Topic perimeter sentence: Discover the art of crafting compelling perimeter sentences to captivate your readers from the very start. In this comprehensive guide, learn the importance of perimeter sentences, how to construct them effectively, and gain valuable insights into examples and tips for improvement. Unlock the potential of your writing with the mastery of perimeter sentences.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Use of "Perimeter" in Sentences
- 1. Understanding Perimeter Sentence
- 2. Importance of Perimeter Sentences
- 3. How to Construct Effective Perimeter Sentences
- 4. Examples of Perimeter Sentences in Various Contexts
- 5. Tips for Improving Perimeter Sentences
- 6. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Sentence Writing
- 7. Perimeter Sentence vs. Topic Sentence: Clarifying the Difference
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu cách phát âm và sử dụng từ 'phạm vi' trong các câu và cụm từ khác nhau.
Understanding the Use of "Perimeter" in Sentences
The term "perimeter" refers to the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure or the outer edge of an area. It is commonly used in various contexts such as construction, geography, and security.
Examples of "Perimeter" in Different Contexts
- In construction, the perimeter often denotes the outer edges of a structure. For instance, "Workers laid bricks along the perimeter of the foundation to create a sturdy base."
- In geography, "perimeter" can describe the boundary of an area. For example, "The hikers followed the perimeter of the lake, enjoying the scenic views along the way."
- In security, it refers to the boundary that must be protected or secured, such as "The security agents formed a perimeter around the president."
Common Mistakes and Considerations
- Confusing perimeter with area: "Perimeter" specifically refers to the boundary, not the size or extent of the space.
- Using "perimeter" in non-physical contexts: It should not be used when discussing time or abstract concepts.
- Incorrect plural form: The term "perimeter" is singular; use "boundaries" or "edges" for multiple perimeters.
Cultural and Regional Differences
The use of "perimeter" might vary slightly based on regional terminology or specific applications. For example, British English often uses "circumference" for circular boundaries, and different regions might prefer metric or imperial units of measurement.
Synonyms for "Perimeter"
- Boundary: The line or limit that separates one area from another. Example: "The boundary of the property was marked by a white picket fence."
- Circumference: The distance around a circular shape. Example: "The circumference of the tree trunk was measured to determine its age."
- Edge: The outer boundary of an object or area, often implying a distinct separation. Example: "The edge of the cliff was dangerously steep."
Using "Perimeter" in Mathematical Contexts
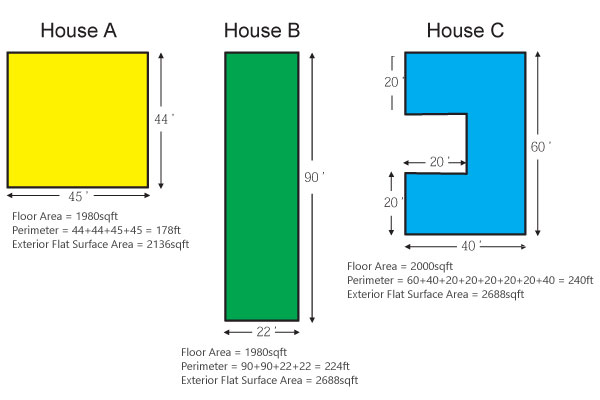
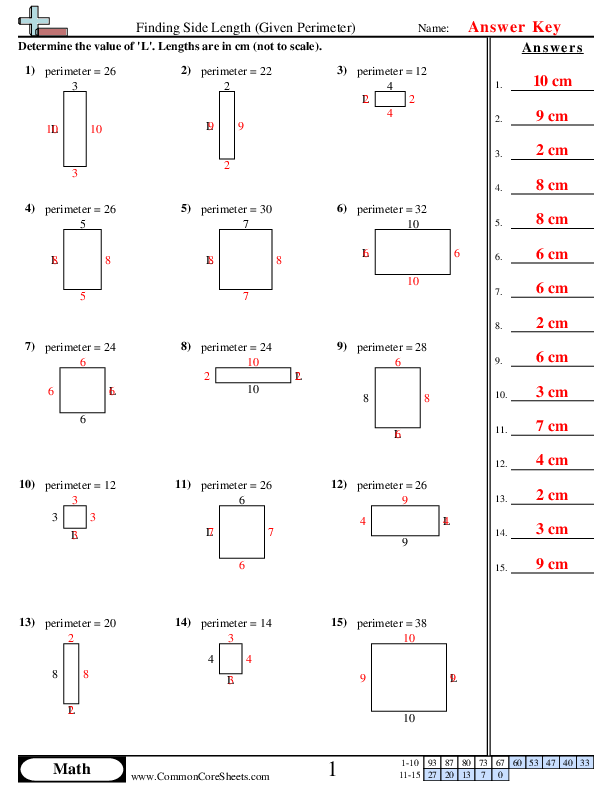
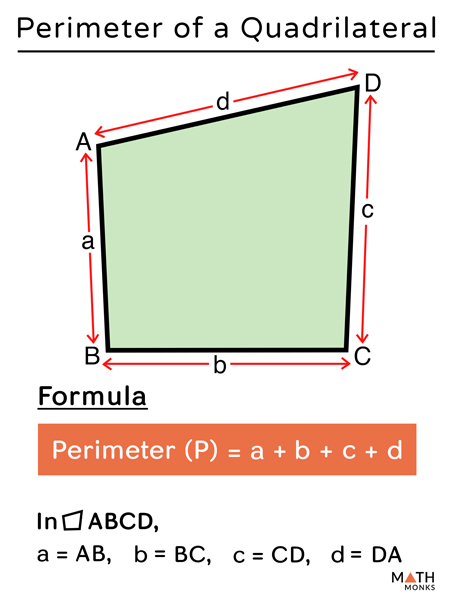
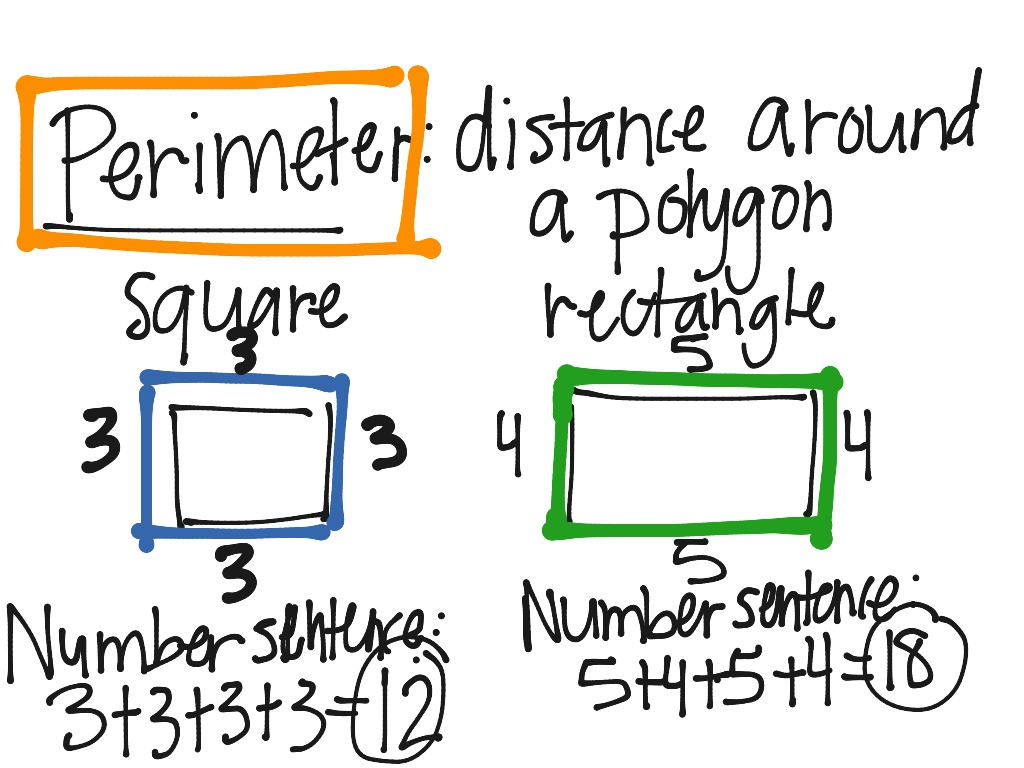
In mathematics, the perimeter is the total distance around a shape. For example, to find the perimeter of a rectangle, you add up the lengths of all four sides.
These examples and explanations demonstrate the versatility and importance of understanding the correct usage of the word "perimeter" in various contexts.
READ MORE:
1. Understanding Perimeter Sentence
A perimeter sentence serves as the boundary or framework for a paragraph or section of text, encapsulating its main idea or theme. Here's a detailed breakdown:
- Definition: Perimeter sentences are concise, clear statements that introduce the central topic or argument of a paragraph.
- Function: They establish the scope and direction of the upcoming content, guiding readers on what to expect.
- Clarity: Perimeter sentences aid comprehension by providing a focal point for the following discussion, ensuring clarity and coherence.
- Importance: They play a crucial role in structuring written material, facilitating logical flow and organization.
- Variability: Perimeter sentences can vary in complexity and style depending on the nature of the content and intended audience.
- Examples: Examples of perimeter sentences include thesis statements in academic essays, topic sentences in paragraphs, and introductory phrases in articles.
Understanding the significance of perimeter sentences empowers writers to effectively communicate their ideas, engaging readers and enhancing the overall readability of their work.
2. Importance of Perimeter Sentences
Perimeter sentences hold significant importance in the realm of effective communication and writing. Here's why they are essential:
- Clarity: Perimeter sentences provide clarity by succinctly summarizing the main point or theme of a paragraph or section.
- Guidance: They act as guideposts for readers, signaling the direction and focus of the forthcoming content.
- Organization: By establishing a clear perimeter, these sentences aid in organizing ideas and structuring written material cohesively.
- Engagement: Well-crafted perimeter sentences capture readers' attention and encourage them to delve deeper into the text, enhancing engagement.
- Comprehension: They facilitate comprehension by providing a framework for understanding the context and relevance of the subsequent information.
- Persuasion: In persuasive writing, perimeter sentences serve as persuasive hooks, enticing readers to explore further and consider the presented arguments.
Recognizing the importance of perimeter sentences empowers writers to effectively convey their message, foster connection with their audience, and ultimately achieve their communication goals.
3. How to Construct Effective Perimeter Sentences
Constructing effective perimeter sentences is crucial for clear and concise communication. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Main Idea: Before crafting your perimeter sentence, clearly identify the main idea or theme of the paragraph or section it will introduce.
- Be Concise: Keep your perimeter sentence brief and to the point. It should provide a clear overview without delving into too much detail.
- Use Clear Language: Ensure that your perimeter sentence is written in clear and understandable language. Avoid jargon or complex terminology that may confuse readers.
- Include Key Points: Highlight the main points or arguments that will be discussed in the following text. This helps orient readers and prepares them for what's to come.
- Provide Structure: Structure your perimeter sentence in a way that flows naturally from the preceding content and sets the stage for what follows. Consider using transitional words or phrases to connect ideas.
- Review and Revise: Once you've drafted your perimeter sentence, review it carefully to ensure it effectively encapsulates the content that follows. Revise as needed to improve clarity and coherence.
By following these steps, you can construct perimeter sentences that effectively introduce and guide readers through your written work.
4. Examples of Perimeter Sentences in Various Contexts
Perimeter sentences serve as introductory statements that encapsulate the main idea of a paragraph or section. Here are some examples of perimeter sentences in different contexts:
- Academic Essay: "In this paper, we explore the impact of climate change on global biodiversity and propose strategies for conservation and adaptation."
- Business Report: "The following analysis presents key market trends and forecasts for the upcoming fiscal year, highlighting opportunities for growth and potential challenges."
- Legal Brief: "This brief examines the precedent set by recent court rulings on intellectual property rights in the digital age, with implications for future copyright law."
- Journalistic Article: "Amidst growing concerns over public health, this investigative report delves into the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in combating infectious diseases."
- Technical Manual: "This manual provides step-by-step instructions for assembling and calibrating the XYZ-2000 robotic arm, including safety precautions and troubleshooting tips."
These examples demonstrate how perimeter sentences can vary in tone, complexity, and purpose depending on the specific context and audience.

5. Tips for Improving Perimeter Sentences
Crafting effective perimeter sentences is essential for engaging readers and guiding them through your written content. Here are some tips to enhance your perimeter sentences:
- Clarity is Key: Ensure that your perimeter sentence clearly communicates the main idea or purpose of the following text.
- Conciseness: Keep your perimeter sentence brief and focused, avoiding unnecessary details or convoluted language.
- Relevance: Make sure your perimeter sentence directly relates to the content that follows, providing a seamless transition for the reader.
- Engagement: Use compelling language or a thought-provoking statement to capture the reader's attention and encourage them to continue reading.
- Accuracy: Ensure that your perimeter sentence accurately represents the themes or arguments that will be explored in the subsequent text.
- Revision: Take the time to review and revise your perimeter sentence, refining it to maximize clarity and impact.
- Seek Feedback: Consider seeking feedback from peers or colleagues to ensure your perimeter sentence effectively serves its purpose.
By incorporating these tips into your writing process, you can create perimeter sentences that effectively set the stage for the content that follows, enhancing the overall readability and coherence of your work.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Sentence Writing
While crafting perimeter sentences, it's important to steer clear of common pitfalls that can detract from their effectiveness. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
- Vagueness: Avoid vague or ambiguous language that fails to clearly convey the main idea of the following text.
- Overcomplication: Resist the temptation to overcomplicate your perimeter sentence with unnecessary details or convoluted language.
- Irrelevance: Ensure that your perimeter sentence directly relates to the content that follows, avoiding tangents or unrelated topics.
- Weakness: Steer clear of perimeter sentences that lack strength or impact, opting instead for statements that captivate the reader's attention.
- Redundancy: Avoid restating information already presented in the preceding text, focusing instead on introducing new ideas or perspectives.
- Inconsistency: Maintain consistency in tone and style throughout your perimeter sentence and the accompanying text.
- Failure to Revise: Neglecting to review and revise your perimeter sentence can lead to overlooked errors or missed opportunities for improvement.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can enhance the clarity, coherence, and impact of your perimeter sentences, ultimately improving the overall quality of your writing.
7. Perimeter Sentence vs. Topic Sentence: Clarifying the Difference
While both perimeter sentences and topic sentences serve important roles in writing, they have distinct functions and characteristics. Here's a breakdown of the differences between the two:
| Perimeter Sentence | Topic Sentence |
| Introduces the main idea or theme of a paragraph or section. | States the main idea of a single paragraph within a larger piece of writing. |
| Located at the beginning of a paragraph or section to provide context and guide the reader. | Usually found at the beginning of a paragraph to signal its focus and direction. |
| Offers a broader overview of the content that follows. | Focuses specifically on the content of the paragraph it precedes. |
| May encompass multiple paragraphs or sections within a document. | Applies to a single paragraph and does not extend beyond its boundaries. |
| Designed to orient readers and provide a roadmap for navigating the text. | Functions as a concise summary or preview of the paragraph's content. |
Understanding the distinction between perimeter sentences and topic sentences can help writers effectively structure their writing and improve overall clarity and coherence.
Xem video này để hiểu cách phát âm và sử dụng từ 'phạm vi' trong các câu và cụm từ khác nhau.
Phạm vi - Phát âm + Ví dụ trong câu và cụm từ
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu về ý nghĩa của chu vi và cách tính toán chu vi một cách dễ dàng. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm quan trọng này trong toán học.
Chu vi | Ý nghĩa của Chu vi