Topic calculate perimeter of triangle: Learning to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is essential for students and professionals alike. This guide will walk you through simple steps, examples, and tips to master this fundamental geometric calculation. Whether dealing with equilateral, isosceles, or scalene triangles, you'll find the information you need to succeed.
Table of Content
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction to Perimeter of Triangle
- Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
- Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Special Cases in Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Equilateral Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Isosceles Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Scalene Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Real-World Applications of Perimeter Calculation
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi tam giác bằng tiếng Việt. Thích hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên muốn học cách tính chu vi tam giác.
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
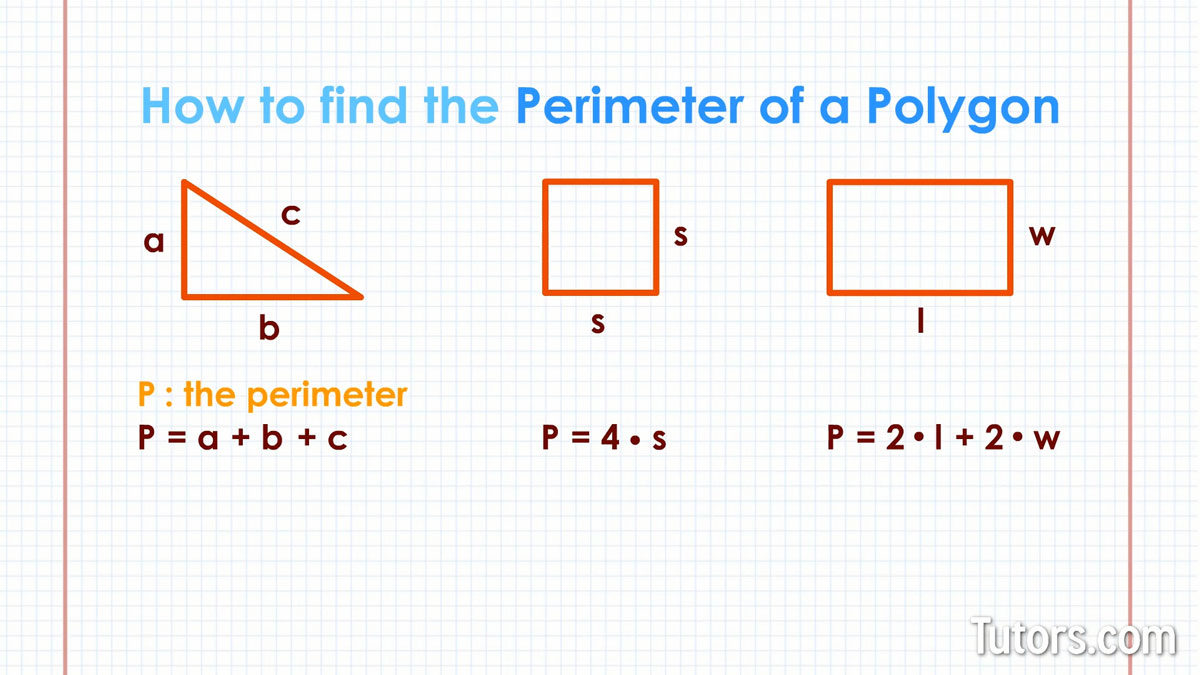
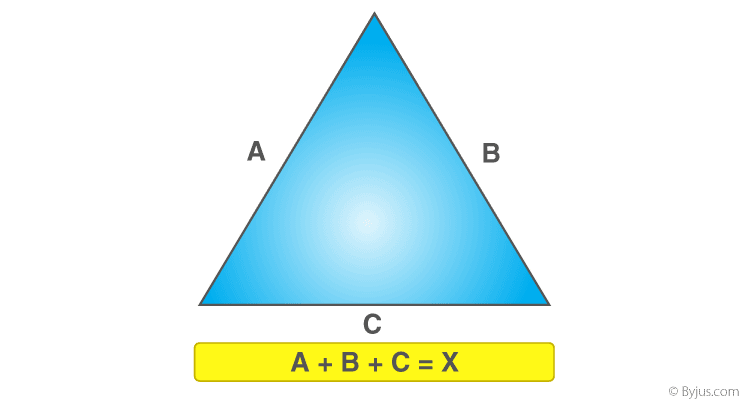
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its three sides. To find the perimeter, simply add the lengths of all the sides together.
Formula
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. Let these lengths be \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Add the three lengths together using the formula:
- The result is the perimeter of the triangle.
Example
Consider a triangle with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm. To find the perimeter:
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 4 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm.
- Use the formula:
- Calculate the sum:
The perimeter of the triangle is 12 cm.
Special Cases
For special types of triangles, such as equilateral and isosceles triangles, the calculation can be simplified:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal (\( a = b = c \)). The perimeter formula simplifies to:
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal (\( a = b \)). The perimeter formula is:
Summary
To calculate the perimeter of any triangle, add up the lengths of all three sides using the formula \( P = a + b + c \). For equilateral and isosceles triangles, use the simplified formulas for quicker calculations.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the triangle, which is found by adding the lengths of all three sides. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is crucial in various fields such as geometry, engineering, and architecture. This section will guide you through the basic concepts and methods for finding the perimeter of different types of triangles.
To calculate the perimeter of a triangle, follow these steps:
- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. Label these sides as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Use the perimeter formula:
- Add the three side lengths together to find the perimeter.
For example, if a triangle has side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 4 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm.
- Apply the formula:
- Calculate the sum:
Thus, the perimeter of the triangle is 12 cm.
This straightforward method can be applied to any triangle, whether it is an equilateral, isosceles, or scalene triangle. Mastering this calculation is a fundamental step in understanding more complex geometric concepts.
Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its three sides. To calculate the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all three sides. This is a fundamental concept in geometry that applies to all types of triangles, whether equilateral, isosceles, or scalene.
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
Here’s a step-by-step guide to using this formula:
- Identify the lengths of the sides of the triangle. Label them as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Write down the perimeter formula:
- Substitute the lengths of the sides into the formula.
- Add the values together to get the perimeter.
For example, if you have a triangle with side lengths of 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm, the calculation would look like this:
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, \( c = 10 \) cm.
- Apply the formula:
- Calculate the sum:
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 22 cm.
This formula is universal and can be applied to any triangle. By mastering this simple calculation, you can easily find the perimeter of any triangle you encounter.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle involves summing the lengths of its three sides. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Identify the Side Lengths
First, measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. Label these sides as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Write Down the Formula
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is:
- Substitute the Side Lengths into the Formula
Replace \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) with the actual measurements of the sides of your triangle.
- Perform the Addition
Add the three side lengths together to find the perimeter.
- For example, if \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, and \( c = 10 \) cm, then:
- Calculate the sum:
- For example, if \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, and \( c = 10 \) cm, then:
- Verify Your Result
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy.
Following these steps will allow you to accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle, whether it’s equilateral, isosceles, or scalene.
Examples of Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is best achieved through examples. Here are a few scenarios to illustrate the process:
Example 1: Equilateral Triangle
In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal in length.
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = b = c = 6 \) cm.
- Use the perimeter formula:
- Substitute the length:
- Calculate the perimeter:
Example 2: Isosceles Triangle
In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length.
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = b = 5 \) cm, \( c = 8 \) cm.
- Use the perimeter formula:
- Substitute the lengths:
- Calculate the perimeter:
Example 3: Scalene Triangle
In a scalene triangle, all three sides are of different lengths.
- Identify the side lengths: \( a = 4 \) cm, \( b = 6 \) cm, \( c = 9 \) cm.
- Use the perimeter formula:
- Substitute the lengths:
- Calculate the perimeter:
These examples demonstrate how to calculate the perimeter of different types of triangles by applying the perimeter formula and following the calculation steps. This process can be used for any triangle, ensuring you can accurately determine the perimeter in various scenarios.

Special Cases in Triangle Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle can vary depending on the type of triangle and the information available. Here are some special cases:
1. Right Triangle
For a right triangle, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the third side if two sides are known. The perimeter is then the sum of all three sides.
Formula:
\[c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\]
Where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse.
The perimeter \(P\) is given by:
\[P = a + b + c\]
2. Isosceles Triangle
For an isosceles triangle with two equal sides, you can use the following formula if the base and height are known:
Formula:
\[P = 2 \sqrt{a^2 - \left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2} + b\]
Where a is the length of the equal sides and b is the base.
3. Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal. The perimeter calculation is straightforward:
Formula:
\[P = 3a\]
Where a is the length of any side.
4. Scalene Triangle
For a scalene triangle, where all sides are different, you simply sum the lengths of all three sides:
Formula:
\[P = a + b + c\]
5. Using Coordinates
If the vertices of the triangle are known in a coordinate plane, the distance formula can be used to find the lengths of the sides, and then sum them to find the perimeter.
Distance Formula:
\[d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\]
Apply this to find each side, then sum them:
\[P = d_1 + d_2 + d_3\]
6. Law of Cosines
If two sides and the included angle are known, use the law of cosines to find the third side, then sum the sides to find the perimeter.
Formula:
\[c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cdot \cos(\gamma)\]
Where \(\gamma\) is the included angle.
Then:
\[P = a + b + c\]
7. Law of Sines
If two angles and a side are known, use the law of sines to find the other sides, then sum them for the perimeter.
Formula:
\[\frac{a}{\sin(\alpha)} = \frac{b}{\sin(\beta)} = \frac{c}{\sin(\gamma)}\]
Where \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), and \(\gamma\) are the angles, and \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the sides opposite those angles.
Then calculate the perimeter:
\[P = a + b + c\]
Conclusion
Understanding the type of triangle and the available measurements is crucial in determining the correct method for calculating the perimeter. Each special case has its own unique formula that simplifies the process.
Equilateral Triangle Perimeter Calculation
An equilateral triangle is a special type of triangle where all three sides are equal in length and all three angles are equal to 60 degrees. The formula for calculating the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is simple and straightforward.
Basic Formula
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 3a \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a \) is the length of one side of the triangle.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the equilateral triangle. Let this length be denoted as \( a \).
- Multiply the length of the side by 3 to get the perimeter.
Example Calculation
For example, if each side of an equilateral triangle is 10 inches, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 3 \times 10 = 30 \text{ inches} \]
Height and Area Calculations
In addition to the perimeter, you might also need to calculate the height and area of an equilateral triangle:
- Height (h):
- Area (A):
\[ h = \frac{a \sqrt{3}}{2} \]
\[ A = \frac{a^2 \sqrt{3}}{4} \]
Example Calculation of Height and Area
Using the same example with side length \( a = 10 \) inches:
- Height:
- Area:
\[ h = \frac{10 \sqrt{3}}{2} = 5\sqrt{3} \approx 8.66 \text{ inches} \]
\[ A = \frac{10^2 \sqrt{3}}{4} = 25\sqrt{3} \approx 43.3 \text{ square inches} \]
Special Considerations
If you know the area or height of the equilateral triangle, you can rearrange the formulas to find the side length and then use it to calculate the perimeter:
- If the area \( A \) is known:
- If the height \( h \) is known:
\[ a = \sqrt{\frac{4A}{\sqrt{3}}} \]
\[ a = \frac{2h}{\sqrt{3}} \]
Summary
In summary, the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is simply three times the length of one of its sides. Additional properties such as the height and area can be calculated using the respective formulas provided above. Understanding these relationships is crucial for solving various geometric problems involving equilateral triangles.
Isosceles Triangle Perimeter Calculation
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and one side of a different length. To calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, we use the formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
Where:
- \( a \) is the length of one of the equal sides.
- \( b \) is the length of the base (the different side).
Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle:
-
Identify the lengths of the sides of the triangle. For example, let's consider an isosceles triangle with equal sides of 10 cm each and a base of 6 cm.
-
Substitute the values into the perimeter formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]Substitute \( a = 10 \, \text{cm} \) and \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \):
\[ P = 2(10) + 6 \]Calculate the result:
\[ P = 20 + 6 = 26 \, \text{cm} \]Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 26 cm.
-
For an isosceles right triangle, the calculation is slightly different. If the hypotenuse is given, the formula is:
\[ P = h (1 + \sqrt{2}) \]Where \( h \) is the hypotenuse. For example, if the hypotenuse is 8 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[ P = 8 (1 + \sqrt{2}) \approx 8 (1 + 1.414) = 8 \times 2.414 = 19.312 \, \text{units} \]
In summary, calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle involves using the appropriate formula and substituting the known side lengths. For general isosceles triangles, use \( P = 2a + b \), and for isosceles right triangles, use \( P = h (1 + \sqrt{2}) \).
Scalene Triangle Perimeter Calculation
A scalene triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are of different lengths, and all three angles are different. The perimeter of a scalene triangle is calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides.
Formula
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a scalene triangle is straightforward:
where a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the scalene triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides using the formula.
- Express the result as the perimeter of the triangle.
Example Calculation
Consider a scalene triangle with side lengths of 9 cm, 13 cm, and 14 cm.
Using the formula:
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 36 cm.
Real-World Application
Calculating the perimeter of a scalene triangle can be useful in various real-world scenarios such as determining the amount of material needed to create a triangular frame, measuring land boundaries, and in construction projects where triangular plots or components are involved.
Practice Problems
Calculate the perimeter of the following scalene triangles:
- Triangle with sides 5 cm, 12 cm, and 13 cm.
- Triangle with sides 7 in, 24 in, and 25 in.
- Triangle with sides 8 m, 15 m, and 17 m.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a scalene triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry. By summing the lengths of its three sides, you can easily determine the perimeter, which has practical applications in various fields.

Real-World Applications of Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle is not just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous practical applications in various fields. Below are some real-world scenarios where perimeter calculations are crucial:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and engineers frequently use perimeter calculations to determine the boundaries of triangular sections in floor plans, roof designs, and structural frameworks. Accurate perimeter measurements ensure that materials are cut to the correct sizes, reducing waste and optimizing construction efficiency.
- Landscaping and Gardening: Landscapers use the perimeter to outline triangular flower beds, ponds, and other garden features. This helps in planning the layout and ensuring that plants and materials are evenly distributed.
- Fencing and Bordering: When installing fences or borders around triangular plots of land, the perimeter is essential to calculate the total length of fencing material needed. This is important for both agricultural and residential purposes.
- Sports Fields: The design and layout of sports fields often involve triangular shapes. For instance, the perimeter of a triangular section of a soccer or football field may need to be measured for proper placement of boundaries and markers.
- Navigation and Mapping: In navigation, particularly in maritime and aerial contexts, the perimeter of triangular zones is calculated to determine travel distances and create accurate maps. Triangulation, a method using triangles to measure distances, relies heavily on perimeter calculations.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use geometric shapes, including triangles, to create patterns and structures. Calculating the perimeter allows them to scale their designs accurately and ensure proportionality.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, particularly in the production of parts and components, calculating the perimeter of triangular shapes ensures that pieces fit together correctly. This is crucial in industries such as automotive and aerospace engineering.
Understanding the perimeter of triangles aids in efficient planning, accurate material estimation, and the creation of precise designs, making it a fundamental concept in various practical applications.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle might seem straightforward, but there are several common mistakes that students and professionals can make. Below are some typical errors and ways to avoid them:
-
Misidentifying the Sides:
Ensure that all three sides of the triangle are correctly identified and measured. Use labels (e.g., \(a\), \(b\), \(c\)) to keep track of each side.
-
Incorrect Unit Conversion:
When dealing with sides measured in different units (e.g., cm and inches), convert all measurements to the same unit before adding them together. For example:
- 1 inch = 2.54 cm
-
Mixing Up Perimeter and Area:
Remember that perimeter is the sum of the lengths of the sides, whereas area is a measure of the surface within the triangle. For perimeter, use the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\] -
Not Using the Correct Formula for Special Triangles:
For equilateral, isosceles, or right triangles, special formulas can simplify calculations. For example, the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3a
\] -
Ignoring Missing Side Lengths:
Sometimes, you may need to find a missing side length before calculating the perimeter. Use the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles or other given information. For example, in a right triangle:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\]
Steps to Avoid Common Mistakes:
-
Identify and Label: Clearly label each side of the triangle to avoid confusion.
-
Convert Units: Ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before performing any calculations.
-
Use the Correct Formula: Apply the appropriate formula based on the type of triangle.
-
Check Your Work: Review calculations to ensure no steps were missed, and all arithmetic is correct.
By following these guidelines and being mindful of common errors, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle.
Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle can extend beyond simple addition of its sides. Here are some advanced techniques to consider:
1. Using the Law of Cosines
If you know two sides of a triangle and the included angle, you can use the Law of Cosines to find the third side and then calculate the perimeter:
Given sides \(a\) and \(b\) with an included angle \(\gamma\):
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cdot \cos(\gamma)}
\]
Then, the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
2. Using the Law of Sines
When you know one side and two angles, you can use the Law of Sines to find the remaining sides and then calculate the perimeter:
Given side \(a\) and angles \(\beta\) and \(\gamma\):
\[
\frac{a}{\sin(\alpha)} = \frac{b}{\sin(\beta)} = \frac{c}{\sin(\gamma)}
\]
Calculate sides \(b\) and \(c\) as:
\[
b = a \cdot \frac{\sin(\beta)}{\sin(\alpha)}
\]
\[
c = a \cdot \frac{\sin(\gamma)}{\sin(\alpha)}
\]
Then, the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
3. Using Coordinates (Analytic Geometry)
If the vertices of the triangle are given in coordinate form, you can use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides:
Given vertices \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), and \((x_3, y_3)\):
\[
a = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
\[
b = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2}
\]
\[
c = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_1)^2 + (y_3 - y_1)^2}
\]
Then, the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
4. Using Heron's Formula
If all sides are known, you can use Heron's formula to first find the area and then verify your perimeter calculation:
Given sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), first find the semi-perimeter \(s\):
\[
s = \frac{a + b + c}{2}
\]
Then, the area \(A\) is:
\[
A = \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}
\]
5. Applications in Trigonometry
Advanced trigonometric identities and methods can simplify complex perimeter calculations in special triangles, such as 30-60-90 or 45-45-90 triangles, using known ratios.
By applying these advanced techniques, you can solve for the perimeter of various types of triangles in more complex scenarios.
Conclusion and Summary
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the various aspects of calculating the perimeter of a triangle. Understanding the perimeter is fundamental for numerous real-world applications, from constructing buildings to creating art. Here's a summary of the key points covered:
- Basic Formula: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides: \( P = a + b + c \).
- Types of Triangles: We examined the specific cases for equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles, each with its unique characteristics and methods for perimeter calculation.
- Special Cases: Special formulas were discussed for right, isosceles, and equilateral triangles, simplifying the calculation process.
- Advanced Techniques: We delved into advanced methods such as using the Law of Cosines and the Law of Sines to determine the perimeter when not all sides are known.
- Common Mistakes: We identified common errors in calculations, such as incorrect side measurements and improper use of formulas, and provided tips to avoid them.
- Real-World Applications: Examples included using perimeter calculations in fencing, construction, and various design projects.
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is not only essential for academic purposes but also highly applicable in practical scenarios. By mastering these techniques, you can efficiently tackle a wide range of geometric problems and projects. Keep practicing, and remember to double-check your work to ensure accuracy.
Thank you for following along this guide. We hope it has provided you with a clear and thorough understanding of triangle perimeter calculations.
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi tam giác bằng tiếng Việt. Thích hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên muốn học cách tính chu vi tam giác.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Tam Giác | Toán Học với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tìm chu vi của tam giác, phù hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên muốn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Tam Giác