Topic perimeter in geometry: The perimeter in geometry refers to the total length around a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by summing the lengths of all sides of the shape. This essential concept is used in various real-life applications and is fundamental in geometric studies. Understanding how to find the perimeter helps in solving complex problems involving different geometric figures.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Understanding Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
- Perimeter of Circles (Circumference)
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về chu vi trong toán học để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này và cách tính toán.
Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
The perimeter of a geometric shape is the total length of its boundary. It is an essential concept in geometry, used to measure the total distance around a two-dimensional shape.
Common Perimeter Formulas
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | P = 4a, where a is the length of a side |
| Rectangle | P = 2(l + w), where l is the length and w is the width |
| Triangle | P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides |
| Circle (Circumference) | P = 2πr, where r is the radius |
| Regular Polygon | P = ns, where n is the number of sides and s is the side length |
How to Calculate Perimeter
- Measure the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
- Add the lengths together to get the total perimeter.
Examples
- Rectangle: For a rectangle with length 30 inches and width 25 inches, the perimeter is calculated as:
P = 2(l + w) = 2(30 + 25) = 2(55) = 110 inches.
- Circle: For a circle with a radius of 7 feet, the perimeter (circumference) is:
P = 2πr = 2 × 22/7 × 7 = 44 feet.
Applications of Perimeter
Perimeter is widely used in various real-life situations, such as determining the amount of material needed to fence a garden, frame a picture, or outline a building.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry, referring to the total length around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Understanding perimeter is essential for solving various geometric problems and has practical applications in everyday life, such as determining the amount of material needed to fence a garden or frame a picture.
In general, the perimeter of a polygon is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. Here are the basic formulas for common shapes:
- Square: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a, b, \) and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius (also known as the circumference).
- Regular Polygon: \( P = n \cdot s \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side.
For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by adding up the individual side lengths, which might require measurement tools like rulers or string for more complex boundaries.
The perimeter is always measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet, depending on the context and the units used for the sides of the shape.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape in geometry is the total length of its boundary. It is a fundamental concept used to measure the distance around two-dimensional shapes. The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of a shape. For different geometric shapes, there are specific formulas to determine the perimeter.
- For a rectangle, the perimeter is calculated as: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- For a square, the perimeter is: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- For a triangle, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides: \( P = a + b + c \).
- For a circle, the perimeter is known as the circumference and is given by: \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
Understanding the perimeter helps in various real-world applications such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or designing any layout that requires the measurement of boundaries.
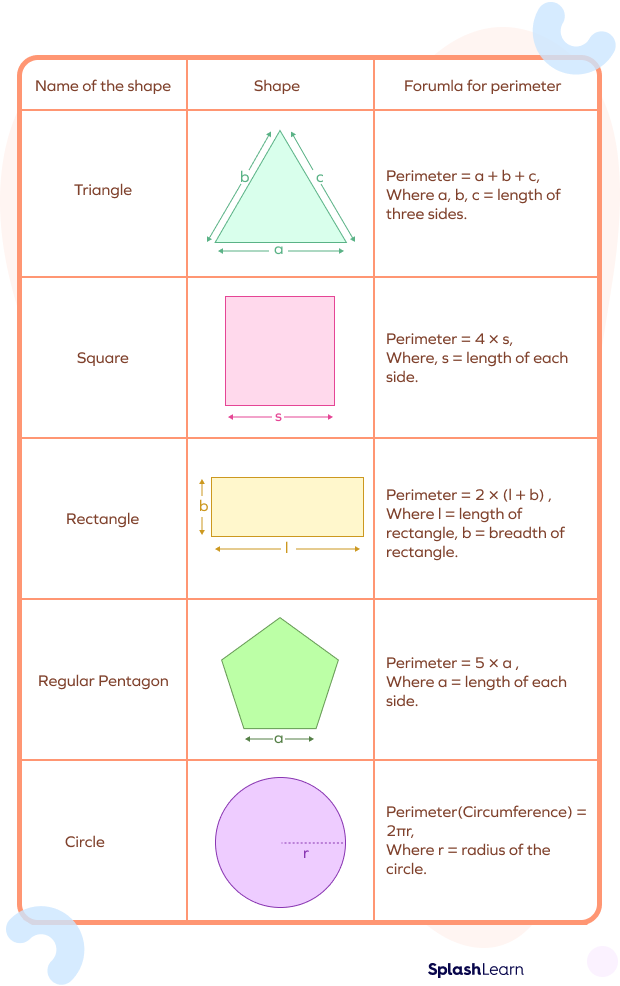
Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Here are the formulas for calculating the perimeter of various common shapes:
- Square: \(P = 4a\), where \(a\) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \(P = 2(l + b)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(b\) is the breadth.
- Triangle: \(P = a + b + c\), where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: \(P = 2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius (also known as the circumference).
- Trapezoid: \(P = a + b + c + d\), where \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Parallelogram: \(P = 2(a + b)\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
- Kite: \(P = 2(a + b)\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the pairs of equal sides.
- Regular Polygon: \(P = n \times s\), where \(n\) is the number of sides and \(s\) is the length of one side.
Understanding these formulas helps in solving various geometric problems and in practical applications such as construction, design, and more.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
The perimeter of a regular polygon is the total length around the polygon. In regular polygons, all sides and angles are equal, making the calculation straightforward. Here are the detailed steps and formulas to find the perimeter of some common regular polygons:
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Formula: \( P = 3a \)
- Where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Square
A square has four sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Formula: \( P = 4a \)
- Where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Formula: \( P = 5a \)
- Where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Formula: \( P = 6a \)
- Where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Regular Octagon
A regular octagon has eight sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Formula: \( P = 8a \)
- Where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Understanding these formulas allows for quick and efficient calculation of the perimeter of any regular polygon. By simply knowing the length of one side, you can easily determine the total perimeter.

Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
The perimeter of an irregular polygon is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. Unlike regular polygons, where each side is of equal length, irregular polygons have sides of varying lengths. To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of each side of the polygon. Ensure all measurements are in the same units.
- Add the lengths of all the sides together.
For example, if you have a pentagon with sides of lengths \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), and \(e\), the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
This method can be applied to any irregular polygon, regardless of the number of sides.
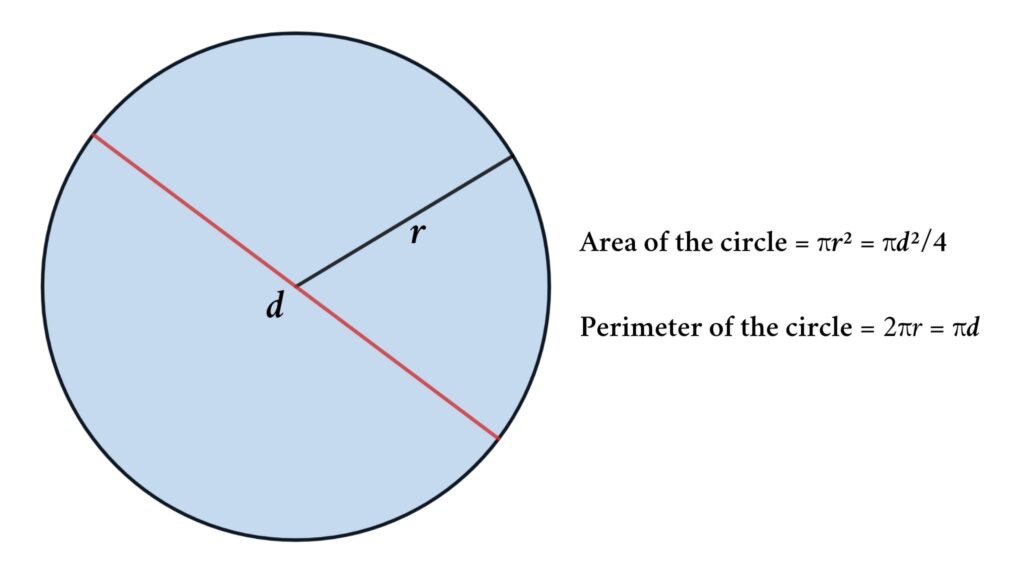
Perimeter of Circles (Circumference)
The perimeter of a circle is known as its circumference. It is the ultimate measurement around the outer boundary of the circle. Calculating the circumference of a circle requires knowing the length of its diameter or radius. The formula to find the circumference of a circle is:
C = 2πr
Where:
- C is the circumference of the circle.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
- r is the radius of the circle.
To use this formula, simply plug in the value of the radius into the equation and solve for C. Alternatively, if the diameter (d) is given instead of the radius, the formula can be written as:
C = πd
This formula states that the circumference is equal to pi times the diameter of the circle.
The circumference of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry and is used extensively in various real-life applications, such as calculating the distance around circular objects like wheels, tires, or the orbits of planets.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of perimeter finds numerous applications in real-life scenarios, where understanding the boundary or total length of an object's outline is crucial. Some practical applications include:
- Fencing: When enclosing a piece of land or property with a fence, calculating the perimeter helps in determining the amount of fencing material required.
- Construction: In construction projects, knowing the perimeter of a foundation or a structure's outline assists in estimating the quantity of materials needed, such as concrete for sidewalks or asphalt for driveways.
- Landscaping: Designing gardens or outdoor spaces often involves measuring perimeters to plan pathways, flower beds, or borders effectively.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use perimeter concepts to create balanced compositions and to ensure that their artworks fit within specified dimensions.
- Urban Planning: City planners use perimeter calculations to delineate boundaries for parks, recreational areas, and zoning districts.
- Sports: Perimeter measurements are essential in sports like basketball and soccer to define the boundaries of the playing area.
- Architecture: Architects use perimeter calculations to design buildings, rooms, and structures, ensuring that spaces are proportionate and functional.
Understanding how to calculate and apply perimeter measurements is valuable not only in mathematical contexts but also in various practical situations encountered in everyday life.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you solidify your understanding of perimeter calculations:
- Rectangle:
- Square:
- Circle:
| Length (l) | Width (w) | Perimeter (P) |
| 5 units | 3 units | 2(5 + 3) = 2(8) = 16 units |
| 8 meters | 4 meters | 2(8 + 4) = 2(12) = 24 meters |
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
| 6 units | 4(6) = 24 units |
| 10 meters | 4(10) = 40 meters |
| Radius (r) | Diameter (d) | Perimeter (P) |
| 4 units | 8 units | 2π(4) = 8π units |
| 5 meters | 10 meters | π(10) = 10π meters |
Practice solving these problems to enhance your proficiency in calculating perimeters across various shapes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some frequently asked questions about perimeter in geometry:
- What is perimeter?
- Why is perimeter important?
- How do you find the perimeter of a shape?
- Can perimeter be negative?
- What units are used to measure perimeter?
- Is perimeter the same as area?
Perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape.
Perimeter is important because it helps in determining the amount of material needed to enclose a shape, estimating distances around objects, and solving various real-life problems.
The method for finding the perimeter depends on the shape. For rectangles and squares, add the lengths of all sides. For triangles, add the lengths of all three sides. For circles, use the formula P = 2πr (if radius is given) or P = πd (if diameter is given).
No, perimeter cannot be negative. It represents a physical length and thus must be a positive value.
Perimeter can be measured in any unit of length, such as meters, centimeters, inches, etc., depending on the context of the problem.
No, perimeter and area are different. Perimeter measures the length of the boundary of a shape, while area measures the amount of space enclosed by the shape.
These answers should help clarify any questions you may have about perimeter in geometry.
Xem video về chu vi trong toán học để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này và cách tính toán.
Video về Chu vi - Giải Đoạn Toán
READ MORE:
Xem video về cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp để hiểu rõ hơn về các khái niệm này trong toán học.
Tìm Chu vi và Diện tích của Hình Hợp | Ví dụ Hình Chữ L | Toán Học | Toán với Thầy J