Topic finding perimeter calculator: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on finding perimeter calculators! This article will help you understand the importance of perimeter calculations, provide formulas for different shapes, and teach you how to use a perimeter calculator effectively. Whether you're a student, teacher, or professional, this guide is designed to make perimeter calculations easy and accurate.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Calculator
- Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
- Understanding Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
- Square Perimeter Formula
- Rectangle Perimeter Formula
- Triangle Perimeter Formula
- Circle (Circumference) Perimeter Formula
- Ellipse Perimeter Formula
- Trapezoid Perimeter Formula
- Parallelogram Perimeter Formula
- Rhombus Perimeter Formula
- Kite Perimeter Formula
- Sector Perimeter Formula
- Annulus Perimeter Formula
- Regular Polygon Perimeter Formula
- How to Use a Perimeter Calculator
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter
- Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật bằng cách sử dụng các công thức đơn giản.
Perimeter Calculator
Use this calculator to find the perimeter of various geometric shapes. Simply select the shape, input the necessary dimensions, and get the perimeter instantly.
How to Find the Perimeter
The perimeter is the total distance around a shape. It is calculated by adding up the lengths of all the sides.
Perimeter Formulas
-
Square
Formula: \( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of a side.
-
Rectangle
Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
-
Triangle
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
-
Circle (Circumference)
Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
-
Ellipse
Approximate Formula: \( P = \pi [ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} ] \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the semi-major and semi-minor axes.
-
Trapezoid
Formula: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
-
Parallelogram
Formula: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
-
Rhombus
Using the Perimeter Calculator
- Select the geometric shape from the drop-down list.
- Input the required dimensions in the provided fields.
- Click the calculate button to see the results.
FAQ
What is the difference between area and perimeter?
The area is the space contained within a shape, measured in square units. The perimeter is the distance around the shape, measured in linear units.
What is the perimeter and area of a circle?
The circumference (perimeter) of a circle is \( 2\pi r \), and the area is \( \pi r^2 \), where \( r \) is the radius.
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4a \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2l + 2w \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Circle | \( P = 2\pi r \) |
| Ellipse | \( P = \pi [ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} ] \) |
| Trapezoid | \( P = a + b + c + d \) |
| Parallelogram | \( P = 2(a + b) \) |
| Rhombus | \( P = 4a \) |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
Perimeter calculation is a fundamental concept in geometry, essential for determining the boundary length of various shapes. Whether you're working with simple polygons like squares and triangles, or more complex shapes like ellipses and trapezoids, understanding how to find the perimeter is crucial. In this guide, we'll explore different methods and formulas for calculating the perimeter of various shapes, helping you master this important mathematical skill.
Let's start by defining the perimeter: it's the total distance around a two-dimensional shape. For polygons, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths. For circles and ellipses, the perimeter is referred to as the circumference, which requires specific formulas to calculate.
Here's a step-by-step approach to finding the perimeter of different shapes:
- Identify the shape you are working with.
- Measure all the necessary dimensions (sides, radii, etc.) using the same unit of measure.
- Apply the appropriate formula for the shape to calculate the perimeter.
Below, we'll provide detailed explanations and formulas for calculating the perimeter of common geometric shapes:
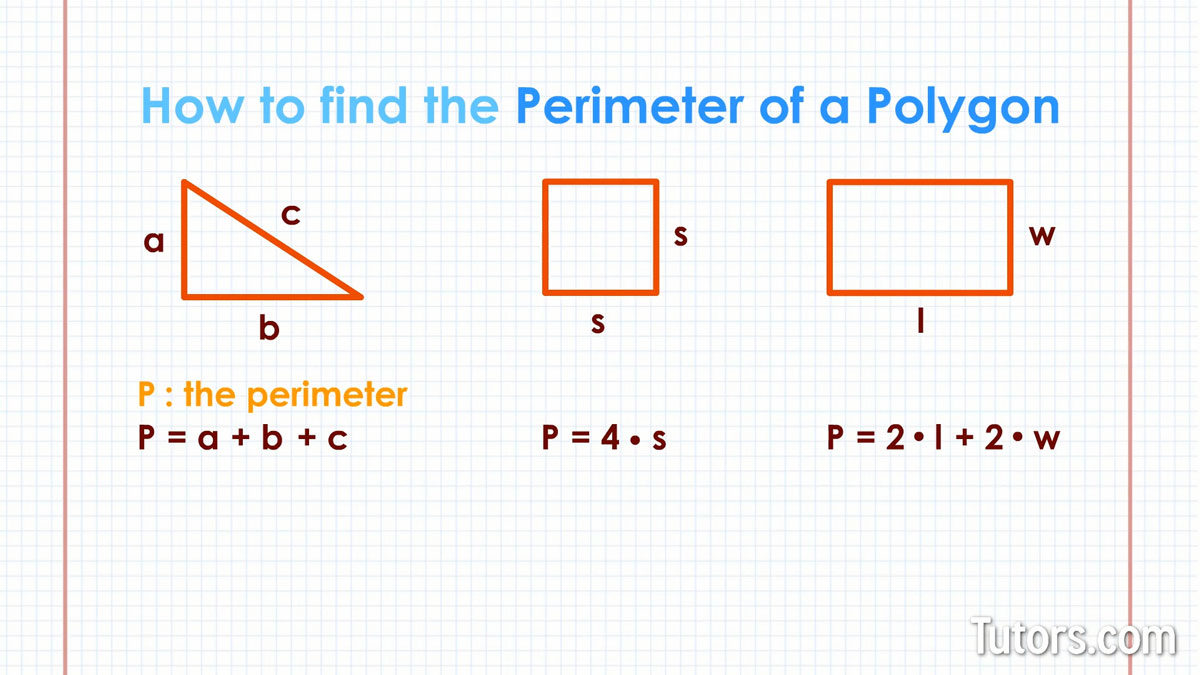
- Square: \(P = 4a\), where \(a\) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \(P = 2l + 2w\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Triangle: \(P = a + b + c\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the side lengths.
- Circle (Circumference): \(C = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- Ellipse: Approximate formula \(P \approx \pi \left(3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)}\right)\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are the semi-major and semi-minor axes.
- Trapezoid: \(P = a + b + c + d\), where \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\) are the lengths of the sides.
Understanding and applying these formulas will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of any shape you encounter. Let's dive deeper into each shape in the following sections to see detailed examples and applications.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary. Derived from the Greek words peri (around) and metron (measure), it represents the measurement around a two-dimensional figure. To calculate the perimeter, you sum the lengths of all sides.
Here is a breakdown of how to understand perimeter:
- Polygons: For polygons, such as squares, rectangles, and triangles, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides.
- Circles: For circles, the perimeter is known as the circumference, calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
To give you a clearer understanding, here are some common perimeter formulas:
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4a \) (where \( a \) is the side length) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2l + 2w \) (where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) (where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths) |
| Circle | \( C = 2\pi r \) (where \( r \) is the radius) |
In summary, understanding perimeter involves recognizing that it is simply the total length around a shape. Whether you are dealing with straight sides or curves, there is a specific formula that makes the calculation straightforward and easy to apply.
Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of different shapes is essential for various practical applications, from construction to academic purposes. Below are the formulas for the perimeters of common geometric shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4.
\( P = 4a \) - Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
\( P = 2l + 2w \) - Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of all its sides.
\( P = a + b + c \) - Circle (Circumference): The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference and is calculated using the radius.
\( P = 2\pi r \) - Ellipse: The perimeter of an ellipse requires an approximation formula due to its complexity.
\( P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \) - Trapezoid: The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of all its sides.
\( P = a + b + c + d \) - Parallelogram: The perimeter of a parallelogram is twice the sum of its base and side.
\( P = 2a + 2b \) - Rhombus: The perimeter of a rhombus is four times the length of one side.
\( P = 4a \) - Kite: The perimeter of a kite is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
\( P = 2a + 2b \) - Sector: The perimeter of a sector of a circle includes the arc length and two radii.
\( P = 2r + r\theta \) - Annulus: The perimeter of an annulus is the sum of the circumferences of the outer and inner circles.
\( P = 2\pi(R + r) \) - Regular Polygon: The perimeter of a regular polygon is the product of the number of sides and the length of one side.
\( P = n \cdot a \)
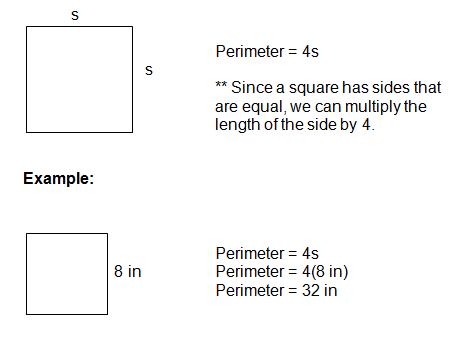
Square Perimeter Formula
Calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward because all four sides are equal in length. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a square is:
where s represents the length of one side of the square.
To use the perimeter calculator for a square:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to find the perimeter.
- Alternatively, enter the side length into the calculator, which will compute the perimeter automatically.
For example, if the side length of a square is 5 units, the perimeter calculation is:
units
Rectangle Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the rectangle. To find the perimeter, you need to add up the lengths of all four sides. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a rectangle is given by:
where:
l = length of the rectanglew = width of the rectangle
Let's break this down step-by-step:
- Measure the length of the rectangle (l).
- Measure the width of the rectangle (w).
- Use the formula:
P = 2l + 2w - Calculate by adding the length and width, then multiplying the sum by 2.
For example, if the length of a rectangle is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter would be calculated as:
This formula works for any rectangle, whether it is small or large, as long as you know the length and width. Using a perimeter calculator can simplify this process by automating the calculation, ensuring accuracy and saving time.
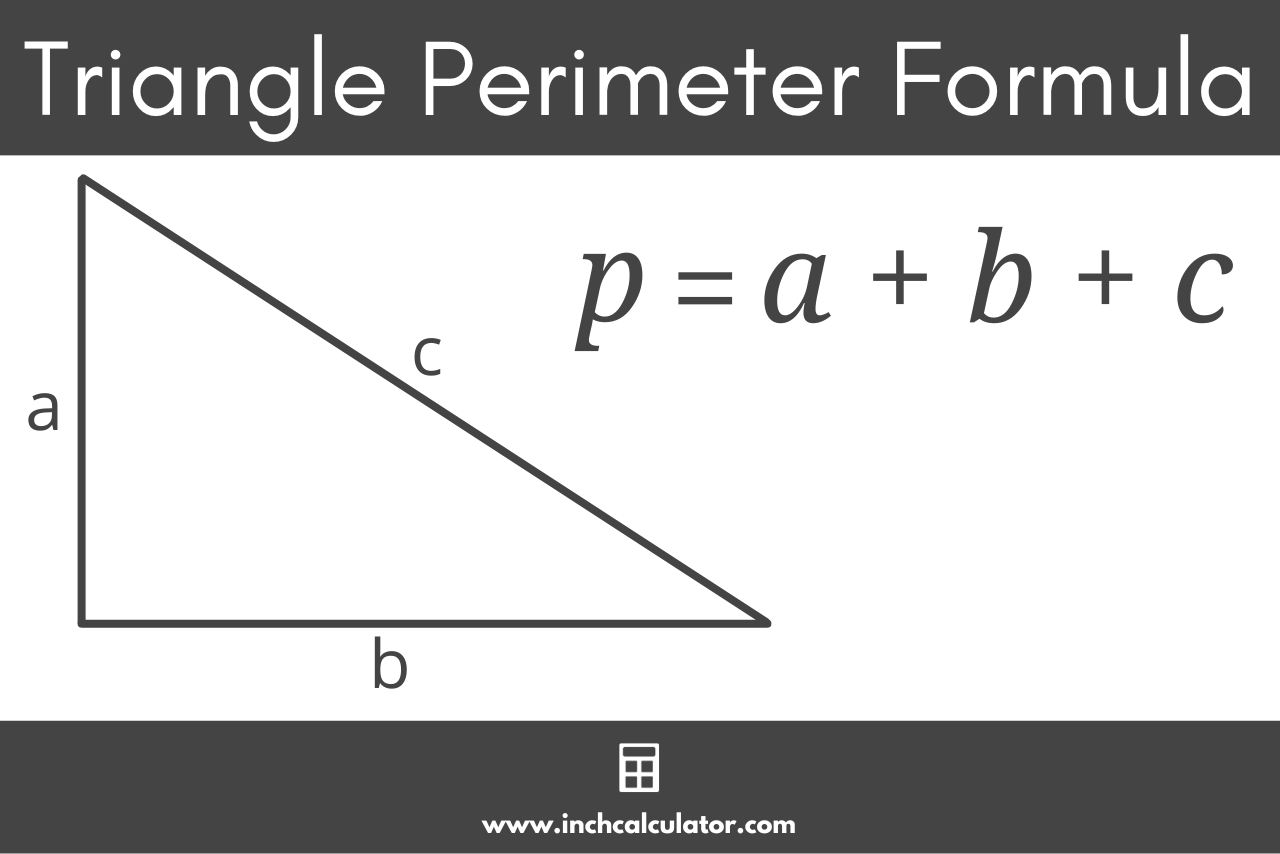
Triangle Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its three sides. To find the perimeter, simply add the lengths of all the sides together.
- Formula for a Triangle with Known Sides (SSS):
If all three sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are known, the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
\(P = a + b + c\)
- Formula for a Triangle with Two Sides and Included Angle (SAS):
If two sides \(a\), \(b\) and the included angle \(\gamma\) are known, use the Law of Cosines to find the third side, then calculate the perimeter:
\(c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma)}\)
Then, \(P = a + b + c\)
- Formula for a Triangle with Two Angles and One Side (ASA):
If one side \(a\) and the two adjacent angles \(\beta\) and \(\gamma\) are known, use the Law of Sines to find the other two sides:
\(b = \frac{a \sin(\beta)}{\sin(\beta + \gamma)}\)
\(c = \frac{a \sin(\gamma)}{\sin(\beta + \gamma)}\)
Then, \(P = a + b + c\)
Circle (Circumference) Perimeter Formula
Calculating the perimeter of a circle, commonly known as its circumference, is a fundamental aspect of geometry. The formula for finding the circumference of a circle is straightforward and involves the mathematical constant π (pi).
The standard formula for the circumference \( C \) of a circle is:
\( C = 2\pi r \)
Where:
- \( C \) is the circumference
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle
- \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159
Alternatively, if you know the diameter \( d \) of the circle, you can use the formula:
\( C = \pi d \)
Where:
- \( d \) is the diameter of the circle
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating the circumference:
- Measure the radius \( r \) of the circle.
- Multiply the radius by 2 to get the diameter \( d \).
- Multiply the diameter by \( \pi \) to find the circumference using the formula \( C = \pi d \).
- If you only have the radius, use the formula \( C = 2\pi r \).
For example, if the radius of a circle is 7 cm, the circumference is calculated as follows:
\( C = 2\pi \times 7 \approx 2 \times 3.14159 \times 7 \approx 43.98 \, \text{cm} \)
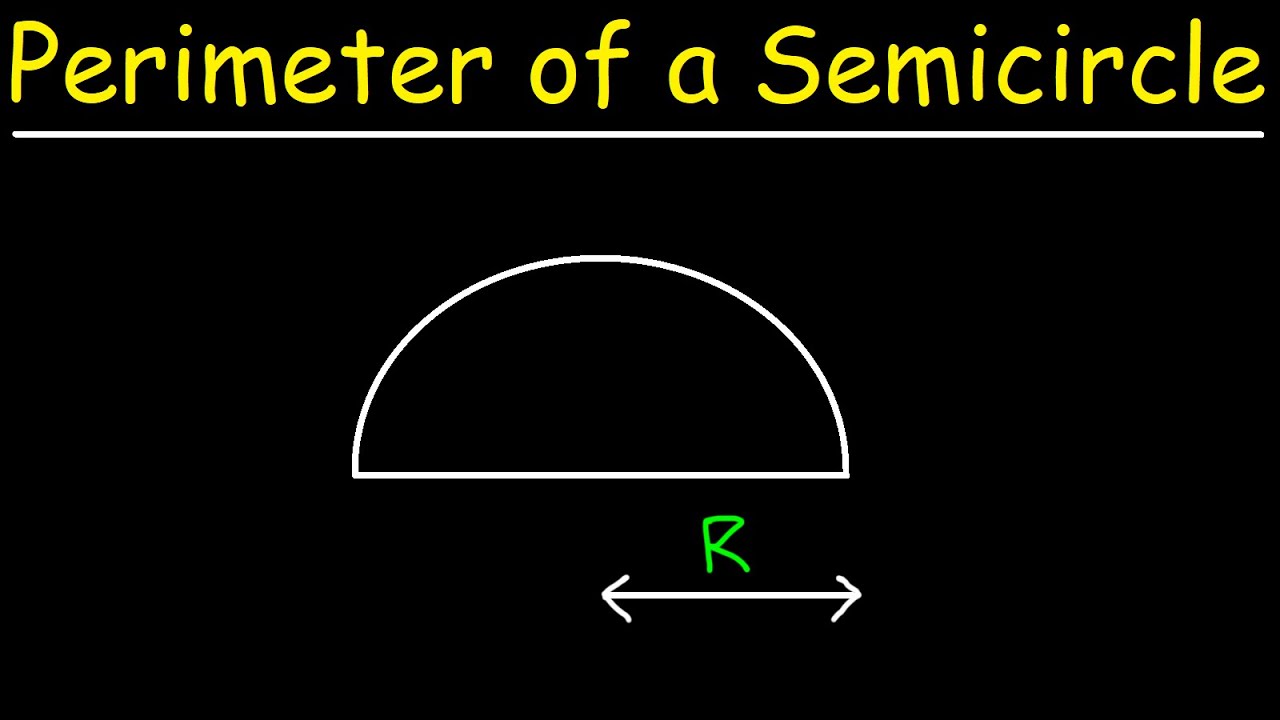
Understanding how to use these formulas ensures accurate calculations whether you're working with full circles or portions of them, such as semicircles or quarter circles.
Ellipse Perimeter Formula
Calculating the perimeter of an ellipse is more complex than that of simpler shapes like rectangles and triangles. The formula involves a special approximation since there isn't a simple exact formula for the perimeter of an ellipse. The most commonly used approximation formula is given by Ramanujan:
\[
P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right]
\]
where a is the semi-major axis and b is the semi-minor axis. Here is a step-by-step guide to using this formula:
- Identify the lengths of the semi-major axis (a) and the semi-minor axis (b).
- Calculate the sum of the semi-major and semi-minor axes: a + b.
- Compute the term \(3(a + b)\).
- Calculate the square root of \((3a + b)(a + 3b)\).
- Subtract the result from step 4 from the result of step 3.
- Multiply the result by π to get the approximate perimeter of the ellipse.
Using this approximation, you can easily find the perimeter of an ellipse for any given lengths of the semi-major and semi-minor axes. This formula provides a good balance between simplicity and accuracy for most practical purposes.
Trapezoid Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all its four sides. A trapezoid is a four-sided polygon with one pair of parallel sides known as the bases and two non-parallel sides known as the legs. To calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid, use the formula:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
- a: Length of the first parallel side (base)
- b: Length of the second parallel side (base)
- c: Length of the first non-parallel side (leg)
- d: Length of the second non-parallel side (leg)
Steps to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid:
- Measure the lengths of the two parallel sides (a and b).
- Measure the lengths of the two non-parallel sides (c and d).
- Add the lengths of all four sides together: \( P = a + b + c + d \).
Example:
If a trapezoid has the following side lengths:
- Base \( a = 8 \, \text{cm} \)
- Base \( b = 12 \, \text{cm} \)
- Leg \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Leg \( d = 7 \, \text{cm} \)
The perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 8 \, \text{cm} + 12 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} = 32 \, \text{cm} \]
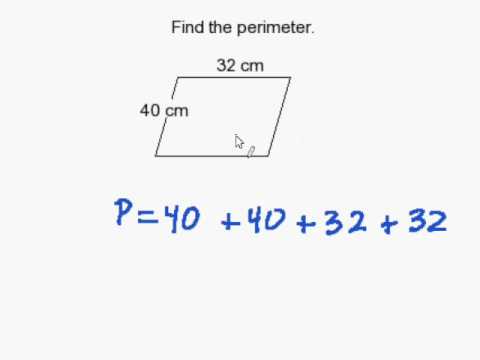
Parallelogram Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a parallelogram is the total length of its boundaries. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are equal in length and parallel. The formula to find the perimeter is quite simple and straightforward.
Formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (a + b) \]
where:
- a is the length of one pair of opposite sides
- b is the length of the other pair of opposite sides
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Measure the length of one pair of opposite sides (a).
- Measure the length of the other pair of opposite sides (b).
- Add the two lengths together: \( a + b \).
- Multiply the sum by 2 to find the perimeter: \( 2 \times (a + b) \).
Example:
Suppose we have a parallelogram where one pair of opposite sides are 8 cm each and the other pair of opposite sides are 5 cm each.
Using the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times 13 \, \text{cm} \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 26 \, \text{cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the parallelogram is 26 cm.
To ensure accuracy, always double-check your measurements and calculations.
Rhombus Perimeter Formula
A rhombus is a type of quadrilateral where all four sides have equal length. To find the perimeter of a rhombus, you simply need to know the length of one of its sides.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a rhombus is:
\[
P = 4a
\]
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the rhombus.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of a rhombus:
- Measure the length of one side of the rhombus. Let this be \( a \).
- Multiply this length by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the rhombus.
For example, if each side of the rhombus is 5 cm, then the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{cm}
\]
This simple formula allows you to quickly and easily calculate the perimeter of any rhombus.
Kite Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a kite is calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. A kite has two pairs of equal-length sides. Therefore, if the lengths of the two pairs of sides are denoted as a and b, the perimeter P is given by:
\[
P = 2a + 2b
\]
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculate the perimeter of a kite:
Identify the lengths of the two distinct pairs of sides. Let these be a and b.
Multiply the length of one pair of sides by 2: \(2a\).
Multiply the length of the other pair of sides by 2: \(2b\).
Add the two results together to get the perimeter: \(P = 2a + 2b\).
For example, if the sides of a kite are 5 cm and 7 cm, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 2(5) + 2(7) = 10 + 14 = 24 \text{ cm}
\]
Therefore, the perimeter of the kite is 24 cm.
| Side Lengths | Perimeter Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 5 cm, 7 cm | \(P = 2(5) + 2(7)\) | 24 cm |
| 8 cm, 6 cm | \(P = 2(8) + 2(6)\) | 28 cm |
| 4 cm, 9 cm | \(P = 2(4) + 2(9)\) | 26 cm |
Using this formula, you can easily find the perimeter of any kite by knowing the lengths of its sides.

Sector Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a sector, also known as the arc length plus the two radii, is a vital aspect of understanding the properties of this geometric figure. A sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc.
To calculate the perimeter of a sector, you need to know the radius (r) and the central angle (θ) in radians. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a sector is:
$$ P = 2r + rθ $$
Where:
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle
- \( θ \) is the central angle in radians
The steps to calculate the perimeter of a sector are:
- Measure the radius (\( r \)) of the circle.
- Determine the central angle (\( θ \)) in radians. If the angle is in degrees, convert it to radians by using the formula \( \theta_{radians} = \theta_{degrees} \times \frac{\pi}{180} \).
- Use the formula \( P = 2r + rθ \) to find the perimeter of the sector.
Here's an example:
- Given a sector with a radius \( r = 5 \, \text{cm} \) and a central angle \( θ = \frac{\pi}{3} \, \text{radians} \).
- Substitute the values into the formula: \( P = 2(5) + 5 \left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right) \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 10 + \frac{5\pi}{3} \).
- Therefore, the perimeter of the sector is \( P = 10 + \frac{5\pi}{3} \, \text{cm} \).
This formula and method provide a straightforward approach to finding the perimeter of a sector, which is essential in various applications such as engineering, design, and more.
Annulus Perimeter Formula
An annulus is a geometric shape that resembles a ring, formed by two concentric circles. To calculate the perimeter of an annulus, you need to determine the sum of the circumferences of both the inner and outer circles.
The formula for the perimeter (or circumference) of an annulus is given by:
\[
P = 2\pi R + 2\pi r
\]
where:
- \(R\) is the radius of the outer circle
- \(r\) is the radius of the inner circle
This can be simplified to:
\[
P = 2\pi (R + r)
\]
To understand this better, let’s break it down step by step:
- Measure the radius of the outer circle (R).
- Measure the radius of the inner circle (r).
- Plug these values into the formula \(P = 2\pi (R + r)\).
- Calculate the sum of the radii: \(R + r\).
- Multiply the result by \(2\pi\).
Let’s look at an example:
| Radius of the outer circle (\(R\)) | 5 cm |
| Radius of the inner circle (\(r\)) | 3 cm |
| Sum of the radii (\(R + r\)) | 8 cm |
| Perimeter (P) | \(2\pi \times 8 = 16\pi \approx 50.27 \text{ cm}\) |
Thus, the perimeter of the annulus is approximately 50.27 cm.
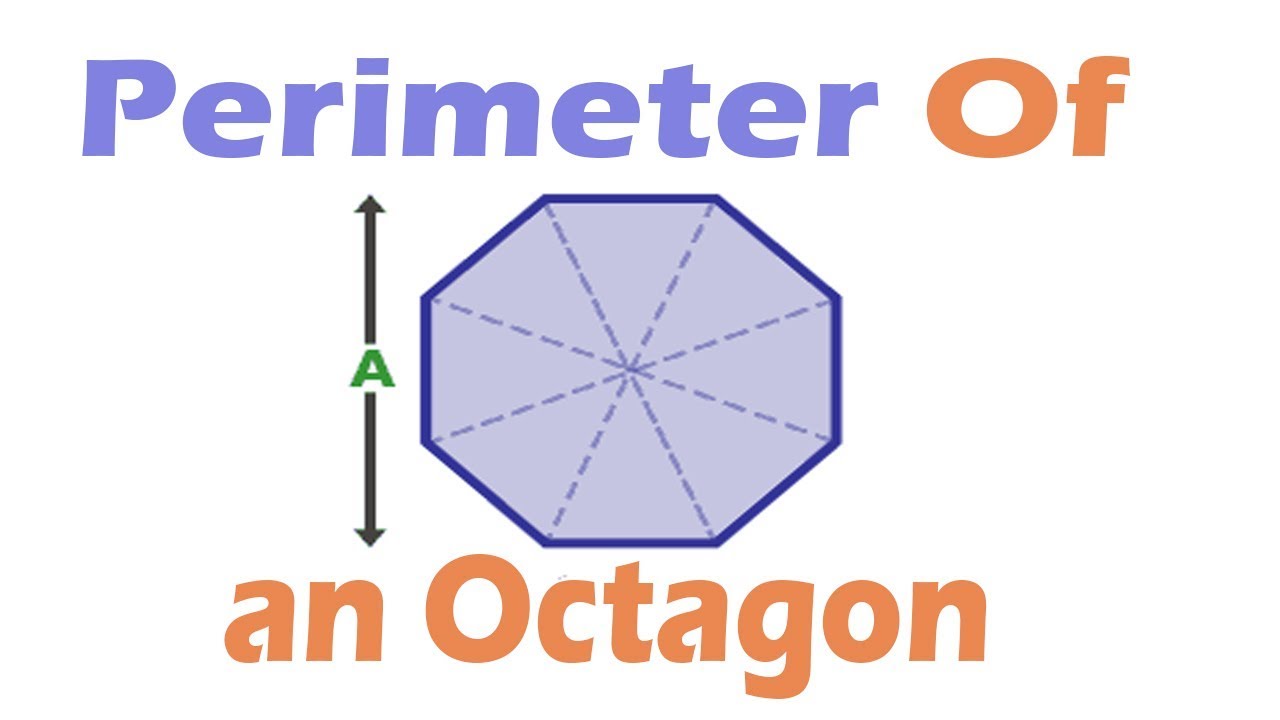
Regular Polygon Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a regular polygon is calculated by multiplying the length of one of its sides by the total number of sides. This is because all sides of a regular polygon are of equal length.
To find the perimeter, you can use the following formula:
Formula:
\[
P = n \times a
\]
- P is the perimeter of the polygon.
- n is the number of sides.
- a is the length of one side.
For example, if you have a regular hexagon (which has 6 sides) with each side measuring 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
Example:
\[
P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units}
\]
To further illustrate, here's a step-by-step guide to using the formula:
- Identify the number of sides (n) of the polygon.
- Measure the length of one side (a).
- Multiply the number of sides by the length of one side using the formula \(P = n \times a\).
Below is a table summarizing the perimeter formulas for different regular polygons:
| Polygon | Number of Sides (n) | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Triangle | 3 | \(P = 3a\) |
| Square | 4 | \(P = 4a\) |
| Pentagon | 5 | \(P = 5a\) |
| Hexagon | 6 | \(P = 6a\) |
| Heptagon | 7 | \(P = 7a\) |
| Octagon | 8 | \(P = 8a\) |
By following these steps, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any regular polygon, ensuring accurate measurements for various applications, from academic exercises to real-life constructions.
How to Use a Perimeter Calculator
Using a perimeter calculator is an efficient way to find the perimeter of various geometric shapes. Follow these steps to accurately calculate the perimeter:
- Select the Shape:
Choose the geometric shape for which you want to calculate the perimeter. Common shapes include squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and polygons.
- Enter the Dimensions:
- Square: Enter the length of one side.
- Rectangle: Enter the lengths of the two adjacent sides (length and width).
- Triangle: Enter the lengths of all three sides.
- Circle: Enter the radius or diameter.
- Polygon: Enter the length of one side and the number of sides.
- Calculate:
Click on the "Calculate" button to compute the perimeter. The calculator will use the appropriate formula for the selected shape to find the perimeter.
- Review the Result:
The perimeter will be displayed in the specified units. You can use this result for further calculations or to solve real-world problems.
Examples
- Square: For a square with a side length of \(a\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 4a\).
- Rectangle: For a rectangle with length \(l\) and width \(w\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = 2l + 2w\).
- Triangle: For a triangle with side lengths \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = a + b + c\).
- Circle: For a circle with radius \(r\), the circumference (perimeter) \(C\) is given by \(C = 2\pi r\).
- Polygon: For a regular polygon with \(n\) sides each of length \(s\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by \(P = ns\).
Tips for Accurate Calculation
- Use Consistent Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before entering them into the calculator.
- Double-Check Measurements: Accurate measurements are crucial for precise perimeter calculation.
- Refer to Diagrams: Visual aids can help in understanding which dimensions to measure and enter.
Using a perimeter calculator can save time and reduce errors, especially for complex shapes. It's a valuable tool for students, teachers, engineers, and anyone needing quick and accurate perimeter measurements.

Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of different shapes involves summing the lengths of their sides. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you calculate the perimeter for various geometric figures:
-
Identify the Shape:
First, determine the type of shape for which you need to find the perimeter. This could be a square, rectangle, triangle, circle (circumference), or any other polygon.
-
Measure or Obtain Side Lengths:
For polygons, measure the lengths of all sides. For circles, you'll need the radius or diameter.
-
Apply the Appropriate Formula:
- Square: \( P = 4a \)
(where \( a \) is the side length) - Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
(where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width) - Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
(where \( a, b, \) and \( c \) are the side lengths) - Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \)
(where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter) - Polygon: \( P = n \times a \)
(where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( a \) is the side length)
- Square: \( P = 4a \)
-
Sum the Sides:
For polygons, sum the lengths of all the sides. For circles, use the circumference formulas.
-
Check Your Calculations:
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy.
Using these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any geometric figure. For complex shapes, break them down into simpler components, calculate each part's perimeter, and sum them up.
Applications of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations are used in various real-life applications, providing essential insights into different fields. Here are some common applications:
Real-Life Applications
-
Construction:
During the construction of homes, buildings, roads, and bridges, perimeter calculations help determine the amount of materials needed for framing, fencing, and other structural elements. Accurate perimeter measurements ensure that the construction process is efficient and cost-effective.
-
Landscaping:
When designing gardens, parks, or other outdoor spaces, the perimeter is used to outline areas for planting, pathways, and borders. This helps in planning the layout and distribution of plants and other features.
-
Fencing and Bordering:
In agricultural and residential areas, perimeter calculations are essential for installing fences and boundaries. Knowing the exact perimeter allows for precise measurement of the fencing material required.
-
Interior Design:
In interior design, calculating the perimeter of rooms is crucial for installing moldings, baseboards, and decorative trims. It also aids in determining the amount of paint or wallpaper needed for walls.
-
Sports Fields:
For sports fields such as basketball courts, soccer fields, and running tracks, perimeter calculations ensure the correct dimensions are maintained, providing a standard playing area.
-
Fashion and Art:
In fashion design, the perimeter is used to measure fabric and create patterns for garments. In art, it helps artists define the boundaries of their work, ensuring precision in their creations.
Educational Applications
-
Teaching Geometry:
Understanding perimeter is a fundamental part of learning geometry. It helps students grasp the concept of boundaries and dimensions, forming the basis for more complex mathematical concepts.
-
Problem-Solving Skills:
Calculating perimeters enhances students' problem-solving and analytical skills. They learn to approach problems methodically, breaking them down into manageable steps.
-
Practical Applications:
Students apply perimeter calculations in real-life scenarios, such as designing school projects, creating models, and understanding space and boundaries in their environment.
Perimeter calculations are not just confined to mathematical problems but extend to practical uses in everyday life, from construction and design to education and beyond.
Video hướng dẫn cách tính diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật bằng cách sử dụng các công thức đơn giản.
Cách tìm Diện tích và Chu vi của Hình chữ nhật
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của một hình ghép, cụ thể là hình chữ L, bằng cách sử dụng các công thức hình học.
Tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình ghép | Ví dụ hình chữ L | Hình học | Toán học với thầy J