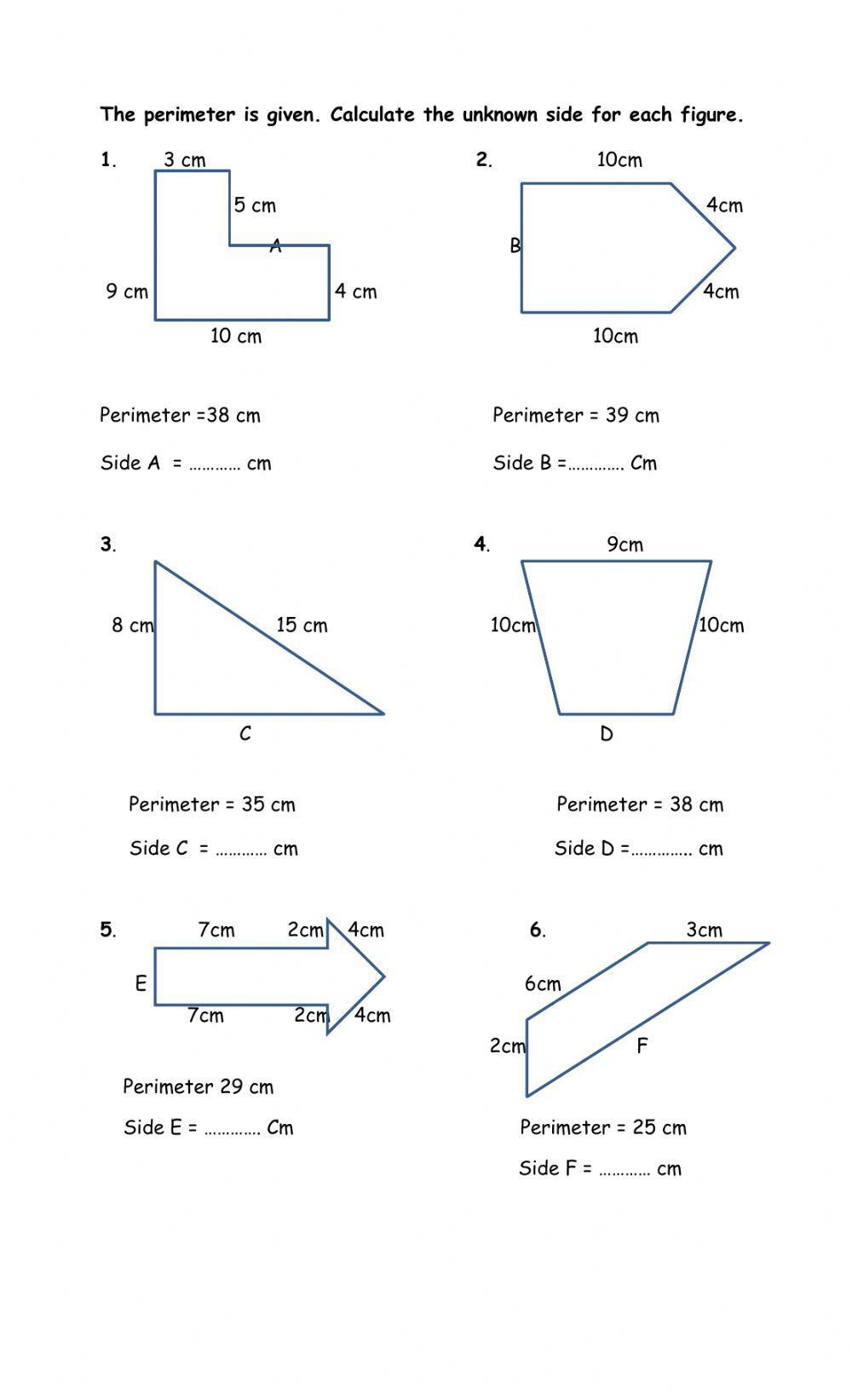
Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 3
Perimeter worksheets for Grade 3 focus on introducing students to the concept of perimeter through simple and engaging problems. These worksheets help students understand how to measure and calculate the perimeter of basic geometric shapes, including rectangles and squares, often with one or more sides missing. Here is a step-by-step guide on how these worksheets are structured:
- Introduction to Perimeter:
Students start with understanding what perimeter is and how to calculate it by summing the lengths of all sides of a shape.
- Definition of perimeter.
- Examples of calculating perimeter with given side lengths.
- Measuring Sides:
Worksheets include exercises where students measure the sides of rectangles and squares using rulers or given measurements.
- Practice with measuring sides accurately.
- Identify and label the sides of shapes.
- Calculating Perimeter:
Students learn to calculate the perimeter by adding the lengths of all sides.
- Use of addition to find the total perimeter.
- Step-by-step problems with clear instructions.
- Finding Missing Sides:
Worksheets present problems where one side length is missing, and students must use their knowledge to find the missing length.
- Given perimeter and some side lengths, solve for the missing side.
- Introduction to basic algebraic thinking.
- Word Problems:
Application of perimeter concepts to real-life scenarios through word problems.
- Examples include finding the perimeter of a garden or a picture frame.
- Encourage logical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Example Problems:
- Example 1:
A rectangle has two sides of 5 cm and two sides of an unknown length. The total perimeter is 20 cm. Find the length of the unknown sides.
Using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
- Example 2:
A square has a perimeter of 24 cm. What is the length of one side?
Using the formula \( P = 4s \):
By practicing with these worksheets, Grade 3 students will develop a solid foundation in calculating perimeters, including solving for missing sides. These exercises are designed to be engaging and educational, ensuring that students build confidence and proficiency in geometry.
Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 4
Enhance your Grade 4 students' understanding of perimeter with these comprehensive worksheets. Each worksheet is designed to help students practice calculating the perimeter of various shapes, including rectangles, squares, triangles, and polygons, especially focusing on problems where one or more sides are missing. Here's a breakdown of the activities and exercises included:
Worksheets Overview
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Review of basic perimeter concepts.
- Understanding the formula:
P = 2(l + w)for rectangles andP = 4sfor squares.
- Perimeter of Rectangles
- Worksheets with given lengths and widths to practice the formula
P = 2(l + w). - Finding missing side lengths when the perimeter and one side length are given.
- Worksheets with given lengths and widths to practice the formula
- Perimeter of Squares
- Exercises to find the perimeter of squares with given side lengths.
- Problems where the perimeter is given, and students must find the side length.
- Perimeter of Triangles
- Calculating the perimeter with all sides given.
- Finding missing side lengths when the perimeter and other sides are provided.
- Perimeter of Polygons
- Worksheets for regular and irregular polygons.
- Problems involving polygons with integer and decimal dimensions.
Sample Problems and Step-by-Step Solutions
Below are examples of the types of problems included in the worksheets, along with step-by-step solutions to help guide students:
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Given: Length = 8 cm, Width = 5 cm
- Use the formula:
P = 2(l + w) - Substitute the values:
P = 2(8 + 5) - Calculate inside the parentheses:
P = 2(13) - Multiply:
P = 26 cm
Example 2: Finding the Missing Side Length of a Rectangle
Given: Perimeter = 24 cm, Length = 7 cm, Width = ?
- Use the formula:
P = 2(l + w) - Rearrange to solve for width:
w = (P / 2) - l - Substitute the values:
w = (24 / 2) - 7 - Calculate:
w = 12 - 7 - Result:
w = 5 cm
Example 3: Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
Given: A regular hexagon with side length = 4 cm
- Count the number of sides: A hexagon has 6 sides.
- Use the formula:
P = number of sides × side length - Substitute the values:
P = 6 × 4 - Calculate:
P = 24 cm
Additional Resources
Printable and Interactive Worksheets
These worksheets are available in both printable and interactive formats, making them ideal for classroom use, homework assignments, and additional practice at home. Download the PDFs for easy printing or use the interactive versions for online practice.
Encouraging Mastery and Confidence
By providing these diverse and detailed worksheets, students will gain confidence in their ability to calculate perimeter, understand geometric concepts, and solve real-world problems involving measurements.
Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 5
Grade 5 students can deepen their understanding of perimeter through a variety of engaging worksheets designed to challenge their skills in finding missing sides. These worksheets will help students apply their knowledge of perimeter formulas and properties of shapes, while also enhancing their problem-solving abilities. Below are some detailed activities and examples:
Activities and Examples
- Understanding Perimeter: Begin by reviewing the concept of perimeter and how it applies to different shapes. For instance, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Finding Missing Sides: Provide worksheets where students need to find the missing side of a shape when the perimeter is given. This involves using algebraic thinking to solve for the unknown side.
- Example: A rectangle has a perimeter of 24 units, with one side measuring 7 units. To find the missing side \( x \), use the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
\[
24 = 2(7 + x) \implies 24 = 14 + 2x \implies 2x = 10 \implies x = 5
\]
- Example: A rectangle has a perimeter of 24 units, with one side measuring 7 units. To find the missing side \( x \), use the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
- Word Problems: Challenge students with word problems that require them to apply their perimeter knowledge to real-world scenarios.
- Example: A garden is in the shape of a triangle with sides measuring 8 meters, 6 meters, and an unknown length. The total perimeter is 21 meters. Find the length of the missing side:
\[
8 + 6 + x = 21 \implies 14 + x = 21 \implies x = 7
- Example: A garden is in the shape of a triangle with sides measuring 8 meters, 6 meters, and an unknown length. The total perimeter is 21 meters. Find the length of the missing side:
- Interactive Worksheets: Use online interactive worksheets to provide instant feedback and allow for more dynamic learning experiences.
Example Worksheet
Here is an example of a Grade 5 perimeter worksheet focusing on finding missing sides:
| Shape | Given Information | Find |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | Perimeter = 30 units, Length = 9 units | Width |
| Triangle | Perimeter = 18 units, Two sides = 5 units, 6 units | Third side |
| Square | Perimeter = 20 units | Side length |
Encourage students to solve these problems using the perimeter formulas they have learned and verify their solutions by re-calculating the perimeter with the found values.
Printable and Interactive Worksheets
For additional practice, students can access a variety of printable and interactive perimeter worksheets online, which cover topics from basic perimeter calculations to complex word problems involving missing sides.
By consistently practicing these types of problems, students will develop a stronger grasp of geometric concepts and improve their overall mathematical skills.
Advanced Perimeter Problems
Advanced perimeter problems involve more complex shapes and scenarios, requiring students to use higher-order thinking skills and multiple mathematical concepts. These problems are designed to challenge students and deepen their understanding of geometry and measurement. Here are some detailed examples and steps to solve advanced perimeter problems:
-
Irregular Polygons
To find the perimeter of an irregular polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify all the sides of the polygon.
- Measure or find the length of each side.
- Add all the side lengths together to find the total perimeter.
Example:
Consider an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 5 cm, 7 cm, 3 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm.
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 3 + 6 + 4 = 25 \, \text{cm} \]
-
Missing Sides in Polygons
When given the perimeter and some side lengths of a polygon, you can find the missing side(s) by following these steps:
- Add the known side lengths.
- Subtract the sum of the known sides from the total perimeter to find the missing side length.
Example:
Given a triangle with a perimeter of 24 cm and two sides of 8 cm and 9 cm, find the missing side length.
\[ \text{Sum of known sides} = 8 + 9 = 17 \, \text{cm} \]
\[ \text{Missing side} = 24 - 17 = 7 \, \text{cm} \]
-
Composite Figures
For composite figures, which are shapes made up of multiple simpler shapes, calculate the perimeter by following these steps:
- Break down the composite figure into simpler shapes.
- Find the perimeter of each simple shape.
- Identify and subtract any shared or overlapping sides.
- Add the perimeters of the simpler shapes together, accounting for the subtracted sides.
Example:
Consider a figure made of a rectangle (8 cm by 4 cm) and a triangle (base 4 cm, height 3 cm) attached to one of the rectangle’s sides.
First, find the perimeter of the rectangle: \[ 2 \times (8 + 4) = 24 \, \text{cm} \]
Next, find the perimeter of the triangle: \[ 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \] (using Pythagoras to find the hypotenuse)
Since the base of the triangle is shared with the rectangle, subtract the overlapping side: \[ 24 + 12 - 4 = 32 \, \text{cm} \]
-
Word Problems
Advanced perimeter problems can also be presented as word problems. Solving these involves:
- Reading the problem carefully to identify relevant information.
- Drawing a diagram to visualize the problem.
- Applying appropriate formulas and mathematical reasoning to find the solution.
Example:
A garden is in the shape of a rectangle with a length that is twice its width. If the perimeter of the garden is 36 meters, find the dimensions of the garden.
Let the width be \( x \) meters. Then, the length is \( 2x \) meters.
Using the perimeter formula: \[ 2(x + 2x) = 36 \]
Simplify and solve for \( x \): \[ 6x = 36 \]
\[ x = 6 \, \text{meters} \]
So, the width is 6 meters and the length is 12 meters.
By working through these advanced problems, students will enhance their problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of perimeter and its applications.

Rectangles and Squares
Rectangles and squares are fundamental geometric shapes that help students understand the basics of perimeter calculations. These worksheets are designed to aid students in calculating the perimeter of rectangles and squares, including scenarios with missing sides.
Understanding the Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares
To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle or square, use the following formulas:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Worksheets Overview
These worksheets include a variety of problems to enhance the learning experience:
- Calculating the perimeter given all side lengths.
- Finding the missing side length when the perimeter and one side length are given.
- Using both integer and decimal dimensions for advanced practice.
Sample Problems and Step-by-Step Solutions
Let's look at a few example problems:
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Given a rectangle with length \( l = 8 \) units and width \( w = 5 \) units:
Using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
\( P = 2(8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \) units
Example 2: Finding the Missing Side Length of a Rectangle
Given a rectangle with a perimeter of 30 units and one side length \( l = 9 \) units, find the width \( w \).
Using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \):
\( 30 = 2(9 + w) \)
\( 30 = 18 + 2w \)
\( 2w = 12 \)
\( w = 6 \) units
Example 3: Perimeter of a Square
Given a square with side length \( s = 7 \) units:
Using the formula \( P = 4s \):
\( P = 4 \times 7 = 28 \) units
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with length 10 units and width 4 units.
- Determine the missing side length of a rectangle with a perimeter of 40 units and one side length of 12 units.
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with side length 9 units.
Additional Resources
Triangles and Polygons
Understanding the perimeter of triangles and polygons is crucial for advancing in geometry. Here, we will explore methods to calculate the perimeter of various shapes, including those with missing sides.
Perimeter of Triangles
To find the perimeter of a triangle, add the lengths of all three sides. If one side is missing, you can use the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles or other geometric properties to find the missing length.
- Example 1: Given a right triangle with sides 3 cm and 4 cm, find the hypotenuse (c) and then the perimeter.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem: \( c = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Calculate the perimeter: \( 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \)
- Example 2: An isosceles triangle has two equal sides of 7 cm and a base of 10 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter: \( 7 + 7 + 10 = 24 \, \text{cm} \)
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides and angles are equal, the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides.
- Example 1: A regular hexagon with each side measuring 6 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter: \( 6 \times 6 = 36 \, \text{cm} \)
- Example 2: A regular pentagon with each side measuring 4 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter: \( 5 \times 4 = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
To find the perimeter of an irregular polygon, add the lengths of all its sides. If some sides are missing, use known lengths and properties of the shape to determine them.
- Example 1: An irregular quadrilateral with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm, and one side missing.
- Calculate the missing side using the given perimeter or other properties.
- Sum all sides to find the perimeter.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides 6 cm, 8 cm, and 10 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 3 cm.
- Determine the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with sides 3 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 9 cm, and a missing side, given the total perimeter is 30 cm.
These exercises will help students develop a strong understanding of calculating perimeters for various geometric shapes, preparing them for more advanced topics in geometry.
Real-world Applications
Understanding perimeter is not only crucial for academic success but also for solving practical, real-world problems. Here are some engaging applications where perimeter calculations are essential:
- Garden Planning: Calculate the perimeter to determine the amount of fencing required for a garden area. This helps in estimating the material needed efficiently.
- Sports Fields: Determine the perimeter of various sports fields, such as soccer or baseball fields, to plan for track layouts or boundary lines.
- Home Improvement Projects: Use perimeter calculations for tasks like installing baseboards, crown molding, or painting walls, ensuring accurate measurements and material usage.
- Event Planning: Calculate the perimeter of event spaces to plan for decorations, table arrangements, and space management effectively.
- Geography and Mapping: Geographers use perimeter to estimate boundaries of natural and man-made features on maps, aiding in accurate representation and planning.
- Technology and Engineering: Engineers and tech professionals use perimeter calculations for component design, layout planning, and resource allocation in various projects.
These real-world applications demonstrate the importance of understanding perimeter beyond the classroom. Here are some step-by-step guides to approach these problems:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the shape you are working with (e.g., rectangle, triangle, polygon).
- Determine the Formula: Use the appropriate formula for calculating the perimeter based on the identified shape.
- List Known Sides: Write down the lengths of the sides that are known.
- Apply the Perimeter Formula: Use the formula to calculate the total perimeter or set up an equation if there are missing sides.
- Solve for Missing Sides: Use algebraic methods or subtract known lengths from the total perimeter to find the missing measurements.
- Check Your Work: Review your calculations to ensure accuracy and consistency within the context of the problem.
By applying these steps, students can solve real-world perimeter problems effectively, enhancing their problem-solving skills and understanding of geometric concepts. Interactive and practical worksheets that incorporate these real-world scenarios make learning engaging and relevant, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Step-by-step Solutions
Understanding how to find the perimeter, especially with missing sides, involves a clear step-by-step approach. Here, we will go through detailed steps to solve perimeter problems with missing sides.
-
Identify Known Sides
First, identify the lengths of all the known sides of the shape. For instance, if dealing with a rectangle, note down the lengths of the sides that are given.
-
Determine Relationships Between Sides
Use the properties of the shape to determine the lengths of the missing sides. For example:
- Rectangles: Opposite sides are equal.
- Squares: All four sides are equal.
- Regular Polygons: All sides are of equal length.
-
Set Up Equations
For shapes where sides are not directly given, set up equations based on the perimeter formula. For example, if the perimeter (P) of a rectangle is known, and one side length (L) is given, use:
Here, solve for the missing side (W).
-
Calculate the Perimeter
Add up all the side lengths to find the total perimeter. Ensure to include all known and calculated sides:
Let’s look at a sample problem and solution:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| A rectangle has one side length of 8 cm and a perimeter of 30 cm. Find the missing side length. |
|
These worksheets will guide you through similar problems, ensuring a thorough understanding of how to approach and solve perimeter problems with missing sides step-by-step.

Printable Worksheets
Our collection of printable perimeter worksheets with missing sides is designed to help students master the concept of perimeter. These worksheets are suitable for various grade levels and cover a range of difficulty levels, ensuring that students can progress at their own pace. Below are some examples and explanations of the types of worksheets available:
-
Basic Perimeter Worksheets:
These worksheets focus on simple shapes such as rectangles and squares. Students are required to find the perimeter by adding the lengths of the sides, some of which may be missing. They will use given side lengths to determine the missing measurements.
Example:

Given: \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = ? \) cm
Perimeter formula: \( P = 2a + 2b \)Calculate the missing side \( b \).
-
Intermediate Perimeter Worksheets:
These worksheets introduce more complex shapes, including triangles and polygons. Students will need to apply their knowledge of geometry to find missing side lengths and calculate the total perimeter.
Example:

Given: \( a = 7 \) cm, \( b = 8 \) cm, \( c = ? \) cm
Perimeter formula: \( P = a + b + c \)Calculate the missing side \( c \).
-
Advanced Perimeter Worksheets:
These worksheets are designed for higher grade levels and include challenging problems involving irregular shapes and real-world scenarios. Students must use logical reasoning and problem-solving skills to find missing sides and calculate the perimeter.
Example:

Given: Various side lengths with one or more missing
Perimeter formula: Sum of all sidesCalculate the missing sides and determine the perimeter.
All worksheets are provided in a printable format, making it easy for teachers to distribute them in the classroom or for parents to use them at home. The worksheets come with step-by-step solutions to help students understand the process of calculating perimeter with missing sides. Download the worksheets below to get started:
Interactive Online Worksheets
Interactive online worksheets provide an engaging way for students to practice and master the concept of finding the perimeter with missing sides. These worksheets are designed to be used on various devices, making learning accessible and interactive. Below are some detailed examples and features of these interactive worksheets:
-
Live Worksheets: These worksheets allow students to find the missing sides and calculate the perimeter directly on the worksheet. The interactive platform provides instant feedback, making it an excellent tool for self-assessment.
- Features include draggable elements, multiple-choice questions, and interactive grid layouts.
- Worksheets cover various shapes such as squares, rectangles, and irregular polygons.
- Teachers can assign these worksheets through Google Classroom or Microsoft Teams.
-
SplashLearn: SplashLearn offers a range of interactive worksheets that help students practice finding the perimeter of shapes with missing side lengths. These worksheets are designed to be engaging and visually appealing.
- Includes exercises on regular and irregular shapes.
- Provides hints and step-by-step solutions to guide students through the problems.
- Tracks progress and adapts the difficulty level based on student performance.
-
K5 Learning: This platform provides interactive perimeter worksheets suitable for various grade levels. These worksheets focus on finding the perimeter of complex shapes and provide a thorough understanding of the concept.
- Interactive elements such as fill-in-the-blank and multiple-choice questions.
- Printable options available for offline practice.
- Detailed solutions and explanations are provided to reinforce learning.
Using interactive online worksheets, students can enjoy a dynamic learning experience that helps them understand and apply the principles of perimeter calculation in various contexts. These resources are valuable for both classroom use and home practice, offering flexibility and comprehensive support for students.
Teacher Resources and Guides
Teachers seeking resources and guides for teaching perimeter with missing sides will find a wealth of materials to support their lessons. These resources range from worksheets and activities to comprehensive guides and lesson plans. Below are some detailed examples and features of these resources:
-
Teachers Pay Teachers (TpT): A vast marketplace offering a variety of perimeter worksheets with missing sides. These resources include activities, games, and interactive notebook pages specifically designed to help students grasp the concept of finding missing sides.
- Includes worksheets for different grade levels with step-by-step instructions.
- Features both printable and digital resources to accommodate different teaching environments.
- Provides detailed answer keys to facilitate easy grading and student feedback.
-
Teach Starter: This platform provides editable and non-editable worksheets for calculating perimeter with missing sides, tailored to curriculum standards like CCSS and TEKS.
- Offers worksheets in PDF and Google Slides formats for flexible use.
- Includes practice problems that mix metric and customary units to enhance students' understanding.
- Suggestions for differentiated instruction to meet the needs of all students.
-
Twinkl: Twinkl offers a comprehensive collection of perimeter resources, including lesson plans, PowerPoints, and assessment tools, aligned with various educational standards.
- Instant access to a variety of teaching materials designed by educators.
- Interactive activities and games to make learning engaging and fun.
- Assessment tools to track student progress and understanding.
By utilizing these resources, teachers can create a dynamic and supportive learning environment where students can practice and master the concept of perimeter, even with missing side lengths. These guides and materials provide structured and comprehensive support, making it easier for educators to deliver effective and engaging math lessons.
Homework Assignments
Homework assignments focused on perimeter with missing sides help students apply classroom learning to individual practice. Here are some ideas and structures for effective homework assignments:
-
Worksheet Assignments: Utilize printable worksheets that offer a variety of problems requiring students to find missing sides to calculate perimeter.
- Include shapes like rectangles, squares, triangles, and polygons with some sides missing.
- Incorporate word problems that place the shapes in real-world contexts, such as finding the missing side length of a garden or a room.
- Encourage students to draw and label diagrams for visual assistance.
-
Interactive Digital Assignments: Assign interactive online worksheets which provide immediate feedback and allow students to practice with engaging digital tools.
- Platforms like Live Worksheets offer self-correcting exercises that students can complete online and submit directly to teachers.
- Google Slides can be used to create editable assignments where students can manipulate shapes and sides.
-
Project-Based Assignments: For a more in-depth understanding, assign projects where students design their own shapes or real-life objects, calculate perimeters, and determine any missing sides.
- Have students create a floor plan of a simple structure, like a house or park, and calculate its perimeter.
- Integrate cross-curricular activities, such as designing a plot in a community garden and calculating the fencing needed.
Here is an example of a structured homework assignment:
| Problem | Instructions |
| 1. A rectangle has a perimeter of 20 cm. One side is 6 cm. What is the length of the other side? | Draw the rectangle, label the known side, write the formula for perimeter, and solve for the missing side. |
| 2. A triangle has sides 5 cm, 7 cm, and one side is missing. The perimeter is 18 cm. Find the missing side. | Sketch the triangle, label the known sides, write the formula for perimeter, and solve for the unknown side. |
Using these diverse homework assignments, students will develop a solid understanding of how to find the perimeter of shapes with missing sides, reinforcing their classroom learning through practical application.

Classroom Activities
Engaging students in hands-on and interactive activities is key to understanding the concept of perimeter, especially with missing sides. Here are several classroom activities that can help:
-
Geoboard Creations: Use geoboards to create various shapes with a given perimeter. Students can stretch rubber bands around pegs to form shapes and calculate the missing sides.
-
Pentomino Perimeters: Have students measure the perimeter of pentominos, order them based on their perimeters, and observe how combining shapes affects the total perimeter.
-
Painter's Tape Shapes: Use painter's tape to outline shapes on the classroom floor. Students guess and then measure the perimeters, helping them understand how to calculate missing sides.
-
Outdoor Measurements: Take learning outside by measuring the perimeter of various objects or areas such as playgrounds, buildings, or sports fields using a measuring tape, string, or even steps.
-
Straw and Pipe Cleaner Polygons: Students create polygons using straws, pipe cleaners, or sticks, then calculate the perimeter and find any missing sides.
-
Chalk Drawings: Draw shapes with chalk on the playground. Students guess the perimeter, measure it, and verify their calculations.
-
Perimeter Stories: Read books that integrate math concepts, such as "Perimeter, Area, and Volume" by David Adler or "Spaghetti and Meatballs for All!" by Marilyn Burns, and discuss the stories' applications to real-world perimeter problems.
These activities not only make learning fun but also ensure that students gain a thorough understanding of how to find the perimeter of shapes, even when some sides are missing. Combining practical exercises with creative tasks helps solidify their knowledge and application of perimeter concepts.
Fun Perimeter Challenges
Engaging students in perimeter challenges can be both educational and fun. Here are some interactive and creative activities that can help students better understand and enjoy calculating the perimeter of various shapes.
- Shape Hunt: Organize a scavenger hunt where students find and measure the perimeter of various objects around the classroom or playground. This activity encourages practical application of their knowledge.
- Perimeter Puzzles: Provide students with puzzles where they must find missing side lengths to complete the perimeter of different shapes. This can be done using printed worksheets or interactive online tools.
- Design a Park: Ask students to design a park with specific features such as a playground, a garden, and a walking path. They must calculate the perimeter of each feature and the entire park.
- Math Relay: Set up a relay race where students solve perimeter problems at different stations. Each correct answer allows them to move to the next station.
- Art and Math Integration: Combine art and math by having students create colorful geometric patterns or designs. They must then calculate the perimeter of their artwork.
- Interactive Online Games: Utilize online math games that focus on perimeter calculations. These games can provide instant feedback and keep students engaged.
These activities not only make learning fun but also help students to see the practical applications of perimeter in everyday life. Encourage students to think creatively and work collaboratively to solve perimeter challenges.
Video hướng dẫn học sinh lớp 5 cách tính chu vi và tìm cạnh thiếu.
Toán học - Lớp 5: Chu vi - Giải phương trình tìm cạnh thiếu
READ MORE:
Video giúp học sinh hiểu cách tính chu vi một cách vui nhộn và dễ hiểu.
Toán Học Vui Nhộn - Chu Vi