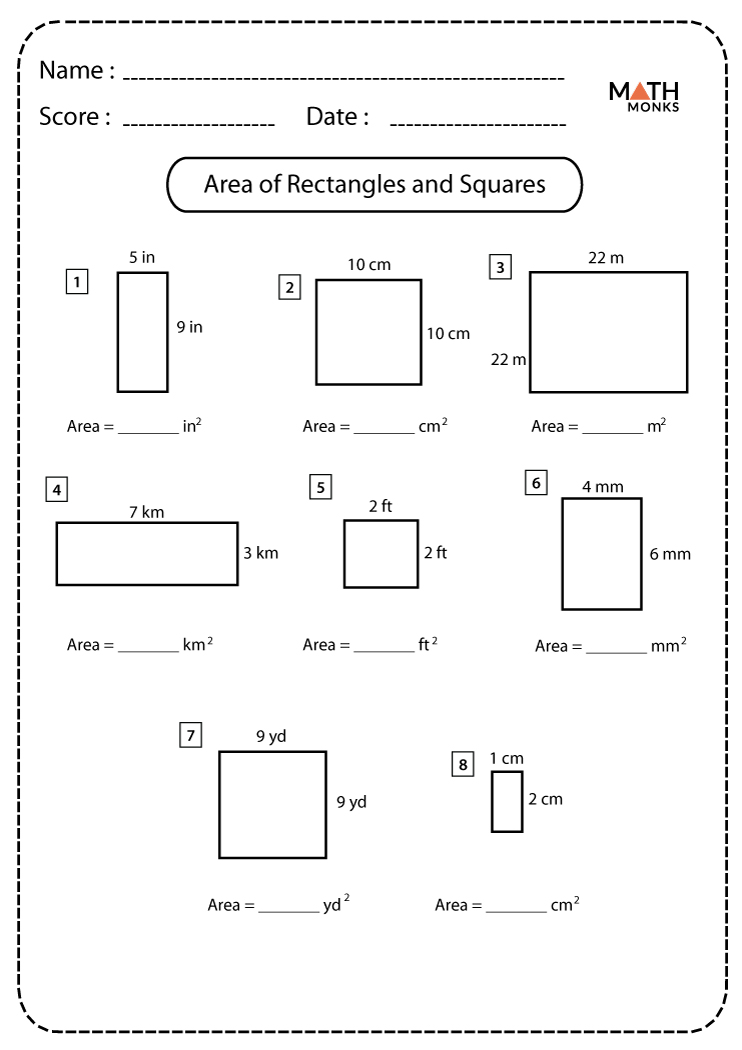
Topic perimeter of square and rectangle: Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the "Perimeter of Square and Rectangle", delving into the core concepts and practical applications of these fundamental shapes in everyday life.
Table of Content
- How do I calculate the perimeter of a square and rectangle?
- Definition and Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Square
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Comparison Between Perimeter of Square and Rectangle
- Practical Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Perimeter of a Square
- Common Misconceptions and Errors
- Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
- Advanced Concepts Related to Perimeter
- Tools and Resources for Learning Perimeter
- Tips for Teachers and Educators
How do I calculate the perimeter of a square and rectangle?
To calculate the perimeter of a square, you can use the formula:
Perimeter = 4 * side length
And to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, you can use the formula:
Perimeter = 2 * (length + width)
If you know the side length of the square or the length and width of the rectangle, you can plug those values into the respective formulas to find the perimeter.
Here\'s a step-by-step guide for finding the perimeter of a square:
- Identify the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the length of one side by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
And here\'s a step-by-step guide for finding the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Identify the length and width of the rectangle.
- Add the length and the width together.
- Multiply the sum by 2.
- The result is the perimeter of the rectangle.
READ MORE:
Definition and Basic Concepts of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. This fundamental geometric concept is key in understanding various shapes, including squares and rectangles. The perimeter is measured by summing the lengths of all sides of the shape.
- Square: A square has four equal sides. To calculate its perimeter, multiply the length of one side by 4. For example, if each side of a square is 5 units, its perimeter is 20 units.
- Rectangle: A rectangle has two pairs of equal sides. Its perimeter is calculated by adding twice the length and twice the width. For a rectangle with a length of 10 units and a width of 5 units, the perimeter would be 30 units.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial for various applications, from everyday measurements to advanced geometry. It is a linear measure and can be expressed in any unit of length, such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet.
- Identify the lengths of all sides of the shape.
- Add the lengths of all sides together for rectangles, or multiply one side by 4 for squares.
- Express the result in the appropriate unit of measurement.
This concept not only forms the basis for more complex geometrical studies but also has practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.

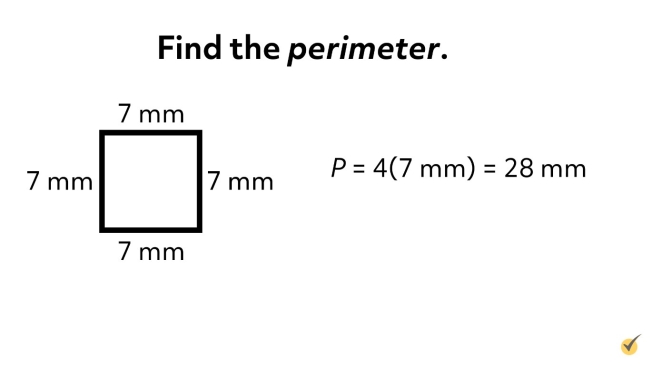
Calculating the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square, a fundamental shape in geometry, is simple to calculate. A square is a four-sided polygon with equal sides and each angle measuring 90 degrees. The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of the square.
- Measure the Length of One Side: Begin by measuring the length of one side of the square. As all sides are equal, only one side needs to be measured.
- Use the Perimeter Formula: The formula for the perimeter (P) of a square is P = 4 × side length. Multiply the length of one side by 4.
- Calculate the Perimeter: If the side of the square is 5 units, for example, the perimeter would be 5 units × 4, equalling 20 units.
This method of calculation is used in various applications, such as construction, fabric design, and more. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is essential for practical problem-solving and mathematical reasoning.

Calculating the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle is a straightforward process, essential in various fields like architecture, interior design, and mathematics. A rectangle is a four-sided figure with opposite sides being equal in length.
- Measure the Length and Width: Begin by measuring the length and the width of the rectangle. Remember, opposite sides are equal in a rectangle.
- Use the Perimeter Formula: The formula for the perimeter (P) of a rectangle is P = 2 × (Length + Width). Add the length and the width, and then multiply the sum by 2.
- Calculate the Perimeter: For instance, if the length is 8 units and the width is 5 units, the perimeter would be 2 × (8 + 5) = 2 × 13 = 26 units.
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle is crucial for spatial planning and efficient design. This geometric concept applies to real-life scenarios, enhancing practical problem-solving skills.
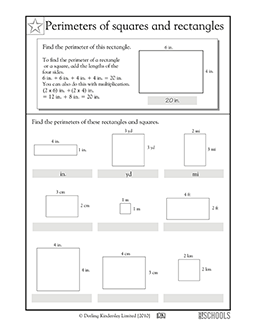
Comparison Between Perimeter of Square and Rectangle
Understanding the differences and similarities in calculating the perimeter of a square and a rectangle is important for grasping basic geometric principles. Both shapes are quadrilaterals, but they have distinct characteristics affecting their perimeter calculations.
- Perimeter Formula: The formula for a square\"s perimeter is simpler (4 × side length) due to all sides being equal. For a rectangle, the formula is 2 × (length + width), reflecting its unequal pair of sides.
- Impact of Side Lengths: In a square, changing the length of one side alters the perimeter proportionally. In a rectangle, altering one side length impacts the perimeter differently, depending on whether it’s the length or the width.
- Geometric Properties: A square is a special case of a rectangle with equal sides, which simplifies its perimeter calculation. A rectangle, having varied side lengths, requires the measurement of both length and width.
The comparison highlights the unique aspects of each shape\"s perimeter calculation, demonstrating the importance of understanding their geometric properties for accurate measurement and application in various fields.

_HOOK_
Practical Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the concept of perimeter, especially for squares and rectangles, has numerous practical applications in everyday life. These applications range from simple tasks to complex projects in various fields.
- Home and Interior Design: Calculating the perimeter of rooms helps in planning the layout, determining how much paint or wallpaper is needed, and installing baseboards or crown moldings.
- Landscaping and Gardening: Perimeter measurements are vital in planning garden layouts, installing fencing, and arranging flower beds or walkways.
- Construction and Architecture: Accurate perimeter calculations are crucial in designing floor plans, estimating building materials, and planning construction projects.
- Educational Tools: In education, understanding perimeter assists students in developing spatial awareness and problem-solving skills through practical examples.
- Sports: In sports fields and courts, perimeter measurements determine the playing area\"s dimensions and help in designing the layout of sports facilities.
The concept of perimeter in squares and rectangles is not just a mathematical theory but a practical tool used in a wide range of real-world applications, demonstrating its importance beyond the classroom.

Finding the Perimeter of a Square
\"Discover the fascinating world of perimeter and unravel the secrets behind finding the perfect measurements in this captivating video. Learn how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes and unlock the key to problem-solving mastery!\"
Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle
\"Unlock the realm of rectangles with this mesmerizing video that will take you through the ins and outs of this versatile shape. Dive into the realm of angles, sides, and formulas, and witness the beauty of rectangles unfold before your eyes!\"
Common Misconceptions and Errors
When learning about the perimeter of squares and rectangles, certain misconceptions and errors frequently occur. Recognizing and addressing these can enhance understanding and accuracy in calculations.
- Misconception of Equal Sides: A common error is the assumption that all four sides of a rectangle are equal, which is true only for squares. This leads to incorrect perimeter calculations.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: Another frequent misunderstanding is confusing perimeter (a measure of boundary) with area (a measure of surface). These are distinct concepts and require different calculations.
- Ignoring Units of Measurement: Failing to use consistent units of measurement or to convert units appropriately can lead to errors in the final result.
- Incorrect Formula Application: Misapplying the formulas, such as using the square\"s formula for a rectangle or vice versa, is a common mistake.
- Oversimplification: Overlooking the need to measure each side, especially in irregular shapes, can lead to inaccuracies in perimeter calculations.
Addressing these misconceptions and errors is crucial for accurate and effective understanding and application of geometric principles in various contexts.
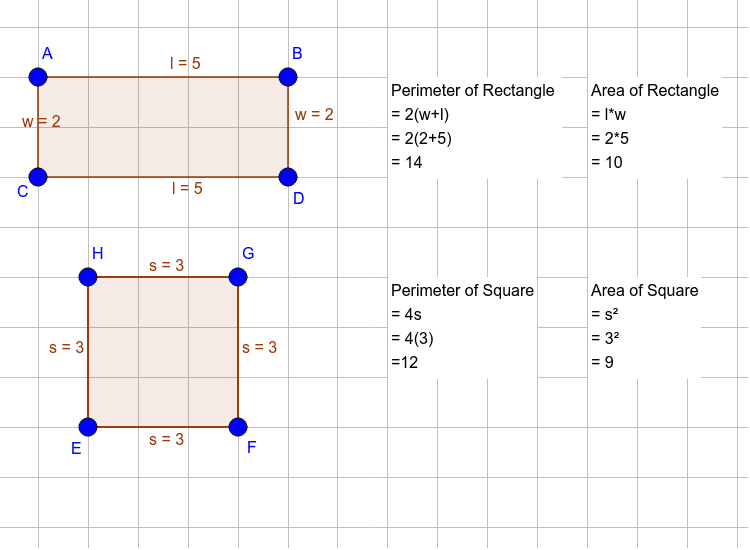
Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
Engaging with interactive examples and practice problems is a great way to deepen your understanding of the perimeter of squares and rectangles. Here are some exercises to help reinforce these concepts.
- Example 1: Calculating Square Perimeter
- Imagine a square garden with each side measuring 6 meters. Calculate its perimeter.
- Solution: Perimeter = 4 × side length = 4 × 6 = 24 meters.
- Example 2: Perimeter of a Rectangle
- A rectangular room measures 8 meters in length and 5 meters in width. What is the perimeter?
- Solution: Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) = 2 × (8 + 5) = 26 meters.
- Practice Problem 1
- Find the perimeter of a square whose side is 9 centimeters.
- Practice Problem 2
- A rectangular pool is 10 meters long and 7 meters wide. Calculate its perimeter.
These examples and problems offer a practical way to apply the formulas for perimeters, enhancing both understanding and problem-solving skills.
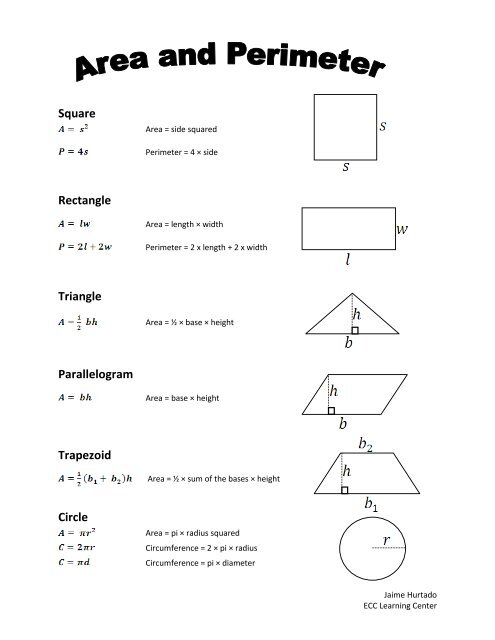
Advanced Concepts Related to Perimeter
Exploring advanced concepts related to the perimeter broadens understanding and application in more complex scenarios. These concepts are essential in higher-level mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry: In coordinate geometry, calculating the perimeter involves determining the distances between points on a plane. This requires understanding the Cartesian coordinate system and the distance formula.
- Application in Calculus: Calculus introduces the concept of a perimeter for shapes with curved sides. This involves integrating the length element over the curve, a fundamental concept in differential geometry.
- Perimeter and Trigonometry: In trigonometry, the perimeter can involve calculations using angles and lengths, especially in non-rectangular shapes. Understanding sine, cosine, and tangent ratios is crucial here.
- Optimization Problems: Advanced applications often include optimization problems where one might need to maximize or minimize the perimeter given certain constraints, applicable in fields like design and economics.
- Perimeter in Irregular Shapes: Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes often involves summing the lengths of various segments, each possibly requiring different calculation methods.
These advanced concepts illustrate the perimeter\"s versatility and its relevance in a variety of complex and practical fields.
Tools and Resources for Learning Perimeter
There are various tools and resources available for learning and teaching the concept of perimeter, especially for squares and rectangles. These resources are valuable for students, educators, and self-learners to enhance understanding and application.
- Online Calculators: Websites offering geometric calculators can help in quickly determining the perimeter of various shapes, providing a practical way to check manual calculations.
- Educational Apps: Interactive apps designed for learning math can provide engaging ways to explore perimeter concepts through games and interactive problems.
- Geometry Software: Advanced software like GeoGebra allows for visual representation and manipulation of shapes, aiding in a deeper understanding of perimeter calculations.
- Mathematics Textbooks: Standard textbooks often have dedicated sections for geometry, including detailed explanations and examples of perimeter calculations.
- Online Tutorials and Courses: Video tutorials, MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses), and educational websites offer structured lessons on geometry, including perimeter concepts.
- Worksheets and Practice Problems: Printable worksheets available online are excellent for practice and can be used by teachers in classrooms or by students for self-study.
These tools and resources are instrumental in making the learning process more effective and enjoyable, catering to a wide range of learning styles and preferences.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Tips for Teachers and Educators
Teaching the concept of perimeter, particularly for squares and rectangles, can be enriched with certain strategies and approaches. These tips are designed to enhance the learning experience for students.
- Use Real-Life Examples: Incorporate everyday objects and scenarios to demonstrate how perimeter is used, making the concept more relatable and understandable for students.
- Interactive Learning: Utilize interactive tools like geometry software or educational apps to provide a hands-on experience in calculating perimeters.
- Visual Aids: Employ diagrams and visual aids to illustrate the concept of perimeter, aiding in better comprehension for visual learners.
- Encourage Group Activities: Group projects and activities can foster collaborative learning and allow students to explore perimeter concepts together.
- Problem-Solving Sessions: Regular problem-solving sessions with varying difficulty levels can help students apply the concept of perimeter in different contexts.
- Integration with Other Concepts: Connect perimeter lessons with other geometric concepts like area, to give students a holistic understanding of geometry.
- Regular Assessments: Conduct assessments and quizzes to monitor progress and understand areas where students may need more support.
These tips aim to create an engaging and effective learning environment, helping students grasp the practical and theoretical aspects of perimeter in geometry.
In conclusion, the study of perimeters of squares and rectangles opens a gateway to understanding essential geometric principles, fostering practical skills applicable in diverse real-life scenarios and advanced mathematical contexts.