Topic perimeter of scalene triangle: Discover how to calculate the perimeter of a scalene triangle, a type of triangle with three unequal sides. This article will guide you through the process, provide practical examples, and explain related concepts in geometry. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, you'll find valuable information to deepen your understanding of scalene triangles.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of Scalene Triangle
- Introduction to Scalene Triangles
- Definition of Scalene Triangle
- Properties of Scalene Triangles
- Formulas Related to Scalene Triangles
- Examples and Solved Problems
- Applications of Scalene Triangles
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về giới thiệu về tam giác nhọn cạnh và cách tính diện tích cũng như chu vi của tam giác nhọn cạnh.
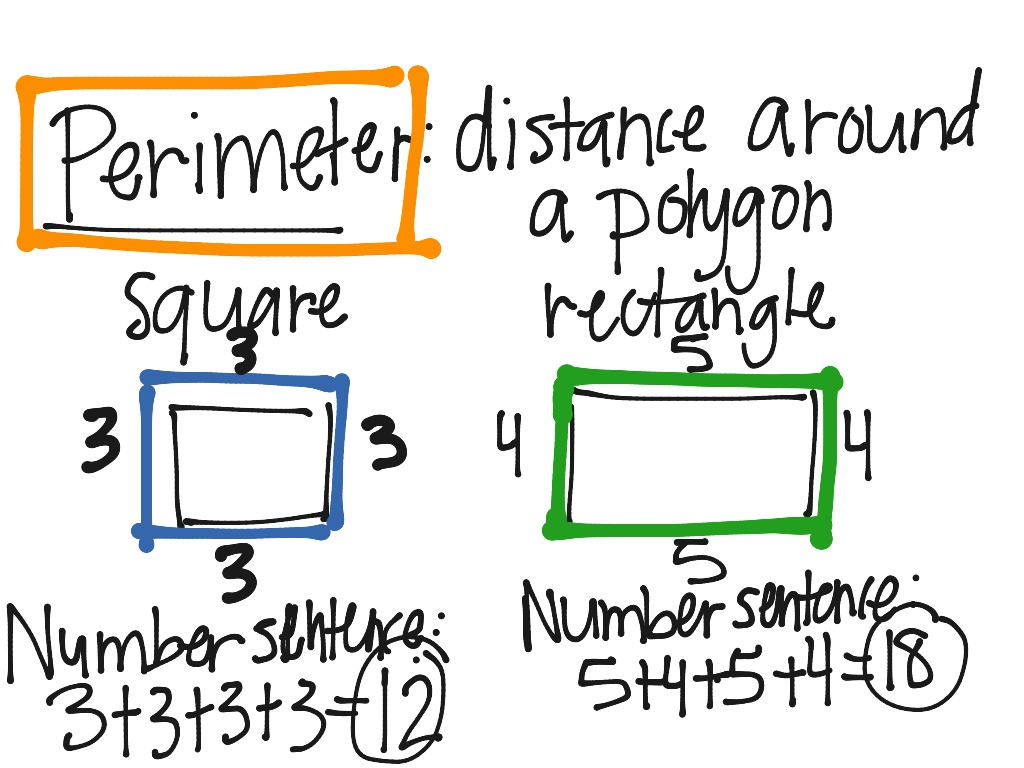
Perimeter of Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle where all three sides have different lengths and all three angles have different measures. The perimeter of a scalene triangle can be calculated using the lengths of its sides.
Definition
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of all its sides. For a scalene triangle, this can be calculated with the formula:
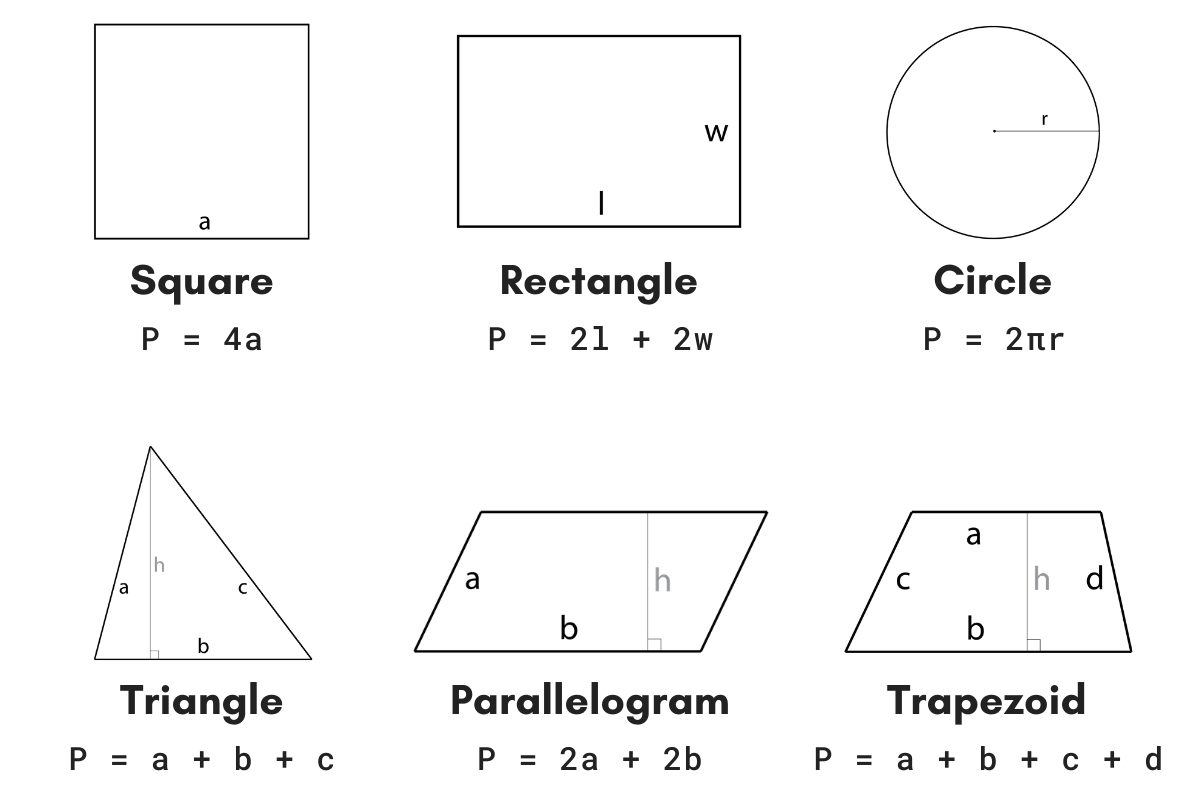
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Properties of a Scalene Triangle
- All three sides have different lengths.
- All three angles have different measures.
- No sides are parallel.
- No line of symmetry.
- The sum of the angles is always 180 degrees.
- Can be acute, obtuse, or right-angled.
Example Calculation
Consider a scalene triangle with sides of lengths 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm.
Using the perimeter formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 \, \text{cm} \]
Types of Scalene Triangles
Scalene triangles can be further classified into:
- Acute scalene triangle: All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse scalene triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
- Right scalene triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
Using the Law of Cosines
If two sides and the included angle are known, the third side can be calculated using the Law of Cosines:
\[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma) \]
where \( \gamma \) is the angle opposite side \( c \).
Semi-Perimeter
The semi-perimeter (\( s \)) is half of the perimeter of the triangle:
\[ s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \]
The semi-perimeter is often used in Heron's formula to calculate the area of the triangle:
\[ \text{Area} = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \]
| Side | Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| a | 5 |
| b | 7 |
| c | 9 |
| Perimeter | 21 |
Conclusion
Understanding the properties and formulas related to the perimeter of a scalene triangle helps in solving various geometric problems. Whether the triangle is defined by its sides or by its angles and one side, knowing how to calculate the perimeter is fundamental in geometry.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Scalene Triangles
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle where all three sides have different lengths, and all three angles are of different measures. Unlike isosceles and equilateral triangles, scalene triangles do not have any sides or angles that are equal.
Scalene triangles can be classified based on their angles into three types:
- Acute Scalene Triangle: All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Scalene Triangle: One of the angles is greater than 90 degrees.
- Right Scalene Triangle: One of the angles is exactly 90 degrees.
Some key properties of scalene triangles include:
- No sides of equal length.
- No angles of equal measure.
- No lines of symmetry.
Scalene triangles are versatile and can appear in various geometric problems and real-life applications. Their unique property of having all sides and angles different makes them an interesting subject in geometry.
The perimeter of a scalene triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. If the sides of the triangle are denoted as \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
The area of a scalene triangle can be calculated using different methods depending on the known values. If the base \(b\) and height \(h\) are known, the area \(A\) is given by:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \]
Alternatively, if the lengths of all three sides are known, Heron's formula can be used to find the area. First, calculate the semi-perimeter \(s\) as:
\[ s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \]
Then, the area \(A\) is given by:
\[ A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \]
Understanding these basic properties and formulas of scalene triangles is essential for solving various geometric problems and appreciating their unique characteristics.
Definition of Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle in which all three sides are of different lengths, and consequently, all three internal angles are also of different measures. Unlike isosceles or equilateral triangles, scalene triangles have no sides or angles that are equal.
- Unequal Sides: Each side of a scalene triangle has a distinct length.
- Unequal Angles: Each angle within a scalene triangle has a different measure, summing up to 180 degrees.
- No Lines of Symmetry: Scalene triangles do not have any lines of symmetry, meaning they cannot be divided into two identical halves.
To identify a scalene triangle, measure all three sides and angles. If none of the sides or angles are equal, the triangle is scalene.
Scalene triangles can be further classified based on their angles:
- Acute Scalene Triangle: All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Scalene Triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
- Right Scalene Triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees.
In geometry, understanding scalene triangles is crucial for solving various problems related to triangle properties, perimeter, and area calculations.
Properties of Scalene Triangles
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle where all three sides have different lengths. Understanding the properties of scalene triangles is essential for various mathematical calculations and geometric analyses.
Here are some key properties of scalene triangles:
- Unequal Sides: As mentioned, all three sides of a scalene triangle have different lengths.
- Unequal Angles: Corresponding to the unequal sides, the angles of a scalene triangle are also different from one another.
- No Symmetry: Unlike equilateral or isosceles triangles, scalene triangles lack any form of symmetry. This absence of symmetry complicates their geometric properties and calculations.
- No Congruent Parts: Since all sides and angles are different, there are no congruent parts within a scalene triangle.
- Unique Perimeter: The perimeter of a scalene triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Due to the unequal sides, the perimeter is unique for each scalene triangle.
- Unique Area: Similarly, the area of a scalene triangle is determined by its base and height, following the formula: Area = ½ × base × height. Alternatively, Heron's formula can be used if all three side lengths are known.
Formulas Related to Scalene Triangles
When dealing with scalene triangles, several formulas come in handy for various calculations. Let's explore some of the most important ones:
- Perimeter Formula:
- Semi-Perimeter Formula:
- Area Formulas:
- Using Base and Height:
- Using Heron's Formula:
The perimeter of any triangle, including a scalene triangle, is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
For a scalene triangle with side lengths a, b, and c, the perimeter (P) is given by:
\( P = a + b + c \)
The semi-perimeter of a triangle is half of its perimeter. It's often denoted by \( s \).
For a scalene triangle with perimeter P, the semi-perimeter (s) is calculated as:
\( s = \frac{P}{2} \)
Calculating the area of a scalene triangle can be done using various methods, including:
If the base (b) and the corresponding height (h) of the triangle are known, the area (A) can be calculated using the formula:
\( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
Heron's Formula is particularly useful when the lengths of all three sides are known. It calculates the area (A) using the lengths of the sides: a, b, and c.
Let \( s \) be the semi-perimeter of the triangle, then the area (A) is given by:
\( A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \)

Examples and Solved Problems
Let's dive into some examples and solved problems to better understand how to calculate the perimeter of a scalene triangle:
- Example 1:
- Example 2:
- Example 3:
Find the perimeter of a scalene triangle with side lengths \( a = 5 \), \( b = 7 \), and \( c = 9 \).
Solution:
Using the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \), we can plug in the given side lengths:
\( P = 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 \)
So, the perimeter of the triangle is 21 units.
Given a scalene triangle with side lengths \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), and \( c = 6 \), determine its perimeter.
Solution:
Applying the perimeter formula:
\( P = 3 + 4 + 6 = 13 \)
Therefore, the perimeter of this triangle is 13 units.
Calculate the perimeter of a scalene triangle with side lengths \( a = 8 \), \( b = 12 \), and \( c = 15 \).
Solution:
Using the perimeter formula:
\( P = 8 + 12 + 15 = 35 \)
Hence, the perimeter of this triangle is 35 units.
Applications of Scalene Triangles
Scalene triangles find various applications in real-life scenarios. Let's explore some of them:
- Architecture and Construction:
- Engineering and Mechanics:
- Surveying and Mapping:
- Art and Design:
- Geometry and Mathematics:
In architecture and construction, scalene triangles are often encountered when designing irregular-shaped structures, such as roofs, facades, and bridges.
Engineers use scalene triangles in structural analysis and design. They are essential in calculating forces and stresses in trusses, frames, and other mechanical systems.
Surveyors rely on scalene triangles for measuring distances and angles in land surveying and cartography. They help create accurate maps and plans of land areas.
Artists and designers often incorporate scalene triangles in their compositions to create dynamic and visually appealing arrangements. They provide balance and asymmetry in various art forms.
Scalene triangles serve as important subjects for geometric studies and mathematical analyses. They help in understanding concepts such as trigonometry, similarity, and the Pythagorean theorem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions regarding the perimeter of scalene triangles:
- What is a scalene triangle?
- How do you find the perimeter of a scalene triangle?
- Can a scalene triangle have sides with negative lengths?
- Is the perimeter of a scalene triangle always greater than the sum of its two shortest sides?
- How do you determine if three given side lengths form a scalene triangle?
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle in which all three sides have different lengths. Unlike equilateral or isosceles triangles, none of the angles are equal.
The perimeter of any triangle, including a scalene triangle, is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. You simply add the lengths of the three sides together to calculate the perimeter.
No, by definition, the lengths of the sides of a triangle must be positive. Negative lengths or zero lengths are not possible for the sides of a triangle, including scalene triangles.
Yes, the perimeter of a scalene triangle is always greater than the sum of its two shortest sides. This is because the third side, being the longest, adds to the total perimeter, making it greater than the sum of the other two sides.
To determine if three given side lengths form a scalene triangle, you need to check if no two sides are equal in length. If all three sides have different lengths, then the triangle is scalene.
Xem video về giới thiệu về tam giác nhọn cạnh và cách tính diện tích cũng như chu vi của tam giác nhọn cạnh.
Khái niệm về Tam giác Nhọn Cạnh|Diện tích và Chu vi của Tam giác Nhọn Cạnh
READ MORE:
Xem video về cách tính chu vi của tam giác nhọn cạnh và các bước thực hiện.
Chu vi của Tam giác Nhọn Cạnh