Topic area and perimeter worksheets pdf: Discover a comprehensive collection of area and perimeter worksheets in PDF format designed to boost your math skills. Perfect for students and teachers, these free resources cover basic to advanced concepts, real-world applications, and include answer keys for effective learning. Download now and start mastering area and perimeter calculations today!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets PDF
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Basic Area and Perimeter Concepts
- Formulas for Area and Perimeter
- Calculating Area and Perimeter
- Worksheets for Rectangles and Squares
- Worksheets for Triangles and Circles
- Worksheets for Compound Shapes
- Advanced Area and Perimeter Problems
- Real-World Applications
- Interactive and Visual Aids
- Answer Keys and Explanations
- Additional Resources and References
- Downloadable PDF Worksheets
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter Worksheets PDF
Enhance your math skills with these comprehensive worksheets focused on area and perimeter calculations. Ideal for students of various grade levels, these worksheets provide a variety of problems to practice and master these essential concepts.
Contents
Basic Area and Perimeter Worksheets
These worksheets cover the fundamentals of area and perimeter, including simple shapes such as rectangles and squares.
- Calculate the perimeter of rectangles and squares.
- Find the area of rectangles and squares using the formulas: \[ \text{Area of a rectangle} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \] \[ \text{Perimeter of a rectangle} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
- Problems range from basic calculations to applying formulas to given dimensions.
Advanced Area and Perimeter Worksheets
For students looking for more challenging problems, these worksheets include compound shapes and irregular polygons.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of compound shapes by breaking them into simpler shapes.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find missing sides of right-angled triangles: \[ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \]
- Solve for area and perimeter of irregular polygons by dividing them into rectangles and triangles.
Word Problems on Area and Perimeter
Apply your knowledge of area and perimeter to real-world scenarios with these word problems.
- Problems involve finding the area and perimeter of gardens, rooms, and other practical spaces.
- Each worksheet includes multiple scenarios to ensure comprehensive understanding.
Rectangles, Squares, and Compound Shapes
Practice problems specifically focused on rectangles, squares, and more complex compound shapes.
- Worksheets include step-by-step solutions to guide students through the problem-solving process.
- Visual aids and diagrams help in understanding the concepts better.
Answer Keys
Each set of worksheets comes with detailed answer keys to help students check their work and understand mistakes.
- Solutions are provided for all problems, with explanations where necessary.
- Use the answer keys to learn the correct approach to solving area and perimeter problems.
Download the worksheets in PDF format and start improving your math skills today!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry and essential for solving various real-world problems. This section provides a detailed introduction to these concepts, including definitions, formulas, and examples.
- Area: The area is the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units.
- Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is measured in linear units.
Basic Formulas:
- Rectangle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
- Square:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
- Triangle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
- Perimeter: Sum of all sides
- Circle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \]
- Circumference: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \]
By mastering the calculation of area and perimeter, students can solve a variety of geometric problems and apply these skills in practical situations such as finding the size of a room, a garden, or any other space. These worksheets provide ample practice to help students gain confidence and proficiency in these essential math concepts.
Basic Area and Perimeter Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of area and perimeter is essential for solving geometric problems. This section introduces these concepts with clear definitions, formulas, and examples for common shapes.
- Area:
The area is the amount of space enclosed within a shape. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square centimeters).
- Perimeter:
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is measured in linear units (e.g., meters, centimeters).
Formulas for Common Shapes:
- Rectangle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
- Square:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
- Triangle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
- Perimeter: Sum of all sides
- Circle:
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \]
- Circumference: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \]
Steps to Calculate Area and Perimeter:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape (rectangle, square, triangle, or circle).
- Measure Dimensions: Measure the necessary dimensions such as length, width, side, base, height, or radius.
- Apply Formulas: Use the appropriate formulas to calculate the area and perimeter based on the measured dimensions.
- Calculate: Perform the calculations to find the area and perimeter.
By understanding and applying these basic concepts and formulas, students can effectively solve a wide range of geometric problems. These foundational skills are crucial for more advanced mathematical studies and practical applications.
Formulas for Area and Perimeter
To calculate the area and perimeter of various geometric shapes, it is essential to know and apply the correct formulas. This section outlines the key formulas for common shapes and provides examples to illustrate their use.
Rectangle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
Square
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
Triangle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 \]
Circle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \]
- Circumference: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \]
Examples
- Example 1: Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length 5 cm and width 3 cm.
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = 5 \, \text{cm} \times 3 \, \text{cm} = 15 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (5 \, \text{cm} + 3 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 8 \, \text{cm} = 16 \, \text{cm} \]
- Example 2: Find the area and perimeter of a square with side length 4 m.
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = 4 \, \text{m} \times 4 \, \text{m} = 16 \, \text{m}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 4 \, \text{m} = 16 \, \text{m} \]
- Example 3: Find the area and perimeter of a circle with radius 7 inches.
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times (7 \, \text{in})^2 = \pi \times 49 \, \text{in}^2 \approx 153.94 \, \text{in}^2 \]
- Circumference: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times 7 \, \text{in} = 14 \pi \, \text{in} \approx 43.98 \, \text{in} \]
By familiarizing yourself with these formulas and practicing their application, you can efficiently solve problems involving the area and perimeter of various shapes. These foundational skills are crucial for both academic success and practical applications in everyday life.
Calculating Area and Perimeter
Calculating the area and perimeter of various geometric shapes is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This section provides a step-by-step guide to calculating these measurements for common shapes.
Steps to Calculate Area:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are working with (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle, circle).
- Measure Dimensions: Measure the necessary dimensions such as length, width, base, height, or radius.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate formula for the shape to calculate the area.
- Perform the Calculation: Complete the mathematical operations to find the area.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are working with.
- Measure Dimensions: Measure the lengths of all sides of the shape.
- Apply the Formula: Use the appropriate formula to calculate the perimeter.
- Perform the Calculation: Sum the lengths of all sides to find the perimeter.
Formulas and Examples:
- Rectangle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
- Example: For a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 3 cm, \[ \text{Area} = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 3 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
- Example: For a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 3 cm, \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 3 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 11 \, \text{cm} = 22 \, \text{cm} \]
- Square
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \]
- Example: For a square with side length 5 m, \[ \text{Area} = 5 \, \text{m} \times 5 \, \text{m} = 25 \, \text{m}^2 \]
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
- Example: For a square with side length 5 m, \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 \, \text{m} = 20 \, \text{m} \]
- Triangle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
- Example: For a triangle with base 6 inches and height 4 inches, \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \, \text{in} \times 4 \, \text{in} = 12 \, \text{in}^2 \]
- Perimeter: Sum of all sides
- Example: For a triangle with sides 3 inches, 4 inches, and 5 inches, \[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 \, \text{in} + 4 \, \text{in} + 5 \, \text{in} = 12 \, \text{in} \]
- Circle
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \]
- Example: For a circle with radius 7 cm, \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times (7 \, \text{cm})^2 = \pi \times 49 \, \text{cm}^2 \approx 153.94 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
- Circumference: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \]
- Example: For a circle with radius 7 cm, \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 14 \pi \, \text{cm} \approx 43.98 \, \text{cm} \]
By following these steps and using the provided formulas, students can accurately calculate the area and perimeter of various shapes. These calculations are vital for understanding geometric properties and solving real-world problems.
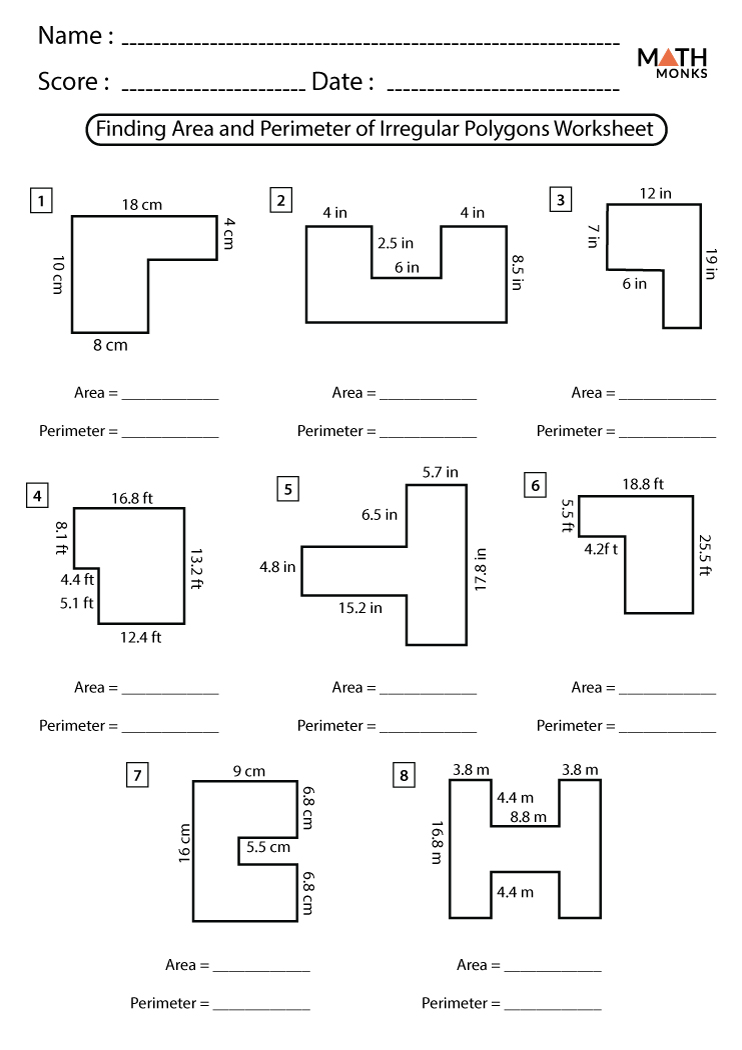
Worksheets for Rectangles and Squares
Practicing with worksheets for rectangles and squares is an excellent way for students to reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter calculations. These worksheets offer a variety of problems, from basic to advanced levels, to ensure comprehensive learning.
Rectangle Worksheets
- Basic Problems:
- Calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles with given lengths and widths.
- Examples:
- Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length 7 cm and width 4 cm.
- Given a rectangle with length 10 inches and width 5 inches, calculate the area and perimeter.
- Intermediate Problems:
- Solve for unknown dimensions given the area or perimeter.
- Examples:
- If the area of a rectangle is 56 square meters and the width is 8 meters, find the length.
- Given a perimeter of 30 cm and a length of 9 cm, find the width of the rectangle.
- Advanced Problems:
- Word problems involving real-life scenarios.
- Examples:
- A garden is shaped like a rectangle with a length of 15 meters and a width of 10 meters. Calculate the amount of fencing needed to enclose the garden and the area available for planting.
- A rectangular room has a floor area of 120 square feet and a length of 12 feet. Determine the width of the room and the perimeter.
Square Worksheets
- Basic Problems:
- Calculate the area and perimeter of squares with given side lengths.
- Examples:
- Find the area and perimeter of a square with a side length of 6 cm.
- Given a square with a side length of 8 inches, calculate the area and perimeter.
- Intermediate Problems:
- Solve for the side length given the area or perimeter.
- Examples:
- If the area of a square is 49 square meters, find the side length.
- Given a perimeter of 32 cm, determine the side length of the square.
- Advanced Problems:
- Word problems involving practical applications.
- Examples:
- A square tile has a side length of 12 inches. Calculate the total area of 15 such tiles and the total perimeter when they are laid out in a straight line.
- A square garden has a perimeter of 40 meters. Determine the side length and the area available for planting.
These worksheets are designed to build confidence and proficiency in calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares. By solving a variety of problems, students can master these fundamental geometric concepts and apply them in real-world situations.
Worksheets for Triangles and Circles
Understanding the area and perimeter of triangles and circles is fundamental in geometry. Below, you will find a variety of worksheets designed to help students master these concepts through detailed practice problems and step-by-step solutions.
Triangles
-
Basic Concepts:
Students will learn to identify different types of triangles (equilateral, isosceles, and scalene) and understand the formulas for calculating their area and perimeter.
-
Area Calculation:
The area of a triangle is given by the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
\]Worksheets will include problems where students need to apply this formula to various triangles.
-
Perimeter Calculation:
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]Students will practice calculating the perimeter using this formula in the worksheets.
Circles
-
Basic Concepts:
Students will understand the properties of circles, including radius, diameter, and circumference.
-
Area Calculation:
The area of a circle is calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \pi r^2
\]where \( r \) is the radius of the circle. Worksheets will provide practice problems to apply this formula.
-
Circumference Calculation:
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula:
\[
\text{Circumference} = 2 \pi r
\]Students will use this formula to solve various circumference problems in the provided worksheets.
Practice Problems
Each worksheet includes a variety of problems, from simple calculations to more complex word problems that require a deeper understanding of the concepts. Answer keys are provided to help students check their work and understand the steps involved in each solution.
Downloadable PDF Worksheets
All worksheets are available in PDF format for easy download and printing. These resources are designed to enhance students' learning experience by providing ample practice and detailed explanations of each concept.
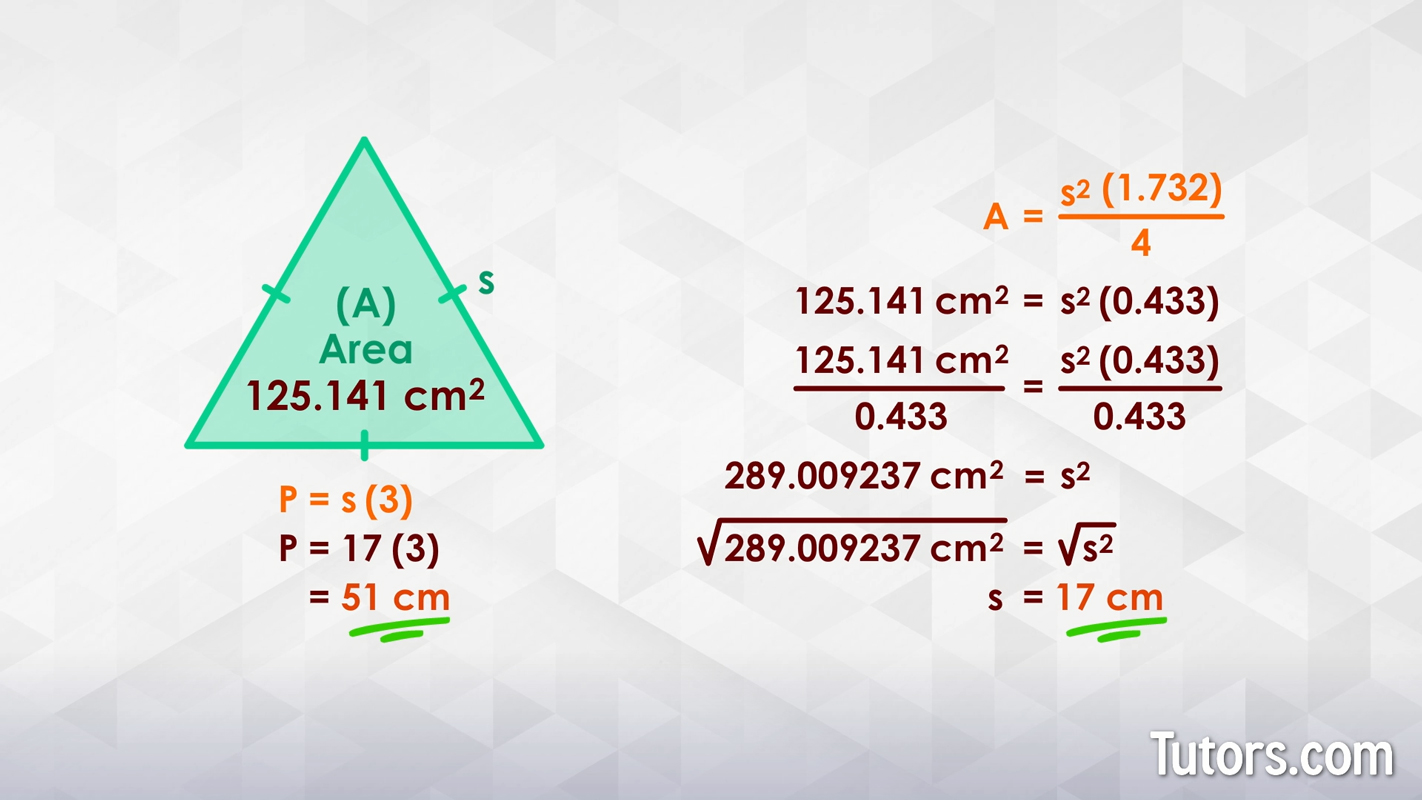
Worksheets for Compound Shapes
Compound shapes are figures that consist of two or more basic geometric shapes. Calculating the area and perimeter of compound shapes involves breaking down the figure into simpler parts, finding the area and perimeter of each part, and then combining these values appropriately.
Steps to Calculate Area and Perimeter of Compound Shapes:
- Identify the simple shapes within the compound shape. These can include rectangles, triangles, circles, and other polygons.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of each simple shape using the appropriate formulas:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) and \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) and \( \text{Perimeter} = \text{sum of all sides} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \) and \( \text{Perimeter (Circumference)} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \)
- Add or subtract the areas of the simple shapes to find the total area of the compound shape. If shapes overlap, subtract the overlapping area.
- Combine the perimeters of the simple shapes, ensuring that shared sides between shapes are not counted twice.
Example Problems:
Consider a compound shape made up of a rectangle and a semicircle:
- Rectangle:
- Length: 10 cm
- Width: 5 cm
- Area: \( 10 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 50 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( 2 \times (10 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
- Semicircle:
- Radius: 5 cm
- Area: \( \frac{1}{2} \times \pi \times (5 \, \text{cm})^2 = 39.27 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( \pi \times 5 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} = 25.71 \, \text{cm} \)
- Total Area: \( 50 \, \text{cm}^2 + 39.27 \, \text{cm}^2 = 89.27 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Total Perimeter: \( 30 \, \text{cm} + 25.71 \, \text{cm} - 10 \, \text{cm} = 45.71 \, \text{cm} \)
Practice Worksheets:
Here are some worksheets to help you practice calculating the area and perimeter of compound shapes:
These worksheets come with answer keys that provide step-by-step solutions, ensuring that you can check your work and understand the process of calculating the area and perimeter of compound shapes accurately.
Advanced Area and Perimeter Problems
Advanced area and perimeter problems often involve complex shapes, irregular polygons, and require the application of various mathematical concepts. Below are some examples and exercises designed to challenge and enhance problem-solving skills in calculating area and perimeter.
Examples and Steps
Let's go through some examples to understand how to approach advanced problems:
Example 1: Irregular Polygon
Given an irregular polygon, divide it into regular shapes like triangles and rectangles. Calculate the area and perimeter of each smaller shape, then sum them up.
- Step 1: Identify the smaller shapes within the irregular polygon.
- Step 2: Calculate the area of each smaller shape.
- Step 3: Calculate the perimeter of each smaller shape.
- Step 4: Sum the areas to find the total area.
- Step 5: Add the perimeters, ensuring not to double-count shared sides.
Example 2: Composite Shape with a Hole
For a composite shape with a hole, such as a rectangle with a circular hole:
- Step 1: Calculate the area and perimeter of the outer shape (rectangle).
- Step 2: Calculate the area and perimeter of the inner shape (circle).
- Step 3: Subtract the area of the circle from the area of the rectangle.
- Step 4: The perimeter remains the same as the outer shape unless specifically needing the inner boundary.
Example 3: Using Trigonometry
For shapes requiring trigonometry, such as finding the height of a triangle using sine or cosine:
- Step 1: Use the given angle and side length to find the height.
- Step 2: Apply the formula: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
Practice Problems
Try solving these advanced problems:
- Calculate the area of an irregular pentagon by dividing it into triangles and rectangles.
- Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with a semi-circular extension on one side.
- Determine the area of a sector of a circle with a given radius and central angle.
Useful Formulas
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( A = l \times w \) | \( P = 2(l + w) \) |
| Triangle | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \) | \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Circle | \( A = \pi r^2 \) | \( P = 2 \pi r \) |
| Irregular Polygon | Sum of areas of simpler shapes | Sum of lengths of all sides |
By practicing these advanced problems, students can develop a deeper understanding of geometric properties and enhance their problem-solving skills in calculating area and perimeter.
Real-World Applications
Understanding the area and perimeter of shapes is crucial in various real-world scenarios. Here, we explore some practical applications of these concepts:
1. Construction and Architecture
Calculating the area and perimeter is fundamental in construction and architecture. For instance, architects need to determine the floor area to plan the layout of rooms and other spaces efficiently.
- Floor Plans: Architects use the area to determine how much space is available for different rooms and how to allocate this space effectively.
- Fencing and Borders: Perimeter calculations are essential for determining the length of fencing required to enclose a property or garden.
2. Interior Design
Interior designers use area and perimeter calculations to choose the right amount of materials and design elements.
- Flooring: To lay down tiles, carpets, or hardwood floors, designers need to know the exact area of the space.
- Paint and Wallpaper: Calculating the area of walls helps in determining the amount of paint or wallpaper needed.
3. Agriculture
Farmers and gardeners use these concepts to optimize their land use.
- Crop Planning: Knowing the area of a field helps in planning the number of crops that can be planted.
- Irrigation: Perimeter calculations are used to design efficient irrigation systems that cover the entire field.
4. Real Estate
Real estate agents and buyers use area and perimeter to assess property size and value.
- Property Valuation: Larger areas typically have higher values, so accurate area measurement is crucial.
- Legal Documentation: Exact measurements are needed for legal descriptions of properties.
5. Sports
In sports, the dimensions of fields and courts are critical for fairness and regulation adherence.
- Field Markings: The perimeter is used to mark the boundaries of sports fields and courts.
- Track Design: Track areas are calculated to ensure lanes are equal and meet regulatory standards.
6. Urban Planning
Urban planners use area and perimeter measurements to design and organize city spaces efficiently.
- Parks and Public Spaces: Planning the area of parks and recreational areas ensures adequate space for public use.
- Infrastructure Development: Calculating the perimeter helps in designing roads, pavements, and other infrastructure elements.
7. Environmental Science
Environmental scientists calculate the area and perimeter for various ecological studies.
- Habitats: Determining the area of animal habitats is essential for conservation efforts.
- Pollution Control: Understanding the area of affected regions helps in planning cleanup and pollution control measures.
These real-world applications highlight the importance of mastering area and perimeter calculations. By practicing with our comprehensive worksheets, students can develop the skills needed to tackle these practical problems effectively.
Interactive and Visual Aids
Interactive and visual aids are essential tools to enhance students' understanding of area and perimeter concepts. These aids can include dynamic software, engaging activities, and visual tools that bring mathematical concepts to life.
-
Dynamic Geometry Software:
Software such as GeoGebra allows students to manipulate shapes and observe how changes affect area and perimeter. This hands-on approach helps solidify understanding.
-
Interactive Whiteboards:
Using interactive whiteboards, teachers can display and manipulate shapes, making it easier for students to visualize changes and understand the underlying concepts.
-
Visual Aids:
- Graph Paper: Students can draw shapes accurately, calculate area and perimeter, and understand the importance of precision.
- Color-Coded Shapes: Using different colors for different shapes can help students distinguish and remember various formulas.
-
Online Games and Activities:
There are numerous online platforms offering games and activities focused on area and perimeter. These interactive tools make learning fun and engaging.
-
Video Tutorials:
Educational videos can explain concepts step-by-step, providing visual and auditory learning experiences.
Example Activities:
-
Shape Manipulation:
Students use software to change the dimensions of various shapes and observe how area and perimeter are affected. This activity encourages exploration and discovery.
-
Real-World Applications:
Using interactive maps, students can measure real-world objects and spaces, such as classrooms or playgrounds, to calculate area and perimeter.
-
Group Projects:
Students work in groups to create posters displaying different shapes and their properties, using visual aids and interactive tools to present their findings.
Incorporating these interactive and visual aids into the curriculum not only makes learning more engaging but also helps students develop a deeper understanding of area and perimeter concepts.
Answer Keys and Explanations
Having access to accurate answer keys and thorough explanations is essential for students to verify their work and understand the underlying concepts of area and perimeter calculations. Below, we provide detailed answer keys and explanations for various types of problems covered in the worksheets.
Answer Key for Rectangles and Squares
For worksheets involving rectangles and squares, the answers typically involve straightforward application of formulas:
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Area of a Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Perimeter of a Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Area of a Square: \( A = s^2 \)
Example:
| Length (l) | Width (w) | Perimeter (P) | Area (A) |
| 5 | 3 | \( 2(5 + 3) = 16 \) | \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) |
Answer Key for Triangles
For triangles, the formulas involve base and height or side lengths for different types:
- Perimeter of a Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Area of a Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
Example:
| Base (b) | Height (h) | Side a | Side b | Side c | Perimeter (P) | Area (A) |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | \( 5 + 6 + 7 = 18 \) | \( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \) |
Answer Key for Circles
For circles, calculations involve the radius or diameter:
- Circumference of a Circle: \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \)
- Area of a Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Example:
| Radius (r) | Diameter (d) | Circumference (C) | Area (A) |
| 3 | 6 | \( 2\pi \times 3 = 6\pi \) | \( \pi \times 3^2 = 9\pi \) |
Step-by-Step Explanations
Detailed explanations are provided to help students understand the process of solving problems:
- Identify the shape and relevant dimensions.
- Choose the appropriate formula for perimeter or area.
- Substitute the known values into the formula.
- Perform the necessary calculations.
- Double-check the work for accuracy.
These explanations aim to build a strong foundation in understanding geometric concepts, ensuring students can apply these skills in various contexts.
Additional Resources and References
For further study and practice on area and perimeter, the following resources offer a variety of worksheets, guides, and tools to enhance understanding and proficiency:
-
Printable Worksheets:
- : Offers comprehensive worksheets on area and perimeter, including various shapes and compound figures. These worksheets are interactive and come with detailed answer keys.
- : Provides grade-specific worksheets for calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles, squares, triangles, and more. Answer keys with step-by-step explanations are included.
- : Features a range of worksheets focusing on the area and perimeter of basic and complex shapes, complete with answer keys that outline the problem-solving strategies.
-
Online Tools and Calculators:
- : These tools assist in quickly calculating area and perimeter for various shapes.
- : Offers both printable worksheets and interactive calculators for a comprehensive learning experience.
-
Interactive Lessons and Visual Aids:
- : Provides worksheets along with visual aids that help in understanding the concepts of area and perimeter through engaging activities.
- : Includes interactive lessons and printable worksheets, enhancing both conceptual and practical understanding of area and perimeter.
-
Video Tutorials and Guides:
- : Offers free video tutorials on geometry topics, including area and perimeter, to provide a thorough understanding through visual learning.
- : Channels like Math Antics and Numberphile offer easy-to-understand videos explaining area and perimeter concepts and problem-solving techniques.
-
Books and Publications:
- : A variety of books on area and perimeter are available for different grade levels, including practice books and comprehensive guides.
- : Find textbooks and workbooks that provide detailed lessons and exercises on area and perimeter.
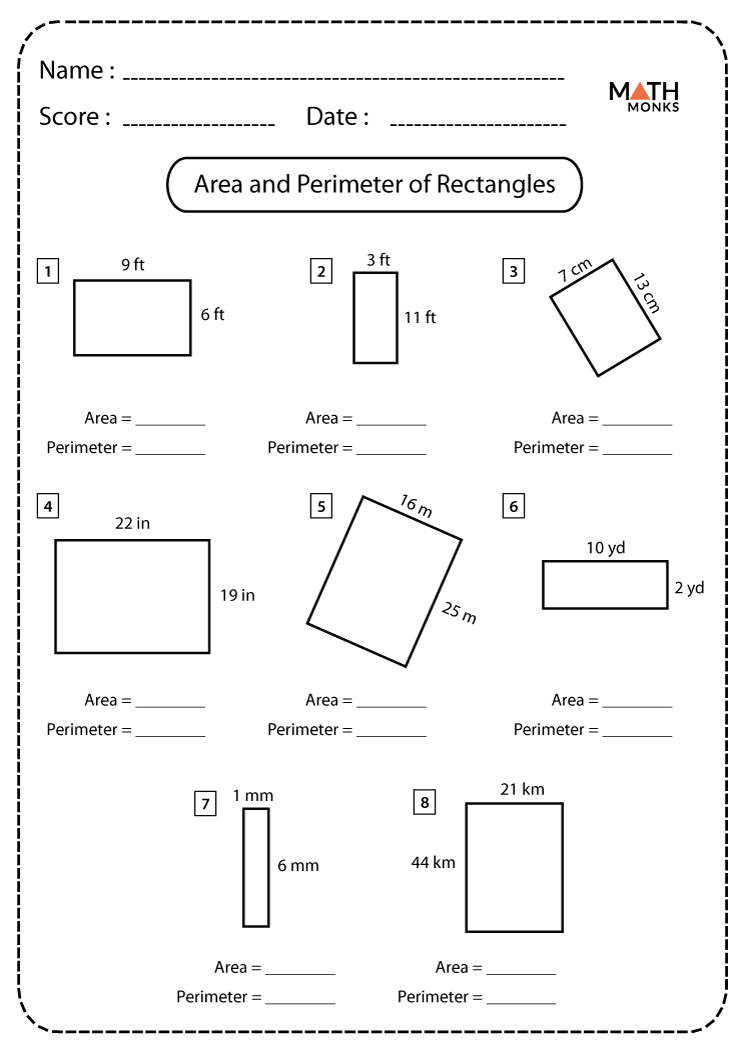
Downloadable PDF Worksheets
Enhance your understanding of area and perimeter with our comprehensive collection of downloadable PDF worksheets. These worksheets cater to various grade levels and cover a wide range of topics, ensuring students can find the practice they need.
-
Basic Area and Perimeter Worksheets:
-
Advanced Area and Perimeter Worksheets:
Grade-Specific Worksheets
Each worksheet is designed to provide students with practical problems that enhance their understanding of geometric concepts. By practicing regularly, students can build confidence and improve their skills in calculating area and perimeter.
For more specialized worksheets and tailored resources, explore our partners:
- - Interactive and visually engaging worksheets.
- - Customizable worksheets with endless variations.
Download these worksheets today and start mastering the concepts of area and perimeter!
Chu vi, Diện tích và Thể tích
READ MORE:
Toán Học Vui - Chu Vi