Topic difference between area and perimeter: The difference between area and perimeter is crucial for mastering geometry. While area measures the space within a shape, perimeter measures the boundary around it. This article explores these concepts, providing clear definitions, formulas, and practical examples to enhance your understanding and application in real-life scenarios. Dive in to grasp these fundamental mathematical ideas effectively.
Table of Content
- Difference Between Area and Perimeter
- Introduction
- Mathematical Formulas
- Key Differences
- Practical Examples
- Applications in Real Life
- Common Mistakes
- Visual Representations
- Interactive Learning Tools
- Practice Problems
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video giải thích sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi trong toán học cấp độ 2.
Difference Between Area and Perimeter
The concepts of area and perimeter are fundamental in geometry, often applied to various shapes and figures. Understanding their differences is essential for solving many mathematical problems. Below, we explore the definitions, formulas, and examples of both area and perimeter.
Definitions
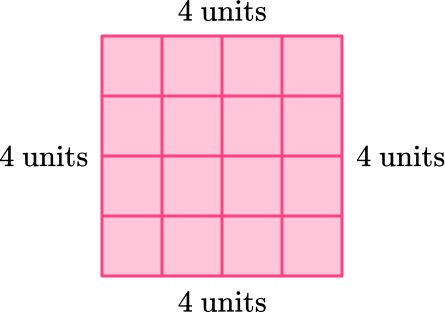
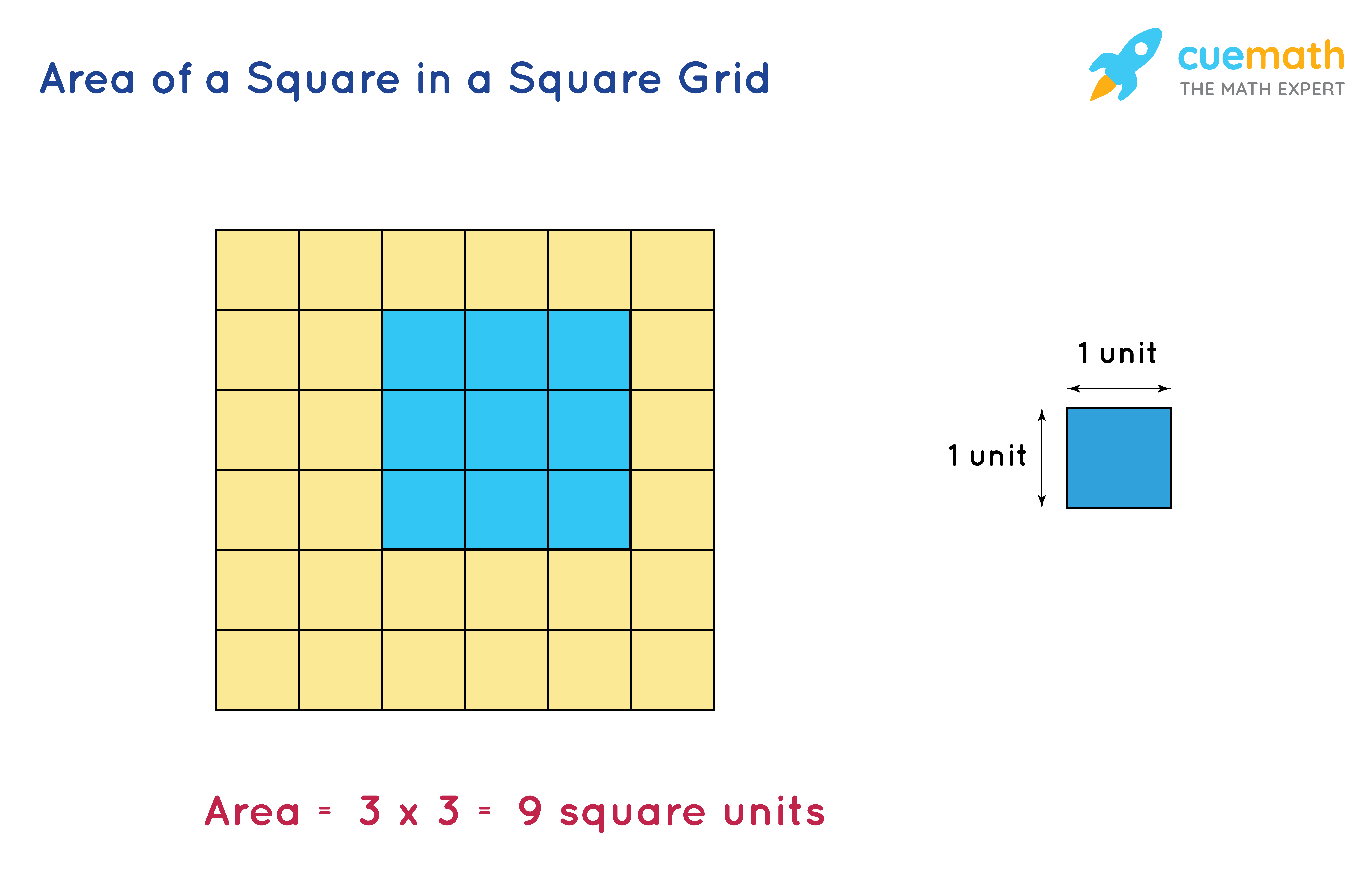
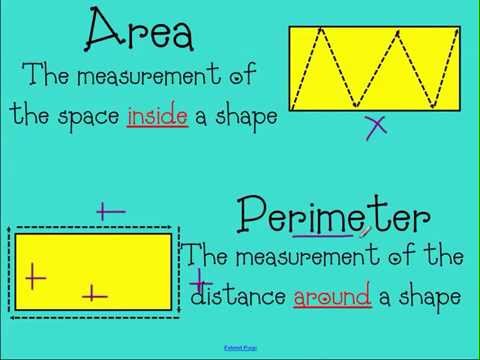
- Area: The amount of space enclosed within a shape. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet).
- Perimeter: The total distance around the boundary of a shape. It is measured in linear units (e.g., meters, feet).
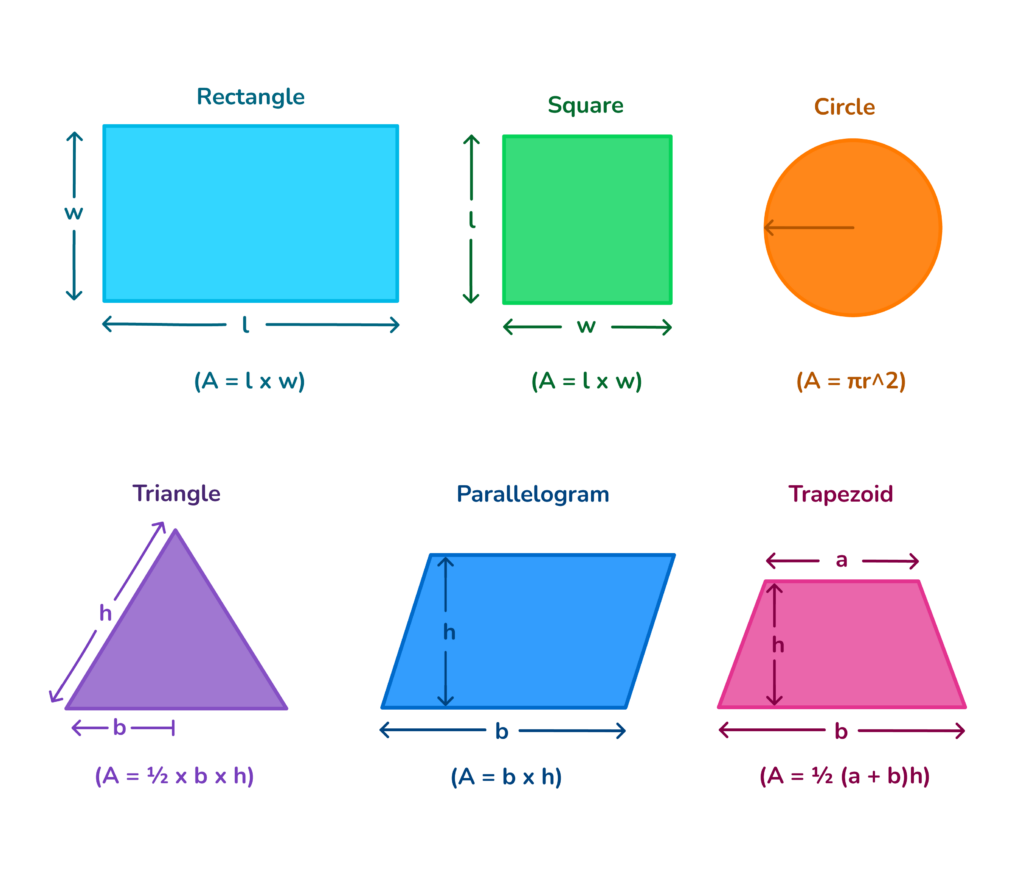
Formulas
| Shape | Area | Perimeter |
| Square | \(A = a^2\) | \(P = 4a\) |
| Rectangle | \(A = l \times w\) | \(P = 2(l + w)\) |
| Triangle | \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\) | \(P = a + b + c\) |
| Circle | \(A = \pi r^2\) | \(P = 2\pi r\) (Circumference) |
Examples
-
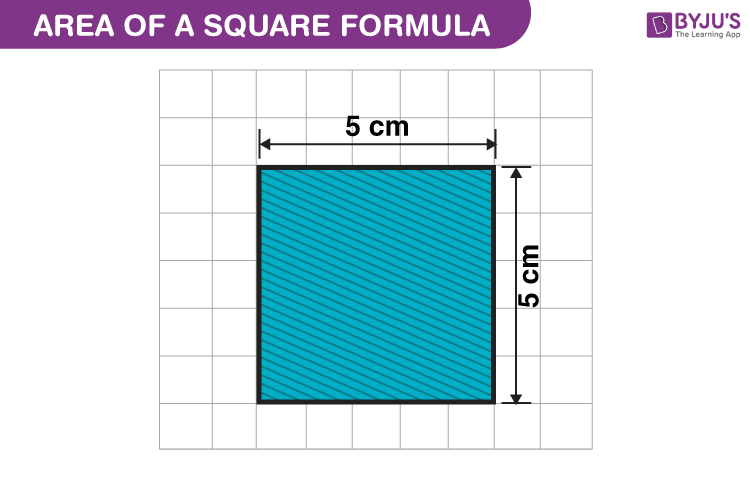
Square: A square with a side length of 5 units.
- Area: \(5^2 = 25\) square units
- Perimeter: \(4 \times 5 = 20\) units
-
Rectangle: A rectangle with a length of 6 units and a width of 3 units.
- Area: \(6 \times 3 = 18\) square units
- Perimeter: \(2(6 + 3) = 18\) units
-
Triangle: A triangle with a base of 4 units and a height of 5 units.
- Area: \(\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 5 = 10\) square units
- Perimeter: Sum of all sides (depending on the given sides)
-
Circle: A circle with a radius of 7 units.
- Area: \(\pi \times 7^2 \approx 154\) square units
- Perimeter (Circumference): \(2\pi \times 7 \approx 44\) units
In conclusion, while the area measures the space within a shape, the perimeter measures the distance around the shape. Both concepts are crucial for different applications in geometry and real-life scenarios.
READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the difference between area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry. Both are crucial concepts used to measure various properties of shapes. Area refers to the amount of space enclosed within a shape, calculated in square units, while perimeter is the total length of the boundaries of a shape, measured in linear units. These concepts are widely applicable in real-world scenarios, such as in construction, architecture, and various fields of engineering.
The area of a shape can be found using specific formulas depending on the type of shape, such as squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles. For example, the area of a rectangle is calculated as length multiplied by width, while the area of a circle is found using the formula \(A = \pi r^2\), where \(r\) is the radius.
Perimeter, on the other hand, involves summing the lengths of all sides of a shape. For instance, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated as \(P = 2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width. The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is found using \(C = 2\pi r\).
Both area and perimeter are essential for solving practical problems. For instance, determining the amount of paint needed to cover a wall requires knowing its area, while calculating the length of fencing required to enclose a garden involves its perimeter. These measurements are vital tools in various fields, demonstrating the importance of understanding their differences and applications.
Mathematical Formulas
Understanding the mathematical formulas for area and perimeter is crucial for solving geometry problems. Here, we present the formulas for various common shapes:
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \( \text{Area} = a^2 \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 4a \) |
| Rectangle | \( \text{Area} = l \times w \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) \) |
| Triangle | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \) |
| Circle | \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \) | \( \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r \) |
| Parallelogram | \( \text{Area} = \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b) \) |
| Trapezoid | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d \) |
Let's break down these formulas step by step for better understanding:
-
Square:
- Area: Multiply the length of one side by itself: \( a \times a = a^2 \).
- Perimeter: Add up all four sides: \( 4 \times a \).
-
Rectangle:
- Area: Multiply the length by the width: \( l \times w \).
- Perimeter: Add together the lengths of all four sides: \( 2(l + w) \).
-
Triangle:
- Area: Multiply the base by the height, then divide by 2: \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- Perimeter: Add the lengths of all three sides: \( a + b + c \).
-
Circle:
- Area: Multiply pi by the radius squared: \( \pi r^2 \).
- Perimeter (Circumference): Multiply 2 by pi and the radius: \( 2\pi r \).
-
Parallelogram:
- Area: Multiply the base by the height: \( \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- Perimeter: Add the lengths of the opposite sides: \( 2(a + b) \).
-
Trapezoid:
- Area: Add the lengths of the two bases, multiply by the height, and then divide by 2: \( \frac{1}{2} (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \).
- Perimeter: Add the lengths of all four sides: \( a + b + c + d \).
Key Differences
Understanding the differences between area and perimeter is essential for solving various mathematical problems and applying these concepts in real-life scenarios. Below are the key differences between area and perimeter:
- Definition: The area is the measurement of the surface of an object, whereas the perimeter is the measurement of the boundary that surrounds a closed geometrical figure.
- Units: Area is measured in square units such as square meters (m²), square feet (ft²), etc., while perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters (m), feet (ft), etc.
- Dimensions: Area involves two dimensions (length and width), making it a measure of the space inside a shape. Perimeter involves only one dimension, measuring the total length around a shape.
- Applications: Area is used to determine the amount of space inside a boundary, useful in contexts like tiling a floor or painting a wall. Perimeter is used to determine the length of the boundary, useful in contexts like fencing a garden or framing a picture.
- Formulas:
- For a square: Area = \(a^2\) and Perimeter = \(4a\), where \(a\) is the length of a side.
- For a rectangle: Area = \(l \times w\) and Perimeter = \(2(l + w)\), where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- For a circle: Area = \(\pi r^2\) and Perimeter (circumference) = \(2\pi r\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- For a triangle: Area = \(\frac{1}{2} b h\) and Perimeter = \(a + b + c\), where \(b\) is the base, \(h\) is the height, and \(a, b, c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- For a parallelogram: Area = \(b \times h\) and Perimeter = \(2(a + b)\), where \(b\) is the base, \(h\) is the height, and \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the sides.
- For a trapezoid: Area = \(\frac{1}{2}(a + b)h\) and Perimeter = \(a + b + c + d\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the parallel sides, \(h\) is the height, and \(c\) and \(d\) are the lengths of the non-parallel sides.
In summary, while both area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in mathematics, they serve different purposes and are applied in various practical situations. Mastery of these concepts allows for accurate measurement and efficient problem-solving in both academic and real-world contexts.
Practical Examples
Understanding the practical application of the concepts of area and perimeter is crucial in various real-life scenarios. Let's delve into some examples:
- Fencing a Garden: Imagine you have a rectangular garden and want to install a fence around it. To determine the amount of fencing material needed, you would calculate the perimeter of the garden, which is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. This helps you purchase the right amount of fencing material.
- Tiling a Floor: When tiling a floor, you need to know the area of the floor space to estimate the number of tiles required. Area calculation involves multiplying the length by the width. Knowing the area helps you purchase the correct quantity of tiles and adhesive.
- Painting a Wall: Before painting a wall, you calculate its surface area to determine how much paint is needed. This involves measuring the length and height of the wall and multiplying these dimensions to get the area. Accurate calculation ensures you buy the right amount of paint without excess or shortage.
- Wrapping Gifts: When wrapping gifts, the amount of wrapping paper needed depends on the surface area of the item being wrapped. Irregularly shaped items may require additional paper to cover them adequately, making area calculation essential for minimizing waste.

Applications in Real Life
Understanding how area and perimeter concepts apply to real-life situations is essential for practical problem-solving. Here are some everyday applications:
- Construction: In construction projects, understanding area and perimeter helps in estimating material quantities. For example, calculating the area of land for building foundations and determining the perimeter for fencing or landscaping.
- Architecture: Architects use area and perimeter calculations extensively when designing buildings. They consider the floor area for space planning and the perimeter for designing exteriors and landscaping.
- Interior Design: Interior designers rely on area calculations to optimize space utilization. They measure room dimensions to determine furniture layouts and calculate the perimeter for installing moldings or trim.
- Landscaping: Landscapers use area measurements to plan garden layouts and determine the amount of sod or mulch needed. Perimeter calculations help in designing pathways, retaining walls, and fencing.
- Education: Teachers use practical examples involving area and perimeter to enhance students' understanding of geometry. Real-life applications make learning more engaging and relevant.
Common Mistakes
Understanding the distinctions between area and perimeter can help avoid common errors. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
- Confusing Definitions: One common mistake is mixing up the definitions of area and perimeter. Area refers to the space enclosed within a shape, while perimeter is the distance around the boundary of the shape.
- Incorrect Units: Using incorrect units or forgetting to include units in calculations can lead to errors. It's essential to ensure consistency in units (e.g., square meters for area, meters for perimeter).
- Ignoring Dimensional Differences: Sometimes, people overlook the dimensional differences between area and perimeter. Area is measured in square units, while perimeter is measured in linear units.
- Underestimating Importance: Another mistake is underestimating the importance of understanding area and perimeter in various contexts, leading to inaccurate estimations or decisions in real-life situations.
- Overlooking Irregular Shapes: Ignoring irregular shapes and treating them as regular shapes can result in inaccurate calculations. It's crucial to apply appropriate formulas or techniques for irregular geometries.
Visual Representations
Visual aids are valuable tools for understanding the concepts of area and perimeter. Here are some effective visual representations:
- Diagrams: Simple diagrams illustrating the difference between area and perimeter can enhance comprehension. Visualizing shapes and their dimensions helps in grasping the concepts.
- Interactive Apps: There are various interactive apps and online tools available that allow users to manipulate shapes, change dimensions, and observe how it affects area and perimeter. These apps provide hands-on learning experiences.
- Graphical Comparisons: Graphical comparisons, such as bar charts or pie charts, can visually represent the relationship between area and perimeter. These comparisons can highlight differences in magnitude or proportions.
- Real-Life Examples: Using real-life examples, such as images of buildings, gardens, or sports fields, can help relate abstract concepts to concrete situations. Visualizing familiar scenarios enhances understanding.
- Animated Tutorials: Animated tutorials or videos can dynamically illustrate concepts of area and perimeter. Seeing shapes change and measurements adjust in real-time enhances engagement and retention.
Interactive Learning Tools
Interactive learning tools offer engaging ways to explore the differences between area and perimeter. Here are some examples:
- Geometry Apps: Numerous mobile apps and web-based platforms provide interactive geometry lessons. These apps often include quizzes, games, and simulations to reinforce understanding of area and perimeter concepts.
- Online Calculators: There are many online calculators specifically designed for calculating area and perimeter of various shapes. These calculators often allow users to input dimensions and instantly see the calculated results.
- Virtual Manipulatives: Virtual manipulatives allow users to manipulate geometric shapes on a digital platform. These tools enable hands-on exploration of area and perimeter, making abstract concepts more tangible.
- Math Games: Educational games focused on geometry can be effective interactive learning tools. Games that involve constructing shapes, solving puzzles, or completing challenges help reinforce understanding while keeping learners entertained.
- Simulations: Interactive simulations provide visual representations of geometric concepts in action. Users can adjust parameters, observe changes in shape or size, and analyze the effects on area and perimeter, fostering deeper understanding.
Practice Problems
Practice problems are an excellent way to reinforce understanding and mastery of area and perimeter concepts. Here are some sample problems to try:
- Rectangle Area: Calculate the area of a rectangle with length 8 units and width 5 units.
- Square Perimeter: Find the perimeter of a square with sides measuring 10 meters each.
- Circle Area: Determine the area of a circle with a radius of 6 centimeters (use π = 3.14).
- Triangle Perimeter: Calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 7 cm, 10 cm, and 12 cm.
- Irregular Shape Area: Find the area of an irregular shape by breaking it down into simpler shapes and summing their areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between area and perimeter is essential for various practical applications in everyday life. While area represents the space enclosed within a shape, perimeter denotes the distance around its boundary. Mastery of these concepts enables accurate measurements, efficient planning, and informed decision-making in fields such as construction, architecture, and interior design. By utilizing visual representations, interactive learning tools, and practicing with sample problems, individuals can enhance their understanding and proficiency in applying area and perimeter calculations. Embracing these concepts not only enriches mathematical skills but also fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, ultimately empowering individuals to tackle real-world challenges with confidence.
Video giải thích sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi trong toán học cấp độ 2.
Sự khác biệt giữa diện tích và chu vi? Toán học cấp độ 2
READ MORE:
Video giải thích sự khác biệt giữa chu vi và diện tích, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về hai khái niệm này trong toán học.
Sự Khác Biệt Giữa Chu Vi và Diện Tích