Topic perimeter to area calculator: Discover how to effortlessly calculate the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes with our comprehensive perimeter to area calculator. This tool simplifies complex calculations, making it perfect for students, professionals, and anyone looking to enhance their mathematical skills. Start exploring now to unlock a world of easy, accurate geometric calculations.
Table of Content
- Perimeter to Area Calculator
- Introduction to Perimeter and Area
- Understanding Perimeter and Area
- Step-by-Step Calculation Methods
- Applications of Perimeter and Area
- Advanced Topics
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video này hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của một hình hợp thành, sử dụng ví dụ về hình chữ L. Rất phù hợp cho những ai quan tâm đến việc tính toán chu vi và diện tích của các hình học phức tạp.
Perimeter to Area Calculator
This calculator helps you find the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes. Understanding these calculations is fundamental in fields like architecture, design, and agriculture.
What is Perimeter?
The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in units of length, such as meters, centimeters, or feet.
What is Area?
The area is the amount of space enclosed within the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units, such as square meters, square centimeters, or square feet.
Formulas for Common Shapes
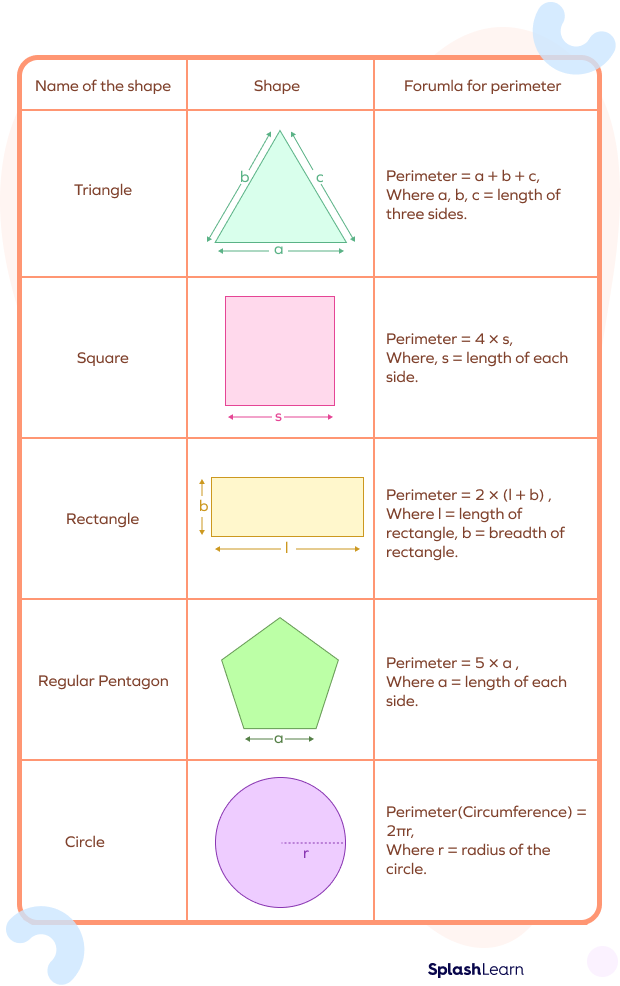
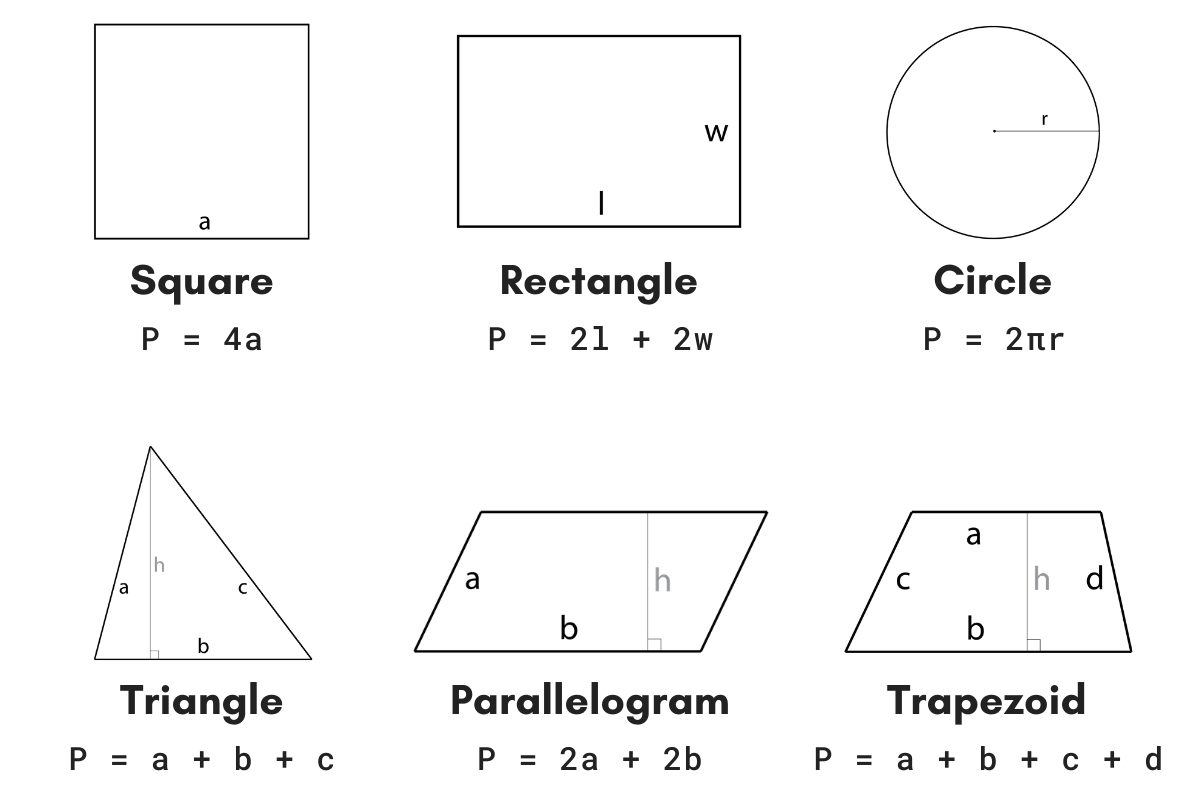
- Square
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \)
- Area: \( A = a^2 \)
- Rectangle
- Perimeter: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Area: \( A = lw \)
- Triangle
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
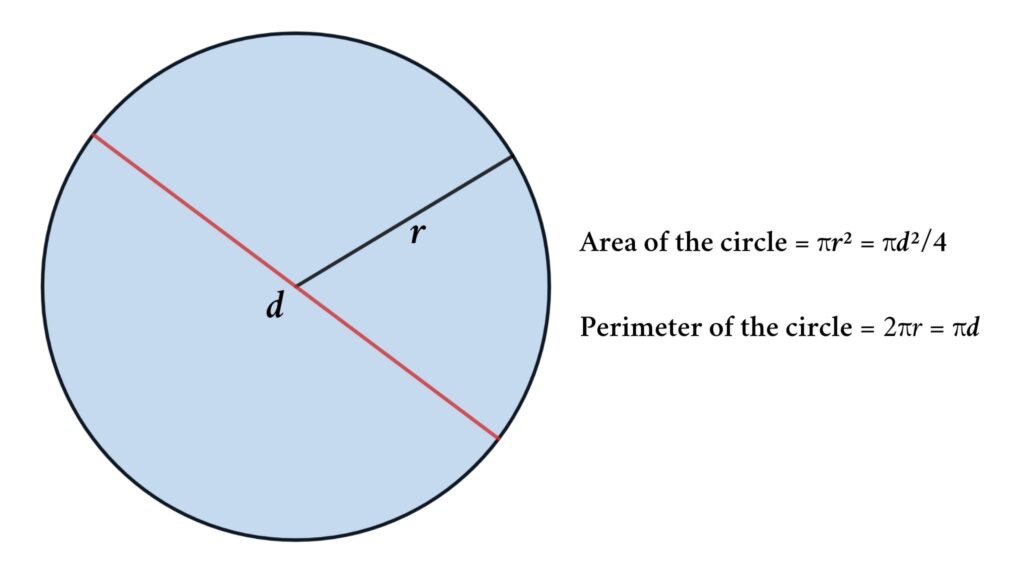
- Circle
- Circumference (Perimeter): \( P = 2\pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Parallelogram
- Perimeter: \( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Area: \( A = bh \)
- Trapezoid
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} h (a + b) \)
How to Use the Calculator
- Select the geometric shape you want to calculate.
- Enter the required dimensions (e.g., side lengths, base, height, radius).
- Click the "Calculate" button to see the results.
Applications of Perimeter and Area Calculations
These calculations have numerous practical applications:
- Architecture and Construction: Determining the size of buildings, rooms, and the amount of materials needed.
- Design and Art: Planning dimensions, calculating materials, and fitting shapes into specific spaces.
- Agriculture: Calculating the area for planting crops and the perimeter for fencing.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter and Area
Perimeter and area are fundamental concepts in geometry, frequently used in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday calculations. Understanding these concepts is essential for solving many real-world problems.
Perimeter refers to the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of a shape. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle can be calculated as P = 2(l + w), where l is the length and w is the width.
Area, on the other hand, measures the space enclosed within the boundary of a shape. It is expressed in square units. For instance, the area of a rectangle is given by the formula A = l \times w.
Below are detailed calculations for various common shapes:
- Square
- Area: \(A = a^2\)
- Perimeter: \(P = 4a\)
- Rectangle
- Area: \(A = l \times w\)
- Perimeter: \(P = 2(l + w)\)
- Triangle
- Area: \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height\)
- Perimeter: \(P = a + b + c\)
- Circle
- Area: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Perimeter (Circumference): \(C = 2\pi r\)
- Parallelogram
- Area: \(A = base \times height\)
- Perimeter: \(P = 2(a + b)\)
- Trapezoid
- Area: \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times height \times (base1 + base2)\)
- Perimeter: \(P = a + b + c + d\)
Understanding Perimeter and Area
Perimeter and area are fundamental concepts in geometry that are used to measure the size and shape of two-dimensional figures. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various fields such as mathematics, engineering, architecture, and design.
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary or the sum of all its sides. It is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, etc. For example, the perimeter of a square is the sum of all four sides, while the perimeter of a circle is the circumference.
The area of a shape, on the other hand, is the measure of the space enclosed within its boundary. It is measured in square units such as square meters, square centimeters, square inches, etc. Finding the area involves multiplying the length by the width for rectangles, base by height divided by 2 for triangles, and π times the radius squared for circles.
Understanding the relationship between perimeter and area is essential. While perimeter focuses on the boundary of a shape, area deals with the space enclosed by it. It's possible for two shapes to have the same perimeter but different areas, or vice versa. For instance, a square and a rectangle with the same perimeter will have different areas.
Moreover, as the size of a shape changes, its perimeter and area also change. This relationship is important in various real-world applications, such as determining the amount of fencing needed for a garden or calculating the material required for a construction project.
Step-by-Step Calculation Methods
Calculating the perimeter and area of geometric shapes can be straightforward with the right approach. Here are step-by-step methods to help you:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the shape of the object you are dealing with. Is it a square, rectangle, triangle, circle, or another shape?
- Measure the Dimensions: Take measurements of the sides, lengths, widths, radii, or any other relevant dimensions of the shape.
- Use the Appropriate Formula: Refer to the formulas for perimeter and area of the specific shape you are working with.
- Plug in the Values: Substitute the measured dimensions into the respective formula.
- Perform Calculations: Use arithmetic operations to compute the values of perimeter and area.
- Round if Necessary: Depending on the context, you may need to round the calculated values to a certain number of decimal places or significant figures.
- Check Units: Make sure that the units of measurement for the final answers are appropriate and consistent.
For more complex shapes or situations, such as irregular polygons or composite figures, the process may involve breaking down the shape into simpler components and applying the relevant formulas for each component before summing up the results.
Applications of Perimeter and Area
The concepts of perimeter and area have numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some common areas where they are utilized:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and builders use perimeter and area calculations extensively in designing and constructing buildings, roads, bridges, and other structures. These calculations help in determining the amount of materials needed and ensuring accurate measurements for construction projects.
- Design and Art: Artists and designers often use geometric shapes and patterns in their work. Understanding perimeter and area allows them to create visually appealing compositions, plan layouts, and calculate proportions effectively.
- Agriculture: Farmers and landowners use perimeter and area measurements to plan and manage agricultural land. This includes determining the area of fields for planting crops, calculating fencing requirements for livestock enclosures, and optimizing irrigation systems based on land area.
- Landscaping: Landscape designers use perimeter and area calculations to plan and layout outdoor spaces such as gardens, parks, and recreational areas. By accurately measuring the area of land and considering perimeter dimensions, they can create aesthetically pleasing and functional landscapes.
- Education: Perimeter and area concepts are taught in mathematics education at various levels, from elementary school to higher education. They serve as foundational concepts in geometry and provide students with practical problem-solving skills applicable in real-life situations.
These are just a few examples of how the concepts of perimeter and area play a vital role in different aspects of our daily lives and professional endeavors.
Advanced Topics
For those seeking deeper insights into the relationship between perimeter and area, as well as exploring more complex geometric concepts, here are some advanced topics to delve into:
- Circle Sector: A circle sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. Advanced discussions may involve calculating the perimeter and area of sectors, understanding central angles, and exploring applications in trigonometry and calculus.
- Circle Zone: The circle zone refers to the region between two concentric circles. Advanced topics in this area may include calculating the perimeter and area of annular sectors, exploring properties of circular segments, and investigating relationships with other geometric shapes.
- Fractal Geometry: Fractal geometry deals with complex shapes that exhibit self-similar patterns at different scales. Advanced discussions may involve exploring fractal dimensions, understanding fractal patterns in nature and art, and applications in computer graphics and modeling.
- Spatial Geometry: Spatial geometry extends the study of two-dimensional shapes to three-dimensional space. Advanced topics may include calculating the surface area and volume of three-dimensional figures, understanding spatial relationships, and applications in architecture, engineering, and physics.
- Non-Euclidean Geometry: Non-Euclidean geometry explores geometries that deviate from the principles of Euclidean geometry. Advanced discussions may involve understanding hyperbolic and elliptic geometries, exploring curved surfaces, and applications in cosmology and relativity theory.
These advanced topics offer avenues for further exploration and deeper understanding of geometric concepts, making them suitable for students, educators, researchers, and enthusiasts interested in the beauty and complexity of mathematics.
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of perimeter and area is essential for various practical applications and academic pursuits. From basic calculations to advanced topics, the study of geometric properties enriches our understanding of the world around us and opens doors to creative problem-solving.
Whether you're an architect designing a skyscraper, an artist creating a masterpiece, or a student learning the foundations of mathematics, the principles of perimeter and area play a significant role in your endeavors.
As you continue to explore and apply these concepts, remember that mathematics is not just about numbers and formulas—it's about curiosity, discovery, and the beauty of patterns and relationships.
So, whether you're calculating the dimensions of a garden or unraveling the mysteries of fractal geometry, embrace the journey of learning and let the wonder of mathematics guide you.
Video này hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của một hình hợp thành, sử dụng ví dụ về hình chữ L. Rất phù hợp cho những ai quan tâm đến việc tính toán chu vi và diện tích của các hình học phức tạp.
Tìm chu vi và diện tích của Hình hợp thành | Ví dụ Hình chữ L | Hình học | Toán cùng Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video này hướng dẫn cách tình diện tích và chu vi của một hình chữ nhật. Đây là bài giảng phù hợp cho những ai muốn hiểu cách tính toán diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật.
Cách tính Diện tích và Chu vi của Hình chữ nhật