Topic perimeter of half circle: Understanding the perimeter of a half circle is crucial for various practical applications in mathematics and engineering. This guide will take you through the basics, provide step-by-step calculations, and highlight common mistakes to avoid. Dive in to enhance your knowledge and apply these concepts with confidence in real-world scenarios.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Basic Concepts and Definitions
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Step-by-Step Derivation of the Formula
- Example Calculations
- Applications in Real Life
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Topics Related to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Summary and Key Takeaways
- Further Reading and Resources
- YOUTUBE:
Perimeter of a Half Circle
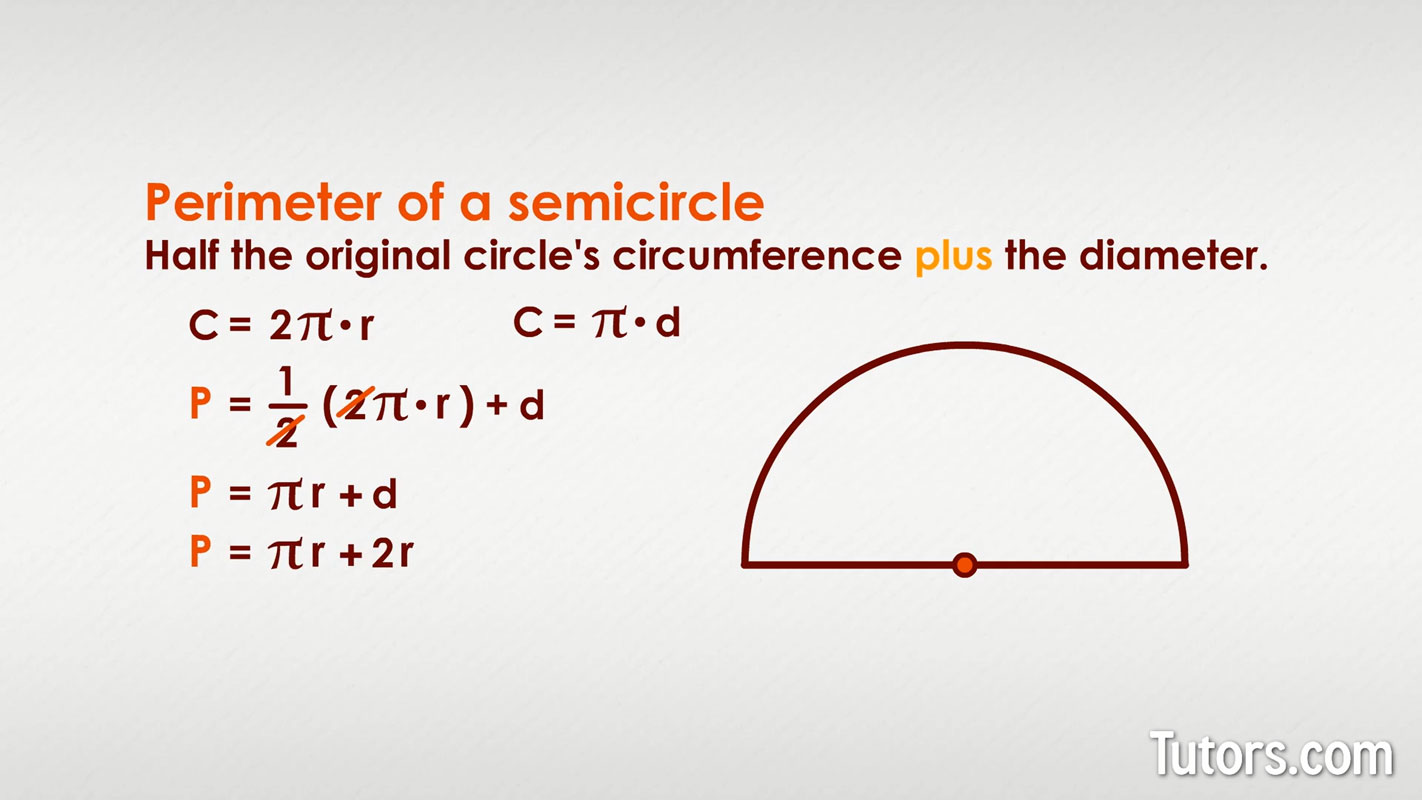
The perimeter (or circumference) of a half circle consists of the curved part of the semicircle and the diameter. To calculate the perimeter, you need the radius (r) of the circle.
Formula
The formula to find the perimeter (P) of a half circle is given by:
Where:
- r is the radius of the circle
- π (pi) is approximately 3.14159
Derivation
The perimeter of a half circle is derived from the sum of the semicircle's arc length and the diameter. The arc length of a semicircle is half the circumference of the full circle, which is πr. The diameter of the circle is 2r. Therefore, the total perimeter is:
Example Calculation
For a half circle with a radius of 5 units:
Thus, the perimeter of the half circle is approximately 25.7079 units.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle is an important concept in geometry, combining both the straight-line distance of the diameter and the curved edge of the semicircle. It is essential for solving various practical problems and understanding more complex geometrical shapes.
To calculate the perimeter of a half circle, follow these steps:
- Determine the radius (r) of the full circle.
- Calculate the diameter, which is twice the radius: .
- Compute the circumference of the full circle using the formula: .
- Since a half circle is half of a full circle, its curved edge (semicircular arc) is: .
- Add the diameter to the semicircular arc to get the total perimeter: .
Thus, the formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
This calculation is fundamental in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and any discipline requiring geometric computations.
Basic Concepts and Definitions
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle involves several fundamental geometric concepts and definitions. Let's explore these key elements in detail.
- Circle: A circle is a two-dimensional shape where all points are equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is known as the radius.
- Radius (r): The radius of a circle is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
- Diameter (d): The diameter of a circle is twice the radius, extending from one point on the circumference, through the center, to another point on the circumference. Mathematically, it is represented as .
- Circumference: The circumference of a circle is the total distance around the circle. It can be calculated using the formula , where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Semi-circle: A semi-circle is half of a circle, formed by cutting a whole circle along its diameter.
- Perimeter of a Half Circle: The perimeter (P) of a half circle includes the length of the curved edge (half the circumference) and the diameter. This can be represented as .
In summary, the perimeter of a half circle is derived from its radius, diameter, and the unique properties of the circle itself. By understanding these basic concepts and definitions, one can easily compute the perimeter and apply it in various practical scenarios.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle is the sum of its curved edge (semicircular arc) and its straight edge (diameter). To calculate this, we follow a few straightforward steps using basic geometry.
Let's break down the formula step-by-step:
- Identify the radius (r) of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
- Calculate the diameter (d) of the circle, which is twice the radius: .
- Determine the circumference of the full circle using the formula: .
- Since a half circle is half of a full circle, its curved edge (semicircular arc) is: .
- Add the diameter to the semicircular arc to get the total perimeter: .
Thus, the formula for the perimeter (P) of a half circle is:
This formula combines both the linear distance of the diameter and the curved distance of the semicircle, providing a comprehensive measure of the perimeter.
Step-by-Step Derivation of the Formula
Deriving the formula for the perimeter of a half circle involves understanding the components that make up this shape and their relationships. Follow these steps for a detailed derivation:
- Understand the Structure:
A half circle consists of two parts: the curved part (semicircular arc) and the straight part (diameter).
- Identify the Radius (r):
The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. This is a fundamental measure in our calculation.
- Calculate the Diameter:
The diameter of a circle is twice the radius:
. - Determine the Full Circumference:
The circumference of a full circle is calculated using the formula:
. - Find the Semicircular Arc Length:
Since a half circle is half of a full circle, the length of the semicircular arc is:
. - Add the Diameter to the Arc Length:
To find the perimeter of the half circle, combine the length of the semicircular arc with the diameter:
.
Thus, the derived formula for the perimeter (P) of a half circle is:
This formula effectively combines the linear distance of the diameter and the curved distance of the semicircle, giving a comprehensive measure of the perimeter.

Example Calculations
To better understand how to calculate the perimeter of a half circle, let's go through a few example calculations step-by-step.
Example 1: Radius = 5 units
- Determine the radius: r = 5 units.
- Calculate the diameter:
- Calculate the semicircular arc length:
- Add the diameter to the arc length to get the perimeter:
Example 2: Radius = 7 units
- Determine the radius: r = 7 units.
- Calculate the diameter:
- Calculate the semicircular arc length:
- Add the diameter to the arc length to get the perimeter:
Example 3: Radius = 10 units
- Determine the radius: r = 10 units.
- Calculate the diameter:
- Calculate the semicircular arc length:
- Add the diameter to the arc length to get the perimeter:
These examples demonstrate how to apply the formula for the perimeter of a half circle in different scenarios. By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter for any given radius.
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a half circle has several practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, design, and everyday problem-solving. Understanding how to calculate this perimeter can help in numerous real-life scenarios.
Architectural Design
In architecture, semicircular shapes are often used in the design of arches, windows, and decorative elements. Knowing the perimeter is essential for accurate measurements and material estimations.
- Designing archways and doorways with curved tops.
- Creating window designs that incorporate half-circle shapes.
- Planning landscaping elements like semicircular pathways and garden beds.
Engineering Projects
Engineers frequently encounter semicircular shapes in various structures and components. Calculating the perimeter is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and precision.
- Designing culverts and tunnels with semicircular cross-sections.
- Creating mechanical parts that include half-circle components.
- Planning bridges and overpasses with semicircular arches.
Urban Planning and Landscaping
Urban planners and landscapers use half-circle designs in public spaces and garden layouts. Understanding the perimeter helps in planning and implementing these designs effectively.
- Designing roundabouts and semicircular road intersections.
- Creating park layouts with semicircular benches and pathways.
- Planning water features like fountains with semicircular basins.
Everyday Problem-Solving
Even in everyday scenarios, the knowledge of calculating the perimeter of a half circle can be useful. It helps in various DIY projects and practical applications around the home.
- Crafting projects that involve semicircular shapes, such as making semicircular shelves or tabletops.
- Calculating the fabric needed for sewing projects that incorporate half-circle designs.
- Measuring the perimeter for painting or tiling semicircular areas.
Overall, understanding the perimeter of a half circle provides valuable insights and skills applicable in many professional and personal projects. This knowledge aids in precision, efficiency, and creativity in various domains.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a half circle can sometimes lead to errors if certain common mistakes are made. Here are some of these mistakes and tips on how to avoid them.
Misidentifying the Radius and Diameter
Mistake: Confusing the radius with the diameter or vice versa can lead to incorrect calculations.
Solution: Always remember that the diameter is twice the radius:
.
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure you're using the correct values.
Forgetting to Include the Diameter
Mistake: Only calculating the length of the semicircular arc and forgetting to add the diameter can result in an incomplete perimeter.
Solution: Always remember that the perimeter of a half circle includes both the semicircular arc and the diameter:
.
Incorrectly Using the Value of π (Pi)
Mistake: Using an incorrect value for π (pi) can lead to significant errors in the final calculation.
Solution: Use a precise value for π, such as 3.14159, or use the π function on a calculator to ensure accuracy.
Errors in Measurement
Mistake: Inaccurate measurement of the radius can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations.
Solution: Use a reliable measuring tool and take multiple measurements to ensure accuracy. Verify your measurements before proceeding with calculations.
Neglecting Units
Mistake: Forgetting to include units or using inconsistent units can cause confusion and errors.
Solution: Always include units in your measurements and ensure consistency throughout your calculations. If you measure the radius in centimeters, the perimeter will also be in centimeters.
Rounding Errors
Mistake: Rounding intermediate values too early can lead to less accurate results.
Solution: Perform calculations with as many decimal places as possible and only round the final result to the desired precision.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following these tips, you can ensure accurate and reliable calculations of the perimeter of a half circle.
Advanced Topics Related to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle opens up several advanced topics in geometry and practical applications. Here, we explore some of these concepts:
- Arc Length of a Semicircle: The curved part of a semicircle's perimeter is essentially an arc of the full circle. The length of this arc is given by: \[ \text{Arc Length} = \pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
- Sectors and Segments Involving a Semicircle: When dealing with semicircles, it is essential to understand the relationship between sectors and segments. A sector of a circle is formed by two radii and an arc, while a segment is formed by a chord and an arc. The formulas for these can be extended to semicircles.
- Composite Shapes: Semicircles are often part of composite shapes. For instance, a rectangle with a semicircular end is a common shape in architecture and engineering. The perimeter of such shapes includes the straight edges and the curved boundary of the semicircle: \[ \text{Perimeter of Composite Shape} = \text{Straight Edges} + \pi r + d \] where \( d \) is the diameter of the semicircle.
- Moment of Inertia: In physics and engineering, the moment of inertia of a semicircle is a critical concept. It is used to calculate the rotational behavior of objects. The moment of inertia about the diameter of a semicircle is: \[ I = \frac{1}{8} \pi r^4 \]
- Applications in Real Life: The perimeter of a semicircle is applied in various real-life scenarios. Examples include designing semicircular arches, windows, and elements in landscaping. Knowing the perimeter helps in material estimation and structural analysis.
Example Calculations
- Finding the Perimeter of a Semicircle:
Given a semicircle with a radius of 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \]
Substituting the value of \( r \):
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 = 5\pi + 10 \approx 25.7 \text{ units} \] - Moment of Inertia Calculation:
For a semicircle with a radius of 3 units, the moment of inertia about the diameter is:
\[ I = \frac{1}{8} \pi r^4 \]
Substituting \( r \):
\[ I = \frac{1}{8} \pi \times 3^4 = \frac{1}{8} \pi \times 81 = 10.125\pi \approx 31.8 \text{ units}^4 \]
Practice Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 units.
- Determine the moment of inertia for a semicircle with a radius of 4 units about its diameter.
- Find the total perimeter of a composite shape consisting of a rectangle with dimensions 8 units by 5 units, and a semicircle with a diameter of 8 units attached to one of the shorter sides.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Here are some practice problems related to the perimeter of a half circle along with detailed solutions:
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a half circle with a radius of 7 cm.
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Given \( r = 7 \) cm,
\[ P = \pi \times 7 + 2 \times 7 \]
\[ P = 7\pi + 14 \]
Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \),
\[ P \approx 7 \times 3.14 + 14 \]
\[ P \approx 21.98 + 14 \]
\[ P \approx 35.98 \] cm
-
Problem 2: A half circle has a diameter of 10 meters. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
First, find the radius \( r \):
\[ r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \] meters
Then, use the perimeter formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
\[ P = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 \]
\[ P = 5\pi + 10 \]
Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \),
\[ P \approx 5 \times 3.14 + 10 \]
\[ P \approx 15.7 + 10 \]
\[ P \approx 25.7 \] meters
-
Problem 3: Calculate the perimeter of a half circle with a radius of 3.5 cm.
Solution:
Using the formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Given \( r = 3.5 \) cm,
\[ P = \pi \times 3.5 + 2 \times 3.5 \]
\[ P = 3.5\pi + 7 \]
Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \),
\[ P \approx 3.5 \times 3.14 + 7 \]
\[ P \approx 10.99 + 7 \]
\[ P \approx 17.99 \] cm
-
Problem 4: If the perimeter of a half circle is 31.4 cm, find the radius.
Solution:
Given the perimeter formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \):
\[ 31.4 = \pi r + 2r \]
Factor out \( r \):
\[ 31.4 = r(\pi + 2) \]
Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \):
\[ 31.4 = r(3.14 + 2) \]
\[ 31.4 = r \times 5.14 \]
\[ r = \frac{31.4}{5.14} \]
\[ r \approx 6.11 \] cm
Summary and Key Takeaways
Understanding the perimeter of a half-circle involves grasping fundamental concepts of geometry and the properties of circles. Here are the key points summarized:
- Definition: The perimeter of a half-circle includes both the curved edge and the diameter. It can be expressed as \( \pi r + 2r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter of a half-circle is \( P = \pi r + 2r \). This accounts for the curved part (\( \pi r \)) and the straight part (the diameter, \( 2r \)).
- Derivation: This formula is derived by combining the length of the semicircle (\( \pi r \)) and the diameter (2r).
- Practical Applications: This concept is used in various real-life contexts such as architecture, engineering, and everyday problem-solving involving semi-circular shapes.
- Common Mistakes: A frequent error is neglecting to include the diameter in the calculation, leading to an incomplete perimeter.
- Advanced Topics: More complex applications might involve integration for variable radii or using the formula in conjunction with other geometric properties for more complex shapes.
Understanding these key points ensures a solid foundation in both the basic and advanced applications of calculating the perimeter of a half-circle.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in deepening their understanding of the perimeter of a half circle and related concepts, the following resources provide comprehensive information, advanced problems, and interactive learning opportunities:
-
Brighterly - Semicircle Basics and Advanced Concepts:
This resource covers the basic definitions, formula derivations, and application problems related to semicircles. It also includes practice problems and solutions to help solidify understanding.
Link:
-
Cuemath - Perimeter and Area of Semicircles:
Cuemath offers detailed explanations of the perimeter and area formulas for semicircles. The site includes example problems, step-by-step solutions, and practice questions to test your knowledge.
Link:
-
Wolfram MathWorld - Semicircle:
Wolfram MathWorld provides a mathematical perspective on semicircles, including definitions, properties, and advanced mathematical contexts where semicircles are applied.
Link:
-
Khan Academy - Circles and Sectors:
Khan Academy offers video tutorials and exercises on circles, sectors, and related geometric properties. This includes a section on semicircles with interactive practice problems.
Link:
-
Math is Fun - Circle Geometry:
This site provides an easy-to-understand introduction to circle geometry, including semicircles. It covers the basics and offers interactive tools to explore different geometric properties.
Link:
These resources will guide you through both the fundamental and advanced aspects of semicircles, enhancing your understanding and problem-solving skills.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn - Video Hướng Dẫn
READ MORE:
Tìm Chu Vi của Nửa Hình Tròn Kết Hợp với Hình Vuông!