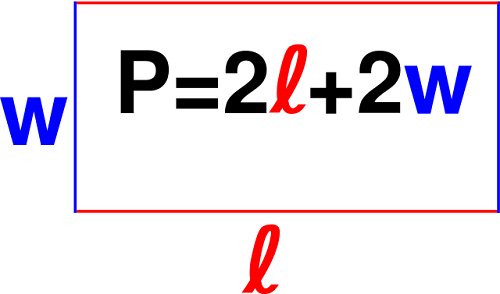Topic perimeter geometry: Unlock the secrets of perimeter geometry in this comprehensive guide. From understanding basic formulas to solving complex problems, this article delves into the fundamentals and explores advanced topics. Whether you're a student seeking clarity or a math enthusiast hungry for knowledge, embark on a journey through the world of perimeter geometry.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Perimeter Geometry
- 2. Understanding Perimeter Formulas
- 3. Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- 4. Perimeter of Basic Shapes
- 5. Perimeter of Composite Shapes
- 6. Perimeter Problems and Solutions
- 7. Perimeter and Area Relationship
- 8. Advanced Topics in Perimeter Geometry
- 9. Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và cách tính chu vi của các hình học đơn giản và phức tạp.
Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
In geometry, the perimeter refers to the total length around a two-dimensional shape. It is a fundamental concept used to determine the boundary length of various geometric figures. Below is a detailed explanation of the perimeter for different shapes, along with their formulas and applications.
Perimeter of Common Geometric Shapes
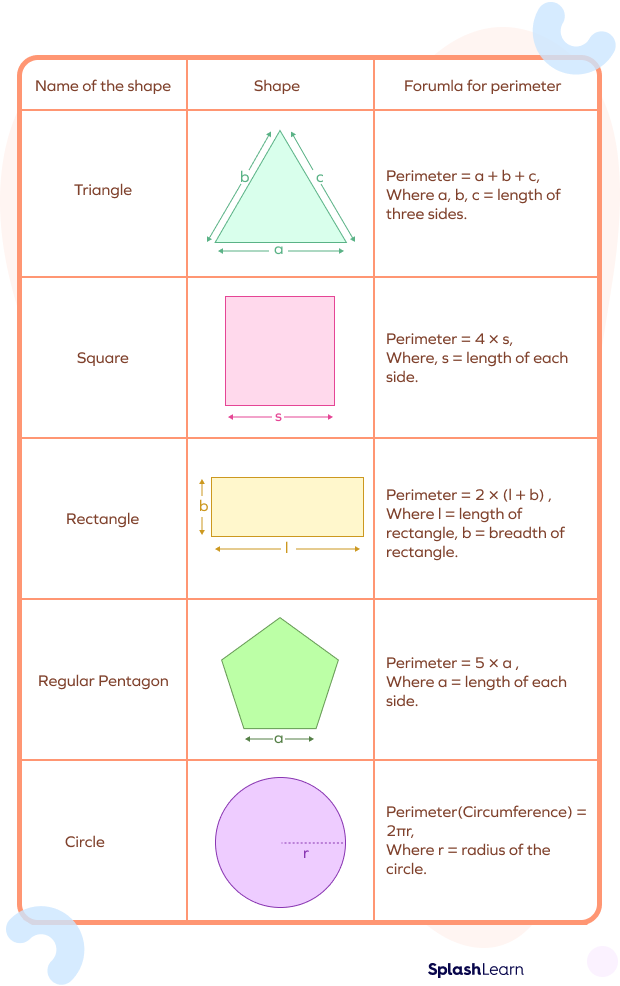
- Square: The perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4.
Formula: \( P = 4 \times a \)
- Rectangle: The perimeter is the sum of twice the length and twice the width.
Formula: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \)
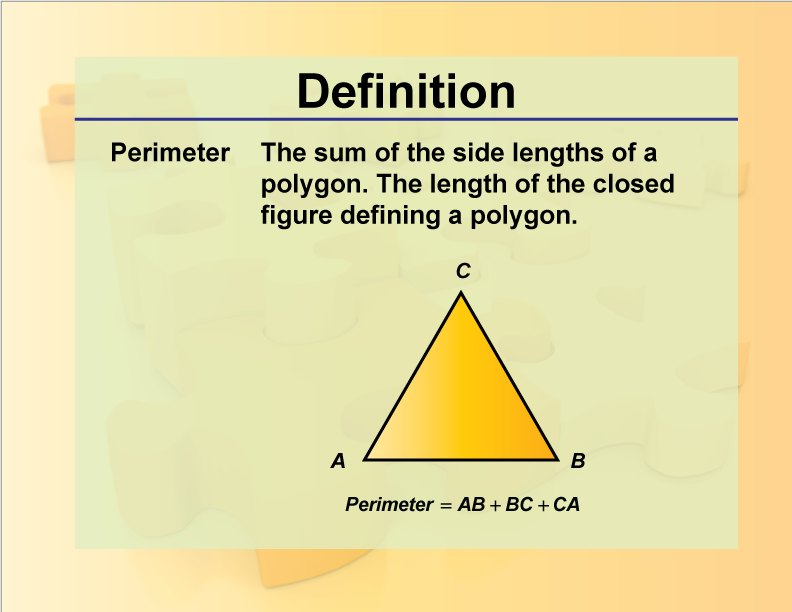
- Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of all three sides.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
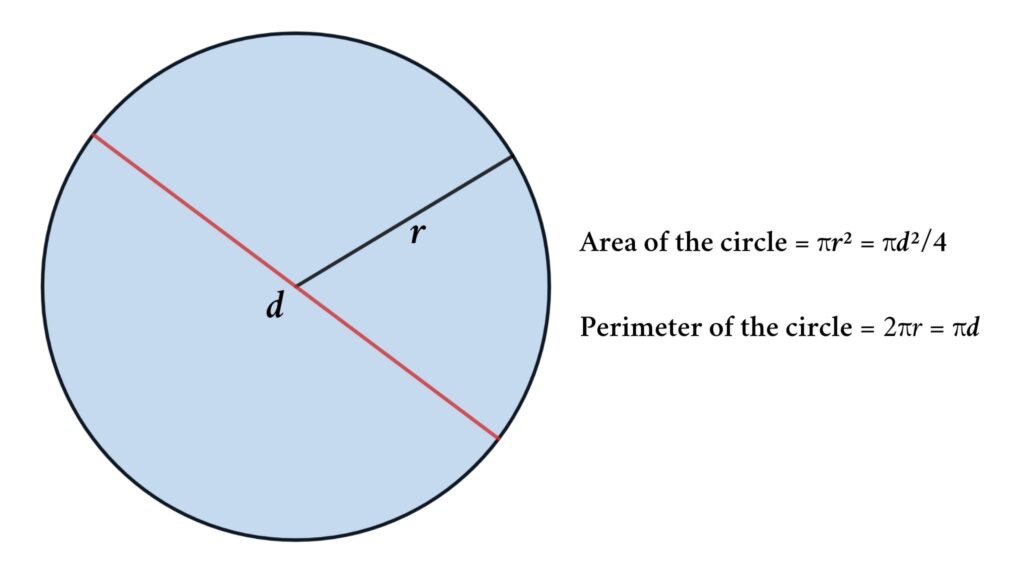
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference.
Formula: \( C = 2 \pi r \)
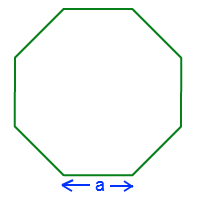
- Polygon: For a regular polygon, the perimeter is the product of the number of sides and the length of one side.
Formula: \( P = n \times s \)
Perimeter Formulas
| Shape | Perimeter Formula |
| Square | \( P = 4 \times a \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Circle (Circumference) | \( C = 2 \pi r \) |
| Regular Polygon | \( P = n \times s \) |
Applications of Perimeter
The concept of perimeter is widely used in various real-world applications, such as:
- Construction and Landscaping: Calculating the amount of material needed to fence a plot or outline a garden.
- Sports Fields: Determining the boundary length of fields and tracks.
- Art and Design: Measuring the edges of shapes in various design projects.
Visual Representations
Visual aids are highly effective for understanding the concept of perimeter. Below are some examples of how perimeters are represented in different shapes:
- Square with side length \( a \):

- Rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \):

- Circle with radius \( r \):

Interactive Learning
There are various online tools and games available that make learning about the perimeter fun and interactive. These resources provide step-by-step instructions and examples to help deepen the understanding of geometric concepts.
Explore more about perimeters and their calculations through interactive platforms and visual examples.
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Perimeter Geometry
2. Understanding Perimeter Formulas
3. Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
4. Perimeter of Basic Shapes
- 4.1 Perimeter of Squares
- 4.2 Perimeter of Rectangles
- 4.3 Perimeter of Circles
- 4.4 Perimeter of Triangles
5. Perimeter of Composite Shapes
6. Perimeter Problems and Solutions
7. Perimeter and Area Relationship
8. Advanced Topics in Perimeter Geometry
9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Perimeter Geometry
Perimeter geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of the boundaries of geometric shapes. In this section, we will explore the fundamental concepts of perimeter geometry, its importance, and how it relates to everyday life. Get ready to delve into the world of shapes and measurements!
2. Understanding Perimeter Formulas
In this section, we will delve into the various formulas used to calculate the perimeter of different geometric shapes. From simple formulas for basic shapes like squares and rectangles to more complex ones for irregular shapes, we'll cover it all. Get ready to master the art of perimeter calculation with easy-to-follow explanations and examples!
3. Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
Perimeter geometry isn't just confined to textbooks; its applications extend into various aspects of our daily lives. In this section, we'll explore how understanding perimeter helps us in real-world scenarios. From measuring fences in our backyard to calculating the amount of material needed for construction projects, discover the practical significance of perimeter geometry.

4. Perimeter of Basic Shapes
Understanding the perimeter of basic shapes is fundamental in geometry. Let's explore the perimeters of some common basic shapes:
- Rectangle:
- Square:
- Triangle:
- Circle:
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides. If the length is denoted by \(l\) and the width by \(w\), then the perimeter \(P\) can be calculated using the formula:
\(P = 2l + 2w\)
Since all sides of a square are equal, its perimeter is simply four times the length of one side. If \(s\) represents the length of a side, then the perimeter \(P\) of a square is:
\(P = 4s\)
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the three sides, then the perimeter \(P\) is:
\(P = a + b + c\)
For a circle, the perimeter is referred to as the circumference. It can be calculated using the formula:
\(C = 2\pi r\)
Where \(r\) is the radius of the circle and \(\pi\) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to \(3.14159\).
5. Perimeter of Composite Shapes
Composite shapes are combinations of two or more basic shapes. Calculating the perimeter of composite shapes involves breaking them down into simpler components and then finding the sum of their perimeters. Let's explore some common scenarios:
- L-shaped figure:
- Triangular figure:
- Combination of rectangle and semicircle:
This composite shape consists of a rectangle and a square attached to it. To find the perimeter, calculate the perimeter of each shape separately and then add them together.
If a composite shape is formed by combining two or more triangles, calculate the perimeter by summing the perimeters of individual triangles.
For this composite shape, calculate the perimeter by summing the perimeter of the rectangle and the circumference of the semicircle (which is half of the circumference of a full circle).
Remember to carefully identify the individual shapes within a composite shape and apply the appropriate perimeter formulas to each component. Then, add up the perimeters to find the total perimeter of the composite shape.
6. Perimeter Problems and Solutions
Perimeter problems often involve finding the total distance around a shape or combination of shapes. Let's explore some common types of perimeter problems and their solutions:
- Finding missing side lengths:
- Word problems:
- Composite shapes:
- Application in geometry proofs:
In some problems, you may be given the perimeter of a shape and the lengths of some sides but need to find the length of one or more missing sides. Use the perimeter formula for the given shape and the information provided to solve for the missing side lengths.
Perimeter word problems often describe real-life situations where you need to find the total distance around a given area, such as fencing a garden or outlining a picture frame. Read the problem carefully, identify the shape(s) involved, and use the appropriate perimeter formula to solve.
When dealing with composite shapes, break them down into simpler components, find the perimeters of each component, and then add them together to find the total perimeter.
Perimeter can also play a role in geometry proofs, where you may need to use the properties of perimeter to justify certain conclusions about shapes and their measurements.
By understanding different types of perimeter problems and applying the appropriate strategies, you can effectively solve perimeter-related challenges in geometry.
7. Perimeter and Area Relationship
In geometry, the relationship between perimeter and area varies depending on the shape. Let's explore this relationship for some common geometric shapes:
- Rectangle:
- Square:
- Circle:
For a rectangle, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides, while the area is the product of its length and width. As the dimensions change, the perimeter and area change accordingly, but their relationship is not directly proportional.
A square has equal sides, so its perimeter is four times the length of one side, while its area is the square of the side length. Again, as the side length changes, both the perimeter and area change, but not in a linear fashion.
For a circle, as the radius increases, both the perimeter (circumference) and area increase. However, the relationship between the two is not straightforward because the area increases with the square of the radius, while the perimeter increases linearly with the radius.
In general, while changes in perimeter and area are related, their exact relationship depends on the specific shape and its dimensions. Understanding this relationship is essential for solving geometric problems involving perimeter and area.
8. Advanced Topics in Perimeter Geometry
Advanced topics in perimeter geometry delve into more complex concepts and applications. Here are some advanced areas to explore:
- Perimeter of irregular shapes:
- Optimization problems:
- Fractal geometry:
- Perimeter in higher dimensions:
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes involves breaking them down into simpler components or using advanced techniques such as approximation methods or calculus.
In optimization problems, you aim to maximize or minimize the perimeter of a shape given certain constraints. These problems often require the use of calculus and involve finding critical points of perimeter functions.
Fractals are complex geometric shapes that exhibit self-similar patterns at different scales. Understanding the perimeter of fractals involves advanced mathematical concepts such as Hausdorff dimension and fractal dimension.
Perimeter concepts extend beyond two-dimensional shapes to higher dimensions. In three-dimensional space, perimeter is referred to as surface area, and in n-dimensional space, it is known as hypersurface area.
These advanced topics offer deeper insights into the complexities of perimeter geometry and its applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science.
9. Conclusion
Perimeter geometry is a fundamental aspect of mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields. Through this comprehensive guide, we've explored the basics of perimeter, including its definition, formulas for basic and composite shapes, common problems and solutions, the relationship between perimeter and area, and advanced topics.
By understanding perimeter geometry, individuals can solve practical problems involving measurements, design, and optimization. Moreover, exploring advanced concepts in perimeter geometry provides insights into the complexities of shape analysis and mathematical modeling.
As you continue to study and apply perimeter geometry, remember to practice problem-solving techniques, explore real-world applications, and embrace the beauty of geometric concepts.
Xem video này để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và cách tính chu vi của các hình học đơn giản và phức tạp.
Video: Toán học Hấp dẫn - Chu vi
READ MORE:
Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình hợp thành, sử dụng ví dụ về hình L.
Video: Tìm Chu vi và Diện tích của Hình Hợp thành | Ví dụ Hình L | Hình học | Toán với Thầy J