Topic hexagon perimeter calculator: Understanding the perimeter of a hexagon is essential for various mathematical and practical applications. Our Hexagon Perimeter Calculator helps you easily find the perimeter by inputting the side length. Whether you're working on a school project, design work, or just curious, this tool is perfect for you.
Table of Content
- Hexagon Perimeter Calculator
- Introduction to Hexagon Perimeter
- What is a Hexagon?
- Properties of a Regular Hexagon
- Types of Hexagons
- Hexagon Perimeter Formula
- How to Calculate Hexagon Perimeter
- Examples of Hexagon Perimeter Calculation
- Applications of Hexagon Shapes
- Using a Hexagon Perimeter Calculator
- Related Calculations
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính hình lục giác, giúp bạn tính chu vi và diện tích hình lục giác một cách nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Hexagon Perimeter Calculator
Calculate the perimeter of a hexagon using the formula below:
For a regular hexagon, all sides are equal in length.
Formula
The perimeter \(P\) of a regular hexagon with side length \(a\) is given by:
\[ P = 6a \]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Multiply the length of one side by 6.
- The result is the perimeter of the hexagon.
Example Calculation
If the side length \(a\) of the hexagon is 5 units:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Interactive Calculator
Use the interactive calculator below to find the perimeter of your hexagon:
| Side Length (a): | |
| Perimeter (P): |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Hexagon Perimeter
A hexagon is a polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles. The perimeter of a hexagon is the total length around its edges, which is straightforward to calculate due to its regular shape. This introduction will cover the basic concepts of hexagon perimeter calculation, the formula used, and step-by-step examples.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular hexagon is simple:
\[ P = 6a \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a \) is the length of one side. This formula stems from the fact that all six sides of a regular hexagon are of equal length.
Let's delve into the details of calculating the perimeter with some examples:
- Example 1: If a hexagon has a side length of 5 units, the perimeter \( P \) is: \[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
- Example 2: For a hexagon with a side length of 8 cm, the perimeter \( P \) will be: \[ P = 6 \times 8 = 48 \text{ cm} \]
Understanding the perimeter of a hexagon is essential in various fields such as mathematics, engineering, and architecture, where precise measurements are crucial. The regular hexagon's properties, such as equal side lengths and angles, make these calculations straightforward and consistent.
What is a Hexagon?
A hexagon is a two-dimensional geometric shape with six sides, six vertices, and six interior angles. It is commonly found in nature and human-made structures. There are different types of hexagons, each with unique properties and characteristics.
- Regular Hexagon: All six sides and angles are equal. Each interior angle is 120 degrees, and each exterior angle is 60 degrees. The sum of all interior angles is 720 degrees.
- Irregular Hexagon: Sides and angles are not equal. The shape does not have the symmetrical properties of a regular hexagon.
- Convex Hexagon: All vertices point outward, and all interior angles are less than 180 degrees.
- Concave Hexagon: At least one vertex points inward, creating an interior angle greater than 180 degrees.
Hexagons are prevalent in various fields, from natural formations like honeycombs to human applications such as tiling and architectural designs. The properties of regular hexagons make them especially interesting in mathematics and engineering, as they maximize space and minimize materials.
| Property | Regular Hexagon |
| Sides | 6 equal sides |
| Interior Angles | 6 angles of 120 degrees each |
| Vertices | 6 vertices |
| Sum of Interior Angles | 720 degrees |
| Exterior Angles | 6 angles of 60 degrees each |
Properties of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles. It has several unique properties that make it an interesting and useful shape in various fields such as mathematics, architecture, and nature. Below are some key properties of a regular hexagon:
- All sides are equal in length.
- All interior angles measure 120°.
- All exterior angles measure 60°.
- It can be divided into six equilateral triangles.
- The opposite sides are parallel to each other.
The formulas for calculating different properties of a regular hexagon are as follows:
| Perimeter (P) | The perimeter of a regular hexagon is the total length of its six sides. The formula is: | \[ P = 6a \] |
| Area (A) | The area of a regular hexagon can be found by considering it as six equilateral triangles. The formula is: | \[ A = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}a^2 \] |
| Apothem (r) | The apothem is the distance from the center to the midpoint of one of its sides. The formula is: | \[ r = \frac{a\sqrt{3}}{2} \] |
| Circumradius (R) | The circumradius is the distance from the center to a vertex. The formula is: | \[ R = a \] |
| Height (h) | The height of a regular hexagon is the distance between two opposite sides. The formula is: | \[ h = 2r = a\sqrt{3} \] |
| Width (w) | The width is the distance between two opposite vertices. The formula is: | \[ w = 2R = 2a \] |
These properties and formulas highlight the regular hexagon's symmetry and mathematical significance, making it a fascinating shape to study and utilize.
Types of Hexagons
Hexagons are six-sided polygons that can be categorized into two main types: regular hexagons and irregular hexagons.
- Regular Hexagons
A regular hexagon has all six sides of equal length and all internal angles equal to 120 degrees. Due to these symmetrical properties, regular hexagons have some unique characteristics:
- Diagonals: A regular hexagon has nine diagonals, three of which are long diagonals crossing the center and six shorter ones that do not cross the center.
- Circumradius: The distance from the center to any vertex (circumradius) is equal to the side length \( R = a \).
- Inradius: The distance from the center to the midpoint of any side (inradius) is \( r = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a \).
- Irregular Hexagons
Irregular hexagons do not have equal sides and angles. Each side and angle can be of different lengths and degrees, making them less symmetrical. Irregular hexagons can take various forms and do not possess the uniform properties seen in regular hexagons.
Understanding the different types of hexagons is crucial when calculating their perimeters and other properties. Regular hexagons, with their equal sides and angles, allow for straightforward mathematical formulas, whereas irregular hexagons may require more complex calculations.
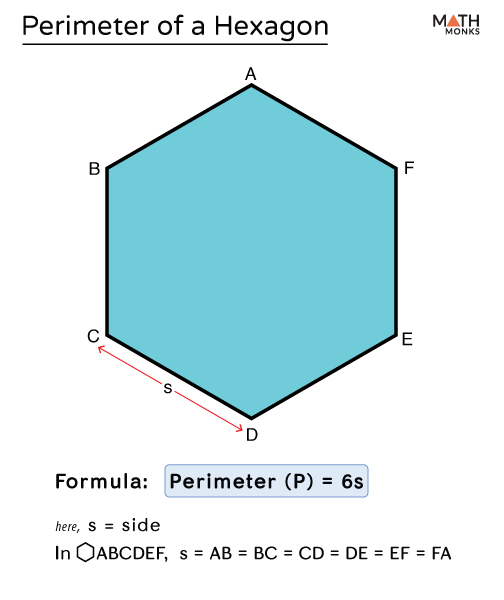
Hexagon Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a hexagon is the total length around the hexagon. There are different formulas depending on whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has all six sides of equal length. The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular hexagon is:
\[ P = 6a \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the hexagon
- \( a \) is the length of one side of the hexagon
For example, if each side of a regular hexagon is 5 units, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all six sides:
\[ P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 + a_6 \]
Where:
- \( a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, a_5, a_6 \) are the lengths of the six sides
For example, if the sides of an irregular hexagon are 4 units, 5 units, 3 units, 6 units, 5 units, and 7 units, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 4 + 5 + 3 + 6 + 5 + 7 = 30 \text{ units} \]
How to Calculate Hexagon Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a hexagon, particularly a regular hexagon where all sides are of equal length, is straightforward. Here are the steps you need to follow:
-
Identify the Length of One Side: To begin, determine the length of one side of the hexagon. Let's denote this side length as a.
-
Use the Perimeter Formula: For a regular hexagon, the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 6a
\] -
Perform the Calculation: Multiply the length of one side by 6 to find the perimeter. For example, if each side of the hexagon is 5 units long, the perimeter will be:
\[
P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units}
\]
Below is a summary in tabular form for quick reference:
| Step | Description | Example Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the length of one side \(a\) | 5 units |
| 2 | Apply the formula \(P = 6a\) | \(P = 6 \times 5\) |
| 3 | Calculate the perimeter | 30 units |
Using a hexagon perimeter calculator can simplify this process by allowing you to input the side length and automatically computing the perimeter. This is especially useful for quick and accurate results.
Examples of Hexagon Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a regular hexagon is straightforward since all six sides are of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a hexagon is:
P = 6a
where a is the length of one side of the hexagon.
Example 1:
Find the perimeter of a hexagon whose side length is 8 units.
- Given: side length, a = 8 units
- Using the formula: P = 6a
- P = 6 × 8
- P = 48 units
Example 2:
Find the perimeter of a hexagon whose side length is 5 units.
- Given: side length, a = 5 units
- Using the formula: P = 6a
- P = 6 × 5
- P = 30 units
Example 3:
Find the perimeter of a hexagon whose side length is 12 units.
- Given: side length, a = 12 units
- Using the formula: P = 6a
- P = 6 × 12
- P = 72 units
Additional Example:
Find the perimeter of a hexagon whose side length is 9.5 units.
- Given: side length, a = 9.5 units
- Using the formula: P = 6a
- P = 6 × 9.5
- P = 57 units
Using these examples, you can see how simple it is to calculate the perimeter of a hexagon. Just multiply the side length by 6, and you have the perimeter.
Applications of Hexagon Shapes
Hexagons are not only fascinating geometric shapes but also have numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some key examples:
- Urban Planning: Hexagonal grids are used in urban planning and city layout for efficient land use and infrastructure design. Their compact and uniform shape allows for optimal space utilization and ease of navigation.
- Manufacturing: The hexagonal pattern is common in the manufacturing industry for designing products such as nuts, bolts, and honeycomb structures. These shapes provide strength and durability while minimizing material usage.
- Computer Graphics: Hexagonal grids are employed in computer graphics for rendering textures, terrain generation, and game development. The symmetry and uniformity of hexagons allow for seamless and efficient mapping of surfaces.
- Biology: Honeybees construct their honeycombs in hexagonal shapes to optimize space and resources. This natural efficiency is an excellent example of how hexagons can provide strength and minimal material use.
- Engineering and Construction:
- Structural Design: Hexagonal structures offer strength and stability, making them suitable for applications such as bridges, pavements, and roofing systems.
- Tiling Patterns: Hexagonal tiles are commonly used in flooring, bathrooms, and kitchen backsplashes. They require accurate calculations for perfect fitting and aesthetic appeal.
These examples highlight the versatility and efficiency of hexagon shapes in various real-world applications, showcasing their importance beyond mere geometry.

Using a Hexagon Perimeter Calculator
Using a hexagon perimeter calculator can simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of a hexagon. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use such a calculator:
- Access the Calculator: Open a reliable hexagon perimeter calculator tool online. These calculators are typically available on educational websites or specialized calculator platforms.
- Input the Side Length: Locate the input field labeled "Side" or "Side Length." Enter the length of one side of the hexagon into this field. Make sure to use consistent units (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches).
- Select the Units: If the calculator provides an option to select units, choose the appropriate unit of measurement that matches the side length you entered.
- Calculate the Perimeter: Click on the "Calculate" button or equivalent. The calculator will compute the perimeter based on the formula for a regular hexagon: \( P = 6a \), where \( a \) is the side length.
- View the Result: The calculator will display the perimeter of the hexagon in the selected units. This value represents the total distance around the hexagon.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
| Step | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Open the hexagon perimeter calculator | - |
| 2 | Enter the side length (e.g., 5 cm) | 5 cm |
| 3 | Select the units (if applicable) | centimeters |
| 4 | Click "Calculate" | - |
| 5 | View the perimeter | 30 cm |
This method ensures an accurate and quick calculation of the hexagon's perimeter, making it a useful tool for students, teachers, and professionals who work with geometric shapes.
Related Calculations
Hexagon-related calculations extend beyond just finding the perimeter. Understanding these related calculations can help in various practical applications, from designing structures to solving complex mathematical problems. Here are some important related calculations for hexagons:
- Area Calculation:
The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula:
\[
A = \frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2} a^2
\]
where \( a \) is the side length of the hexagon. - Diagonal Calculation:
A regular hexagon has several diagonals of different lengths:
- Long diagonal: connects two opposite vertices.
\[
d_{\text{long}} = 2a
\] - Short diagonal: connects two adjacent vertices.
\[
d_{\text{short}} = a
\]
- Long diagonal: connects two opposite vertices.
- Circumcircle Radius:
The radius of the circumcircle (circle passing through all vertices) of a regular hexagon is equal to the side length:
\[
R = a
\] - Incircle Radius:
The radius of the incircle (circle tangent to all sides) can be calculated as:
\[
r = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a
\] - Interior Angle:
Each interior angle of a regular hexagon measures:
\[
\text{Angle} = 120^\circ
\] - Volume of Hexagonal Prism:
If the hexagon is used as the base of a prism with height \( h \), the volume can be calculated as:
\[
V = \text{Base Area} \times h = \left(\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2} a^2\right) \times h
\]
These calculations are essential for various applications in engineering, architecture, and even computer graphics. Accurate knowledge and use of these formulas ensure precision in design and construction, enhancing the effectiveness and aesthetic of hexagonal shapes.
Conclusion
The study of hexagon perimeters reveals both the simplicity and versatility of this geometric shape. By understanding the basic properties and formulas, one can easily calculate the perimeter of a hexagon, whether it is regular or irregular.
Hexagon perimeter calculators streamline this process, making it quick and accessible. These tools are particularly useful in various practical applications, from architectural design to urban planning and natural structures.
Using a hexagon perimeter calculator involves a few straightforward steps: inputting the side length or other known dimensions, selecting the desired calculation, and interpreting the results. This ensures accuracy and efficiency, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
In conclusion, mastering hexagon perimeter calculations enriches our understanding of geometry and its real-world applications. Embracing both manual calculations and digital tools empowers us to approach geometric problems with confidence and precision.
Video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính hình lục giác, giúp bạn tính chu vi và diện tích hình lục giác một cách nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Máy Tính Hình Lục Giác
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính hình lục giác, giúp bạn tính chu vi và diện tích hình lục giác một cách nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Máy Tính Hình Lục Giác