Topic what is the square root of 1/9: Understanding the square root of 1/9 is straightforward and essential for grasping basic mathematical concepts. In this article, we will explore the calculation process step-by-step, simplifying the math to make it accessible for everyone. Whether you're a student or just curious, you'll find the explanation easy to follow and informative.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 1/9
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding Fractions
- What is the Square Root?
- Calculating the Square Root of 1/9
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Numerical Approach
- Square Root of the Numerator
- Square Root of the Denominator
- Combining the Results
- Simplifying the Result
- Decimal Representation
- Visual Representation
- Applications of Square Roots
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Problems
- Summary
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của 1/9 với video hướng dẫn chi tiết. Thu hút người xem bằng cách giải thích từng bước.
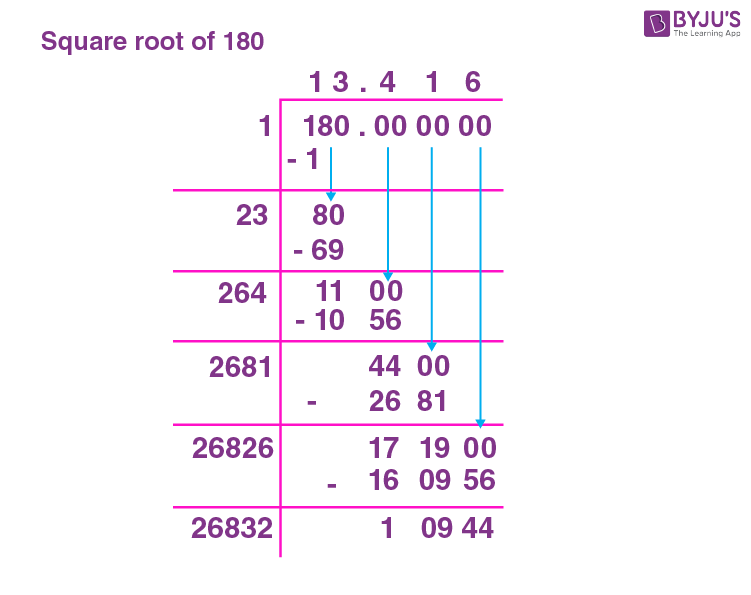
Square Root of 1/9
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the fraction , the square root can be found as follows:
Calculation Steps
- Express the fraction as a number:
- Find the square root of the numerator (1):
- Find the square root of the denominator (9):
- Combine these results into a fraction:
Result
The square root of
is
, or approximately 0.333 when expressed as a decimal.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\). The symbol for the square root is \( \sqrt{} \). The square root function is one of the most common operations in mathematics, often used in geometry, algebra, and calculus.
Square roots are particularly useful in solving quadratic equations and in various applications involving areas and volumes. They also play a significant role in statistics, physics, and engineering.
To understand square roots better, let's review some key concepts:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers that have integer square roots (e.g., 1, 4, 9, 16).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that do not have integer square roots and result in irrational numbers (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7).
- Principal Square Root: The non-negative square root of a number. For any positive number \(a\), the principal square root is denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \).
- Negative Square Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For instance, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3.
Let's illustrate the concept with a few examples:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \) |
| 4 | \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) |
| 9 | \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) |
| 16 | \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) |
| 25 | \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) |
Square roots can also be expressed in decimal form, especially for non-perfect squares. For example, the square root of 2 is approximately 1.414, and the square root of 3 is approximately 1.732.
Understanding square roots is fundamental to advancing in various fields of mathematics. In the next sections, we will explore how to calculate the square root of fractions, specifically the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \).
Understanding Fractions
A fraction represents a part of a whole and is composed of two numbers: the numerator and the denominator. The numerator, positioned above the fraction line, indicates how many parts are being considered, while the denominator, located below the line, specifies the total number of equal parts in the whole.
Fractions can be categorized into several types:
- Proper Fractions: The numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., \( \frac{1}{3} \), \( \frac{2}{5} \)).
- Improper Fractions: The numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., \( \frac{5}{3} \), \( \frac{7}{4} \)).
- Mixed Numbers: A whole number combined with a proper fraction (e.g., \( 2 \frac{1}{2} \), \( 3 \frac{3}{4} \)).
- Equivalent Fractions: Different fractions that represent the same value (e.g., \( \frac{1}{2} \) and \( \frac{2}{4} \)).
Fractions are often simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For instance, \( \frac{8}{12} \) can be simplified to \( \frac{2}{3} \) by dividing both 8 and 12 by their GCD, which is 4.
In algebra, understanding fractions is crucial when dealing with rational expressions and equations. Now, let's delve into the specific case of the fraction \( \frac{1}{9} \) and its square root.
The square root of a fraction can be found by taking the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}}
\]
Since the square root of 1 is 1 and the square root of 9 is 3, we get:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\]
This demonstrates that the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is \( \frac{1}{3} \). Understanding this process helps in simplifying expressions and solving equations involving fractions and their square roots.
What is the Square Root?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is represented by the radical symbol (√). For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 * 3 = 9.
In mathematical terms, if y is the square root of x, then:
\( y = \sqrt{x} \)
The process of finding the square root is the inverse operation of squaring a number. Squaring a number involves multiplying it by itself. Conversely, finding the square root involves determining the number which, when squared, returns the original number.
Square roots have important properties and applications in various mathematical contexts:
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive real number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, both 3 and -3 are square roots of 9.
- Principal Square Root: By convention, when we refer to the square root, we typically mean the principal (non-negative) square root.
Here are some key examples:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
For fractions, the square root can be calculated separately for the numerator and the denominator:
\( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \)
For example, to find the square root of \(\frac{1}{9}\), you calculate the square root of 1 and the square root of 9 separately:
\( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3} \)
Thus, the square root of \(\frac{1}{9}\) is \(\frac{1}{3}\).
Understanding square roots is fundamental in algebra, geometry, and many areas of advanced mathematics. They play a crucial role in solving equations, analyzing quadratic functions, and exploring various mathematical concepts.
Calculating the Square Root of 1/9
Calculating the square root of a fraction, such as \( \frac{1}{9} \), involves taking the square root of both the numerator and the denominator separately. Here are the steps to calculate the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \):
Rewrite the expression:
The square root of a fraction can be written as the fraction of the square roots:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}}
\]Calculate the square root of the numerator:
The numerator is 1, and the square root of 1 is:
\[
\sqrt{1} = 1
\]Calculate the square root of the denominator:
The denominator is 9, and the square root of 9 is:
\[
\sqrt{9} = 3
\]Combine the results:
Now, place the results of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator into the fraction:
\[
\frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\]
Thus, the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is \( \frac{1}{3} \). This process demonstrates how the square root of a fraction can be simplified by separately calculating the square roots of the numerator and the denominator and then combining the results.
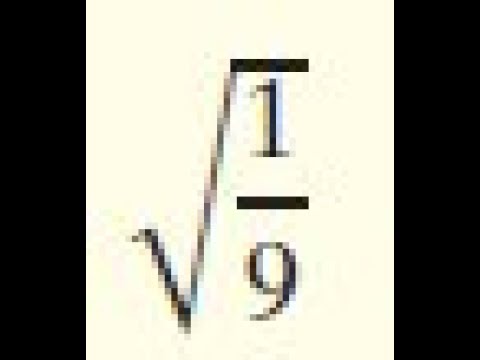
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the square root of a fraction involves breaking down the process into simpler steps. Let's calculate the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \) step by step.
- Express the fraction under the square root:
We start with the expression \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} \).
- Separate the numerator and the denominator:
Using the property of square roots that states \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \), we can rewrite our expression as:
\[ \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} \]
- Calculate the square root of the numerator:
The square root of 1 is 1:
\[ \sqrt{1} = 1 \]
- Calculate the square root of the denominator:
The square root of 9 is 3:
\[ \sqrt{9} = 3 \]
- Combine the results:
Putting it all together, we get:
\[ \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3} \]
Therefore, the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is \( \frac{1}{3} \). This process shows that by breaking down the fraction into its numerator and denominator, calculating their square roots separately, and then combining the results, we can simplify the square root of a fraction.
Numerical Approach
The numerical approach to finding the square root of a fraction, such as \( \frac{1}{9} \), involves several steps that simplify the process. Below, we detail these steps in a clear and structured manner:
-
Identify the fraction and its components. In this case, the fraction is \( \frac{1}{9} \), where 1 is the numerator and 9 is the denominator.
-
Apply the square root to both the numerator and the denominator separately. This means you calculate \( \sqrt{1} \) and \( \sqrt{9} \).
- \(\sqrt{1} = 1\)
- \(\sqrt{9} = 3\)
-
Combine the results to form the new fraction. After taking the square roots, the new fraction is:
\[
\frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\] -
Verify the result by squaring it to see if you get back the original fraction:
\[
\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^2 = \frac{1^2}{3^2} = \frac{1}{9}
\]This confirms that \( \frac{1}{3} \) is indeed the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \).
This step-by-step numerical approach simplifies the process of finding the square root of fractions, ensuring accuracy and a clear understanding of the method.
Square Root of the Numerator
The numerator of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is 1. To find the square root of 1, we can use the following steps:
- Identify the number to be squared (1 in this case).
- Apply the square root operation: \( \sqrt{1} \).
- Since the square root of 1 equals 1, the result is \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \).
Therefore, the square root of the numerator \( \sqrt{1} \) is 1.
Square Root of the Denominator
The denominator of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is 9. To find the square root of 9, follow these steps:
- Identify the number to be squared (9 in this case).
- Apply the square root operation: \( \sqrt{9} \).
- The square root of 9 is \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \).
Therefore, the square root of the denominator \( \sqrt{9} \) is 3.
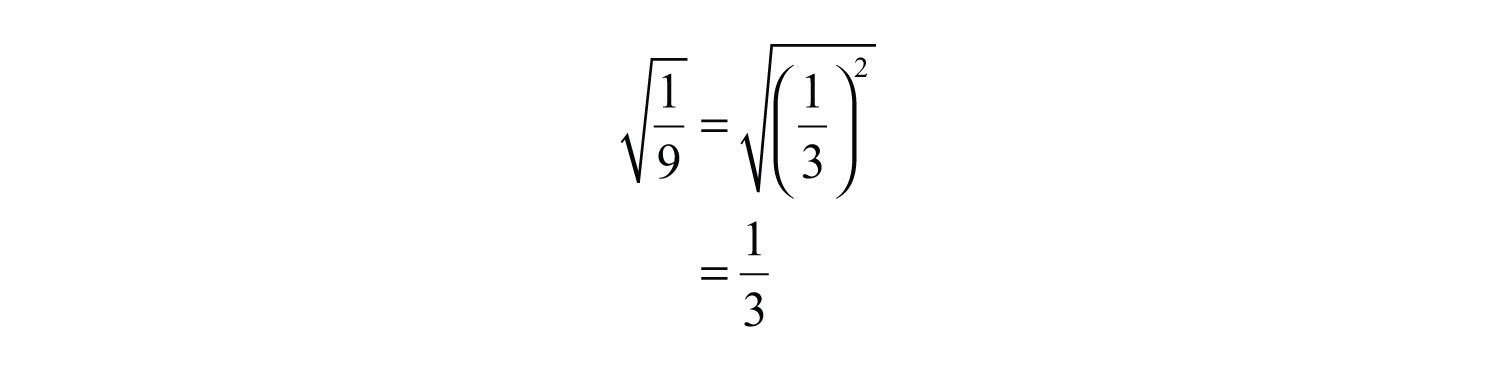
Combining the Results
Now that we have found the square roots of both the numerator and the denominator of \( \frac{1}{9} \), we can combine these results:
| Square root of the numerator: | \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \) |
| Square root of the denominator: | \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) |
Combining these results gives us:
Therefore, the square root of \( \frac{1}{9} \) is \( \frac{1}{3} \).
Simplifying the Result
To simplify \( \frac{1}{3} \), follow these steps:
- Recognize that \( \frac{1}{3} \) is already in its simplest form because 1 and 3 have no common factors other than 1.
- Therefore, \( \frac{1}{3} \) cannot be simplified further.
Hence, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} \) is \( \frac{1}{3} \).
Decimal Representation
To understand the decimal representation of the square root of 1/9, we need to follow a few steps. Let's break it down:
-
Understanding the Fraction: The fraction 1/9 represents one divided by nine. We need to find the square root of this fraction.
-
Calculating the Square Root: The square root of a fraction is the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator.
So, we calculate:
- The square root of the numerator (1) is \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \).
- The square root of the denominator (9) is \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \).
Thus, the square root of 1/9 is:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\] -
Converting to Decimal: Now, we convert the fraction 1/3 to its decimal form.
When we divide 1 by 3, we get:
1 ÷ 3 = 0.3333...
This can be represented as \( 0.\overline{3} \), which is a repeating decimal.
In conclusion, the decimal representation of the square root of 1/9 is \( 0.\overline{3} \) or approximately 0.3333 when rounded to four decimal places.
Visual Representation
To visually represent the square root of 1/9, we can use several methods including number lines, geometric shapes, and graphical plotting. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
-
Number Line:
On a number line, you can represent the square root of 1/9 (which is 1/3) by marking the point 0.333... or \( \frac{1}{3} \). This helps in understanding its relative position among other numbers.

-
Geometric Shapes:
A square's side length representing \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} \) can be illustrated. Since the area of the square is 1/9, the side length is 1/3.

-
Graphical Plotting:
You can plot the function \( y = \sqrt{x} \) and highlight the point where \( x = \frac{1}{9} \). This point will be at \( (\frac{1}{9}, \frac{1}{3}) \).

-
Fraction Representation:
Represent the fraction and its square root visually:
- \( \frac{1}{9} \) can be shown as a pie chart divided into 9 parts, with 1 part shaded.
- \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{1}{3} \) can be represented by shading one-third of another pie chart.

These visual representations help in understanding the concept of square roots and fractions better. By seeing the fraction 1/9 and its square root 1/3 in different visual formats, one can grasp the relationships between these mathematical concepts more intuitively.

Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have a wide array of applications in various fields, ranging from everyday life to advanced scientific research. Here’s a detailed exploration of some key applications:
-
Architecture and Engineering:
In architecture and engineering, square roots are used to calculate areas and dimensions accurately. For example, the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots, helps in determining distances and designing structures.
- Calculating the diagonal of a square or rectangular space using the formula \( d = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \).
- Determining natural frequencies of buildings and bridges to predict how they will react to various forces.
-
Finance:
Square roots are used in financial calculations to assess risks and returns. For instance:
- Calculating the volatility of stock prices by taking the square root of the variance.
- Determining compound interest rates and returns over multiple periods.
-
Science:
In scientific research, square roots are essential in various calculations, such as:
- Determining the standard deviation in statistics, which is the square root of the variance.
- Calculating the velocity of an object under the influence of gravity using the formula \( v = \sqrt{2gh} \), where \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity and \( h \) is the height.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development:
Square roots are frequently used in computer graphics and game development to calculate distances and rendering shapes.
- Calculating the distance between two points in a 2D or 3D space using the distance formula.
- Generating realistic movement and physics in games.
-
Medicine:
In medical imaging and radiation therapy, square roots are used to determine the dosage of radiation absorbed by tissues and to process images.
- Calculating the intensity of X-rays and other imaging techniques.
- Determining the appropriate dosage in radiation therapy based on the inverse square law.
-
Navigation:
Square roots help in navigation to calculate distances between geographical locations.
- Using the haversine formula to calculate the distance between two points on the Earth’s surface.
- Determining the shortest path in GPS navigation systems.
These applications highlight the importance of square roots in both practical and theoretical contexts, demonstrating their versatility and necessity in various domains.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the square root of 1/9, there are several common mistakes that students often make. Here’s a detailed list of these mistakes and how to avoid them:
-
Incorrectly Simplifying the Fraction:
One common error is not correctly simplifying the fraction before taking the square root. Always remember that the square root of a fraction is the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator.
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\] -
Forgetting to Simplify Radicals:
Another mistake is forgetting to simplify the radicals. Ensure you simplify the square root of both the numerator and the denominator separately before combining them.
- \(\sqrt{1} = 1\)
- \(\sqrt{9} = 3\)
-
Incorrectly Applying the Square Root Property:
Some students mistakenly apply the square root property by incorrectly handling negative signs or misinterpreting the square root function. Remember that the principal square root is always positive.
\[
\text{If } x = \sqrt{y}, \text{ then } x \geq 0 \text{ when } y \geq 0.
\] -
Mixing Up Numerator and Denominator:
When dealing with fractions, ensure you do not mix up the numerator and denominator. Double-check your work to make sure you have applied the square root to the correct parts of the fraction.
-
Misinterpreting Decimal Representation:
Another frequent mistake is misinterpreting the decimal representation of the square root of 1/9. Remember, \( \frac{1}{3} \) as a decimal is \( 0.\overline{3} \) or approximately 0.3333.
-
Ignoring the Need for Exact and Approximate Forms:
Sometimes it’s important to provide both exact and approximate forms of your answer. For example:
- Exact Form: \( \frac{1}{3} \)
- Approximate Form: 0.3333
-
Failing to Recognize Perfect Squares:
It’s crucial to recognize perfect squares in both the numerator and the denominator. This simplifies calculations significantly and reduces errors.
- \(1 = 1^2\)
- \(9 = 3^2\)
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure accurate calculations when finding the square root of 1/9.
Practice Problems
To solidify your understanding of square roots, particularly the square root of 1/9, here are some practice problems. These problems will help you apply the concepts and ensure you can handle similar calculations confidently.
-
Basic Problems:
- Calculate \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} \)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{16}} \)
- Find the square root of \( \frac{1}{25} \)
-
Intermediate Problems:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{81}} \)
- Calculate \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{49}} \)
- Find the value of \( \sqrt{\frac{16}{64}} \)
-
Advanced Problems:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{144}} \)
- Calculate \( \sqrt{\frac{25}{625}} \)
- Find the square root of \( \frac{36}{1296} \)
Below are detailed solutions for a few problems to guide you through the steps:
-
Example 1: Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} \)
- Separate the numerator and the denominator: \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}} \)
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \)
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \)
- Combine the results: \( \frac{2}{3} \)
So, \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} = \frac{2}{3} \)
-
Example 2: Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{16}} \)
- Separate the numerator and the denominator: \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{16}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{16}} \)
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \)
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \)
- Combine the results: \( \frac{1}{4} \)
So, \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{16}} = \frac{1}{4} \)
-
Example 3: Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{81}} \)
- Separate the numerator and the denominator: \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{81}} = \frac{\sqrt{9}}{\sqrt{81}} \)
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \)
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{81} = 9 \)
- Combine the results: \( \frac{3}{9} = \frac{1}{3} \)
So, \( \sqrt{\frac{9}{81}} = \frac{1}{3} \)
These practice problems will help reinforce your understanding of simplifying square roots involving fractions. Keep practicing to build your confidence and accuracy.
Summary
Understanding the square root of a fraction like \( \frac{1}{9} \) involves several key concepts and steps. Let's summarize the essential points:
-
Definition and Calculation:
The square root of a fraction is calculated by taking the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately. For \( \sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} \), this is done as follows:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{1}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{1}{3}
\] -
Decimal Representation:
The result \( \frac{1}{3} \) can be expressed in decimal form as approximately 0.3333, or \( 0.\overline{3} \) for a repeating decimal.
-
Visual Representation:
Visually, this can be represented on a number line, in a geometric shape like a square, or through graphical plotting to enhance understanding of the concept.
-
Applications:
Square roots have various applications in fields such as architecture, finance, science, computer graphics, and navigation. They are used in calculating areas, assessing risks, analyzing data, and more.
-
Common Mistakes:
Common mistakes include not simplifying the fraction correctly, misinterpreting the principal square root, and mixing up the numerator and denominator. Ensuring proper steps and understanding helps avoid these errors.
-
Practice Problems:
Practicing problems involving square roots of fractions helps reinforce understanding and accuracy. Problems can range from basic to advanced levels, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the concept.
By following these steps and understanding the principles, one can confidently calculate and apply the square root of fractions like \( \frac{1}{9} \). Keep practicing and exploring various applications to master this fundamental mathematical concept.
Additional Resources
Here are some additional resources to help you understand the square root of 1/9 in greater detail:
-
This resource provides an in-depth explanation of square roots, including video tutorials and practice problems.
-
An interactive guide to understanding square roots, complete with diagrams and examples.
-
This site offers a step-by-step tutorial on simplifying square roots and includes practice exercises.
-
Use Wolfram Alpha to perform calculations and explore more about the square root of fractions.
-
A detailed explanation and calculation of the square root of 1/9, including its properties and decimal representation.
These resources will provide you with comprehensive information and practice to master the concept of square roots, particularly the square root of 1/9.
Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của 1/9 với video hướng dẫn chi tiết. Thu hút người xem bằng cách giải thích từng bước.
Căn bậc hai của 1/9 | Căn(1/9)
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách rút gọn căn bậc hai của 1/9. Video hấp dẫn và dễ hiểu để thu hút người xem.
Rút gọn căn bậc hai của 1/9