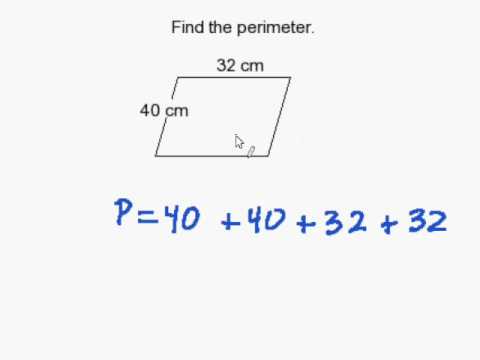
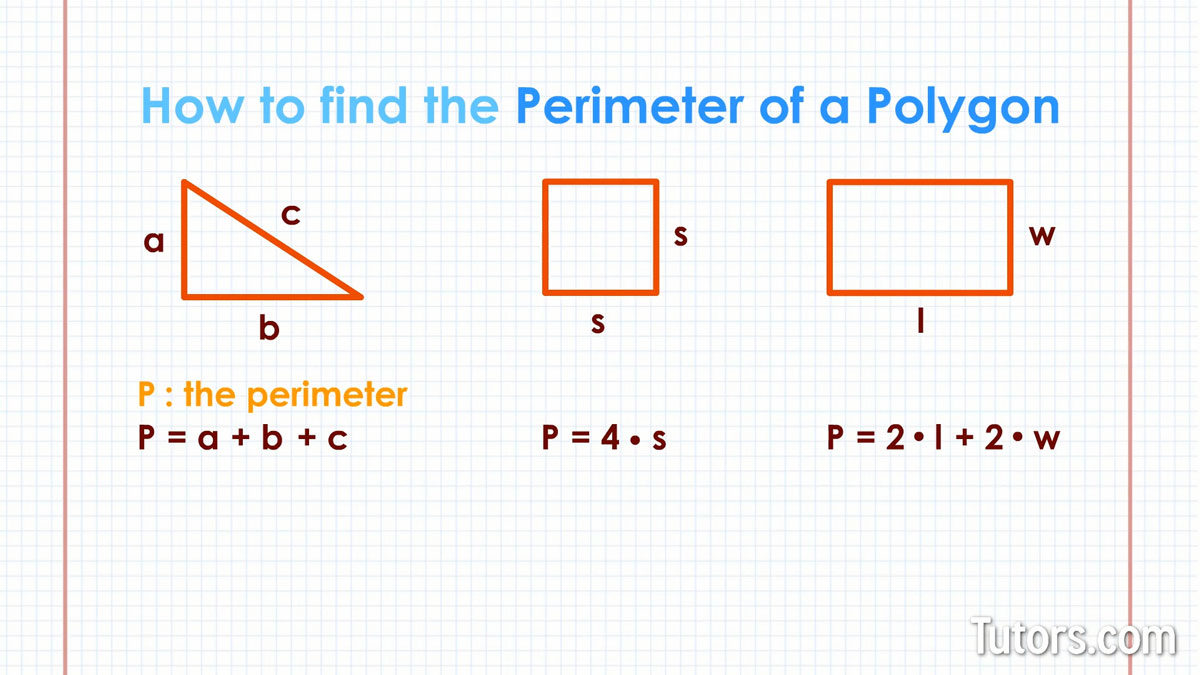
Topic finding the perimeter of a square: Discover how to effortlessly find the perimeter of a square with our comprehensive guide. Learn the simple formula, see step-by-step examples, and explore practical applications. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone looking to enhance their math skills. Let's make calculating the perimeter of a square easy and fun!
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Understanding the Basics
- Mathematical Formula for Perimeter
- Example Problems and Solutions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Applications
- Advanced Perimeter Concepts
- Practice Exercises
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Summary and Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Finding the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all four sides of the square. Since all sides of a square are of equal length, calculating the perimeter is straightforward.
Formula for Perimeter
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by:
Where:
- \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the length of the side by 4 to find the perimeter.
Example
If the length of one side of a square is 5 units, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as follows:
Applications
Finding the perimeter of a square can be useful in various real-world situations, such as:
- Determining the length of fencing required to enclose a square garden.
- Calculating the border length needed for a square-shaped artwork.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its sides. Understanding the concept of perimeter is fundamental in geometry, as it helps in determining the boundary length of shapes. For a square, since all sides are equal in length, calculating the perimeter is straightforward and follows a simple formula.
The formula for finding the perimeter \( P \) of a square is:
Where:
- \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
To find the perimeter, you simply need to multiply the length of one side by 4. This is because a square has four sides of equal length.
For example, if the length of one side of a square is 6 units, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as follows:
This simple calculation is essential for various real-world applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for a border or the total distance around a square plot of land.
Understanding the Basics
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its sides. Since a square has four equal sides, the perimeter is simply four times the length of one side. This can be expressed with the formula:
Where:
- is the perimeter of the square.
- is the length of one side of the square.
To find the perimeter of a square, you can follow these steps:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if one side of a square is 5 meters, the perimeter would be:
This method works for any unit of measurement, such as centimeters, inches, or feet.
Understanding this basic formula is crucial because it lays the foundation for solving more complex problems involving the perimeter of a square. By mastering this concept, you will be able to calculate the perimeter efficiently in various practical scenarios.
Mathematical Formula for Perimeter
The perimeter of a square is the total length around the boundary of the square. To calculate the perimeter, you need to know the length of one side of the square. All sides of a square are of equal length.
The formula to find the perimeter of a square is:
\[ P = 4 \times \text{side} \]
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the square
- side is the length of one side of the square
Let's break down the steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to get the perimeter.
For example, if one side of a square is 5 units long, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the square is 20 units.
Here are a few more examples:
| Side Length (units) | Perimeter (units) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 12 |
| 7 | 28 |
| 10 | 40 |
It's important to ensure that the units used for the side length are consistent. If the side length is given in centimeters, the perimeter will be in centimeters as well.
Remember, the formula for the perimeter of a square is derived from the fact that all four sides are equal. Therefore, multiplying the length of one side by 4 gives the total length around the square.
Example Problems and Solutions
Here are some example problems with detailed solutions to help you understand how to find the perimeter of a square.
Example Problem 1
Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 cm.
- Use the formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute \( s = 7 \): \( P = 4 \times 7 \)
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 28 \) cm
The perimeter of the square is 28 cm.
Example Problem 2
A square has an area of 49 square meters. What is its perimeter?
- Find the side length using the area formula: \( A = s^2 \)
- Given \( A = 49 \): \( s = \sqrt{49} = 7 \)
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute \( s = 7 \): \( P = 4 \times 7 \)
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 28 \) meters
The perimeter of the square is 28 meters.
Example Problem 3
A square has a perimeter of 40 inches. What is the length of one side?
- Use the formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute \( P = 40 \): \( 40 = 4s \)
- Solve for \( s \): \( s = \frac{40}{4} = 10 \) inches
The side length of the square is 10 inches.
Example Problem 4
A square's diagonal is 10√2 meters. What is its perimeter?
- Use the relationship between the side length and diagonal: \( d = s\sqrt{2} \)
- Given \( d = 10\sqrt{2} \): \( s = \frac{10\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = 10 \)
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute \( s = 10 \): \( P = 4 \times 10 \)
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 40 \) meters
The perimeter of the square is 40 meters.
Example Problem 5
If each side of a square park is increased by 3 meters, making the new side length 15 meters, what is the new perimeter?
- Original side length: \( s = 12 \) meters
- New side length: \( s' = s + 3 = 12 + 3 = 15 \) meters
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = 4s' \)
- Substitute \( s' = 15 \): \( P = 4 \times 15 \)
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 60 \) meters
The new perimeter of the square park is 60 meters.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the perimeter of a square might seem straightforward, but there are common pitfalls that can lead to errors. Here are some mistakes to watch out for and tips on how to avoid them:
- Not Using Uniform Units:
Always use the same unit for all measurements. Mixing different units of measurement, like inches and centimeters, can lead to errors. Convert all measurements to the same unit before calculating.
- Misidentifying the Shape:
Ensure that the shape is indeed a square, where all sides are of equal length. Mistaking a rectangle or another quadrilateral for a square will result in incorrect calculations.
- Incorrect Multiplication:
Remember, the perimeter of a square is 4 times the length of one side. Ensure that you multiply the side length by 4 accurately to avoid simple multiplication errors.
- Rounding Errors:
When measuring sides, avoid rounding numbers too early. Rounding can significantly affect the final perimeter, especially in larger squares. Use precise measurements for accurate results.
- Ignoring Measurement Precision:
Use precise measuring tools and techniques. Approximations can lead to inaccurate perimeter calculations. Tools like rulers, tape measures, and laser distance meters can help achieve more accurate measurements.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure more accurate and reliable perimeter calculations for squares.
Practical Applications
Understanding the perimeter of a square is not just an academic exercise; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are some key examples:
- Fencing: When you need to enclose a garden or a yard with a fence, calculating the perimeter helps you determine the total length of fencing material required. For instance, if your garden is a square with each side measuring 10 feet, the total perimeter would be \(4 \times 10 = 40\) feet. Therefore, you would need 40 feet of fencing material.
- Construction: In construction projects, knowing the perimeter of a plot is essential for planning the layout and foundation of buildings. For example, if a building plot is square and measures 50 meters on each side, the perimeter is \(4 \times 50 = 200\) meters. This helps in calculating the boundary walls or other periphery installations.
- Landscaping: Landscaping projects often require precise measurements of garden beds, lawns, and other features. Calculating the perimeter helps determine the amount of materials needed for edging, pathways, and decorative borders. For example, a square flower bed with 5 meters on each side has a perimeter of \(4 \times 5 = 20\) meters.
- Interior Design: When installing baseboards, crown molding, or other trim in a room, knowing the perimeter of the floor plan is crucial. For a square room with each wall measuring 12 feet, the perimeter is \(4 \times 12 = 48\) feet, indicating how much material is needed.
- Surveying and Property Boundaries: Surveyors use the perimeter to delineate property boundaries. Accurate perimeter measurements ensure legal compliance and prevent disputes between property owners. For a square plot of land with 100 meters on each side, the perimeter is \(4 \times 100 = 400\) meters.
- Decorative Arts: In crafts like picture framing or quilting, knowing the perimeter helps in determining the amount of framing material or fabric required. For example, a square quilt with each side measuring 3 feet has a perimeter of \(4 \times 3 = 12\) feet.
These practical applications demonstrate the importance of understanding and accurately calculating the perimeter of squares and other geometric shapes in various fields and everyday situations.
Advanced Perimeter Concepts
The perimeter of a square, given by the formula \( P = 4s \) (where \( s \) is the length of a side), is a fundamental concept that can be extended to more advanced mathematical applications and geometric problems.
Here are several advanced concepts related to the perimeter of a square:
1. Perimeter in Relation to Area
The relationship between the perimeter and area of a square can be explored through algebraic manipulation. Given the area \( A \) of a square, the side length \( s \) can be found using \( s = \sqrt{A} \). Consequently, the perimeter \( P \) can be expressed as:
\[
P = 4s = 4\sqrt{A}
\]
This relationship highlights how changes in the area of a square affect its perimeter.
2. Perimeter of Squares with Diagonals
The length of the diagonal \( d \) of a square is related to the side length by \( d = s\sqrt{2} \). This leads to the perimeter in terms of the diagonal being:
\[
P = 4 \left( \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \right) = 2\sqrt{2}d
\]
This formula is useful in problems where the diagonal length is known or needs to be calculated.
3. Perimeter and Inscribed/Circumscribed Circles
For a square inscribed in a circle, the circle's diameter equals the diagonal of the square. If the radius of the circle is \( r \), the diagonal of the square is \( 2r \), and thus the side length \( s \) is \( s = r\sqrt{2} \). The perimeter can be calculated as:
\[
P = 4r\sqrt{2}
\]
Conversely, for a square circumscribed around a circle, the circle's diameter equals the side length of the square, leading to:
\[
P = 4d
\]
where \( d \) is the diameter of the inscribed circle.
4. Application in Optimization Problems
Advanced optimization problems often involve minimizing or maximizing the perimeter under certain constraints. For instance, given a fixed area, determining the dimensions that yield the minimum perimeter involves calculus and algebraic techniques.
5. Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a square can be found when the vertices are given. For a square with vertices at \( (x_1, y_1) \), \( (x_2, y_2) \), \( (x_3, y_3) \), and \( (x_4, y_4) \), the side length can be calculated using the distance formula, and subsequently, the perimeter is four times the side length.
Understanding these advanced concepts not only enhances your comprehension of geometry but also equips you with the tools to tackle more complex mathematical problems.
Practice Exercises
Below are some practice exercises to help reinforce your understanding of how to find the perimeter of a square.
-
Find the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 5 cm.
Solution:
\( P = 4 \times s \)
\( P = 4 \times 5 \)
\( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
-
A square garden has a side length of 12 meters. Calculate its perimeter.
Solution:
\( P = 4 \times s \)
\( P = 4 \times 12 \)
\( P = 48 \, \text{m} \)
-
The perimeter of a square is 40 inches. What is the length of one side?
Solution:
\( P = 4 \times s \)
\( 40 = 4 \times s \)
\( s = \frac{40}{4} \)
\( s = 10 \, \text{in} \)
-
A square has a perimeter of 64 feet. Determine the length of one side and verify by calculating the perimeter again.
Solution:
\( P = 4 \times s \)
\( 64 = 4 \times s \)
\( s = \frac{64}{4} \)
\( s = 16 \, \text{ft} \)
Verification:
\( P = 4 \times 16 \)
\( P = 64 \, \text{ft} \)
-
If the side length of a square is tripled, how does the perimeter change? Calculate the new perimeter if the original side length was 7 cm.
Solution:
Original side length \( s = 7 \, \text{cm} \)
New side length \( s_{\text{new}} = 3 \times s \)
\( s_{\text{new}} = 3 \times 7 \)
\( s_{\text{new}} = 21 \, \text{cm} \)
New perimeter \( P_{\text{new}} = 4 \times s_{\text{new}} \)
\( P_{\text{new}} = 4 \times 21 \)
\( P_{\text{new}} = 84 \, \text{cm} \)
These exercises cover a range of problems involving the perimeter of squares to help solidify your understanding. Practice regularly to master these concepts.
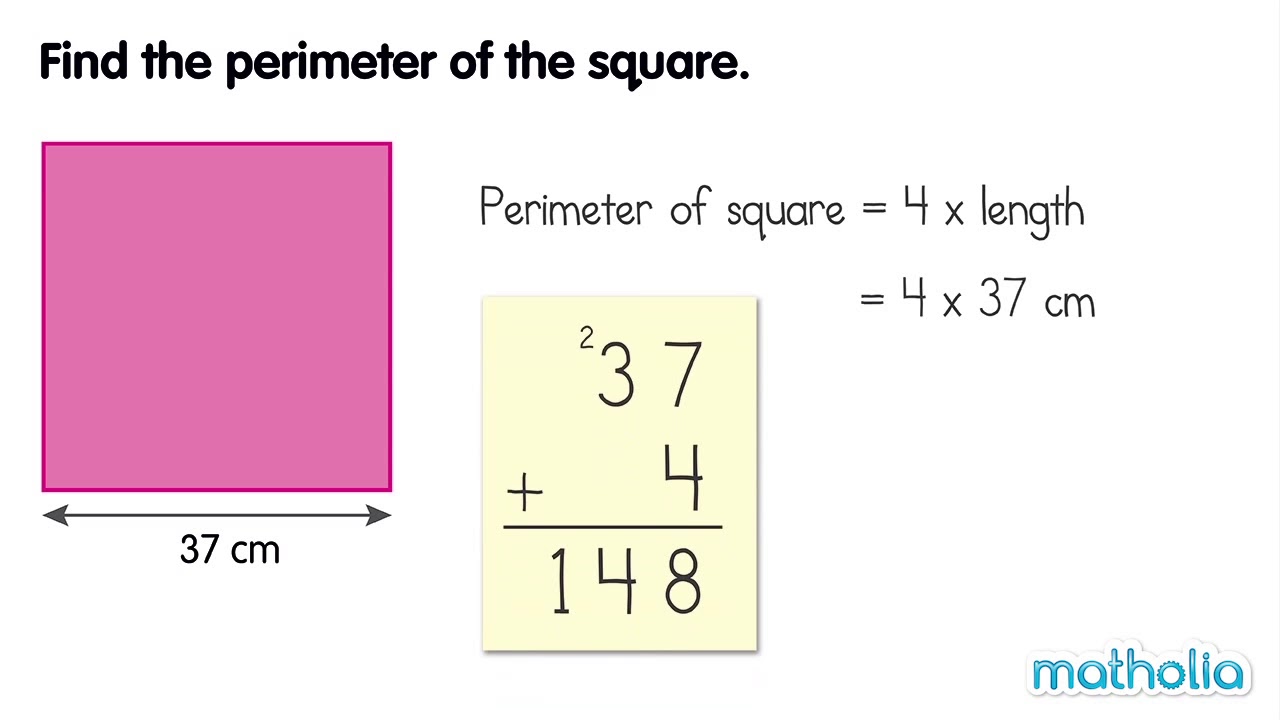
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to finding the perimeter of a square:
-
What is the perimeter of a square?
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four.
-
How do you find the perimeter of a square?
To find the perimeter of a square, you can use the formula:
\( P = 4s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side. If the side length is unknown, you can derive it from the diagonal or the area of the square using these formulas:
- If the diagonal (\( d \)) is known: \( s = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \)
- If the area (\( A \)) is known: \( s = \sqrt{A} \)
-
Can you find the perimeter of a square with just the area?
Yes, you can find the perimeter of a square if you know the area. First, find the side length by taking the square root of the area:
\( s = \sqrt{A} \)
Then, use the side length to find the perimeter:
\( P = 4s \)
-
What units are used to measure the perimeter?
The perimeter is a measure of distance, so it can be expressed in any units of length, such as millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), kilometers (km), inches (in), feet (ft), yards (yd), or miles (mi).
-
What is the difference between a square and a rhombus?
A square has four equal sides and four right angles, whereas a rhombus also has four equal sides but does not necessarily have right angles. Both are types of parallelograms.
-
Are all squares rectangles?
Yes, all squares are rectangles because they have four right angles and opposite sides that are equal in length.
-
What is the formula for the area of a square?
The area of a square is calculated using the formula:
\( A = s^2 \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Summary and Conclusion
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that represents the total distance around the boundary of the square. It is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four, which can be expressed mathematically as:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( P \) stands for the perimeter and \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial because it applies to various practical situations, from measuring land boundaries to constructing objects. This knowledge helps in determining the amount of material needed for tasks such as fencing a property or framing a picture.
In summary:
- The formula for the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4s \).
- This formula is derived from the fact that all sides of a square are equal in length.
- Knowing how to find the perimeter is useful in everyday life and various professional fields.
By mastering the concept of the perimeter, you can solve related mathematical problems with confidence and apply this knowledge effectively in practical scenarios.
In conclusion, the perimeter of a square is a simple yet powerful concept that lays the foundation for understanding more complex geometrical principles and their applications. Keep practicing to enhance your proficiency and ensure that you can utilize this knowledge in diverse contexts.
Làm thế nào để tìm chu vi của hình vuông | Toán học với thầy J
READ MORE:
Làm thế nào để tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình vuông