Topic what is the perimeter of a circle: Understanding what the perimeter of a circle is and how to calculate it is fundamental in geometry. This article will provide a simple yet comprehensive explanation of the concept, detailed formulas, and practical examples to help you master the calculation of a circle's circumference effortlessly.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Circle
- Introduction to the Perimeter of a Circle
- Definition and Concept of Circumference
- Formulas for Calculating the Circumference
- Using Radius to Calculate Circumference
- Using Diameter to Calculate Circumference
- Step-by-Step Calculation Examples
- Applications in Real Life
- Visual Representations and Diagrams
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để biết cách tính chu vi của hình tròn từ đường kính một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng. Hãy tìm hiểu cách áp dụng kiến thức này vào bài viết về chu vi của hình tròn!
Understanding the Perimeter of a Circle
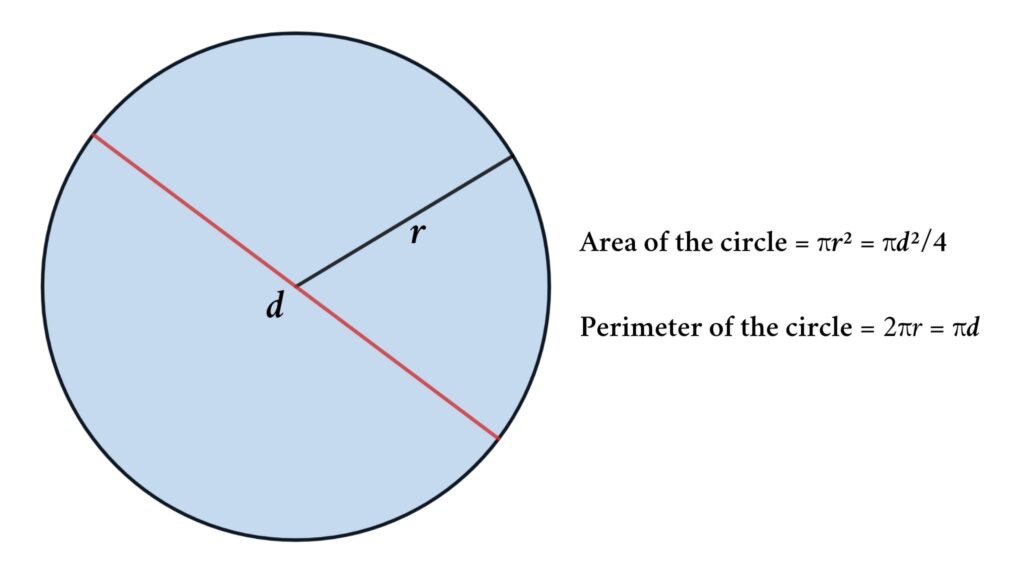
The perimeter of a circle is more commonly referred to as the circumference. It is the distance around the circle, and it can be calculated using the radius or the diameter of the circle.
Formula for the Circumference of a Circle
The formula to find the circumference of a circle is:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
where \( C \) is the circumference, \( r \) is the radius, and \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
Alternatively, if you know the diameter \( d \) of the circle, you can use the formula:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
where \( d \) is the diameter of the circle.
Examples
- If the radius of a circle is 5 units, the circumference is: \[ C = 2\pi \times 5 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ units} \]
- If the diameter of a circle is 10 units, the circumference is: \[ C = \pi \times 10 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ units} \]
Applications of the Circumference
The circumference of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry and is used in various real-world applications, including:
- Calculating the distance around circular tracks or fields.
- Determining the length of materials needed to create circular objects.
- Understanding the properties of circular objects in physics and engineering.
Visual Representation
Here is a visual representation of the elements involved in calculating the circumference of a circle:
| Element | Representation |
| Radius (\( r \)) | The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge. |
| Diameter (\( d \)) | The distance across the circle through its center; \( d = 2r \). |
| Circumference (\( C \)) | The total distance around the circle; \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \). |

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Perimeter of a Circle
The perimeter of a circle, more commonly known as the circumference, is the total distance around the circle. Understanding the circumference is a fundamental concept in geometry and has numerous practical applications. The circumference is calculated using specific formulas involving the radius or the diameter of the circle.
Key concepts to understand:
- Radius (\( r \)): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Diameter (\( d \)): The distance across the circle through its center, which is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)).
- Circumference (\( C \)): The total distance around the circle.
The formulas to calculate the circumference are:
Using the radius:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
Using the diameter:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Where \( \pi \) (pi) is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
Let's go through a step-by-step example:
- Identify the radius or diameter of the circle.
- Use the appropriate formula based on the known value (radius or diameter).
- Calculate the circumference by substituting the value into the formula.
For instance, if the radius of a circle is 7 units:
\[
C = 2\pi \times 7 = 14\pi \approx 43.98 \text{ units}
\]
If the diameter of a circle is 10 units:
\[
C = \pi \times 10 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ units}
\]
Understanding these calculations helps in various real-world scenarios, such as determining the length of materials needed to create circular objects or calculating the distance around circular tracks.
Definition and Concept of Circumference
The circumference of a circle is the distance around the outer edge of the circle. It is a linear measurement and represents the perimeter in the context of circular shapes. Understanding the concept of circumference is essential in various fields, including geometry, engineering, and everyday life.
The circumference is directly related to two main properties of the circle:
- Radius (\( r \)): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Diameter (\( d \)): The distance across the circle through its center, which is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)).
The relationship between the circumference and these properties is described by the following formulas:
Using the radius:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
Using the diameter:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Where \( \pi \) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. Pi is an irrational number, meaning it has an infinite number of decimal places without repeating.
To better understand the concept of circumference, consider the following step-by-step explanation:
- Identify the Circle's Radius or Diameter: Determine the length of the radius or diameter based on the given information.
- Choose the Appropriate Formula: Use \( C = 2\pi r \) if the radius is known, or \( C = \pi d \) if the diameter is known.
- Substitute the Values: Insert the known radius or diameter into the formula.
- Calculate the Circumference: Perform the multiplication to find the circumference.
For example, if a circle has a radius of 8 units:
\[
C = 2\pi \times 8 = 16\pi \approx 50.27 \text{ units}
\]
If a circle has a diameter of 12 units:
\[
C = \pi \times 12 = 12\pi \approx 37.70 \text{ units}
\]
Understanding the concept of circumference is crucial for solving problems involving circular shapes, whether in academic settings or practical applications such as construction, manufacturing, and design.
Formulas for Calculating the Circumference
The circumference of a circle can be calculated using two primary formulas, depending on whether you know the radius or the diameter of the circle. These formulas involve the mathematical constant \( \pi \) (pi), which is approximately equal to 3.14159.
Here are the formulas:
- Using the Radius (\( r \)):
The formula to calculate the circumference when the radius is known is:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
Where \( C \) is the circumference and \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
- Using the Diameter (\( d \)):
The formula to calculate the circumference when the diameter is known is:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Where \( C \) is the circumference and \( d \) is the diameter of the circle.
To apply these formulas effectively, follow these steps:
- Determine the Known Value: Identify whether you have the radius or the diameter of the circle.
- Select the Appropriate Formula: Choose \( C = 2\pi r \) if you know the radius, or \( C = \pi d \) if you know the diameter.
- Substitute the Value: Insert the known value (radius or diameter) into the selected formula.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply the known value by the constant \( \pi \) (and by 2 if using the radius) to find the circumference.
Let's look at some examples to illustrate these steps:
- Example 1: Calculating circumference with a known radius.
If the radius of a circle is 6 units:
\[
C = 2\pi \times 6 = 12\pi \approx 37.70 \text{ units}
\]
- Example 2: Calculating circumference with a known diameter.
If the diameter of a circle is 10 units:
\[
C = \pi \times 10 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ units}
\]
By using these formulas, you can easily determine the circumference of any circle, whether you have the radius or the diameter. This knowledge is essential for solving geometric problems and has practical applications in various fields, including engineering, construction, and design.
Using Radius to Calculate Circumference
Calculating the circumference of a circle using the radius is straightforward with the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]
Here, \( C \) represents the circumference and \( r \) represents the radius. The constant \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately equal to 3.14159. Follow these detailed steps to calculate the circumference using the radius:
- Identify the Radius: Measure or obtain the radius of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Write Down the Formula: Use the formula \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Substitute the Radius into the Formula: Replace \( r \) in the formula with the measured radius value.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply the radius by 2, then multiply the result by \( \pi \).
Let's go through an example step-by-step:
- Example: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 4 units.
- Step 1: Identify the radius, which is 4 units.
- Step 2: Write the formula: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
- Step 3: Substitute the radius value: \[ C = 2\pi \times 4 \]
- Step 4: Perform the calculation: \[ C = 8\pi \approx 25.13 \text{ units} \]
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the circumference of any circle when the radius is known. This method is fundamental in geometry and has practical applications in various fields such as engineering, construction, and design.

Using Diameter to Calculate Circumference
Calculating the circumference of a circle using the diameter is a simple process that involves the formula:
\[
C = \pi d
\]
Here, \( C \) represents the circumference and \( d \) represents the diameter. The constant \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately equal to 3.14159. Follow these detailed steps to calculate the circumference using the diameter:
- Identify the Diameter: Measure or obtain the diameter of the circle. The diameter is the distance across the circle through its center.
- Write Down the Formula: Use the formula \( C = \pi d \).
- Substitute the Diameter into the Formula: Replace \( d \) in the formula with the measured diameter value.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply the diameter by \( \pi \).
Let's go through an example step-by-step:
- Example: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 10 units.
- Step 1: Identify the diameter, which is 10 units.
- Step 2: Write the formula: \[ C = \pi d \]
- Step 3: Substitute the diameter value: \[ C = \pi \times 10 \]
- Step 4: Perform the calculation: \[ C = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \text{ units} \]
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the circumference of any circle when the diameter is known. This method is useful for quickly finding the circumference and has practical applications in various fields such as engineering, construction, and design.
Step-by-Step Calculation Examples
Here are some step-by-step examples to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter of a circle:
- Example 1: Calculating the perimeter using the radius
- Example 2: Calculating the perimeter using the diameter
Given a circle with a radius of \( r = 5 \) units:
1. Use the formula for the circumference of a circle: \( C = 2\pi r \)
2. Substitute the given radius into the formula: \( C = 2\pi \times 5 = 10\pi \) units
Given a circle with a diameter of \( d = 10 \) units:
1. Calculate the radius using the formula \( r = \frac{d}{2} \): \( r = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) units
2. Use the formula for the circumference: \( C = 2\pi r \)
3. Substitute the calculated radius into the formula: \( C = 2\pi \times 5 = 10\pi \) units
Applications in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of a circle has various practical applications in real life:
- Construction: Engineers and architects often need to calculate the perimeter of circular structures like pillars, columns, and pipelines. Knowing the perimeter helps them estimate materials required for construction.
- Landscaping: Landscape designers use circle perimeters to plan and create features such as circular gardens, ponds, or pathways. This ensures balanced and aesthetically pleasing designs.
- Infrastructure: Urban planners use circle perimeters to design roundabouts, which efficiently manage traffic flow at intersections. Understanding the perimeter helps optimize road layouts and improve traffic safety.
- Sports: Sports fields, such as soccer and basketball courts, often have circular or semi-circular boundaries. Calculating the perimeter of these boundaries ensures accurate marking and fair play.
- Manufacturing: Machinists and manufacturers utilize the perimeter of circular components in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Precise measurements ensure proper fitting and functionality of parts.
Visual Representations and Diagrams
Visual representations and diagrams are invaluable tools for understanding the concept of the perimeter of a circle. Here are some common visual aids:
- Circle Diagrams: These diagrams illustrate the relationship between the circumference, radius, and diameter of a circle. They help visualize how the perimeter is measured along the curved boundary of the circle.
- Geometric Figures: Including circles within geometric figures, such as squares or rectangles, can demonstrate the concept of perimeter comparison. This shows that the perimeter of a circle is directly related to its diameter or radius.
- Real-Life Examples: Visual representations of real-world objects with circular shapes, like wheels, plates, or clocks, help connect theoretical concepts to practical applications. These examples showcase how understanding circle perimeters is relevant in everyday life.
- Interactive Simulations: Online interactive simulations allow users to manipulate circle parameters like radius or diameter and observe changes in perimeter dynamically. This hands-on approach enhances understanding and engagement with the topic.
- Mathematical Models: Graphical representations of mathematical formulas related to circle perimeters, such as the circumference formula \( C = 2\pi r \), provide a visual framework for calculations. These models aid in conceptualizing the mathematical principles behind perimeter calculations.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Understanding the perimeter of a circle can be challenging, and certain mistakes are commonly made. Here's how to avoid them:
- Confusing Circumference with Diameter: One common mistake is mixing up the circumference (perimeter) of a circle with its diameter. Remember, the diameter is the distance across the circle through its center, while the circumference is the distance around the circle.
- Forgetting to Use the Correct Formula: Using the wrong formula to calculate the perimeter can lead to inaccurate results. Always double-check which formula to use based on the information given—whether it's the formula for circumference using radius or diameter.
- Incorrect Unit Conversion: Failing to convert units consistently can result in errors. Ensure that all measurements are in the same units before performing calculations to avoid inconsistencies in the final perimeter value.
- Not Considering Decimal Places: Rounding errors can occur when working with decimal values, especially when using the approximation of π. Be mindful of the required level of precision and round your final answer accordingly.
- Overlooking Real-Life Context: Sometimes, learners may focus solely on abstract mathematical concepts without considering their real-life applications. Understanding the practical significance of circle perimeters can help prevent misunderstandings and foster deeper comprehension.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about the perimeter of a circle:
- What is the perimeter of a circle?
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a circle?
- What units are used to measure the perimeter of a circle?
- What is π (pi), and why is it important in calculating the perimeter of a circle?
- Can the perimeter of a circle be greater than its area?
The perimeter of a circle, also known as its circumference, is the distance around the outer edge of the circle.
The perimeter of a circle can be calculated using the formula: \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( C \) is the circumference and \( r \) is the radius of the circle. Alternatively, if the diameter (\( d \)) is known, the formula \( C = \pi d \) can be used.
The perimeter of a circle is typically measured in linear units, such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet, depending on the context of the problem.
π (pi) is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. It is crucial in circle geometry as it relates the circumference, radius, and diameter of a circle through various formulas.
No, the perimeter of a circle cannot be greater than its area. The area of a circle is determined by the formula \( A = \pi r^2 \), where \( A \) is the area and \( r \) is the radius. The perimeter (circumference) is purely a measure of the boundary length and cannot exceed the area enclosed by the circle.
Conclusion and Summary
In conclusion, understanding the perimeter of a circle is essential for various mathematical and real-life applications. Through this comprehensive guide, we've covered:
- The definition and concept of circumference, which is synonymous with the perimeter of a circle.
- Formulas for calculating the circumference using either the radius or diameter of the circle.
- Step-by-step calculation examples demonstrating the application of these formulas in practice.
- Real-life applications of circle perimeters in fields such as construction, landscaping, and infrastructure design.
- Visual representations and diagrams that aid in understanding circle perimeters visually.
- Common mistakes to avoid when working with circle perimeters, along with tips for accuracy.
- Answers to frequently asked questions to address any lingering doubts or confusion.
By mastering the concept of circle perimeters, you'll not only enhance your mathematical skills but also gain valuable insights into their relevance in everyday life scenarios.
Xem video này để biết cách tính chu vi của hình tròn từ đường kính một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng. Hãy tìm hiểu cách áp dụng kiến thức này vào bài viết về chu vi của hình tròn!
Hướng dẫn tính Chu vi của Hình tròn từ Đường kính
READ MORE:
Xem video này để biết cách tính chu vi của hình tròn một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng. Hãy tìm hiểu cách áp dụng kiến thức này vào bài viết về chu vi của hình tròn!
Cách Tính Chu vi của Hình tròn