Topic area and perimeter 3rd grade: Discover the exciting world of area and perimeter tailored for 3rd-grade students! This guide simplifies these essential math concepts with engaging explanations, practical examples, and fun activities. Help your child master area and perimeter effortlessly and build a strong foundation for future math success.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter for 3rd Grade
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Perimeter
- Understanding Area
- Formulas for Perimeter
- Formulas for Area
- Practice Problems for Perimeter
- Practice Problems for Area
- Real-life Applications of Area and Perimeter
- Activities and Games to Learn Area and Perimeter
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Tips for Teachers and Parents
- Additional Resources and Worksheets
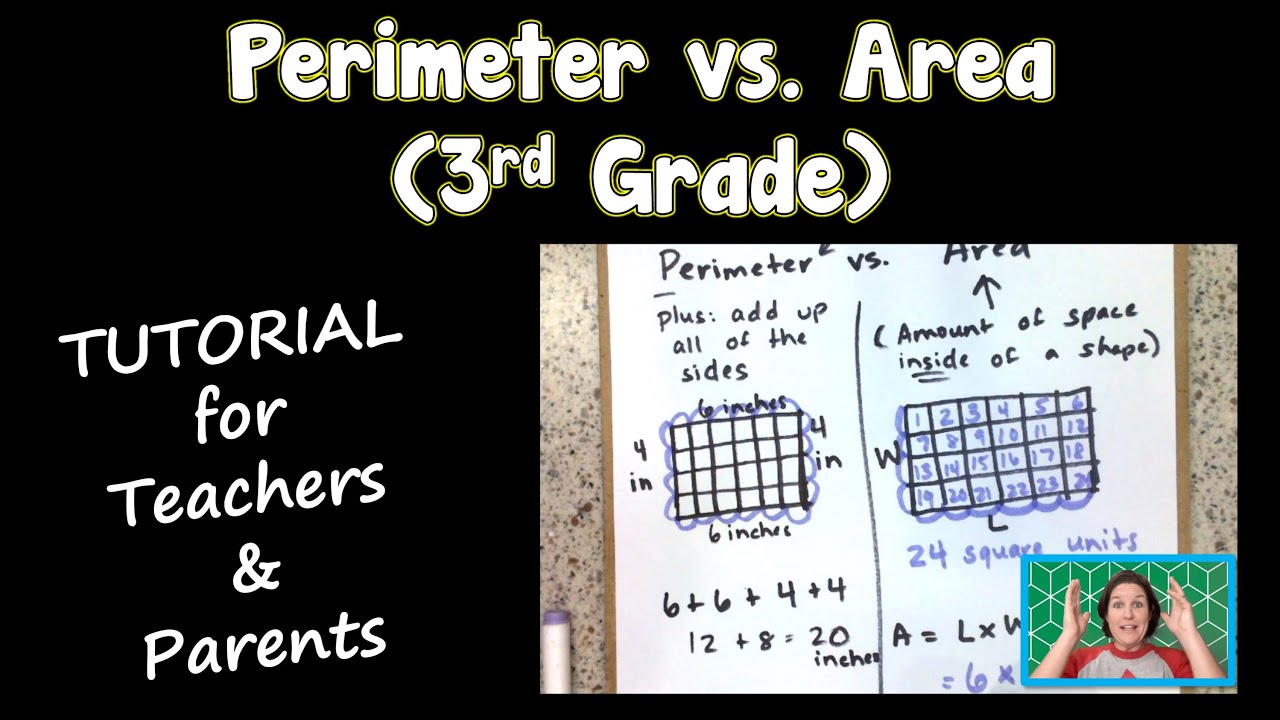
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi qua video 'Diện Tích vs. Chu Vi' từ MightyOwl, được thiết kế đặc biệt cho học sinh lớp 3.
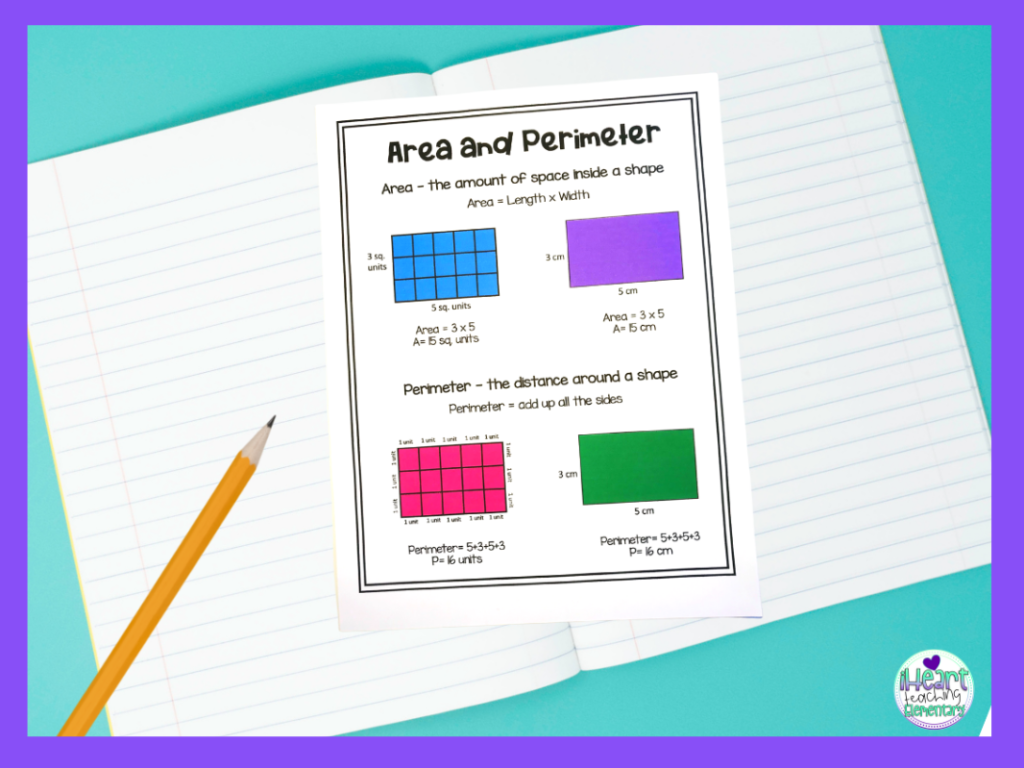
Area and Perimeter for 3rd Grade
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for 3rd-grade students. Here is a detailed explanation to help students learn these important math skills.
What is Perimeter?
The perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. To find the perimeter, you need to add up the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides, or by using the formula:
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is four times the length of one side:
Examples of Perimeter
- If a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, its perimeter is:
- If a square has a side length of 4 units, its perimeter is:
What is Area?
The area is the amount of space inside a shape. It is measured in square units.
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width:
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, the area is the side length squared:
Examples of Area
- If a rectangle has a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units, its area is:
- If a square has a side length of 5 units, its area is:
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units.
- Calculate the area of a square with a side length of 7 units.
- What is the perimeter of a square with a side length of 6 units?
- Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 9 units and a width of 2 units.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial for 3rd-grade students as these concepts form the foundation of geometry. Here's a comprehensive introduction to help students grasp these important topics.
What is Perimeter?
Perimeter is the distance around the edge of a shape. To find the perimeter, you add the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Here are some common shapes and how to calculate their perimeter:
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides, or by using the formula:
- Square: Since all sides are equal, the perimeter is four times the length of one side:
What is Area?
Area is the amount of space inside a shape. It is measured in square units. Here are formulas for calculating the area of common shapes:
- Rectangle: The area is found by multiplying the length by the width:
- Square: The area is the side length squared:
Examples to Illustrate
- If a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units:
- Perimeter:
- Area:
- If a square has a side length of 4 units:
- Perimeter:
- Area:
Step-by-Step Approach to Learning
- Start with understanding the basic definitions of area and perimeter.
- Learn the formulas for calculating area and perimeter for different shapes.
- Practice with examples to reinforce the concepts.
- Apply the knowledge to solve real-life problems.
- Engage in interactive activities and games to make learning fun.
Understanding Perimeter
Perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that 3rd-grade students need to understand. It refers to the total distance around the edge of a shape. Here’s a detailed guide to help students grasp this important topic.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. It is measured in linear units such as centimeters, meters, or inches.
Formulas for Perimeter
- Rectangle: A rectangle has opposite sides that are equal in length. To find the perimeter, add the lengths of all four sides or use the formula:
- Square: All sides of a square are equal. To find the perimeter, multiply the length of one side by four:
- Triangle: To find the perimeter of a triangle, add the lengths of its three sides:
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- If a rectangle has a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units, its perimeter is:
- If a square has a side length of 5 units, its perimeter is:
- If a triangle has sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units, its perimeter is:
Step-by-Step Approach to Finding Perimeter
- Identify the Shape: Determine if the shape is a rectangle, square, triangle, or another polygon.
- Measure the Sides: Use a ruler to measure the length of each side in the same units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate formula to calculate the perimeter based on the shape.
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all the sides together to get the total perimeter.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 7 units and a width of 3 units.
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with a side length of 8 units.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 5 units, 12 units, and 13 units.
Understanding Area
Area is an essential concept in geometry that 3rd-grade students need to understand. It refers to the amount of space inside a shape. Here’s a detailed guide to help students grasp this important topic.
Definition of Area
The area of a shape is the number of square units that cover the shape. It is measured in square units such as square centimeters, square meters, or square inches.
Formulas for Area
- Rectangle: To find the area of a rectangle, multiply the length by the width:
- Square: The area of a square is the side length squared:
- Triangle: To find the area of a triangle, multiply the base by the height and then divide by two:
Examples of Area Calculations
- If a rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units, its area is:
- If a square has a side length of 6 units, its area is:
- If a triangle has a base of 10 units and a height of 4 units, its area is:
Step-by-Step Approach to Finding Area
- Identify the Shape: Determine if the shape is a rectangle, square, triangle, or another polygon.
- Measure the Dimensions: Use a ruler to measure the necessary dimensions such as length, width, base, and height in the same units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate formula to calculate the area based on the shape.
- Calculate: Perform the multiplication and division as required by the formula.
Practice Problems
- Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 9 units and a width of 7 units.
- Calculate the area of a square with a side length of 10 units.
- Determine the area of a triangle with a base of 8 units and a height of 5 units.
Formulas for Perimeter
Knowing the formulas for calculating the perimeter of various shapes is essential for 3rd-grade students. Here’s a detailed guide to help students learn and understand these formulas step by step.
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle can be found by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, the formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the length (l) and the width (w) of the rectangle.
- Step 2: Add the length and the width.
- Step 3: Multiply the sum by 2 to get the perimeter.
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 7 units and a width of 3 units, its perimeter is:
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square can be found by multiplying the length of one side by 4, since all four sides are equal. The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the length of one side (s) of the square.
- Step 2: Multiply the length by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units, its perimeter is:
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle can be found by adding the lengths of its three sides. The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the lengths of all three sides (a, b, and c) of the triangle.
- Step 2: Add the three lengths to get the perimeter.
For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 6 units, 8 units, and 10 units, its perimeter is:
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length. To find the perimeter, multiply the length of one side by the number of sides (n). The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the length of one side (s) of the polygon.
- Step 2: Count the number of sides (n) of the polygon.
- Step 3: Multiply the length of one side by the number of sides to get the perimeter.
For example, if a regular pentagon (5 sides) has a side length of 4 units, its perimeter is:
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 12 units and a width of 5 units.
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 units.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 9 units, 12 units, and 15 units.
- Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon (6 sides) with each side measuring 3 units.
Formulas for Area
Understanding the formulas for calculating the area of various shapes is crucial for 3rd-grade students. Here’s a detailed guide to help students learn and understand these formulas step by step.
Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle can be found by multiplying the length by the width. The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the length (l) and the width (w) of the rectangle.
- Step 2: Multiply the length by the width to get the area.
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 4 units, its area is:
Area of a Square
The area of a square can be found by multiplying the length of one side by itself (squared). The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the length of one side (s) of the square.
- Step 2: Square the length to get the area.
For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units, its area is:
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle can be found by multiplying the base by the height and then dividing by two. The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the base (b) and the height (h) of the triangle.
- Step 2: Multiply the base by the height.
- Step 3: Divide the product by 2 to get the area.
For example, if a triangle has a base of 10 units and a height of 4 units, its area is:
Area of a Parallelogram
The area of a parallelogram can be found by multiplying the base by the height. The formula is:
- Step 1: Measure the base (b) and the height (h) of the parallelogram.
- Step 2: Multiply the base by the height to get the area.
For example, if a parallelogram has a base of 7 units and a height of 3 units, its area is:
Practice Problems
- Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 9 units and a width of 6 units.
- Calculate the area of a square with a side length of 8 units.
- Determine the area of a triangle with a base of 7 units and a height of 5 units.
- Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 6 units and a height of 4 units.
Practice Problems for Perimeter
Practice problems help students solidify their understanding of perimeter. Here are some problems designed for 3rd-grade students to practice calculating the perimeter of various shapes.
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units.
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \).
Substitute the given values:
\( P = 2 \times (5 + 3) \)
\( P = 2 \times 8 \)
\( P = 16 \) units
-
Problem 2: A square has sides of length 4 units. What is the perimeter of the square?
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4 \times s \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
Substitute the given value:
\( P = 4 \times 4 \)
\( P = 16 \) units
-
Problem 3: A triangle has sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Substitute the given values:
\( P = 3 + 4 + 5 \)
\( P = 12 \) units
-
Problem 4: A rectangular garden has a length of 7 meters and a width of 2 meters. Calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \).
Substitute the given values:
\( P = 2 \times (7 + 2) \)
\( P = 2 \times 9 \)
\( P = 18 \) meters
-
Problem 5: If a square playground has a perimeter of 20 units, what is the length of each side?
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4 \times s \).
Given \( P = 20 \) units, we can find the length of each side \( s \) by solving:
\( 20 = 4 \times s \)
\( s = \frac{20}{4} \)
\( s = 5 \) units
These problems are designed to reinforce the concept of perimeter in various shapes. Encourage students to solve these problems step-by-step to enhance their understanding.
Practice Problems for Area
Below are several practice problems to help you understand and calculate the area of various shapes. Remember, the area is the amount of space inside a shape.
-
Problem 1: Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units.
Formula: Area = length × width
Solution: \( \text{Area} = 8 \text{ units} \times 3 \text{ units} = 24 \text{ square units} \)
-
Problem 2: Calculate the area of a square with each side measuring 5 units.
Formula: Area = side × side
Solution: \( \text{Area} = 5 \text{ units} \times 5 \text{ units} = 25 \text{ square units} \)
-
Problem 3: A rectangle has an area of 54 square units and a width of 6 units. What is the length?
Formula: Area = length × width
Solution: \( \text{Length} = \frac{\text{Area}}{\text{width}} = \frac{54 \text{ square units}}{6 \text{ units}} = 9 \text{ units} \)
-
Problem 4: Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 units and a height of 5 units.
Formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height
Solution: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \text{ units} \times 5 \text{ units} = 25 \text{ square units} \)
-
Problem 5: Calculate the area of a parallelogram with a base of 7 units and a height of 4 units.
Formula: Area = base × height
Solution: \( \text{Area} = 7 \text{ units} \times 4 \text{ units} = 28 \text{ square units} \)
Use these problems to practice and strengthen your understanding of how to calculate the area of different shapes. For additional practice, try creating your own problems or use online resources and worksheets available for further learning.
Real-life Applications of Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential because these measurements are used in various real-life situations. Here are some common applications:
- Construction of Homes and Buildings: When building a house, the perimeter is used to determine the amount of fencing needed for the yard, while the area helps in calculating the flooring, painting walls, and laying tiles.
- Gardening: When planning a garden, the perimeter is useful for placing a fence around the garden, and the area is needed to determine how many plants or how much soil is required to fill the garden space.
- Roads and Bridges: Engineers use area and perimeter to plan the dimensions and layout of roads and bridges. This ensures they use the right amount of materials and maintain structural integrity.
- Interior Design: Interior designers calculate the area of rooms to determine how much paint, wallpaper, or flooring materials they need. The perimeter helps in planning the placement of furniture and other design elements.
- Fashion and Art: In fashion, designers use the area to calculate the amount of fabric required to create clothes. Artists use these measurements for planning their canvases and frames.
Here are some detailed examples:
| Application | Use of Area | Use of Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Planting a Garden | Calculating the space each plant needs | Determining the length of the garden fence |
| Building a House | Calculating flooring, tiling, and painting areas | Determining the length of materials for borders and fences |
| Renovating a Room | Measuring wall space for painting or wallpaper | Measuring for baseboards and crown molding |
| Party Planning | Determining the area needed for tables and seating | Planning the perimeter for decoration placement |
| Quilting | Calculating the fabric needed for quilt blocks | Measuring the border around the quilt |
These examples illustrate how understanding area and perimeter can help students see the relevance of math in everyday life and inspire practical problem-solving skills.
Activities and Games to Learn Area and Perimeter
Learning area and perimeter can be fun and engaging with various activities and games designed for 3rd graders. Here are some creative ideas to help students understand these concepts:
-
Conquer the Area Game
Materials: Two dice, grid paper, colored pencils.
Instructions: Each player rolls the dice to determine the dimensions of a rectangle they will draw on the grid paper. For example, if a player rolls a 3 and a 4, they draw a rectangle with a length of 3 units and a width of 4 units. Players take turns and try to cover the most area on the grid. The player with the most area covered wins.
-
Area and Perimeter Bingo
Materials: Bingo cards with different shapes and dimensions, markers.
Instructions: Play Bingo as usual, but instead of calling out numbers, call out area or perimeter values. Students must find a shape on their Bingo card that matches the called value and mark it. The first to get five in a row wins.
-
Geoboard Shapes
Materials: Geoboards, rubber bands.
Instructions: Students use rubber bands to create shapes on the geoboard. They can calculate the area by counting the square units inside the shape and the perimeter by counting the units along the edges. Students can switch boards with a partner to solve each other's shapes.
-
Area and Perimeter Scavenger Hunt
Materials: Various items around the classroom, rulers, recording sheets.
Instructions: Hide items with known dimensions around the classroom. Students use rulers to measure the dimensions of each item and calculate the area and perimeter. They record their findings on a sheet. This activity encourages movement and practical application of measurement skills.
-
Interactive Notebook Activities
Materials: Notebooks, printables, glue, scissors.
Instructions: Students create interactive pages in their notebooks with flaps and foldables that explain the formulas for area and perimeter, provide examples, and include practice problems. These notebooks serve as a great reference tool throughout the year.
-
Area and Perimeter Robot
Materials: Graph paper, colored pencils.
Instructions: Students use graph paper to design robots with specific area and perimeter measurements. This project allows for creativity while reinforcing measurement skills. Students can present their robots and explain the math behind their designs.
These activities not only make learning area and perimeter enjoyable but also help students understand the practical applications of these concepts in a hands-on way.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When learning about area and perimeter, students often make common mistakes. Here are some of those mistakes and how to avoid them:
-
Confusing Area and Perimeter:
Students often mix up area and perimeter, calculating one when asked for the other. To avoid this:
- Define clearly: Explain that perimeter is the distance around a shape, while area is the space inside it.
- Use visual aids: Show examples of shapes with marked perimeters and areas.
- Practice terminology: Frequently use terms "perimeter" and "area" in context to reinforce their meanings.
-
Incorrectly Adding Side Lengths for Perimeter:
Students may forget to add all sides or add incorrectly. To avoid this:
- Check all sides: Ensure students count all sides of a shape.
- Repetition and practice: Provide multiple practice problems to solidify the process.
-
Misidentifying Units:
Students may confuse units for area and perimeter (e.g., square units vs. linear units). To avoid this:
- Emphasize units: Always include units in problems and solutions.
- Visual reminders: Use charts or posters that distinguish between linear and square units.
-
Errors in Multiplication for Area:
Students may struggle with the multiplication required to find the area. To avoid this:
- Use arrays: Teach area using arrays to visualize multiplication.
- Practice multiplication: Ensure students are comfortable with basic multiplication facts.
-
Not Using Formulas:
Students might forget or incorrectly apply formulas for area and perimeter. To avoid this:
- Memorization techniques: Use songs, rhymes, or mnemonic devices to help remember formulas.
- Consistent practice: Regularly practice using the formulas in various problems.
By addressing these common mistakes and providing strategies to overcome them, students can improve their understanding and accuracy in calculating area and perimeter.
Tips for Teachers and Parents
Teaching area and perimeter to 3rd graders can be challenging but rewarding. Here are some effective tips for teachers and parents to help students grasp these concepts:
-
Use Real-life Examples: Relate area and perimeter to everyday objects. For example, discuss the perimeter of a garden or the area of a room. This makes the concepts more tangible and easier to understand.
-
Interactive Anchor Charts: Create visual aids that students can reference. Include definitions, formulas, and examples. Interactive charts can be particularly useful, allowing students to engage with the material directly.
-
Hands-on Activities: Use manipulatives like tiles or blocks to let students physically build shapes and measure their area and perimeter. This hands-on approach helps solidify their understanding.
-
Graph Paper Exercises: Have students use graph paper to draw shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This visual method helps them see the concepts more clearly and practice precise measurements.
-
Separate Lessons: Teach area and perimeter separately before combining them. This helps prevent confusion and allows students to focus on one concept at a time.
-
Incorporate Games: Use educational games that involve calculating area and perimeter. Games make learning fun and can improve retention.
-
Encourage Collaboration: Let students work in pairs or groups to solve problems. Collaborative learning allows them to explain their thinking and learn from each other.
-
Emphasize Units: Teach students the importance of using appropriate units for area (square units) and perimeter (linear units). This helps them understand the difference between the two measurements.
-
Regular Review: Revisit area and perimeter throughout the year to reinforce learning. Regular practice helps students retain the information and become more confident in their skills.
-
Use Technology: Incorporate digital tools and resources, such as online games and interactive lessons, to engage students and provide additional practice opportunities.
By using these tips, teachers and parents can help 3rd graders develop a solid understanding of area and perimeter, setting a strong foundation for future math learning.
Additional Resources and Worksheets
Enhance your understanding of area and perimeter with these additional resources and worksheets tailored for 3rd graders. These materials provide a variety of activities, practice problems, and visual aids to help students grasp these fundamental math concepts effectively.
- K5 Learning offers a range of worksheets focusing on the area and perimeter of rectangles. These worksheets help students practice calculating the dimensions of various shapes and understand the application of these measurements in real-world scenarios.
- Cuemath provides downloadable PDFs of area and perimeter worksheets. These resources include visually appealing exercises that gradually increase in complexity, allowing students to build their skills step-by-step. The worksheets also emphasize logical and reasoning skills.
- Turtle Diary features a comprehensive collection of worksheets for 3rd graders, covering topics such as the area of figures formed with unit squares, area of irregular figures on graphs, and perimeter of polygons. These resources are available for download and include multiple-choice questions to test comprehension.
For more practice, here are some specific worksheets you can use:
These resources offer various approaches to learning and practicing area and perimeter calculations, ensuring students have a well-rounded understanding of the concepts. Teachers and parents can use these worksheets to provide extra practice and support, helping students master these essential math skills.

Khám phá sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi qua video 'Diện Tích vs. Chu Vi' từ MightyOwl, được thiết kế đặc biệt cho học sinh lớp 3.
Diện Tích vs. Chu Vi | Toán Học MightyOwl | Lớp 3
READ MORE:
Khám phá sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi trong video 'DIỆN TÍCH VS CHU VI' cho học sinh lớp 3, theo chuẩn Common Core.
DIỆN TÍCH VS CHU VI // Toán Lớp 3 // Toán Common Core