Topic find perimeter calculator: Discover the most efficient way to calculate perimeters with our Find Perimeter Calculator. This user-friendly tool helps you quickly and accurately determine the perimeter of various geometric shapes. Whether you're a student, teacher, or DIY enthusiast, our calculator simplifies the process, saving you time and ensuring precision in your measurements.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Calculator
- Introduction to Perimeter Calculators
- Understanding Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeters
- Types of Shapes and Their Perimeters
- Square Perimeter Calculation
- Rectangle Perimeter Calculation
- Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Circle Perimeter Calculation
- Perimeter Calculation Examples
- Online Perimeter Calculators
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using Perimeter Calculators
- Common Mistakes in Perimeter Calculation
- Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculations
- Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Frequently Asked Questions About Perimeter Calculators
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Perimeter Calculator
This calculator helps you find the perimeter of various geometric shapes. The perimeter is the total length of the sides or edges of a polygon or the circumference in the case of circles.
Perimeter Formulas
- Square: \( P = 4 \times a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: \( P = 2 \pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius (Circumference).
Calculate Perimeter
Enter the dimensions of the shape to calculate its perimeter:
| Square Side (a): | Perimeter: | ||||
| Rectangle Length (l): | Width (w): | Perimeter: | |||
| Triangle Side a: | Side b: | Side c: | Perimeter: | ||
| Circle Radius (r): | Perimeter: |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter Calculators
A perimeter calculator is a practical tool designed to help you quickly and accurately determine the perimeter of various geometric shapes. Whether you are dealing with simple shapes like squares and rectangles or more complex polygons, a perimeter calculator simplifies the process, saving you time and effort.
Using a perimeter calculator involves the following steps:
- Select the shape for which you need to find the perimeter.
- Enter the required dimensions (e.g., side lengths, radius).
- Click the calculate button to get the result instantly.
Here are the perimeter formulas for some common shapes:
- Square: \( P = 4 \times a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: \( P = 2 \pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius (Circumference).
Perimeter calculators are beneficial for various applications, including:
- Academic purposes: helping students and teachers with geometry problems.
- DIY projects: assisting hobbyists in measuring materials accurately.
- Professional use: aiding architects and engineers in precise measurements.
Overall, perimeter calculators are invaluable tools for anyone needing accurate perimeter measurements, making complex calculations straightforward and accessible to all.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary. It is a crucial concept in geometry and has various practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday measurements. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter helps in solving real-world problems involving dimensions and spaces.
In simple terms, the perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of the shape. The formula for the perimeter depends on the type of shape.
Here are some common shapes and their perimeter formulas:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the diameter or the radius.
or
Each of these formulas is derived from the fundamental property of the shape, ensuring an accurate measurement of the perimeter. Understanding these basic formulas allows for calculating the perimeter of more complex shapes by breaking them down into simpler components.
Additionally, using online perimeter calculators can simplify these calculations, especially for complex shapes or when precise measurements are required. These tools often require inputting the dimensions of the shape, and they provide quick and accurate results.
Formulas for Calculating Perimeters
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing the lengths of its sides. Here are the formulas for the most common shapes:
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square with side length \( a \) is given by: \[ P = 4a \]
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is: \[ P = 2l + 2w \]
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is: \[ P = a + b + c \]
- Circle: The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle with radius \( r \) is: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
- Parallelogram: The perimeter \( P \) of a parallelogram with base \( b \) and side length \( a \) is: \[ P = 2a + 2b \]
- Trapezoid: The perimeter \( P \) of a trapezoid with sides \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) is: \[ P = a + b + c + d \]
- Rhombus: The perimeter \( P \) of a rhombus with side length \( a \) is: \[ P = 4a \]
- Ellipse: The perimeter \( P \) of an ellipse with semi-major axis \( a \) and semi-minor axis \( b \) can be approximated by: \[ P \approx 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{a^2 + b^2}{2}} \]
These formulas can be used to find the perimeter of basic geometric shapes. For more complex shapes, the perimeter can often be determined by breaking the shape into simpler components and summing their perimeters.
Types of Shapes and Their Perimeters
Understanding the perimeter of various shapes is essential in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. Here are the formulas for calculating the perimeters of some common shapes:
- Square: The perimeter (P) of a square is calculated by the formula:
\( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is given by:
\( P = 2l + 2w \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of all its sides:
\( P = a + b + c \)
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated by:
\( C = 2\pi r \)
where \( r \) is the radius.
- Ellipse: The perimeter of an ellipse can be approximated using:
\( P \approx \pi [ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} ] \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the semi-major and semi-minor axes respectively.
- Trapezoid: The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of all its sides:
\( P = a + b + c + d \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the parallel sides, and \( c \) and \( d \) are the lengths of the non-parallel sides.
- Parallelogram: The perimeter of a parallelogram is given by:
\( P = 2(a + b) \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
- Rhombus: The perimeter of a rhombus is:
\( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Pentagon: For a regular pentagon, the perimeter is:
\( P = 5a \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Hexagon: For a regular hexagon, the perimeter is:
\( P = 6a \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
Each shape has a specific formula based on its properties. Understanding these formulas is crucial for accurate perimeter calculations, especially in fields like architecture, engineering, and various design disciplines.
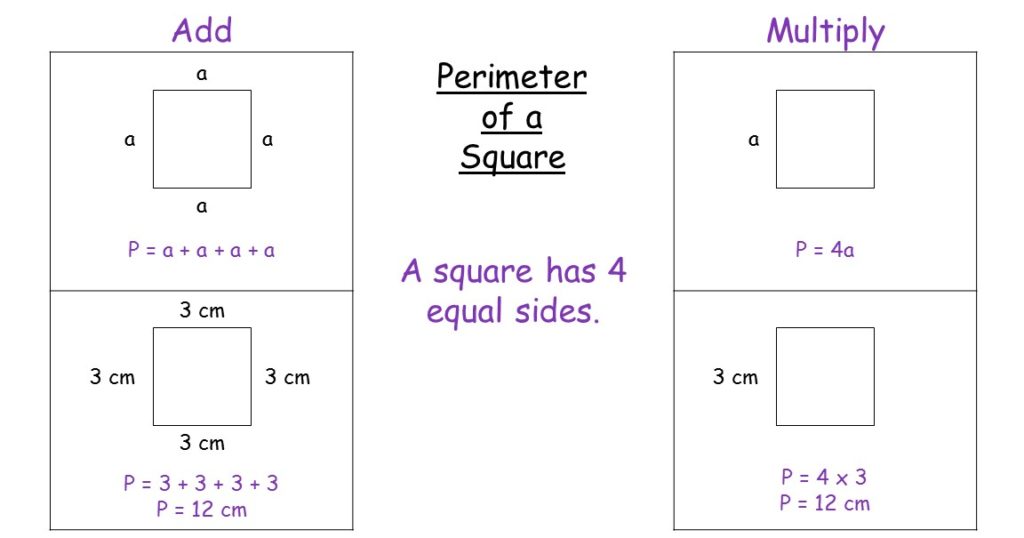
Square Perimeter Calculation
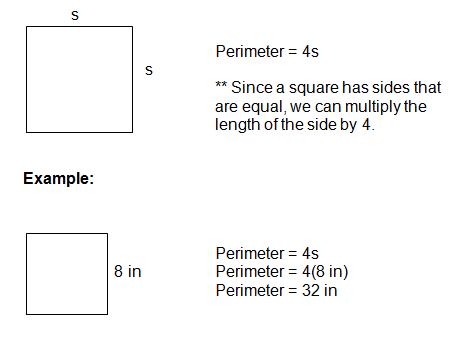
The perimeter of a square is the total distance around the outside of the square. Since a square has four equal sides, calculating its perimeter is straightforward.
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a square is:
\( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
Here’s how to calculate the perimeter step-by-step:
- Measure the length of one side of the square. Let's denote this length as \( a \).
- Multiply the length of the side by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if one side of the square is 5 meters long, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ meters} \)
This means the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 meters is 20 meters.
Using an online perimeter calculator, you can easily compute the perimeter by entering the side length, and the calculator will automatically perform the multiplication for you.
Let's summarize with a table:
| Side Length (a) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 2 cm | 8 cm |
| 5 m | 20 m |
| 7 in | 28 in |
| 10 ft | 40 ft |
For more accurate results, especially when working with large measurements or needing precise values, using an online perimeter calculator can be very helpful. These calculators often allow you to input different units and convert them as necessary.
Always remember, the key to accurate perimeter calculation is ensuring that all measurements are in the same unit before performing the calculations.
Rectangle Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle involves summing the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, the formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is:
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Measure the length \( l \) of the rectangle.
- Measure the width \( w \) of the rectangle.
- Apply the formula:
- Multiply the length by 2: \( 2l \)
- Multiply the width by 2: \( 2w \)
- Add these two results together: \( 2l + 2w \)
- The resulting sum is the perimeter of the rectangle.
For example, if the length \( l \) is 5 units and the width \( w \) is 3 units:
\[ P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \text{ units} \]
This means the perimeter of the rectangle is 16 units.
Additionally, for more complex calculations or to verify your results, you can use an online that allows you to input the length and width to find the perimeter instantly.
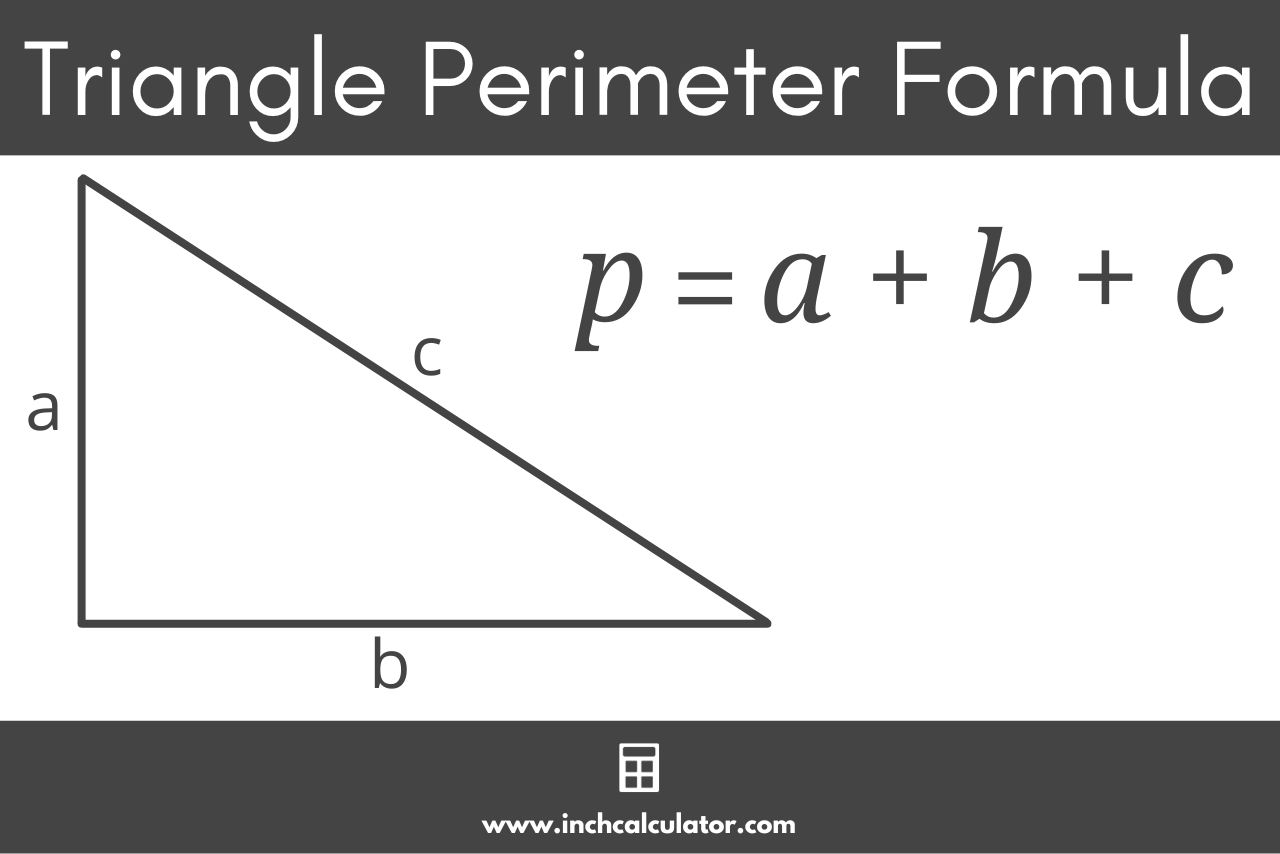
Triangle Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length around the shape, calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. Depending on the information available, different methods can be used to find the perimeter.
Basic Formula
When the lengths of all three sides are known, the formula is straightforward:
\(\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c\)
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
Examples
For a triangle with sides \(a = 3 \, \text{cm}\), \(b = 4 \, \text{cm}\), and \(c = 5 \, \text{cm}\), the perimeter is:
\(\text{Perimeter} = 3 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} = 12 \, \text{cm}\)
Using Two Sides and the Included Angle (SAS)
If two sides and the included angle are known, use the law of cosines to find the third side, then calculate the perimeter:
\(\text{Perimeter} = a + b + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma)}\)
where \(\gamma\) is the angle between sides \(a\) and \(b\).
Example
Given \(a = 8 \, \text{ft}\), \(b = 6 \, \text{ft}\), and \(\gamma = 75^\circ\):
\(\text{Perimeter} = 8 \, \text{ft} + 6 \, \text{ft} + \sqrt{8^2 + 6^2 - 2 \cdot 8 \cdot 6 \cdot \cos(75^\circ)} \approx 22.67 \, \text{ft}\)
Using Two Angles and the Included Side (ASA)
If two angles and the included side are known, use the law of sines to find the other two sides, then calculate the perimeter:
\(\text{Perimeter} = a + \frac{a \sin(\beta)}{\sin(\alpha)} + \frac{a \sin(\gamma)}{\sin(\alpha)}\)
where \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), and \(\gamma\) are the angles, and \(a\) is the known side.
Example
Given \(a = 7 \, \text{m}\), \(\alpha = 30^\circ\), \(\beta = 45^\circ\), and \(\gamma = 105^\circ\):
\(\text{Perimeter} = 7 \, \text{m} + \frac{7 \sin(45^\circ)}{\sin(30^\circ)} + \frac{7 \sin(105^\circ)}{\sin(30^\circ)} \approx 28.7 \, \text{m}\)
Common Scenarios
- SSS (Side-Side-Side): Known three sides, use \(\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c\).
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side): Known two sides and included angle, use the law of cosines.
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): Known two angles and included side, use the law of sines.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the given information (sides and/or angles).
- Select the appropriate formula based on the given data.
- Substitute the known values into the formula.
- Perform the calculations to find the perimeter.
Circle Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a circle is also known as the circumference. Calculating the circumference of a circle is straightforward once you know the circle's radius or diameter.
Here are the steps to calculate the circumference of a circle:
- Identify the radius (r) or diameter (d) of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge, while the diameter is twice the radius.
- Use the formula for the circumference:
- When the radius is known: \( C = 2 \pi r \)
- When the diameter is known: \( C = \pi d \)
- Here, \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately equal to 3.14159.
For example, let's calculate the circumference of a circle:
- If the radius (r) is 5 units:
- Using the formula \( C = 2 \pi r \), we get \( C = 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 \).
- This simplifies to \( C \approx 31.4159 \) units.
- If the diameter (d) is 10 units:
- Using the formula \( C = \pi d \), we get \( C = 3.14159 \times 10 \).
- This simplifies to \( C \approx 31.4159 \) units.
To ensure accuracy in your calculations, use a calculator or an online perimeter calculator.
| Shape | Formula | Example Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Circle (using radius) | \( C = 2 \pi r \) | If \( r = 5 \), then \( C = 2 \times 3.14159 \times 5 = 31.4159 \) |
| Circle (using diameter) | \( C = \pi d \) | If \( d = 10 \), then \( C = 3.14159 \times 10 = 31.4159 \) |
Perimeter Calculation Examples
In this section, we will explore examples of calculating the perimeter for different shapes. Each example will demonstrate the steps required to find the perimeter using the appropriate formulas.
Example 1: Square Perimeter
Given a square with a side length of 5 cm:
- Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Substitute \( a = 5 \): \( P = 4 \times 5 \)
- Calculate: \( P = 20 \) cm
Example 2: Rectangle Perimeter
Given a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 3 cm:
- Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Substitute \( l = 8 \) and \( w = 3 \): \( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 \)
- Calculate: \( P = 16 + 6 = 22 \) cm
Example 3: Triangle Perimeter
Given a triangle with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm:
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Substitute \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), and \( c = 5 \): \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 \)
- Calculate: \( P = 12 \) cm
Example 4: Circle Perimeter (Circumference)
Given a circle with a radius of 7 cm:
- Formula: \( P = 2 \pi r \)
- Substitute \( r = 7 \): \( P = 2 \pi \times 7 \)
- Calculate: \( P \approx 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 = 43.96 \) cm
Example 5: Parallelogram Perimeter
Given a parallelogram with side lengths of 6 cm and 10 cm:
- Formula: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute \( a = 6 \) and \( b = 10 \): \( P = 2 \times 6 + 2 \times 10 \)
- Calculate: \( P = 12 + 20 = 32 \) cm
Example 6: Trapezoid Perimeter
Given a trapezoid with side lengths of 4 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm:
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Substitute \( a = 4 \), \( b = 5 \), \( c = 7 \), and \( d = 8 \): \( P = 4 + 5 + 7 + 8 \)
- Calculate: \( P = 24 \) cm
These examples demonstrate how to apply the formulas for different shapes to find their perimeters. Practice with various measurements to enhance your understanding of perimeter calculations.
Online Perimeter Calculators
Online perimeter calculators are valuable tools that simplify the process of finding the perimeter of various geometric shapes. These calculators are designed to handle multiple shapes and measurement units, making them versatile and user-friendly. Here is a detailed guide on using online perimeter calculators effectively:
Features of Online Perimeter Calculators
- Multi-Shape Support: Most calculators support a range of shapes including squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, ellipses, parallelograms, trapezoids, polygons, and rhombuses.
- Measurement Units: Users can input measurements in various units such as inches, feet, yards, millimeters, centimeters, and meters.
- Easy Input Fields: Users simply select the shape and enter the required dimensions in the provided fields.
- Automatic Calculations: The calculators perform the calculations instantly and display the perimeter based on the entered dimensions.
Steps to Use an Online Perimeter Calculator
- Select the Shape: Choose the geometric shape for which you want to calculate the perimeter. Common options include square, rectangle, triangle, circle, and more.
- Input the Measurements:
- Square: Enter the length of one side.
- Rectangle: Enter the length and width.
- Triangle: Enter the lengths of all three sides.
- Circle: Enter the radius or diameter.
- Select the Unit of Measurement: Choose the appropriate unit for your measurements (e.g., inches, feet, centimeters).
- Calculate: Click the calculate button to get the perimeter.
Examples of Popular Online Perimeter Calculators
- : This tool supports a wide variety of shapes and provides detailed formulas for each shape. It is user-friendly and allows measurements in multiple units.
- : Offers specific calculators for different shapes, including circles, with a simple interface for quick calculations.
- : A versatile calculator that covers numerous shapes and includes additional helpful tools for various measurement needs.
Benefits of Using Online Perimeter Calculators
- Accuracy: These calculators ensure precise calculations, reducing the risk of errors.
- Convenience: They save time and effort, especially when dealing with complex shapes or multiple calculations.
- Educational Value: They help users understand the formulas and concepts behind perimeter calculations by providing step-by-step breakdowns.
In summary, online perimeter calculators are essential tools for students, teachers, engineers, and anyone needing to calculate the perimeter of various shapes accurately and efficiently. With easy-to-use interfaces and support for multiple units and shapes, these calculators make mathematical tasks simpler and more accessible.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Perimeter Calculators
Using a perimeter calculator can simplify the process of finding the perimeter of various shapes. Follow these steps for an accurate calculation:
-
Select the Shape:
Most perimeter calculators offer a variety of shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Choose the shape for which you need to calculate the perimeter.
-
Input the Required Dimensions:
Depending on the selected shape, input the necessary dimensions. Below are examples of common shapes and their required dimensions:
- Square: Enter the length of one side (s).
- Rectangle: Enter the length (l) and width (w).
- Triangle: Enter the lengths of all three sides (a, b, c).
- Circle: Enter the radius (r) or diameter (d).
-
Click Calculate:
After entering the dimensions, click the 'Calculate' button. The calculator will process the input and display the perimeter.
-
Review the Results:
The perimeter will be displayed on the screen. Make sure to double-check the input values if the result seems incorrect.
Below is a summary of the formulas used by the calculator for different shapes:
| Shape | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \(P = 4s\) | If \(s = 5\), \(P = 4 \times 5 = 20\) |
| Rectangle | \(P = 2(l + w)\) | If \(l = 6\) and \(w = 3\), \(P = 2 \times (6 + 3) = 18\) |
| Triangle | \(P = a + b + c\) | If \(a = 3\), \(b = 4\), and \(c = 5\), \(P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12\) |
| Circle | \(P = 2\pi r\) or \(P = \pi d\) | If \(r = 7\), \(P = 2 \pi \times 7 \approx 44\) |
Using these steps and understanding the formulas will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of various shapes using online perimeter calculators.
Common Mistakes in Perimeter Calculation
When calculating the perimeter of various shapes, it's essential to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are some of the most frequent errors and tips on how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Formula Usage: Each shape has a specific formula for calculating its perimeter. Ensure you are using the correct formula for the shape in question. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated as \(2(l + w)\), not \(l \times w\).
- Measurement Units: Always use consistent measurement units. Mixing different units (e.g., meters and centimeters) without proper conversion will result in errors.
- Misidentifying Shape Properties: Sometimes, identifying all the sides of an irregular shape can be challenging. Ensure you accurately measure or calculate each side before summing them up.
- Rounding Errors: When dealing with calculations that require precision, such as with circles or polygons, rounding intermediate steps can lead to significant errors in the final result. Use full precision until the final step.
- Ignoring Missing Sides: For shapes like triangles, make sure to account for all sides. If only two sides are known, use the appropriate methods (e.g., the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles) to determine the missing side before calculating the perimeter.
By paying attention to these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure more accurate perimeter calculations.

Tips for Accurate Perimeter Calculations
Accurate perimeter calculations are essential in various fields, from construction to academic purposes. Here are some tips to ensure precision:
- Understand the Shape: Ensure you clearly understand the geometric shape you are working with. Different shapes have different perimeter formulas.
- Double-Check Measurements: Always measure sides, radii, or other relevant dimensions carefully and double-check them to avoid errors.
- Use the Correct Formula: Use the appropriate perimeter formula for the shape. Here are some common formulas:
- Square: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Use Reliable Tools: Utilize accurate and reliable measuring tools. Digital calipers, laser measures, and other advanced tools can improve accuracy.
- Consider All Sides: Ensure all sides are included in the calculation, especially for irregular shapes or polygons with more than four sides.
- Convert Units: Make sure all measurements are in the same unit before performing calculations. Convert units where necessary.
- Recheck Calculations: After performing the calculation, recheck your math. This is especially important in complex shapes where multiple steps are involved.
- Account for Curves: For shapes with curves, such as circles or ellipses, use the correct formulas and consider using tools like string or flexible measuring tapes to measure the curved lines.
- Use Online Calculators: Online perimeter calculators can provide quick and accurate results. Ensure the calculator is reputable and suitable for the specific shape you are working with.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze any errors in previous calculations to understand where mistakes were made and how to avoid them in the future.
By following these tips, you can achieve accurate perimeter calculations for any geometric shape.
Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Advanced perimeter calculation techniques involve more complex geometric shapes and mathematical methods. These techniques are useful for shapes with curves, multiple sides, and irregularities. Below are some advanced methods for calculating the perimeter:
Using Calculus for Curved Shapes
For shapes with curved edges, such as circles and ellipses, calculus can be used to find the perimeter. The arc length formula is integral to this process:
For a function \( y = f(x) \) from \( x = a \) to \( x = b \), the arc length \( L \) is given by:
\[
L = \int_{a}^{b} \sqrt{1 + \left( \frac{dy}{dx} \right)^2} \, dx
\]
This method is particularly useful for calculating the perimeter of parts of curves or irregular curved shapes.
Parametric Equations
Parametric equations are used to describe shapes where traditional Cartesian coordinates are insufficient. For instance, the perimeter of an ellipse can be approximated using Ramanujan's formula:
\[
P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right]
\]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the ellipse.
Perimeter of Fractals
Fractals, such as the Koch snowflake, have perimeters that can be calculated using iterative methods. Each iteration increases the complexity and length of the perimeter. The perimeter of the Koch snowflake after \( n \) iterations is given by:
\[
P_n = P_0 \left( \frac{4}{3} \right)^n
\]
where \( P_0 \) is the initial perimeter of the base triangle.
Geometric Decomposition
For complex polygons, decomposing the shape into simpler components can simplify the perimeter calculation. For instance, breaking down a polygon into triangles or rectangles allows for the application of basic perimeter formulas to each component:
- Divide the polygon into simpler shapes (triangles, rectangles).
- Calculate the perimeter of each individual shape.
- Sum the perimeters, accounting for shared sides only once.
Numerical Methods
When analytical solutions are impractical, numerical methods can provide approximate solutions. Techniques like the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule can approximate the perimeter by summing small segments:
\[
P \approx \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sqrt{(x_{i} - x_{i-1})^2 + (y_{i} - y_{i-1})^2}
\]
This approach is particularly useful for complex, irregular shapes where exact solutions are difficult to derive.
Applications of Advanced Techniques
These advanced perimeter calculation techniques are applicable in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and computer graphics. Understanding these methods enables precise measurements and modeling of complex structures and forms.
Using these advanced techniques, you can handle a wider range of geometric problems with higher accuracy and efficiency.
Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations have a wide range of applications in various fields. Here are some key areas where knowing how to calculate the perimeter is essential:
-
Architecture and Construction:
Accurate perimeter calculations are crucial for designing building layouts, fencing properties, and planning landscaping projects. Architects and builders use perimeter measurements to estimate the amount of materials needed, such as fencing, edging, and flooring.
-
Landscaping and Gardening:
Landscapers use perimeter calculations to determine the boundary of gardens, lawns, and other outdoor spaces. This helps in designing pathways, installing borders, and planning irrigation systems efficiently.
-
Interior Design:
In interior design, knowing the perimeter of rooms is necessary for tasks such as installing moldings, laying carpets, and positioning furniture. It ensures a precise fit and optimal use of space.
-
Education:
Teachers use perimeter calculations to help students understand geometric concepts and improve their problem-solving skills. It is a fundamental part of math curricula in schools.
-
Sports and Recreation:
Perimeter measurements are used to design and mark sports fields and courts. For example, in tennis, basketball, and soccer, the exact dimensions of the playing area are defined by its perimeter.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter calculations for designing roads, sidewalks, and public spaces. It helps in creating efficient layouts and ensuring that spaces are used effectively.
-
Crafts and DIY Projects:
Hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts often use perimeter calculations for various projects, such as sewing, woodworking, and crafting. Knowing the perimeter helps in cutting materials accurately and planning designs.
In all these applications, perimeter calculators can save time and reduce errors by providing quick and accurate measurements. They are valuable tools for professionals and hobbyists alike, ensuring precision and efficiency in their work.
Frequently Asked Questions About Perimeter Calculators
Perimeter calculators are useful tools for determining the total length around various shapes. Here are some common questions and answers about using these calculators:
-
What is the difference between perimeter and area?
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape, while the area measures the space contained within the shape. For example, the perimeter of a square is calculated by summing the lengths of all four sides, whereas the area is found by multiplying the length of one side by itself.
-
How do you calculate the perimeter of different shapes?
The formula for the perimeter varies by shape:
- Square: \(P = 4 \times \text{side}\)
- Rectangle: \(P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width})\)
- Triangle: \(P = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3\)
- Circle (Circumference): \(P = 2 \pi r\)
- Polygon: \(P = \text{sum of all sides}\)
-
Can a perimeter calculator be used for irregular shapes?
Yes, perimeter calculators can be used for irregular shapes by summing the lengths of all the sides. For complex shapes, you might need to measure each side individually before using the calculator.
-
Are perimeter calculators accurate?
Perimeter calculators are generally accurate as long as the input measurements are correct. Precision in measuring the sides of the shape will ensure the accuracy of the calculated perimeter.
-
What units can be used with a perimeter calculator?
Perimeter calculators typically support a variety of units such as millimeters, centimeters, meters, inches, feet, and yards. Make sure to use consistent units for all measurements to get an accurate result.
-
Why is knowing the perimeter important?
Knowing the perimeter is important for various practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for a fence, the length of trim required for a room, or the distance around a track.

Conclusion
Perimeter calculators are valuable tools for quickly determining the perimeter of various shapes, ranging from simple figures like squares and rectangles to more complex forms such as ellipses and polygons. These calculators offer a convenient and accurate way to perform perimeter calculations without manual effort.
To summarize the benefits and applications of perimeter calculators:
- Ease of Use: Online perimeter calculators simplify the process by allowing users to input relevant measurements and obtain results instantly.
- Accuracy: These tools eliminate human error, ensuring precise calculations every time.
- Versatility: Perimeter calculators support a wide range of shapes, including irregular polygons, making them versatile for various mathematical and real-world applications.
- Educational Value: They serve as excellent educational aids, helping students and learners understand the concepts of perimeter and geometry more effectively.
- Time-Saving: By automating calculations, these tools save significant time, especially when dealing with complex shapes or large data sets.
In practical terms, perimeter calculators are used in fields such as architecture, engineering, landscaping, and interior design, where precise measurements are crucial. They are also helpful in academic settings for teaching geometry concepts and for students completing homework or projects.
As technology advances, the functionality and user-friendliness of online perimeter calculators continue to improve, making them an indispensable tool for both professionals and students. Embracing these tools can lead to more efficient and accurate mathematical practices.
In conclusion, perimeter calculators offer a robust solution for calculating the perimeter of various shapes. Their ease of use, accuracy, and versatility make them an essential tool in both educational and professional settings. Whether you are a student learning geometry or a professional needing precise measurements, perimeter calculators can greatly enhance your efficiency and accuracy.
For anyone looking to explore or use these tools, numerous reliable perimeter calculators are available online, offering user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive support for a wide range of shapes and measurements. Leveraging these tools can significantly enhance your mathematical calculations and applications.
Tìm Chu Vi
READ MORE:
Tìm Chu Vi | Toán học với thầy J